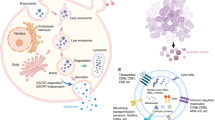
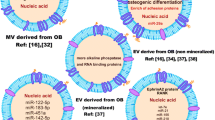
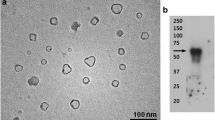
Abstract
Inflammatory bone disease is a general term for a series of diseases caused by chronic inflammation, which leads to the destruction of bone homeostasis, that is, the osteolytic activity of osteoclasts increases, and the osteogenic activity of osteoblasts decreases, leading to osteolysis. Macrophages are innate immune cell with plasticity, and their polarization is related to inflammatory bone diseases. The dynamic balance of macrophages between the M1 phenotype and the M2 phenotype affects the occurrence and development of diseases. In recent years, an increasing number of studies have shown that extracellular vesicles existing in the extracellular environment can act on macrophages, affecting the progress of inflammatory diseases. This process is realized by influencing the physiological activity or functional activity of macrophages, inducing macrophages to secrete cytokines, and playing an anti-inflammatory or pro-inflammatory role. In addition, by modifying and editing extracellular vesicles, the potential of targeting macrophages can be used to provide new ideas for developing new drug carriers for inflammatory bone diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Shao H, Im H, Castro CM et al (2018) New technologies for analysis of extracellular vesicles. Chem Rev 118:1917–1950. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00534
Wiklander OPB, Brennan MÁ, Lötvall J et al (2019) Advances in therapeutic applications of extracellular vesicles. Sci Transl Med 11:eaav8521. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aav8521
Elsharkasy OM, Nordin JZ, Hagey DW et al (2020) Extracellular vesicles as drug delivery systems: why and how? Adv Drug Deliv Rev 159:332–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2020.04.004
Hu Y, Wang Y, Chen T et al (2021) Exosome: function and application in inflammatory bone diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6324912
Michalski MN, McCauley LK (2017) Macrophages and skeletal health. Pharmacol Ther 174:43–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.02.017
Horwood NJ (2016) Macrophage polarization and bone formation: a review. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 51:79–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-015-8519-2
Wang J, Huang R, Xu Q et al (2020) Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles alleviate acute lung injury via transfer of miR-27a-3p. Critical Care Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000004315
Kooijmans SAA, de Jong OG, Schiffelers RM (2021) Exploring interactions between extracellular vesicles and cells for innovative drug delivery system design. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 173:252–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2021.03.017
Kalluri R, LeBleu VS (2020) The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 367:eaau6977. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aau6977
(2018) Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines Journal of Extracellular Vesicles 7(1) 1535750. https://doi.org/10.1080/20013078.2018.1535750
Fei, Teng Martin, Fussenegger (2021) Shedding Light on Extracellular Vesicle Biogenesis and Bioengineering Advanced Science 8(1) 2003505. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.v8.110.1002/advs.202003505
Teng F, Fussenegger M (2021) Shedding light on extracellular vesicle biogenesis and bioengineering. Adv Sci 8:2003505. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202003505
Cabral J, Ryan AE, Griffin MD, Ritter T (2018) Extracellular vesicles as modulators of wound healing. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 129:394–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2018.01.018
Cocozza F, Grisard E, Martin-Jaular L et al (2020) SnapShot: extracellular Vesicles. Cell 182:262-262.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.054
Tkach M, Théry C (2016) Communication by extracellular vesicles: where we are and where we need to go. Cell 164:1226–1232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.01.043
Théry C (2015) Diagnosis by extracellular vesicles. Nature 523:161–162. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14626
Lai J, Huang C, Guo Y, Rao L (2022) Engineered extracellular vesicles and their mimics in cardiovascular diseases. J Control Release 347:27–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.04.046
Martinez Escudé, de Castilla P, Tong L, Huang C et al (2021) Extracellular vesicles as a drug delivery system: a systematic review of preclinical studies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 175:113801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2021.05.011
Le Saux S, Aubert-Pouëssel A, Mohamed KE et al (2021) Interest of extracellular vesicles in regards to lipid nanoparticle based systems for intracellular protein delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 176:113837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2021.113837
Zhang X, Zhang H, Gu J et al (2021) Engineered extracellular vesicles for cancer therapy. Adv Mater 33:2005709. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202005709
Wynn TA, Vannella KM (2016) Macrophages in tissue repair, regeneration, and fibrosis. Immunity 44:450–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2016.02.015
Martin KE, García AJ (2021) Macrophage phenotypes in tissue repair and the foreign body response: implications for biomaterial-based regenerative medicine strategies. Acta Biomater 133:4–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2021.03.038
Schlundt C, Fischer H, Bucher CH et al (2021) The multifaceted roles of macrophages in bone regeneration: a story of polarization, activation and time. Acta Biomater 133:46–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2021.04.052
Chao, Liu Dewei, Chu Kourosh, Kalantar‐Zadeh Jacob, George Howard A., Young Guozhen, Liu (2021) Cytokines: From Clinical Significance to Quantification Advanced Science 8(15) 2004433-10.1002/advs.v8.15 10.1002/advs.202004433
Jia Y-C, Ding Y-X, Mei W-T et al (2021) Extracellular vesicles and pancreatitis: mechanisms, status and perspectives. Int J Biol Sci 17:549–561. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.54858
Basu Mallik S, Jayashree BS, Shenoy RR (2018) Epigenetic modulation of macrophage polarization- perspectives in diabetic wounds. J Diabetes Complicat 32:524–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2018.01.015
Schmidt-Bleek K, Schell H, Schulz N et al (2012) Inflammatory phase of bone healing initiates the regenerative healing cascade. Cell Tissue Res 347:567–573. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-011-1205-7
Ge X, Meng Q, Wei L et al (2021) Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion induced cardiac extracellular vesicles harbour proinflammatory features and aggravate heart injury. J Extracell Vesicles. https://doi.org/10.1002/jev2.12072
Cai M, Shi Y, Zheng T et al (2020) Mammary epithelial cell derived exosomal MiR-221 mediates M1 macrophage polarization via SOCS1/STATs to promote inflammatory response. International Immunopharmacology 83:106493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106493
Lv L-L, Feng Y, Wu M et al (2020) Exosomal miRNA-19b-3p of tubular epithelial cells promotes M1 macrophage activation in kidney injury. Cell Death Differ 27:210–226. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-019-0349-y
Pan Y, Hui X, Hoo RLC et al (2019) Adipocyte-secreted exosomal microRNA-34a inhibits M2 macrophage polarization to promote obesity-induced adipose inflammation. J Clin Investig 129:834–849. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI123069
Louiselle AE, Niemiec SM, Zgheib C, Liechty KW (2021) Macrophage polarization and diabetic wound healing. Transl Res 236:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trsl.2021.05.006
Ma W, Zhang W, Cui B et al (2021) Functional delivery of lncRNA TUG1 by endothelial progenitor cells derived extracellular vesicles confers anti-inflammatory macrophage polarization in sepsis via impairing miR-9-5p-targeted SIRT1 inhibition. Cell Death Dis 12:1056. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-04117-5
Kang M, Huang C-C, Gajendrareddy P et al (2022) Extracellular vesicles from TNFα Preconditioned MSCs: effects on Immunomodulation and bone regeneration. Front Immunol 13:878194. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.878194
Ye Q, Xu H, Liu S et al (2022) Apoptotic extracellular vesicles alleviate Pg-LPS induced inflammatory responses of macrophages via AMPK/SIRT1/NF-κB pathway and inhibit osteoclast formation. J Periodontol 93:1738–1751. https://doi.org/10.1002/JPER.21-0657
Ning H, Chen H, Deng J et al (2021) Exosomes secreted by FNDC5-BMMSCs protect myocardial infarction by anti-inflammation and macrophage polarization via NF-κB signaling pathway and Nrf2/HO-1 axis. Stem Cell Res Ther 12:519. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-021-02591-4
Zheng J, Kong Y, Hu X et al (2020) MicroRNA-enriched small extracellular vesicles possess odonto-immunomodulatory properties for modulating the immune response of macrophages and promoting odontogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther 11:517. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-020-02039-1
Dalirfardouei R, Jamialahmadi K, Jafarian AH, Mahdipour E (2019) Promising effects of exosomes isolated from menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell on wound-healing process in diabetic mouse model. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 13:555–568. https://doi.org/10.1002/term.2799
Woo CH, Kim HK, Jung GY et al (2020) Small extracellular vesicles from human adipose-derived stem cells attenuate cartilage degeneration. J Extracell Vesicles 9:1735249. https://doi.org/10.1080/20013078.2020.1735249
Zhao H, Shang Q, Pan Z et al (2018) Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells attenuate adipose inflammation and obesity through polarizing M2 macrophages and beiging in white adipose tissue. Diabetes 67:235–247. https://doi.org/10.2337/db17-0356
Liu J, Qiu X, Lv Y et al (2020) Apoptotic bodies derived from mesenchymal stem cells promote cutaneous wound healing via regulating the functions of macrophages. Stem Cell Res Ther 11:507. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-020-02014-w
Li J, Wei C, Yang Y et al (2022) Apoptotic bodies extracted from adipose mesenchymal stem cells carry microRNA-21–5p to induce M2 polarization of macrophages and augment skin wound healing by targeting KLF6. Burns 48:1893–1908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.burns.2021.12.010
Park J, Kim S, Lim H et al (2019) Therapeutic effects of human mesenchymal stem cell microvesicles in an ex vivo perfused human lung injured with severe E. coli pneumonia. Thorax 74:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1136/thoraxjnl-2018-211576
Lo Sicco C, Reverberi D, Balbi C et al (2017) Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles as mediators of anti-inflammatory effects: endorsement of macrophage polarization. Stem Cells Transl Med 6:1018–1028. https://doi.org/10.1002/sctm.16-0363
Willis GR, Fernandez-Gonzalez A, Anastas J et al (2018) Mesenchymal stromal cell exosomes ameliorate experimental bronchopulmonary dysplasia and restore lung function through macrophage immunomodulation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 197:104–116. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201705-0925OC
Yuana Y, Sturk A, Nieuwland R (2013) Extracellular vesicles in physiological and pathological conditions. Blood Rev 27:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.blre.2012.12.002
Mayadas TN, Cullere X, Lowell CA (2014) The multifaceted functions of neutrophils. Annu Rev Pathol Mech Dis 9:181–218. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-020712-164023
Eken C, Gasser O, Zenhaeusern G et al (2008) Polymorphonuclear Neutrophil-derived ectosomes interfere with the maturation of monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J Immunol 180:817–824. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.180.2.817
Gasser O, Schifferli JA (2004) Activated polymorphonuclear neutrophils disseminate anti-inflammatory microparticles by ectocytosis. Blood 104:2543–2548. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-01-0361
Eken C, Martin PJ, Sadallah S et al (2010) Ectosomes released by polymorphonuclear neutrophils induce a MerTK-dependent Anti-inflammatory pathway in macrophages. J Biol Chem 285:39914–39921. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.126748
Cheng L, Wang Y, Huang L (2017) Exosomes from M1-polarized macrophages potentiate the cancer vaccine by creating a pro-inflammatory microenvironment in the lymph node. Mol Ther 25:1665–1675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.02.007
Tang D, Cao F, Yan C et al (2022) Extracellular vesicle/macrophage axis: potential targets for inflammatory disease intervention. Front Immunol 13:705472. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.705472
Deng H, Wu L, Liu M et al (2020) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes attenuate LPS-induced ARDS by modulating macrophage polarization through inhibiting glycolysis in macrophages. Shock 54:828–843. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0000000000001549
Deng H, Zhu L, Zhang Y et al (2022) Differential lung protective capacity of exosomes derived from human adipose tissue, bone marrow, and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7837837
Morrison TJ, Jackson MV, Cunningham EK et al (2017) Mesenchymal stromal cells modulate macrophages in clinically relevant lung injury models by extracellular vesicle mitochondrial transfer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 196:1275–1286. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201701-0170OC
Xia L, Zhang C, Lv N et al (2022) AdMSC-derived exosomes alleviate acute lung injury via transferring mitochondrial component to improve homeostasis of alveolar macrophages. Theranostics 12:2928–2947. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.69533
Phinney DG, Di Giuseppe M, Njah J et al (2015) Mesenchymal stem cells use extracellular vesicles to outsource mitophagy and shuttle microRNAs. Nat Commun 6:8472. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9472
Ravichandran KS (2011) Beginnings of a good apoptotic meal: the find-me and Eat-Me signaling pathways. Immunity 35:445–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2011.09.004
de Couto G, Jaghatspanyan E, DeBerge M et al (2019) Mechanism of enhanced MerTK-dependent macrophage efferocytosis by extracellular vesicles. ATVB 39:2082–2096. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.313115
Mentkowski KI, Mursleen A, Snitzer JD et al (2020) CDC-derived extracellular vesicles reprogram inflammatory macrophages to an arginase 1-dependent proangiogenic phenotype. Am J Physiol-Heart Circ Physiol 318:H1447–H1460. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00155.2020
Zhang M, Johnson-Stephenson TK, Wang W et al (2022) Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome-educated macrophages alleviate systemic lupus erythematosus by promoting efferocytosis and recruitment of IL-17+ regulatory T cell. Stem Cell Res Ther 13:484. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-022-03174-7
Tang D, Cao F, Yan C et al (2022) Acinar cell-derived extracellular vesicle MiRNA-183–5p aggravates acute pancreatitis by promoting m1 macrophage polarization through downregulation of FoxO1. Front Immunol 13:869207. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.869207
Patil M, Saheera S, Dubey PK et al (2021) Novel mechanisms of exosome-mediated phagocytosis of dead cells in injured heart. Circ Res 129:1006–1020. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317900
Zheng C, Sui B, Zhang X et al (2021) Apoptotic vesicles restore liver macrophage homeostasis to counteract type 2 diabetes. J Extracell Vesicles. https://doi.org/10.1002/jev2.12109
Xu X, Lai Y, Hua Z-C (2019) Apoptosis and apoptotic body: disease message and therapeutic target potentials. Bioscience Reports 39:BSR20180992
Wu Y, Zhang Y, Dai L et al (2019) An apoptotic body-biomimic liposome in situ upregulates anti-inflammatory macrophages for stabilization of atherosclerotic plaques. J Control Release 316:236–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.10.043
Bao L, Dou G, Tian R et al (2022) Engineered neutrophil apoptotic bodies ameliorate myocardial infarction by promoting macrophage efferocytosis and inflammation resolution. Bioact Mater 9:183–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.08.008
Zhou M, Li Y-J, Tang Y-C et al (2022) Apoptotic bodies for advanced drug delivery and therapy. J Control Release 351:394–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.09.045
Gao W-J, Liu J-X, Liu M-N et al (2021) Macrophage 3D migration: a potential therapeutic target for inflammation and deleterious progression in diseases. Pharmacol Rese 167:105563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105563
Murray PJ, Wynn TA (2011) Protective and pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets. Nat Rev Immunol 11:723–737. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3073
Xu X, Poulsen KL, Wu L et al (2022) Targeted therapeutics and novel signaling pathways in non-alcohol-associated fatty liver/steatohepatitis (NAFL/NASH). Sig Transduct Target Ther 7:287. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-01119-3
Chen L, Chen R, Kemper S et al (2018) Therapeutic effects of serum extracellular vesicles in liver fibrosis. J Extracell Vesicles 7:1461505. https://doi.org/10.1080/20013078.2018.1461505
Liao C-Y, Song MJ, Gao Y et al (2018) Hepatocyte-derived lipotoxic extracellular vesicle sphingosine 1-phosphate induces macrophage chemotaxis. Front Immunol 9:2980. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.02980
Guo Q, Furuta K, Lucien F et al (2019) Integrin β1-enriched extracellular vesicles mediate monocyte adhesion and promote liver inflammation in murine NASH. J Hepatol 71:1193–1205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2019.07.019
Chang Y-J, Li Y-S, Wu C-C et al (2019) Extracellular MicroRNA-92a mediates endothelial cell-macrophage communication. ATVB 39:2492–2504. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.312707
Nguyen M-A, Karunakaran D, Geoffrion M et al (2018) Extracellular vesicles secreted by atherogenic macrophages transfer MicroRNA to inhibit cell migration. ATVB 38:49–63. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309795
Sun Y, Zhou Y, Shi Y et al (2021) Expression of miRNA-29 in pancreatic β cells promotes inflammation and diabetes via TRAF3. Cell Rep 34:108576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108576
Bonjoch L, Casas V, Carrascal M, Closa D (2016) Involvement of exosomes in lung inflammation associated with experimental acute pancreatitis: exosomes in acute pancreatitis. J Pathol 240:235–245. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.4771
Zou X, Zhang G, Cheng Z et al (2014) Microvesicles derived from human Wharton’s Jelly mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by suppressing CX3CL1. Stem Cell Res Ther 5:40. https://doi.org/10.1186/scrt428
Yu B, Shao H, Su C et al (2016) Exosomes derived from MSCs ameliorate retinal laser injury partially by inhibition of MCP-1. Sci Rep 6:34562. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep34562
Shen B, Liu J, Zhang F et al (2016) CCR2 positive exosome released by mesenchymal stem cells suppresses macrophage functions and alleviates ischemia/reperfusion-induced renal injury. Stem Cells Int 2016:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1240301
Li J, Xue H, Li T et al (2019) Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells attenuate the progression of atherosclerosis in ApoE−/- mice via miR-let7 mediated infiltration and polarization of M2 macrophage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 510:565–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.02.005
Qiao S, Zhang W, Yin Y et al (2020) Extracellular vesicles derived from Krüppel-Like Factor 2-overexpressing endothelial cells attenuate myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by preventing Ly6C high monocyte recruitment. Theranostics 10:11562–11579. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.45459
Liu M, Sun Y, Zhang Q (2018) Emerging role of extracellular vesicles in bone remodeling. J Dent Res 97:859–868. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034518764411
Kim HY, Song M, Gho YS et al (2021) Extracellular vesicles derived from the periodontal pathogen Filifactor alocis induce systemic bone loss through Toll-like receptor 2. J Extracell Vesicles 10:e12157. https://doi.org/10.1002/jev2.12157
Hajishengallis G (2015) Periodontitis: from microbial immune subversion to systemic inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 15:30–44. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3785
Pan W, Wang Q, Chen Q (2019) The cytokine network involved in the host immune response to periodontitis. Int J Oral Sci 11:30. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41368-019-0064-z
Preshaw PM, Alba AL, Herrera D et al (2012) Periodontitis and diabetes: a two-way relationship. Diabetologia 55:21–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-011-2342-y
Sanz M, Marco del Castillo A, Jepsen S et al (2020) Periodontitis and cardiovascular diseases: consensus report. J Clin Periodontol 47:268–288. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.13189
Naderi S, Merchant AT (2020) The association between periodontitis and cardiovascular disease: an update. Curr Atheroscler Rep 22:52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-020-00878-0
Sadrameli M, Bathini P, Alberi L (2020) Linking mechanisms of periodontitis to Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Opin Neurol 33:230–238. https://doi.org/10.1097/WCO.0000000000000797
Pihlstrom BL, Michalowicz BS, Johnson NW (2005) Periodontal diseases. The Lancet 366:1809–1820. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67728-8
Wang Z, Maruyama K, Sakisaka Y et al (2019) Cyclic stretch force induces periodontal ligament cells to secrete exosomes that suppress IL-1β production through the inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway in macrophages. Front Immunol 10:1310. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01310
Sima C (2000) Glogauer M (2013) Macrophage subsets and osteoimmunology: tuning of the immunological recognition and effector systems that maintain alveolar bone. Periodontol 63:80–101. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12032
Kang H, Lee M-J, Park S, Lee M-S (2018) Lipopolysaccharide-preconditioned periodontal ligament stem cells induce M1 polarization of macrophages through extracellular vesicles. IJMS 19:3843. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123843
Xia Y, Zhou K, Sun M et al (2021) The miR-223-3p regulates pyroptosis through NLRP3-caspase 1-GSDMD signal axis in periodontitis. Inflammation 44:2531–2542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-021-01522-y
Chen X, Wan Z, Yang L et al (2022) Exosomes derived from reparative M2-like macrophages prevent bone loss in murine periodontitis models via IL-10 mRNA. J Nanobiotechnol 20:110. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-022-01314-y
Lin H, Chen H, Zhao X et al (2022) Advances of exosomes in periodontitis treatment. J Transl Med 20:279. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-022-03487-4
Li Y, Duan X, Chen Y et al (2022) Dental stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles as promising therapeutic agents in the treatment of diseases. Int J Oral Sci 14:2. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41368-021-00152-2
Joswig A-J, Mitchell A, Cummings KJ et al (2017) Repeated intra-articular injection of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells causes an adverse response compared to autologous cells in the equine model. Stem Cell Res Ther 8:42. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-017-0503-8
Lee AS, Tang C, Rao MS et al (2013) Tumorigenicity as a clinical hurdle for pluripotent stem cell therapies. Nat Med 19:998–1004. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3267
Nakao Y, Fukuda T, Zhang Q et al (2021) Exosomes from TNF-α-treated human gingiva-derived MSCs enhance M2 macrophage polarization and inhibit periodontal bone loss. Acta Biomater 122:306–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2020.12.046
Wang R, Ji Q, Meng C et al (2020) Role of gingival mesenchymal stem cell exosomes in macrophage polarization under inflammatory conditions. Int Immunopharmacol 81:106030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2019.106030
Sun J, Wang Z, Liu P et al (2022) Exosomes derived from human gingival mesenchymal stem cells attenuate the inflammatory response in periodontal ligament stem cells. Front Chem 10:863364. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2022.863364
Zhang Y, Wang Z, Shi B et al (2021) Effect of gingival mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on inflammatory macrophages in a high-lipid microenvironment. Int Immunopharmacol 94:107455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107455
Huang Y, Liu Q, Liu L et al (2022) Lipopolysaccharide-preconditioned dental follicle stem cells derived small extracellular vesicles treating periodontitis via reactive oxygen species/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling-mediated antioxidant effect. IJN 17:799–819. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S350869
Liu L, Guo S, Shi W et al (2021) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles promote periodontal regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A 27:962–976. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.tea.2020.0141
Chen Z, Bozec A, Ramming A, Schett G (2019) Anti-inflammatory and immune-regulatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 15:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41584-018-0109-2
Tardito S, Martinelli G, Soldano S et al (2019) Macrophage M1/M2 polarization and rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review. Autoimmun Rev 18:102397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2019.102397
Udalova IA, Mantovani A, Feldmann M (2016) Macrophage heterogeneity in the context of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 12:472–485. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2016.91
Boutet M-A, Courties G, Nerviani A et al (2021) Novel insights into macrophage diversity in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Autoimmun Rev 20:102758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2021.102758
Alghamdi M, Alamry SA, Bahlas SM et al (2022) Circulating extracellular vesicles and rheumatoid arthritis: a proteomic analysis. Cell Mol Life Sci 79:25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-021-04020-4
Withrow J, Murphy C, Liu Y et al (2016) Extracellular vesicles in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 18:286. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-016-1178-8
Cloutier N, Tan S, Boudreau LH et al (2013) The exposure of autoantigens by microparticles underlies the formation of potent inflammatory components: the microparticle-associated immune complexes. EMBO Mol Med 5:235–249. https://doi.org/10.1002/emmm.201201846
Tran T-H, Mattheolabakis G, Aldawsari H, Amiji M (2015) Exosomes as nanocarriers for immunotherapy of cancer and inflammatory diseases. Clin Immunol 160:46–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2015.03.021
Boilard E, Blanco P, Nigrovic PA (2012) Platelets: active players in the pathogenesis of arthritis and SLE. Nat Rev Rheumatol 8:534–542. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2012.118
Austin-Williams S, Hussain MT, Oggero S, Norling LV (2021) Enhancing extracellular vesicles for therapeutic treatment of arthritic joints. Free Radical Biol Med 175:80–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.08.235
Ni Z, Zhou S, Li S et al (2020) Exosomes: roles and therapeutic potential in osteoarthritis. Bone Res 8:25. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41413-020-0100-9
Domenis R, Zanutel R, Caponnetto F et al (2017) Characterization of the proinflammatory profile of synovial fluid-derived exosomes of patients with osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm 2017:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4814987
Yang Y, Guo L, Wang Z et al (2021) Targeted silver nanoparticles for rheumatoid arthritis therapy via macrophage apoptosis and Re-polarization. Biomaterials 264:120390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120390
Ni Z, Kuang L, Chen H et al (2019) The exosome-like vesicles from osteoarthritic chondrocyte enhanced mature IL-1β production of macrophages and aggravated synovitis in osteoarthritis. Cell Death Dis 10:522. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1739-2
Rhys HI, Dell’Accio F, Pitzalis C et al (2018) Neutrophil microvesicles from healthy control and rheumatoid arthritis patients prevent the inflammatory activation of macrophages. EBioMedicine 29:60–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.02.003
Zheng L, Wang Y, Qiu P et al (2019) Primary chondrocyte exosomes mediate osteoarthritis progression by regulating mitochondrion and immune reactivity. Nanomedicine 14:3193–3212. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm-2018-0498
Yang J-H, Liu F-X, Wang J-H et al (2020) Mesenchymal stem cells and mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: potential roles in rheumatic diseases. WJSC 12:688–705. https://doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i7.688
Tofiño-Vian M, Guillén MI, Alcaraz MJ (2018) Extracellular vesicles: a new therapeutic strategy for joint conditions. Biochem Pharmacol 153:134–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2018.02.004
Zhang S, Chuah SJ, Lai RC et al (2018) MSC exosomes mediate cartilage repair by enhancing proliferation, attenuating apoptosis and modulating immune reactivity. Biomaterials 156:16–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.11.028
Cosenza S, Ruiz M, Toupet K et al (2017) Mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes and microparticles protect cartilage and bone from degradation in osteoarthritis. Sci Rep 7:16214. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-15376-8
Li K, Yan G, Huang H et al (2022) Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of the extracellular vesicles derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on osteoarthritis via M2 macrophages. J Nanobiotechnol 20:38. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-021-01236-1
Kim H, Back JH, Han G et al (2022) Extracellular vesicle-guided in situ reprogramming of synovial macrophages for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Biomaterials 286:121578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121578
Castegna A, Gissi R, Menga A et al (2020) Pharmacological targets of metabolism in disease: opportunities from macrophages. Pharmacol Ther 210:107521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107521
He H, Ghosh S, Yang H (2017) Nanomedicines for dysfunctional macrophage-associated diseases. J Control Release 247:106–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.12.032
Lim GT, You DG, Han HS et al (2021) Bioorthogonally surface-edited extracellular vesicles based on metabolic glycoengineering for CD44-mediated targeting of inflammatory diseases. J Extracell Vesicles. https://doi.org/10.1002/jev2.12077
Xu H, Jia S, Xu H (2019) Potential therapeutic applications of exosomes in different autoimmune diseases. Clin Immunol 205:116–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2019.06.006
Turpin D, Truchetet M-E, Faustin B et al (2016) Role of extracellular vesicles in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev 15:174–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2015.11.004
Yan F, Zhong Z, Wang Y et al (2020) Exosome-based biomimetic nanoparticles targeted to inflamed joints for enhanced treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. J Nanobiotechnol 18:115. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-020-00675-6
Takenaka M, Yabuta A, Takahashi Y, Takakura Y (2021) Interleukin-4-carrying small extracellular vesicles with a high potential as anti-inflammatory therapeutics based on modulation of macrophage function. Biomaterials 278:121160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.121160
Li H, Feng Y, Zheng X et al (2022) M2-type exosomes nanoparticles for rheumatoid arthritis therapy via macrophage re-polarization. J Control Release 341:16–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.11.019
Zhang M, Hu W, Cai C et al (2022) Advanced application of stimuli-responsive drug delivery system for inflammatory arthritis treatment. Materi Today Bio 14:100223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100223
Lew DP, Waldvogel FA (2004) Osteomyelitis. Lancet 364:369–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16727-5
Kavanagh N, Ryan EJ, Widaa A et al (2018) Staphylococcal osteomyelitis: disease progression, treatment challenges, and future directions. Clin Microbiol Rev 31:e00084-e117. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00084-17
Rao N, Ziran BH, Lipsky BA (2011) Treating Osteomyelitis: antibiotics and Surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 127:177S-187S. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3182001f0f
Jahan N, Patton T, O’Keeffe M (2022) The influence of antibiotic resistance on innate immune responses to Staphylococcus aureus infection. Antibiotics 11:542. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11050542
Chen H, Zhang J, He Y et al (2022) Exploring the role of Staphylococcus aureus in inflammatory diseases. Toxins (Basel) 14:464. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14070464
Zaborowska M, Vazirisani F, Shah FA et al (2021) Immunomodulatory effects exerted by extracellular vesicles from Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bone-anchored prostheses. Biomaterials 278:121158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.121158
Missiakas D, Winstel V (2021) Selective host cell death by Staphylococcus aureus: a strategy for bacterial persistence. Front Immunol 11:621733. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.621733
Gimza BD, Cassat JE (2021) Mechanisms of antibiotic failure during Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis. Front Immunol 12:638085. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.638085
Rowe SE, Wagner NJ, Li L et al (2020) Reactive oxygen species induce antibiotic tolerance during systemic Staphylococcus aureus infection. Nat Microbiol 5:282–290. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-019-0627-y
Rowe SE, Beam JE, Conlon BP (2021) Recalcitrant Staphylococcus aureus infections: obstacles and solutions. Infect Immun 89:e00694-e720. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00694-20
Yu K, Song L, Kang HP et al (2020) Recalcitrant methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection of bone cells: Intracellular penetration and control strategies. Bone & Joint Research 9:49–59. https://doi.org/10.1302/2046-3758.92.BJR-2019-0131.R1
Zelmer AR, Nelson R, Richter K, Atkins GJ (2022) Can intracellular Staphylococcus aureus in osteomyelitis be treated using current antibiotics? A systematic review and narrative synthesis. Bone Res 10:53. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41413-022-00227-8
Ma J, Jiang L, Liu G (2022) Cell membrane-coated nanoparticles for the treatment of bacterial infection. WIREs Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1002/wnan.1825
Zhang Y, Liang R, Xu J et al (2017) Efficient induction of antimicrobial activity with vancomycin nanoparticle-loaded poly(trimethylene carbonate) localized drug delivery system. IJN 12:1201–1214. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S127715
Trousil J, Dal N-JK, Fenaroli F et al (2022) Antibiotic-Loaded Amphiphilic Chitosan Nanoparticles Target Macrophages and Kill an Intracellular Pathogen. Small 18:2201853. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202201853
Gao Y, Chen Y, Cao Y et al (2021) Potentials of nanotechnology in treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Med Chem 213:113056. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.113056
Yang S, Han X, Yang Y et al (2018) Bacteria-Targeting Nanoparticles with Microenvironment-Responsive Antibiotic Release To Eliminate Intracellular Staphylococcus aureus and Associated Infection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:14299–14311. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b15678
Yang X, Shi G, Guo J et al (2018) Exosome-encapsulated antibiotic against intracellular infections of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. IJN 13:8095–8104. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S179380
Yang X, Xie B, Peng H et al (2021) Eradicating intracellular MRSA via targeted delivery of lysostaphin and vancomycin with mannose-modified exosomes. J Control Release 329:454–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.11.045
Funding
This study was supported by grants from Guangdong Science and Technology Department grant number2021A0505030079; the Key Project of Science and Technology of Liwan District, Guangzhou City (No. 2201006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL has made substantial contributions to conception, design, draft, and revise the manuscript. ZW and SL were involved in drafting the manuscript and revising it critically for important intellectual content. JL, ZZ, YO, ZS, and DC gave final approval of the version to be published. LG and TL agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Y., Wang, Z., Liu, S. et al. Roles of extracellular vesicles on macrophages in inflammatory bone diseases. Mol Cell Biochem (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-023-04809-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-023-04809-w