Abstract
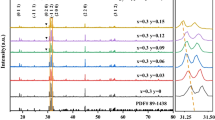
In this paper, 1%Ho3+, 8%Yb3+; x%Mn2+: BaY2F8 phosphors were successfully prepared by the co-precipitation method combined with the fluorinated atmosphere sintering method. The samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscope, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, photoluminescence spectroscopy, and up-conversion fluorescence decay curve test. The results showed that the Mn element was doped into BaY2F8 phosphors in the valence state of Mn2+ ions, and the doped Yb3+, Ho3+, and Mn2+ ions did not change the structure of BaY2F8, and under 980 nm laser pumping, the emission peaks of the phosphors were at 544 nm and 660 nm, which are green and red luminescence, respectively. Through the modification of Mn2+ ions, the relative intensity is increased by 2.79 times and 7.04 times, and the optimal Mn2+ doping concentration was determined to be 4%. Finally, the energy transfer between Ho3+ and Mn2+ ions was explored. It shows that BaY2F8: Ho3+, Yb3+ phosphors doped with transition metal Mn2+ are used as up-conversion luminescent materials and have important potential applications in the fields of biomarkers, high-resolution imaging, and solar cells.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
G. Yi, H. Lu, S. Zhao, Y. Ge, W. Yang, D. Chen, L.H. Guo, Synthesis, Characterization, and biological application of size-controlled nanocrystalline NaYF4: Yb, Er infrared to visible up-conversion phosphors. Nano Lett. 4, 2191–2195 (2004)
F. Wang, Y. Han, C.S. Lim, Y. Lu, J. Wang, J. Xu, H. Chen, C. Zhang, M. Hong, X. Liu, Simultaneous phase and size control of upconversion nanocrystals through lanthanide doping. Nature 463, 1061–1065 (2010)
F. Wang, X. Liu, Recent advances in the chemistry of lanthanide-doped upconversion nanocrystals. Chem. Soc. Rev. 38, 976–989 (2009)
X. Wang, C. Zhang, W. Li, D. Hu, S. Li, H. Lin, F. Zeng, C. Li, Z. Su, Effects of Nd ions on the fluorescence properties of Ho: BaY2F8 crystals in the wavelength range of 12.5μm. J. Lumin. 221, 116927 (2020)
S. Li, Y. He, M. Li, F. Zeng, X. Wang, C. Sun, Z. Su, Tunable magnetic and fluorescent properties of Tb3Ga5O12 nanoparticles doped with Er3+, Yb3+, and Sc3+. J. Alloys Compd. 794, 227–235 (2019)
Z. Xia, C. Ma, M.S. Molokeev, Q. Liu, K. Rickert, K.R. Poeppelmeier, Chemical unit cosubstitution and tuning of photoluminescence in the Ca2(Al1−xMgx) (Al1−xSi1+x) O7: Eu2+ phosphor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 12494–12497 (2015)
J.C. Fischer, P.L. Goldschmidt, B.R. Bruggemann, K. Krämer, D. Biner, M. Hermle, S.W. Glunz, J. Appl. Phys. 108, 044912 (2010)
F. Pellé, S. Ivanova, J.F. Guillemoles, Upconversion of 1.54 μm radiation in Er3+ doped fluoride-based materials for c-Si solar cell with improved efficiency. EPJ photovoltaics 2, 20601 (2011)
C. Li, J. Lin, Rare earth fluoride nano-/microcrystals: synthesis, surface modification and application. J. Mater. Chem. 20, 6831–6847 (2010)
G. Chen, H. Liu, H. Liang, G. Somesfalean, Z. Zhang, Upconversion emission enhancement in Yb3+/Er3+-codoped Y2O3 nanocrystals by tridoping with Li+ ions. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 12030–12036 (2008)
C. Lee, H. Park, W. Kim, S. Park, Origin of strong red emission in Er3+-based upconversion materials: role of intermediate states and cross relaxation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 21, 24026–24033 (2019)
D. Avram, C. Colbea, C. Tiseanu, Effects of local symmetry on upconversion emission mechanisms under pulsed excitation. J. Mater. Chem. C. 7, 13770 (2019)
W. Shockley, H.J. Queisser, Detailed balance limit of efficiency of p-n junction solar cells. J. Appl. Phys. 32(3), 510–519 (1961)
T. Trupke et al., Efficiency enhancement of solar cells by luminescent up-conversion of sunlight. Solar Energy Mater Solar Cells 90, 3327–3338 (2006)
M. Yuan, R. Wang, C. Zhang et al., Revisiting the enhanced red upconversion emission from a single β-NaYF4: Yb/Er microcrystal by doping with Mn2+ ions. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 14, 1–10 (2019)
L. Rao, W. Lu, T. Zeng et al., Sub-10 nm BaLaF5: Mn/Yb/Er nanoprobes for dual-modal synergistic in vivo upconversion luminescence and X-ray bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2(38), 6527–6533 (2014)
J.A. DeLuca, F.S. Ham, Efficient luminescent energy transfer from Mn2+ to Yb3+ in CaF2. J. Electrochem. Soc. 124(10), 1592 (1977)
Y. Bai, Y. Wang, K. Yang, X. Zhang, G. Peng, Y. Song, Z. Pan, C.H. Wang, The effect of Li on the spectrum of Er3+in Li- and Er-codoped ZnO nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. C. 112, 12259–12263 (2008)
A. Li, D. Xu, H. Lin, L. Yao, S. Yang, Y. Shao, Y. Zhang, Z. Chen, A novel aniondoping strategy to enhance upconversion luminescence in NaGd(MoO4)2: Yb3+/Er3+nanophosphors. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19, 15693 (2017)
B.S. Richards, A. Shalav, Enhancing the near-infrared spectral response of silicon optoelectronic devices via up-conversion[J]. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 54(10), 2679–2684 (2007)
A. Boccolini, R. Faoro, E. Favilla et al., BaY2F8 doped with Er3+: An upconverter material for photovoltaic application[J]. J. Appl. Phys. 114(6), 064904 (2013)
A. Tonceli, M. Tonelli, A. Cassanho et al., Spectroscopy and dynamic measurements of Tm, Dy:BaY2F8 crystal. J. Lumin. 82(4), 291–298 (1999)
A.A. Kaminsk, New room-temperature diode-laser-pumped efficient quasi-CW and CW single-mode Laser Based on monoclinic BaY2F8:Nd3+crystal. Phys. Status Sol. 137, 61–63 (1993)
A.C.S. de Mello et al., Luminescence properties of Er3+ and Tm3+ doped BaY2F8. J. Lumin. 138, 19–24 (2014)
M. Peng, Z. Pei, G. Hong et al., The reduction of Eu3+ to Eu2+ in BaMgSiO4: Eu prepared in air and the luminescence of BaMgSiO4:Eu2+ phosphor. J. Mater. Chem. 13(5), 1202–1205 (2003)
C. Zhang, X. Wang, C. Li et al., Effect of Li ions on structure and spectroscopic properties of NaY (WO4)2: Yb/Ho phosphor. Ceram Int. 46(15), 24248–24256 (2020)
X. Wang, Y. Hou, J. Qua, J. Ding, H. Lin, L. Liu, Y. Zhou, F. Zeng, C. Li, Z. Su, Up- conversion photoluminescence properties and energy transfer process of Ho3+, Yb3+ Co-doped BaY2F8 fine fibers. J. Lumin. 212, 154–159 (2019)
Z. Kang, L. Li, Q. Wei, Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 12, 281 (1996)
B.R. Strohmeier, D.M. Hercules, Surface spectroscopic characterization of manganese/aluminum oxide catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. 88(21), 4922–4929 (1984)
A. Aoki, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic studies on ZnS: MnF2 phosphors. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 15(2), 305 (1976)
K.L. Reddy, V. Srinivas, K.R. Shankar, S.K. Orcid, V. Sharma, A. Kumar, A. Bahuguna, K. Bhattacharyya, V. Krishnan, Enhancement of luminescence intensity in red emitting NaYF4: Yb/Ho/Mn upconversion nanophosphors by variation of reaction parameters. J. Phys. Chem. C 121, 11783–11793 (2017)
M. Gunaseelan, S. Yamini, G.A. Kumar et al., Photon upconversion characteristics of intense green emitting BaYF5: Yb3+, Er3+ nanoclusters prepared by reverse microemulsion. Mater. Res. Bull. 107, 366–378 (2018)
M. Karbowiak, A. Mech, A. Bednarkiewicz et al., Synthesis and properties of solution-processed Eu3+: BaY2F8. J. Lumin. 114(1), 1–8 (2005)
X. Wang, C. Zhang, D. Hu et al., Influence of Yb ions concentration on Ho: BaY2F8 crystals emission in the range of 1–3 μm. Opt Mater. 109, 110141 (2020)
X. Wang, Y. Xiao, C. Zhang et al., Deactivation effect of Pr ions on the emission performance of Ho: BaY2F8 crystals in the range of 1–4 μm. J. Lumin. 228, 117603 (2020)
X. Jiang, X. Wang, X. Shi et al., Effect of Mn4+ ions on the structure and luminescence properties of NaY (MoO4) 2: Yb3+/Er3+ phosphor. Opt Mater. 113, 110873 (2021)
W. Yang, Z. Zhang, X. Zhang et al., Enhancement of fluorescence and magnetic properties of CeF3: RE3+ (Tb, Gd) phosphors via multi-band UV excitation and Li doping regulation. Ceram. Int. 47(12), 16450–16459 (2021)
A. Li, D. Xu, Y. Zhang et al., Upconversion luminescence and energy-transfer mechanism of NaGd (MoO4) 2: Yb3+/Er3+ microcrystals. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 99(5), 1657–1663 (2016)
J. Li, Y. Wang, Tunable emission with efficient energy transfer in Na2SrSi2O6:Ce3+, Tb3+ phosphor for near-UV LED. Opt Mater. 88, 648–652 (2019)
Y. Chen, Q. Guo, L. Liao et al., Preparation, crystal structure and luminescence properties of a novel single-phase red emitting phosphor CaSr2(PO4)2:Sm3+, Li+. Rsc. Adv. 9(9), 4834–4842 (2019)
X. Zhang, X. Shi, Y. Hou et al., Cubic Ba2LaF7: Yb3+/Ln (Ln= Er3+, Ho3+) up-conversion submicron particles controllable synthesis and luminescence properties. J. Mater. Sci-Mater. El. 32(20), 24856–24870 (2021)
A.G. Makhanek, R.I. Gintoft, A.L. Dzhugury et al., Two-photon spectroscopy of rare-earth ions in crystals. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 40, 684–688 (1984)
Q. Qiang, Y. Wang, Enhanced optical temperature sensing and upconversion emissions based on the Mn2+ codoped NaGdF4: Yb3+, Ho3+ nanophosphor. New. J. Chem. 43(13), 5011–5019 (2019)
Q. Tian, W. Yao, W. Wu, C. Jiang, NIR light-activated upconversion semiconductor photocatalysts. Nanoscale. Horiz. 4, 10–25 (2019)
H. Suo, C. Guo, W. Wang, T. Li, C. Duan, M. Yin, Mechanism and stability of spectrally pure green up-conversion emission in Yb3+/Ho3+ co-doped Ba5Gd8Zn4O21 phosphors. Dalton Trans. 45, 2629–2636 (2016)
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Professor Ligong Zhang, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences for his help in testing.
Funding
This work was supported by Government Funded Projects (627010104), International Science and Technology Cooperation Project of Jilin Province Science, Technology Department (20200801038GH).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZZ: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, writing—original draft. WY: data curation, software, formal analysis, writing—editing. XJ: formal analysis, writing—review. SG: formal analysis, methodology. XZ: investigation, methodology. TZ: investigation, methodology. XW: investigation, methodology. XS: investigation, methodology. ZL: investigation, methodology. HL: investigation, methodology. KH: investigation, methodology. CL: conceptualization, supervision, funding acquisition, resources, supervision. FZ: conceptualization, supervision, funding acquisition, resources, supervision. ZS: conceptualization, supervision, funding acquisition, resources, supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Yang, W., Jiang, X. et al. Influence of Mn2+ ions on the structure and spectral properties of BaY2F8: Yb3+/Ho3+ phosphors. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 21148–21160 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08919-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08919-x