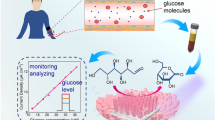
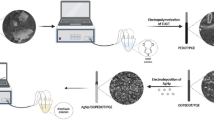
Abstract
The non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor has the advantages of fast response and high sensitivity. In this study, the NiMoO4·xH2O nanowires were quickly grown in situ on the carbon cloth substrate (NiMoO4·xH2O NW/CC) in one step by using the dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) micro-plasma method. With the benefits of the open network of 3D binary metal oxide NiMoO4 nanowire self-supporting electrode, large specific surface area, many active sites and the synergistic effect of Ni and Mo, NiMoO4·xH2O NW/CC show excellent electrocatalytic sensing performance for glucose with a high sensitivity of 4510 μA mM−1 cm−2, and a low detection limit of 63 nM (S/N = 3). There is also good selectivity, stability and practical application prospects. It has been shown that the modified DBD micro-plasma method has the advantages of being low in cost, simple and fast, green and environmentally friendly, and therefore it has good application prospects in the preparation of electrochemical sensing materials.





Similar content being viewed by others

References
Mei H, Wu W, Yu B, Li Y, Wu H, Wang S, Xia Q (2015) Non-enzymatic sensing of glucose at neutral pH values using a glassy carbon electrode modified with carbon supported Co@Pt core-shell nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 182:1869–1875
Wang G, He X, Wang L, Gu A, Huang Y, Fang B, Geng B, Zhang X (2013) Non-enzymatic electrochemical sensing of glucose. Microchim Acta 180:161–186
Ohta KT, Isselbacher RD (1990) Regulation of glucose transporters in LLC-PK1 cells: effects of D-glucose and monosaccharides. Mol Cell Biol 10:6491–6499
Wang Z, Cao X, Liu D, Hao S, Kong R, Du G, Asiri AM, Sun X (2017) Copper-nitride nanowires array: an efficient dual-functional catalyst electrode for sensitive and selective non-enzymatic glucose and hydrogen peroxide sensing. Chem-Eur J 23:4986–4989
Steiner MS, Duerkop A, Wolfbeis OS (2011) Optical methods for sensing glucose. Chem Soc Rev 40:4805–4839
Malchoff CD, Landau JI, Shoukri K, Buchert J (2002) A novel noninvasive blood glucose monitor. Diabetes Care 25:2268–2275
Luo J, Luo P, Xie M, Du K, Zhao B, Pan F, Fan P, Zeng F, Zhang D, Zheng Z, Liang G (2013) A new type of glucose biosensor based on surface acoustic wave resonator using Mn-doped ZnO multilayer structure. Biosens Bioelectron 49:512–518
Gourzi M, Rouane A, Guelaz R, Alavi MS, McHugh MB, Nadi M, Roth P (2005) Noninvasive glycaemia blood measurements by electromagnetic sensor: study in static and dynamic blood circulation. J Med Eng Technol 29:22–26
Wang J (2008) Electrochemical glucose biosensors. Chem Rev 108:814–825
Liu T, Li M, Dong P, Zhang Y, Guo L (2018) Design and facile synthesis of mesoporous cobalt nitride nanosheets modified by pyrolytic carbon for the nonenzymatic glucose detection. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 255:1983–1994
Li M, Bo X, Zhang Y, Han C, Guo L (2014) One-pot ionic liquid-assisted synthesis of highly dispersed PtPd nanoparticles/reduced graphene oxide composites for nonenzymatic glucose detection. Biosens Bioelectron 56:223–230
Pang H, Lu Q, Wang J, Li Y, Gao F (2010) Glucose-assisted synthesis of copper micropuzzles and their application as nonenzymatic glucose sensors. Chem Commun 46:2010–2012
Zhai Y, Li J, Chu X, Xu M, Jin F, Li X, Fang X, Wei Z, Wang X (2016) MoS2 microflowers based electrochemical sensing platform for non-enzymatic glucose detection. J Alloy Compd 672:600–608
Wang Y, Zhu Y, Xing Z, Qian Y (2013) Hydrothermal synthesis of α-MoO3 and the influence of later heat treatment on its electrochemical properties. Int J Electrochem Sci 8:9851–9857
Sharma M, Gangan A, Chakraborty B, Rout CS (2017) Non-enzymatic glucose sensing properties of MoO3 nanorods: experimental & density functional theory investigations. Appl Phys 50(47):475401. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/aa8e7f
Sun T, Zhao X, Li B, Shu H, Luo L, Xia W, Chen M, Zeng P, Yang X, Gao P, Pei Y, Wang X (2021) NiMoO4 nanosheets anchored on N–S doped carbon clothes with hierarchical structure as a bidirectional catalyst toward accelerating polysulfides conversion for Li–S battery. Adv Funct Mater 31:2101285. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202101285
Qu G, Li T, Jia S, Zheng H, Li L, Cao F, Wang H, Ma W, Tang Y, Wang J (2017) Rapid and scalable synthesis of Mo-based binary and ternary oxides for electrochemical applications. Adv Funct Mater 27:1700928. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201700928
Zhang X, Cui S, Wang N, Hou H, Chen W, Mi L (2017) Synergistic effect initiating Ni1−xCoxMoO4·xH2O as electrodes for high-energy-density asymmetric supercapacitors. Electrochim Acta 228:274–281
Ghiasi T, Ahmadi S, Ahmadi E, Olyai MRTB, Khodadadi Z (2021) Novel electrochemical sensor based on modified glassy carbon electrode with graphene quantum dots, chitosan and nickel molybdate nanocomposites for diazinon and optimal design by the Taguchi method. Microchem J 160:105628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.105628
Xu W, Zhang B, Wang X, Wang G, Ding D (2018) The flame retardancy and smoke suppression effect of a hybrid containing CuMoO4 modified reduced graphene oxide/layered double hydroxide on epoxy resin. J Hazard Mater 343:364–375
Zhang L, Mi T, Ziaee MA, Liang L, Wang R (2018) Hollow POM@MOF hybrid-derived porous Co3O4/CoMoO4 nanocages for enhanced electrocatalytic water oxidation. J Mater Chem A 6:1639–1647
Peng S, Li L, Wu H, Madhavi S, Luo X (2015) Controlled growth of NiMoO4 nanosheet and nanorod arrays on various conductive substrates as advanced electrodes for asymmetric supercapacitors. Adv Energy Mater 5:1401172. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201401172
Huang M, He D, Wang M, Jiang P (2018) NiMoO4 nanosheet arrays anchored on carbon cloth as 3D open electrode for enzyme-free glucose sensing with improved electrocatalytic activity. Anal Bioanal Chem 410:7921–7929
Qing C, Liu Y, Sun X, Yang X, Wang H, Sun D, Wang B, Zhou Q, Xu L, Tang Y (2016) Controlled growth of NiMoO4·H2O nanoflake and nanowire arrays on Ni foam for superior performance of asymmetric super capacitor. RSC Adv 6:67785–67793
Rani SD, Ramachandran R, Sheet S, Aziz MA, Lee YS, AlSehemi AG, Pannipara M, Xia Y, Tsai SY, Ng FL, Phang SM, Kumar GG (2020) NiMoO4 nanoparticles decorated carbon nanofiber membranes for the flexible and high performance glucose sensors. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 312:127886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.127886
Govindasamy M, Shanthi S, Elaiyappillai E, Wang SF, Johnson PM, Ikeda H, Hayakawa Y, Ponnusamy S, Muthamizhchelvan C (2019) Fabrication of hierarchical NiCo2S4@CoS2 nanostructures on highly conductive flexible carbon cloth substrate as a hybrid electrode material for supercapacitors with enhanced electrochemical performance. Electrochim Acta 293:328–337
Ray SK, Dhakal D, Lee SW (2018) Rapid degradation of naproxen by AgBr-α-NiMoO4, composite photocatalyst in visible light: mechanism and pathways. Chem Eng J 347:836–848
Park JS, Cho JS, Kang YC (2018) Scalable synthesis of NiMoO4 microspheres with numerous empty nanovoids as an advanced anode material for Li-ion batteries. J Power Sour 379:278–287
Dong T, Li M, Wang P, Yang P (2018) Synthesis of hierarchical tube-like yolk-shell Co3O4@NiMoO4 for enhanced supercapacitor performance. Int J Hydrogen Energ 43:14569–14577
Xu K, Tang Q, Zhao W, Yu X, Yang Y, Yu T, Yuan C (2019) In situ growth of Co3O4@NiMoO4 composite arrays on alumina substrate with improved triethylamine sensing performance. Sens Actuat B Chem 302:127154
Du X, Fu J, Zhang X (2018) NiCo2O4@NiMoO4 supported on nickel foam for electrocatalytic water splitting. Chem Cat Chem 10:5533–5540
Liu C, Cheng HM (2016) Controlled growth of semiconducting and metallic single-wall carbon nanotubes. J Am Chem Soc 138:6690–6698
Lorkit P, Panapoy M, Ksapabutr B (2014) Iron oxide-based supercapacitor from ferratrane precursor via sol-gel-hydrothermal process. Energy Proc 56:466–473
Zhang P, Zhou J, Chen W, Zhao Y, Mu X, Zhang Z, Pan X, Xie E (2017) Constructing highly-efficient electron transport channels in the 3D electrode materials for high-rate supercapacitors: the case of NiCo2O4@NiMoO4 hierarchical nanostructures. Chem Eng J 307:687–695
Yin C, Yang C, Jiang M, Deng C, Yang L, Li J, Qian D (2016) A novel and facile one-pot solvothermal synthesis of PEDOT-PSS/Ni-Mn-Co-O hybrid as an advanced supercapacitor electrode material. ACS Appl Mater Interf 8:2741–2752
Wang Y, Chai H, Dong H, Xu J, Jia D, Zhou W (2016) Superior cycle stability performance of quasi-cuboidal CoV2O6 microstructures as electrode material for supercapacitors. ACS Appl Mater Interf 8:27291–27297
Mariottil D, Sankaran RM (2010) Microplasmas for nanomaterials synthesis. J Phys D Appl Phys 43:323001. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/43/32/323001
Becke KH, Kersten H, Hopwood J, Lopez JL (2010) Microplasmas: scientific challenges & technological opportunities. Eur Phys J D 60:437–439
Wang Z, Xu C, Lu Y, Wei G, Ye G, Sun T, Chen J (2018) Microplasma electrochemistry controlled rapid preparation of fluorescent polydopamine nanoparticles and their application in uranium detection. Chem Eng J 344:480–486
Du C, Xiao M (2014) Cu2O nanoparticles synthesis by microplasma. Sci Rep 4:1–5
Chiang WH, Sankaran RM (2007) Microplasma synthesis of metal nanoparticles for gas-phase studies of catalyzed carbon nanotube growth. Appl Phys Lett 91:121503. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2786835
Wang Z, Lu Y, Yuan H, Ren Z, Xu C, Chen J (2015) Microplasma-assisted rapid synthesis of luminescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots and their application in pH sensing and uranium detection. Nanoscale 7:20743–20748
Wang R, Zuo S, Zhu W, Zhang J, Fang J (2014) Rapid synthesis of aqueous-phase magnetite nanoparticles by atmospheric pressure non-thermal microplasma and their application in magnetic resonance imaging. Plasma Process Polym 11:448–454
Lu X, Jia W, Chai H, Hu J, Wang S, Cao Y (2019) Solid-state chemical fabrication of one-dimensional mesoporous β-nickel molybdate nanorods as remarkable electrode material for supercapacitors. J Colloid Interf Sci 534:322–331
Yan J, Fan Z, Sun W, Ning G, Wei T, Zhang Q, Zhang R, Zhi L, Wei F (2012) Advanced asymmetric supercapacitors based on Ni(OH)2/graphene and porous graphene electrodes with high energy density. Adv Funct Mater 22:2632–2641
Huang L, Xiang J, Zhang W, Chen C, Xu H, Huang Y (2015) 3D interconnected porous NiMoO4 nanoplate arrays on Ni foam as high-performance binder-free electrode for supercapacitors. J Mater Chem A 3:22081–22087
Wang B, Li S, Wu X, Tian W, Liu J, Yu M (2015) Integration of network-like porous NiMoO4 nanoarchitectures assembled with ultrathin mesoporous nanosheets on three-dimensional graphene foam for highly reversible lithium storage. J Mater Chem A 3:13691–13698
Qing C, Yang C, Chen M, Li W, Wang S, Tang Y (2018) Design of oxygen-deficient NiMoO4 nanoflake and nanorod arrays with enhanced supercapacitive performance. Chem Eng J 354:182–190
Ghosh D, Giri S, Das CK (2013) Synthesis, characterization and electrochemical performance of graphene decorated with 1D NiMoO4·nH2O nanorods. Nanoscale 5:10428–10437
Gu Z, Zhang X (2016) NiCo2O4@MnMoO4 core–shell flowers for high performance supercapacitors. J Mater Chem A 4:8249–8254
Xia X, Lei W, Hao Q, Wang W, Wang X (2013) One-step synthesis of CoMoO4/graphene composites with enhanced electrochemical properties for supercapacitors. Electrochim Acta 99:253–261
Kumar V, Matz S, Hoogestraat D, Bhavanasi V, Parida K, Shamery KA, Lee PS (2016) Design of mixed-metal silver decamolybdate nanostructures for high specific energies at high power density. Adv Mater 28:6966–6975
Haetge J, Djerdj I, Brezesinski T (2012) Nanocrystalline NiMoO4 with an ordered mesoporous morphology as potential material for rechargeable thin film lithium batteries. Chem Commun 48:6726–6728
Naik KK, Ratha S, Rout CS (2016) Phase and shape dependent non–enzymatic glucose sensing properties of nickel molybdate. Chem Sel 1:5187–5195
Kannan P, Chen F, Jiang H, Wang H, Wang R, Subramanian P, Ji S (2019) Hierarchical core-shell structured Ni3S2/NiMoO4 nanowires: a high-performance and reusable electrochemical sensor for glucose detection. Analyst 144:4925–4934
Liao S, Lu S, Bao S, Yu Y, Wang M (2016) NiMoO4 nanofibres designed by electrospining technique for glucose electrocatalytic oxidation. Anal Chim Acta 905:72–78
Li Y, Xie M, Zhang X, Liu Q, Lin D, Xu C, Xie F, Sun X (2019) Co-MOF nanosheet array: a high-performance electrochemical sensor for non-enzymatic glucose detection. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 278:126–132
You C, Dai R, Cao X, Ji Y, Qu F, Liu Z, Du G, Asiri AM, Xiong X, Sun X (2017) Fe2Ni2N nanosheet array: an efficient non-noble-metal electrocatalyst for nonenzymatic glucose sensing. Nanotechnology 28:365503. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/aa7c6e
Wang Z, Cao X, Liu D, Hao S, Du G, Asiri AM, Sun X (2016) Ternary NiCoP nanosheet array on a Ti mesh: a high-performance electrochemical sensor for glucose detection. Chem Commun 52:14438–14441
Bai Y, Xu T, Luong JHT, Cui H (2014) Direct electron transfer of glucose oxidase-boron doped diamond interface: a new solution for a classical problem. Anal Chem 86:4910–4918
Gil-Llambias FJ, Rodriguez H, Bouyssieres I, Escudey M, Carkovic I (1986) Hydrodesulfurization catalysts: electrophoretic study of Mo(or W)-Co, Mo(or W)-Ni, and Mo(or W)-Ca sulfided phases. J Catal 102:37–42
Salamon J, Sathishkumar Y, Ramachandran K, Lee YS, Yoo DJ, Kim AR, Kumar GG (2015) One-pot synthesis of magnetite nanorods/graphene composites and its catalytic activity toward electrochemical detection of dopamine. Biosens Bioelectron 64:269–276
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22106113 and 22104103), the Key Project of Sichuan Science and Technology Department of Education (No. 22ZDYF2898), the Open Foundation of MOE Key Laboratory of the Evaluation and Monitoring of Southwest Land Resources, Ministry of Education (No. TDSYS202106), Sichuan Engineering Laboratory of Livestock Manure Treatment and Recycling (202106) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declared that we have no conflicts of interest to this work and we do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Joshua Tong.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Tang, X., Zhao, S. et al. One-step rapid synthesis of NiMoO4·xH2O nanowires by dielectric barrier discharge micro-plasma method for high-efficiency non-enzymatic glucose sensing. J Mater Sci 57, 11673–11683 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07318-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07318-1