Abstract
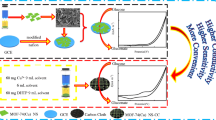
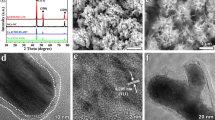
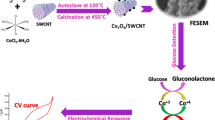
High electrical conductivity and more active sites exposure are crucial for improving the performance of electrocatalyst. Binary metal oxide nanoarray grown on conductive substrate offers a 3D self-supported electrode with a great promise in boosting its performance in enzyme-free glucose sensing. Here, NiMoO4 nanosheet arrays anchored on carbon cloth (NiMoO4 NSA/CC) was prepared via a simple hydrothermal synthesis and used as 3D self-supported electrode for enzyme-free glucose sensing. The morphology and composition of NiMoO4 nanosheet have been characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The electrochemical results show that NiMoO4 NSA/CC exhibits remarkable high catalytic activity towards glucose oxidation, with a wide linear response ranging from 1 μM to 0.9 mM, a high sensitivity of 4.13 mA/mM·cm2, and a low detection limit of 1 μM (S/N = 3). The enhanced performance might be attributed to the merits of nanosheet arrays with large surface area, self-supported electrode with 3D open network, as well as bimetallic component with high conductivity. Furthermore, NiMoO4 NSA/CC also shows good selectivity and reliability for glucose detection in human serum. This work offers a new pathway for the construction of enzyme-free glucose sensor with high performance.

ᅟ






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lu L, Li H, Qu F, Zhang X, Shen G, Yu R. In situ synthesis of palladium nanoparticle-graphene nanohybrids and their application in nonenzymatic glucose biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron. 2011;26:3500–4.
Li J, Hu H, Li H, Yao C. Recent developments in electrochemical sensors based on nanomaterials for determining glucose and its byproduct H2O2. J Mater Sci. 2017;52:10455–69.
Hovancova J, Sisolakova I, Orinakova R, Orinak A. Nanomaterial-based electrochemical sensors for detection of glucose and insulin. J Solid State Electrochem. 2017;21:2147–66.
Kangkamano T, Numnuam A, Limbut W, Kanatharana P, Thavarungkul P. Chitosan cryogel with embedded gold nanoparticles decorated multiwalled carbon nanotubes modified electrode for highly sensitive flow based non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2017;246:854–63.
Nugraha AS, Li C, Bo J, Iqbal M, Alshehri SM, Ahamad T, et al. Block-copolymer-assisted electrochemical synthesis of mesoporous gold electrodes: towards a non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Chem Aust. 2017;4:2571–6.
Xu M, Song Y, Ye Y, Gong C, Shen Y, Wang L, et al. A novel flexible electrochemical glucose sensor based on gold nanoparticles/polyaniline arrays/carbon cloth electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2017;252:1187–93.
Badhulika S, Paul R, Rajesh K, Terse T, Mulchandani A. Nonenzymatic glucose sensor based on platinum nanoflowers decorated multiwalled carbon nanotubes-graphene hybrid electrode. Electroanalysis. 2014;26:103–8.
Li M, Bo X, Mu Z, Zhang Y, Guo L. Electrodeposition of nickel oxide and platinum nanoparticles on electrochemically reduced graphene oxide film as a nonenzymatic glucose sensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2014;192:261–8.
Weremfo A, Fong STC, Khan A, Hibbert DB, Zhao C. Electrochemically roughened nanoporous platinum electrodes for non-enzymatic glucose sensors. Electrochim Acta. 2017;231:20–6.
Ye J, Hong B, Wu Y, Chen H, Lee C. Heterostructured palladium-platinum core-shell nanocubes for use in a nonenzymatic amperometric glucose sensor. Microchim Acta. 2016;183:3311–20.
Huang B, Wang Y, Lu Z, Du H, Ye J. One pot synthesis of palladium-cobalt nanoparticles over carbon nanotubes as a sensitive non-enzymatic sensor for glucose and hydrogen peroxide detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2017;252:1016–25.
Koskun Y, Savk A, Sen B, Sen F. Highly sensitive glucose sensor based on monodisperse palladium nickel/activated carbon nanocomposites. Anal Chim Acta. 2018;1010:37–43.
Ensafi AA, Ahmadi N, Rezaei B. Nickel nanoparticles supported on porous silicon flour, application as a non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2017;239:807–15.
Jothi L, Jayakumar N, Jaganathan SK, Nageswaran G. Ultrasensitive and selective non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor based on hybrid material of graphene nanosheets/graphene nanoribbons/nickel nanoparticle. Mater Res Bull. 2018;98:300–7.
Wang T, Yu Y, Tian H, Hu J. A novel non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on cobalt nanoparticles implantation-modified indium tin oxide electrode. Electroanalysis. 2014;26:2693–700.
Ju L, Wu G, Lu B, Li X, Wu H, Liu A. Non-enzymatic amperometric glucose sensor based on copper nanowires decorated reduced graphene oxide. Electroanalysis. 2016;28:2543–51.
Zheng W, Hu L, Lee LYS, Wong KY. Copper nanoparticles/polyaniline/graphene composite as a highly sensitive electrochemical glucose sensor. J Electroanal Chem. 2016;781:155–60.
Dai H, Cao P, Chen D, Li Y, Wang N, Ma H, et al. Ni-Co-S/PPy core-shell nanohybrid on nickel foam as a non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor. Synth Met. 2018;235:97–102.
Padmanathan N, Shao H, Razeeb KM. Multifunctional nickel phosphate nano/microflakes 3D electrode for electrochemical energy storage, nonenzymatic glucose, and sweat pH sensors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:8599–610.
Liu T, Li M, Guo L. Designing and facilely synthesizing a series of cobalt nitride (Co4N) nanocatalysts as non-enzymatic glucose sensors: a comparative study toward the influences of material structures on electrocatalytic activities. Talanta. 2018;181:154–64.
Xie F, Cao X, Qu F, Asiri AM, Sun X. Cobalt nitride nanowire array as an efficient electrochemical sensor for glucose and H2O2 detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018;255:1254–61.
Liu X, Yang W, Chen L, Jia J. Three-dimensional copper foam supported CuO nanowire arrays: an efficient non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Electrochim Acta. 2017;235:519–26.
Velmurugan M, Karikalan N, Chen SM. Synthesis and characterizations of biscuit-like copper oxide for the non-enzymatic glucose sensor applications. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2017;493:349–55.
Yuan C, Wu HB, Xie Y, Lou XWD. Mixed transition-metal oxides: design, synthesis, and energy-related applications. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2014;53:1488–504.
Shen L, Che Q, Li H, Zhang X. Mesoporous NiCo2O4 nanowire arrays grown on carbon textiles as binder-free flexible electrodes for energy storage. Adv Funct Mater. 2014;24:2630–7.
Han L, Feng K, Chen Z. Self-supported cobalt nickel nitride nanowires electrode for overall electrochemical water splitting. Energy Technol. 2017;5:1908–11.
Wang Z, Cao X, Liu D, Hao S, Du G, Asiri AM, et al. Ternary NiCoP nanosheet array on a Ti mesh: a high-performance electrochemical sensor for glucose detection. Chem Commun. 2016;52:14438–41.
Luo X, Huang M, Bie L, He D, Zhang Y, Jiang P. CuCo2O4 nanowire arrays supported on carbon cloth as an efficient 3D binder-free electrode for non-enzymatic glucose sensing. RSC Adv. 2017;7:23093–101.
Du D, Lan R, Xu W, Beanland R, Wang H, Tao S. Preparation of a hybrid Cu2O/CuMoO4 nanosheet electrode for high-performance asymmetric supercapacitors. J Mater Chem A. 2016;4:17749–56.
Xu W, Zhang B, Wang X, Wang G, Ding D. The flame retardancy and smoke suppression effect of a hybrid containing CuMoO4 modified reduced graphene oxide/layered double hydroxide on epoxy resin. J Hazard Mater. 2018;343:364–75.
Fang L, Wang F, Zhai T, Qiu Y, Lan M, Huang K, et al. Hierarchical CoMoO4 nanoneedle electrodes for advanced supercapacitors and electrocatalytic oxygen evolution. Electrochim Acta. 2018;259:552–8.
Zhang L, Mi T, Ziaee MA, Liang L, Wang R. Hollow POM@MOF hybrid-derived porous Co3O4/CoMoO4 nanocages for enhanced electrocatalytic water oxidation. J Mater Chem A. 2018;6:1639–47.
Peng S, Li L, Wu HB, Madhavi S, Lou XW. Controlled growth of NiMoO4 nanosheet and nanorod arrays on various conductive substrates as advanced electrodes for asymmetric supercapacitors. Adv Energy Mater. 2015;5(2).
Cai D, Wang D, Liu B, Wang L, Liu Y, Li H, et al. Three-dimensional Co3O4@NiMoO4 core/shell nanowire arrays on Ni foam for electrochemical energy storage. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6:5050–5.
Cao Z, Zhang D, Xu C, Zhang R, Yuan B. A novel enzyme-free glucose sensor based on nickel molybdate nanosheets. Inter J Electrochem Sci. 2015;10:3152–9.
Naik KK, Ratha S, Rout CS. Phase and shape dependent non-enzymatic glucose sensing properties of nickel molybdate. Chemistry Select. 2016;1:5187–95.
Wang D, Cai D, Huang H, Liu B, Wang L, Liu Y, et al. Non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor based on NiMoO4 nanorods. Nanotechnology. 2015;26.
Liao S, Lu S, Bao S, Yu Y, Wang M. NiMoO4 nanofibres designed by electrospining technique for glucose electrocatalytic oxidation. Anal Chim Acta. 2016;905:72–8.
Yan J, Fan Z, Sun W, Ning G, Wei T, Zhang Q, et al. Advanced asymmetric supercapacitors based on Ni(OH)2/graphene and porous graphene electrodes with high energy density. Adv Funct Mater. 2012;22:2632–41.
Ghosh D, Giri S, Das CK. Synthesis, characterization and electrochemical performance of graphene decorated with 1D NiMoO4·nH2O nanorods. Nanoscale. 2013;5:10428–37.
Zhang Q, Deng Y, Hu Z, Liu Y, Yao M, Liu P. Seaurchin-like hierarchical NiCo2O4@NiMoO4 core-shell nanomaterials for high performance supercapacitors. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2014;16:23451–60.
Wang L, Xie Y, Wei C, Lu X, Li X, Song Y. Hierarchical NiO superstructures/foam Ni electrode derived from Ni metal-organic framework flakes on foam Ni for glucose sensing. Electrochim Acta. 2015;174:846–52.
Yang J, Cho M, Lee Y. Synthesis of hierarchical Ni(OH)2 hollow nanorod via chemical bath deposition and its glucose sensing performance. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2016;222:674–81.
Zhan B, Liu C, Chen H, Shi H, Wang L, Chen P, et al. Free-standing electrochemical electrode based on Ni(OH)2/3D graphene foam for nonenzymatic glucose detection. Nanoscale. 2014;6:7424–9.
Luo X, Huang M, He D, Wang M, Zhang Y, Jiang P. Porous NiCo2O4 nanoarrays integrating binder-free 3D open electrode offers a highly efficient sensing platform for enzyme-free glucose detection. Analyst. 2018;143:2546–54.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21601022) and the Livelihoods Science and Technology Innovation Project of Chongqing (cstc2016shmszx20004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The sample analysis experimental protocol was approved by the University Ethical Committee of Chongqing Medical University, and their guidelines were followed throughout this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 196 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, M., He, D., Wang, M. et al. NiMoO4 nanosheet arrays anchored on carbon cloth as 3D open electrode for enzyme-free glucose sensing with improved electrocatalytic activity. Anal Bioanal Chem 410, 7921–7929 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1413-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1413-z