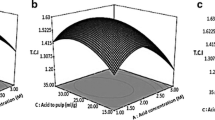
Abstract
This work identifies Pepper (Capsicum annuum L) stems residue as a new potential source for producing high-quality cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs), making a significant contribution to the field of natural waste material utilization and sustainability. It also compares the properties of CNCs produced using two different acids, phosphoric acid and sulfuric acid (CNCPs and CNCSs), providing new insights into their properties and polymer reinforcing ability. Hence, the as-isolated CNCPs (D = 43 ± 15.11 nm, CrI = 84.78%) and CNCSs (D = 31 ± 8.80 nm, CrI = 85.41%) were separately dispersed in starch at different weight loadings, and their reinforcing effects on the chemical, morphological, thermal, transparency and mechanical properties of the resulting starch-based biocomposite films were discussed. Globally, the incorporation of CNCs into starch biopolymer improved all these properties due to their rather similar polysaccharide structure and thus good interfacial interaction. However, the capacity of phosphoric acid to produce char made CNCPs effective flame retardants, thus providing bionanocomposite films with better thermal stability than CNCSs ones. In counterpart, the negative charge provided by the residual sulfate group (SO42−) in CNCSs, coupled with their high aspect ratio, high surface areas and crystallinity, significantly improves the dispersibility of CNCSs in the ST matrix compared to the phosphoric acid-derived CNCs. Hence, adding up to 5 wt% CNCSs improved the film’s transparency by 25%, stiffness by 196%, and ductility by 169%, compared to 11%, 164% and 114%, respectively, for CNCPs. Here, this work offers valuable insights into the utilization of pepper stems residue and the type of acid for CNCs production with outstanding characteristics.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The article contains all the information necessary to understand the findings of this investigation.
References
Abd El-Mageed TA, Rady MM, Taha RS et al (2020) Effects of integrated use of residual sulfur-enhanced biochar with effective microorganisms on soil properties, plant growth and short-term productivity of Capsicum annuum under salt stress. Sci Hortic 261:108930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.108930
Ablouh EH, Kassab Z, Semlali Aouragh Hassani FZ et al (2022) Phosphorylated cellulose paper as highly efficient adsorbent for cadmium heavy metal ion removal in aqueous solutions. RSC Adv 12:1084–1094. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ra08060a
Agustin MB, Ahmmad B, De Leon ERP et al (2013) Starch-based biocomposite films reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals from garlic stalks. Polym Compos 34:1325–1332. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.22546
Anaya-Esparza LM, de la Mora ZV, Vázquez-Paulino O et al (2021) Bell peppers (Capsicum annum l.) losses and wastes: Source for food and pharmaceutical applications. Molecules 26:1–23. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175341
Bahloul A, Kassab Z, El Bouchti M et al (2021) Micro- and nano-structures of cellulose from eggplant plant (Solanum melongena L) agricultural residue. Carbohydr Polym 253:117311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117311
Balakrishnan P, Gopi S, Sreekala MS, Thomas S (2018) UV resistant transparent bionanocomposite films based on potato starch/cellulose for sustainable packaging. Starch/staerke 70:1–34. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.201700139
Bodirlau R, Teaca CA, Spiridon I (2013) Influence of natural fillers on the properties of starch-based biocomposite films. Compos Part B Eng 44:575–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2012.02.039
El Bourakadi K, Semlali Aouragh Hassani FZ, El Achaby M, et al (2022) Packaging and bionanocomposites. In: Bionanocomposites for Food Packaging Applications
Cañigueral N, Vilaseca F, Méndez JA et al (2009) Behavior of biocomposite materials from flax strands and starch-based biopolymer. Chem Eng Sci 64:2651–2658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2009.02.006
Cao X, Chen Y, Chang PR et al (2008) Starch-based nanocomposites reinforced with flax cellulose nanocrystals. Express Polym Lett 2:502–510. https://doi.org/10.3144/expresspolymlett.2008.60
Chen L, Kang YH (2014) In vitro inhibitory potential against key enzymes relevant for hyperglycemia and hypertension of red pepper (Capsicum Annuum L.) including pericarp, placenta, and stalk. J Food Biochem 38:300–306. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.12048
de Azevedo LC, Rovani S, Santos JJ et al (2020) Biodegradable films derived from corn and potato starch and study of the effect of silicate extracted from sugarcane waste ash. ACS Appl Polym Mater 2:2160–2169. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsapm.0c00124
Dhar P, Bhasney SM, Kumar A, Katiyar V (2016) Acid functionalized cellulose nanocrystals and its effect on mechanical, thermal, crystallization and surfaces properties of poly (lactic acid) bionanocomposites films: a comprehensive study. Polymer 101:75–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2016.08.028
El Achaby M, Kassab Z, Aboulkas A et al (2018a) Reuse of red algae waste for the production of cellulose nanocrystals and its application in polymer nanocomposites. Int J Biol Macromol 106:681–691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.08.067
El Achaby M, Kassab Z, Barakat A, Aboulkas A (2018b) Alfa fibers as viable sustainable source for cellulose nanocrystals extraction: application for improving the tensile properties of biopolymer nanocomposite films. Ind Crops Prod 112:499–510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.12.049
Espino E, Cakir M, Domenek S et al (2014) Isolation and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from industrial by-products of Agave tequilana and barley. Ind Crops Prod 62:552–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.09.017
Espinosa SC, Kuhnt T, Foster EJ, Weder C (2013) Isolation of thermally stable cellulose nanocrystals by phosphoric acid hydrolysis. Biomacromol 8:187–203. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2020.07940
Fareez IM, Ibrahim NA, Wan Yaacob WMH et al (2018) Characteristics of cellulose extracted from Josapine pineapple leaf fibre after alkali treatment followed by extensive bleaching. Cellulose 25:4407–4421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1878-0
Fortunati E, Luzi F, Puglia D et al (2015) Processing of PLA nanocomposites with cellulose nanocrystals extracted from Posidonia oceanica waste: innovative reuse of coastal plant. Ind Crops Prod 67:439–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.01.075
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
French AD, Santiago Cintrón M (2013) Cellulose polymorphy, crystallite size, and the Segal Crystallinity Index. Cellulose 20:583–588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9833-y
Gan I, Chow WS (2019) Synthesis of phosphoric acid-treated sugarcane bagasse cellulose nanocrystal and its thermal properties enhancement for poly(lactic acid) nanocomposites. J Thermoplast Compos Mater 32:619–634. https://doi.org/10.1177/0892705718772866
Huang L, Xu H, Zhao H et al (2019) Properties of thermoplastic starch films reinforced with modified cellulose nanocrystals obtained from cassava residues. New J Chem 43:14883–14891. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nj02623a
Huq T, Salmieri S, Khan A et al (2012) Nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC) reinforced alginate based biodegradable nanocomposite film. Carbohydr Polym 90:1757–1763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.07.065
Jagadeesan S, Govindaraju I, Mazumder N (2020) An Insight into the ultrastructural and physiochemical characterization of potato starch: a review. Am J Potato Res 97:464–476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12230-020-09798-w
Kassab Z, Aziz F, Hannache H et al (2019a) Improved mechanical properties of k-carrageenan-based nanocomposite films reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals. Int J Biol Macromol 123:1248–1256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.12.030
Kassab Z, Boujemaoui A, Ben Youcef H et al (2019b) Production of cellulose nanofibrils from alfa fibers and its nanoreinforcement potential in polymer nanocomposites. Cellulose 26:9567–9581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02767-5
Kassab Z, Abdellaoui Y, Salim MH et al (2020a) Micro- and nano-celluloses derived from hemp stalks and their effect as polymer reinforcing materials. Carbohydr Polym 245:116506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116506
Kassab Z, Kassem I, Hannache H et al (2020b) Tomato plant residue as new renewable source for cellulose production: extraction of cellulose nanocrystals with different surface functionalities. Cellulose 27:4287–4303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03097-7
Kassab Z, Kassem I, Hannache H, Bouhfid R (2020c) Tomato plant residue as new renewable source for cellulose production : extraction of cellulose nanocrystals with different surface functionalities. Cellulose. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03097-7
Kassab Z, Mansouri S, Tamraoui Y et al (2020d) Identifying Juncus plant as viable source for the production of micro- and nano-cellulose fibers: Application for PVA composite materials development. Ind Crops Prod 144:112035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.112035
Kassab Z, Syafri E, Tamraoui Y et al (2020e) Characteristics of sulfated and carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals extracted from Juncus plant stems. Int J Biol Macromol 154:1419–1425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.11.023
Khalili H, Bahloul A, Ablouh E et al (2023) Starch biocomposites based on cellulose microfibers and nanocrystals extracted from alfa fibers (Stipa tenacissima). Int J Biol Macromol 226:345–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.11.313
Li W, Guo R, Lan Y et al (2014) Preparation and properties of cellulose nanocrystals reinforced collagen composite films. J Biomed Mater Res Part A 102:1131–1139. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.34792
Liu S, Li X, Chen L et al (2018) Tunable d -limonene permeability in starch-based nanocomposite films reinforced by cellulose nanocrystals. J Agric Food Chem 66:979–987. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b05457
Ludueña LN, Vecchio A, Stefani PM, Alvarez VA (2013) Extraction of cellulose nanowhiskers from natural fibers and agricultural byproducts. Fibers Polym 14:1118–1127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-013-1118-z
Montero B, Rico M, Barral L et al (2021) Preparation and characterization of bionanocomposite films based on wheat starch and reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals. Cellulose 28:7781–7793. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04017-z
Ouarhim W, Semlali Aouragh Hassani F, Qaiss A, Bouhfid R (2019) Rheology of polymer nanocomposites. In: Sabu Thomas, Sarathchandran, C. Nithin Chandran. Rheology of Polymer Blends and Nanocomposites Theory, Modelling and Applications. Elsevier, 1st Edition. pp 73–96
Oumayma M, Hassani FSA, El M et al (2021) Elaboration of a composite material based on plaster reinforced with phase change material/Oakum Fiber : physical, thermal and mechanical properties. J Energy Storage 35:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2021.102321
Pozo C, Rodríguez-Llamazares S, Bouza R et al (2018) Study of the structural order of native starch granules using combined FTIR and XRD analysis. J Polym Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-018-1651-y
Punia Bangar S, Whiteside WS, Dunno KD et al (2022) Starch-based bio-nanocomposites films reinforced with cellulosic nanocrystals extracted from Kudzu (Pueraria montana) vine. Int J Biol Macromol 203:350–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.01.133
Rajinipriya M, Nagalakshmaiah M, Robert M, Elkoun S (2018) Importance of agricultural and industrial waste in the field of Nanocellulose and recent industrial developments of wood based Nanocellulose: a review. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:2807–2828. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b03437
Reddy JP, Rhim JW (2014) Characterization of bionanocomposite films prepared with agar and paper-mulberry pulp nanocellulose. Carbohydr Polym 110:480–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.04.056
Risite H, Salim MH, Oudinot BT et al (2022) Artemisia annua stems a new sustainable source for cellulosic materials: production and characterization of cellulose microfibers and nanocrystals. Waste and Biomass Valorization 13:2411–2423. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-021-01658-w
Salim MH, Kassab Z, Abdellaoui Y et al (2022a) Exploration of multifunctional properties of garlic skin derived cellulose nanocrystals and extracts incorporated chitosan biocomposite films for active packaging application. Int J Biol Macromol 210:639–653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.04.220
Salim MH, Youness A, Ait Benhamou A et al (2022c) Influence of cellulose nanocrystals from pea pod waste on mechanical, thermal, biodegradability, and barrier properties of chitosan-based films. Cellulose. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10570-022-04587-6
Salim MH, Kassab Z, Ablouh E et al (2023) Cellulosic biocomposite foam papers impregnated by crosslinked starch /poly (vinyl alcohol) biopolymers. Ind Crop Prod 192:116074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.116074
Salim MH, Kassab Z, Ablouh E-H, et al (2022b) Alfa fibers, their composites and applications. In: Plant Fibers, their Composites, and Applications. Woodhead Publishing, pp 51–74
Semlali Aouragh Hassani F, Ouarhim W, Raji M et al (2019a) N-silylated benzothiazolium dye as a coupling agent for polylactic acid/date palm Fiber bio-composites. J Polym Environ 27:2974–2987. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-019-01585-x
Semlali Aouragh Hassani F, Ouarhim W, Zari N et al (2019b) Injection molding of short coir fiber polypropylene biocomposites: prediction of the mold filling phase. Polym Compos 40:4042–4055
Semlali Aouragh Hassani F, El Achaby M, Bensalah MO et al (2020a) Injection molding of short fiber thermoplastic bio-composites: prediction of the fiber orientation. J Compos Mater 54:1–11
Semlali Aouragh Hassani F, Salim MH, Kassab Z et al (2022a) Crosslinked starch-coated cellulosic papers as alternative food-packaging materials. RSC Adv 12:8536–8546. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ra00536k
Semlali Aouragh Hassani F, Chakchak H, El Achaby M, et al (2020b) Date palm fiber composites. In: Midani M, Saba N, Alothman OY (Eds) Date palm fiber composites: processing, properties and applications, 1st Edn. Springer, pp 75–91
Semlali Aouragh Hassani F, Ouarhim W, Kassab Z, et al (2021a) Mechanical characterization of cellulose nanoparticle-based advanced materials. In: Thakur VK, Frollini E, Scott J (Eds) Cellulose nanoparticles: volume 2: synthesis and manufacturing. pp 298–322
Semlali Aouragh Hassani FZ, Kassab Z, Achaby M El, et al (2021b) Mechanical modeling of hybrid nanocomposites based on cellulose nanocrystals/nanofibrils and nanoparticles. In: Cellulose Nanocrystal/Nanoparticles Hybrid Nanocomposites. pp 247–270
Semlali Aouragh Hassani FZ, El Achaby M, Qaiss A el kacem, Bouhfid R (2022b) Modeling of natural fiber-based biocomposites. In: Handbook of bioplastics and biocomposites engineering applications, 2nd Edn.
Septevani AA, Burhani D, Sampora Y et al (2022) A systematic study on the fabrication of transparent nanopaper based on controlled cellulose nanostructure from oil palm empty fruit bunch. J Polym Environ 30:3901–3913. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02484-4
Simonovska J, Škerget M, Knez Ž et al (2016) Physicochemical characterization and bioactive compounds of stalk from hot fruits of capsicum annuum L. Maced J Chem Chem Eng 35:199–208
Solouk A, Xu K, Zhang Y et al (2021) Natural cuticle-inspired chitin / silk fibroin / cellulose nanocrystal biocomposite films : fabrication and characterization Natural cuticle-inspired chitin / silk fi broin / cellulose nanocrystal biocomposite films : fabrication and characterization
Sonia A, Priya Dasan K (2013) Chemical, morphology and thermal evaluation of cellulose microfibers obtained from Hibiscus sabdariffa. Carbohydr Polym 92:668–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.09.015
Tabassi N, Moghbeli MR, Ghasemi I (2016) Thermoplastic starch/cellulose nanocrystal green composites prepared in an internal mixer. Iran Polym J 25:45–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-015-0398-0
Tian C, Yi J, Wu Y et al (2016) Preparation of highly charged cellulose nanofibrils using high-pressure homogenization coupled with strong acid hydrolysis pretreatments. Carbohydr Polym 136:485–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.09.055
Tibolla H, Czaikoski A, Pelissari FM et al (2020) Starch-based nanocomposites with cellulose nanofibers obtained from chemical and mechanical treatments. Int J Biol Macromol 161:132–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.194
Warren FJ, Gidley MJ, Flanagan BM (2016) Infrared spectroscopy as a tool to characterise starch ordered structure—a joint FTIR–ATR, NMR, XRD and DSC study. Carbohydr Polym 139:35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2015.11.066
Xie Q, Wang S, Chen X et al (2018) Thermal stability and crystallization behavior of cellulose nanocrystals and their poly(l-lactide) nanocomposites: effects of surface ionic group and poly(d-lactide) grafting. Cellulose 25:6847–6862. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2086-7
Yadav M, Chiu FC (2019) Cellulose nanocrystals reinforced κ-carrageenan based UV resistant transparent bionanocomposite films for sustainable packaging applications. Carbohydr Polym 211:181–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.01.114
Yuan Y, Chen H (2021) Preparation and characterization of a biodegradable starch-based antibacterial film containing nanocellulose and polyhexamethylene biguanide. Food Packag Shelf Life 30:100718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2021.100718
Acknowledgments
The financial assistance of the Office Chérifien des Phosphates (OCP S.A.) in the Moroccan Kingdom toward this research is hereby acknowledged.
Funding
The authors affirm that no funding agency in the public, commercial, or nonprofit sectors has given them a specific grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the writing of the manuscript and approved the final version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests. The manuscript has not been published elsewhere and that it has not been submitted simultaneously for publication elsewhere.
Consent for publication
The authors give the publisher permission to publish the work.
Ethical approval
The article does not include human participants and/or animals research.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bahloul, A., Semlali, FZ., Oumam, M. et al. Starch bio-nanocomposites based on phosphorylated and sulphated cellulose nanocrystals extracted from pepper plant residue: effect of surface functionality on property improvements. Cellulose 30, 5051–5070 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05199-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05199-4