Abstract
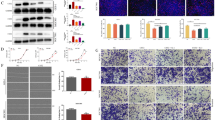
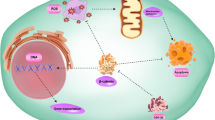
At present, recurrence and metastasis are still important factors that lead to a poor prognosis among colorectal cancer (CRC) patients. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) can promote tumorigenesis and development. Bufalin is the main active monomer of the clinical drug cinobufacini, which exhibits antitumor activity in various cancers. But few research have investigated the effect of bufalin in inhibiting metastasis from the perspective of the tumor microenvironment. We first isolated CAFs from freshly resected colorectal cancer patient specimens and observed the effect of CAFs on CRC cell invasion through a series of experiments. We explored the effect of bufalin on the physiological activity of CRC mediated by CAFs through experiments. In our study, we found that CAFs could promote CRC cell activity through the STAT3 pathway. Bufalin reversed CAF-mediated CRC invasion and metastasis by inhibiting the STAT3 pathway. Overexpression of STAT3 attenuated the inhibitory function of bufalin on invasion and metastasis. Taken together, bufalin can reverse CAF-mediated colorectal cancer metastasis based on inhibiting the STAT3 signaling pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article (and its Supplementary Information Files).
Abbreviations
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- CAFs:
-
Cancer-associated fibroblasts
- FBS:
-
Foetal bovine serum
- CCK-8:
-
Cell Counting Kit-8 assay
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- OE:
-
Overexpressing
- BU:
-
Bufalin
- WB:
-
Western blot
- CM:
-
Conditioned medium
- TME:
-
Tumor microenvironment
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2019) Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin 69:7–34
Roma-Rodrigues C, Mendes R, Baptista PV, Fernandes AR (2019) Targeting tumor microenvironment for cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci 20:840
Chandra R, Karalis JD, Liu C, Murimwa GZ, Voth Park J, Heid CA et al (2021) The colorectal cancer tumor microenvironment and its impact on liver and lung metastasis. Cancers 13:6206
Poon S, Ailles LE (2022) Modeling the role of cancer-associated fibroblasts in tumor cell invasion. Cancers 14:962
Rimal R, Desai P, Daware R, Hosseinnejad A, Prakash J, Lammers T et al (2022) Cancer-associated fibroblasts: origin, function, imaging, and therapeutic targeting. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 189:114504
Li C, Teixeira AF, Zhu HJ, Ten Dijke P (2021) Cancer associated-fibroblast-derived exosomes in cancer progression. Mol Cancer 20:154
Yuan M, Tu B, Li H, Pang H, Zhang N, Fan M et al (2022) Cancer-associated fibroblasts employ NUFIP1-dependent autophagy to secrete nucleosides and support pancreatic tumor growth. Nat Cancer 3(8):945–960
Zhou Z, Zhou Q, Wu X, Xu S, Hu X, Tao X et al (2020) VCAM-1 secreted from cancer-associated fibroblasts enhances the growth and invasion of lung cancer cells through AKT and MAPK signaling. Cancer Lett 473:62–73
Witalisz-Siepracka A, Klein K, Zdársky B, Stoiber D (2022) The multifaceted role of STAT3 in NK-cell tumor surveillance. Front Immunol 13:947568
El-Tanani M, Al Khatib AO, Aladwan SM, Abuelhana A, McCarron PA, Tambuwala MM (2022) Importance of STAT3 signalling in cancer, metastasis and therapeutic interventions. Cell Signal 92:110275
Hashimoto S, Hashimoto A, Muromoto R, Kitai Y, Oritani K, Matsuda T (2022) Central roles of STAT3-mediated signals in onset and development of cancers: tumorigenesis and immunosurveillance. Cells 11:2618
Allam A, Yakou M, Pang L, Ernst M, Huynh J (2021) Exploiting the STAT3 Nexus in cancer-associated fibroblasts to improve cancer therapy. Front Immunol 12:767939
Cheng CS, Wang J, Chen J, Kuo KT, Tang J, Gao H et al (2019) New therapeutic aspects of steroidal cardiac glycosides: the anticancer properties of Huachansu and its main active constituent Bufalin. Cancer Cell Int 19:92
Sun J, Xu K, Qiu YY, Gao H, Xu JH, Tang QF et al (2017) Bufalin reverses acquired drug resistance by inhibiting stemness in colorectal cancer cells. Oncol Rep 38:1420–1430
Chen J, Wang H, Jia L, He J, Li Y, Liu H et al (2021) Bufalin targets the SRC-3/MIF pathway in chemoresistant cells to regulate M2 macrophage polarization in colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett 513:63–74
Fang K, Zhan Y, Zhu R, Wang Y, Wu C, Sun M (2021) Bufalin suppresses tumour microenvironment-mediated angiogenesis by inhibiting the STAT3 signalling pathway. J Transl Med 19:383
Zhan Y, Qiu Y, Wang H, Wang Z, Xu J, Fan G et al (2020) Bufalin reverses multidrug resistance by regulating stemness through the CD133/nuclear factor-κB/ MDR1 pathway in colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci 111:1619–1630
Ding L, Yang Y, Lu Q, Qu D, Chandrakesan P, Feng H et al (2022) Bufalin inhibits tumorigenesis, stemness, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in Colorectal Cancer through a C-Kit/Slug Signaling Axis. Int J Mol Sci 23:13354
Zhang JJ, Zhou XH, Zhou Y, Wang YG, Qian BZ, He AN et al (2019) Bufalin suppresses the migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells through HOTAIR, the sponge of miR-520b. Acta Pharmacol Sin 40:1228–1236
Neophytou CM, Panagi M, Stylianopoulos T, Papageorgis P (2021) The role of tumor microenvironment in cancer metastasis: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Cancers 13:2053
Joshi RS, Kanugula SS, Sudhir S, Pereira MP, Jain S, Aghi MK (2021) The role of cancer-associated fibroblasts in tumor progression. Cancers 13:1399
Guo S, Deng CX (2018) Effect of stromal cells in tumor microenvironment on metastasis initiation. Int J Biol Sci 14:2083–2093
Mao X, Xu J, Wang W, Liang C, Hua J, Liu J et al (2021) Crosstalk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and immune cells in the tumor microenvironment: new findings and future perspectives. Mol Cancer 20:131
Kamali Zonouzi S, Pezeshki PS, Razi S, Rezaei N (2022) Cancer-associated fibroblasts in colorectal cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 24:757–769
Liu J, Wang Y, Qiu Z, Lv G, Huang X, Lin H et al (2021) Impact of TCM on tumor-infiltrating myeloid precursors in the tumor microenvironment. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:635122
Lin WF, Lu JY, Cheng BB, Ling CQ (2017) Progress in research on the effects of traditional chinese medicine on the tumor microenvironment. J Integr Med 15:282–287
Yu H, Lee H, Herrmann A, Buettner R, Jove R (2014) Revisiting STAT3 signalling in cancer: new and unexpected biological functions. Nat Rev Cancer 14:736–746
Johnson DE, O’Keefe RA, Grandis JR (2018) Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 15:234–248
Polak KL, Chernosky NM, Smigiel JM, Tamagno I, Jackson MW (2019) Balancing STAT activity as a therapeutic strategy. Cancers 11:1716
Ham IH, Wang L, Lee D, Woo J, Kim TH, Jeong HY et al (2022) Curcumin inhibits the cancerassociated fibroblastderived chemoresistance of gastric cancer through the suppression of the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway. Int J Oncol 61:85
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This project was sponsored by the Clinical Specialized Disease Construction Project of Shanghai Putuo District Municipal Health Commission (NO. 2020tszb03), the One Hundred Talents Project of Putuo Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2022-RCLH-03), the Shanghai Rising-Star Program (Sailing special Project, 22YF1441400), the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (20ZR1450500), the Budge Project Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2020LK072), the One Hundred Talents Project of Putuo Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2022-RCCY-08) and the research Project of Shanghai Putuo District Central Hospital (2020366 A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WL, PY and YC: conceived or designed the study. HW and JC: collected the data, analysed and interpreted the data. HW, JC and SL: drafted the article. DT, WW and KY: did part of experiments and aided in the construction of tumour model. JY, KX and YC: critically revised the article. All authors approved the final version to be published.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All animal experiments were conducted in accordance with guidelines and protocol approved by the institutional animal care and use committee of Putuo Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Chen, J., Li, S. et al. Bufalin reverses cancer-associated fibroblast-mediated colorectal cancer metastasis by inhibiting the STAT3 signaling pathway. Apoptosis 28, 594–606 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-023-01819-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-023-01819-3