Abstract
Background
Obesity is associated with the development and progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD). In the general population, the amount of renal sinus fat was associated with hypertension and renal impairment. However, its impact upon those with CKD remains uncertain.
Methods
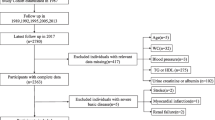
We prospectively included CKD patients who underwent renal biopsy and simultaneously measured their renal sinus fat volume. The association between the percentage of renal sinus fat volume, which was adjusted by kidney volume, and renal outcomes was investigated.
Results
A total of 56 patients (median 55 years old, 35 men) were included. Among baseline characteristics, age and visceral fat volume were positively correlated with the percentage of renal sinus fat volume (p < 0.05). The percentage of renal sinus fat volume was associated with hypertension (p < 0.01) and tended to be associated with max glomerular diameter (p = 0.078) and urine angiotensinogen creatinine ratio (p = 0.064) after adjustment with several clinical factors. The percentage of renal sinus fat volume was significantly associated with a future > 50% decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Among those with CKD who required renal biopsy, the amount of renal sinus fat was associated with poor renal outcomes accompanied by systemic hypertension.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Johansen KL, Chertow GM, Foley RN, Gilbertson DT, Herzog CA, Ishani A, et al. US renal data system 2020 annual data report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021;77(4 Suppl 1):S1–182.
Hsu CY, McCulloch CE, Iribarren C, Darbinian J, Go AS. Body mass index and risk for end-stage renal disease. Ann Intern Med. 2006;144(1):21–8.
Manabe S, Kataoka H, Mochizuki T, Iwadoh K, Ushio Y, Kawachi K, et al. Impact of visceral fat area in patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2021;25(6):608–20.
Lakkis JI, Weir MR. Obesity and kidney disease. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2018;61(2):157–67.
Hall JE, Louis K. Dahl memorial lecture. Renal and cardiovascular mechanisms of hypertension in obesity. Hypertension. 1994;23(3):381–94.
Hall JE, Brands MW, Henegar JR. Mechanisms of hypertension and kidney disease in obesity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;892:91–107.
Foster MC, Hwang SJ, Porter SA, Massaro JM, Hoffmann U, Fox CS. Fatty kidney, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease: the Framingham Heart Study. Hypertension. 2011;58(5):784–90.
Chughtai HL, Morgan TM, Rocco M, Stacey B, Brinkley TE, Ding J, et al. Renal sinus fat and poor blood pressure control in middle-aged and elderly individuals at risk for cardiovascular events. Hypertension. 2010;56(5):901–6.
Abdeldayem EH, Mansour MG, Raief Mosaad BM. Measurement of the surface area of the renal sinus fat using MDCT: correlation with presence and severity of essential hypertension and body mass index. J Belg Soc Radiol. 2022;106(1):91.
Zelicha H, Schwarzfuchs D, Shelef I, Gepner Y, Tsaban G, Tene L, et al. Changes of renal sinus fat and renal parenchymal fat during an 18-month randomized weight loss trial. Clin Nutr. 2018;37(4):1145–53.
Spit KA, Muskiet MHA, Tonneijck L, Smits MM, Kramer MHH, Joles JA, et al. Renal sinus fat and renal hemodynamics: a cross-sectional analysis. MAGMA. 2020;33(1):73–80.
Lamacchia O, Nicastro V, Camarchio D, Valente U, Grisorio R, Gesualdo L, et al. Para- and perirenal fat thickness is an independent predictor of chronic kidney disease, increased renal resistance index and hyperuricaemia in type-2 diabetic patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26(3):892–8.
Moritz E, Dadson P, Saukko E, Honka MJ, Koskensalo K, Seppala K, et al. Renal sinus fat is expanded in patients with obesity and/or hypertension and reduced by bariatric surgery associated with hypertension remission. Metabolites. 2022;12(7):617.
Ubara Y, Kawaguchi T, Nagasawa T, Miura K, Katsuno T, Morikawa T, et al. Kidney biopsy guidebook 2020 in Japan. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2021;25(4):325–64.
Ohshima S, Yamamoto S, Yamaji T, Suzuki M, Mutoh M, Iwasaki M, et al. Development of an automated 3D segmentation program for volume quantification of body fat distribution using CT. Nihon Hoshasen Gijutsu Gakkai Zasshi. 2008;64(9):1177–81.
Muto S, Kawano H, Isotani S, Ide H, Horie S. Novel semi-automated kidney volume measurements in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2018;22(3):583–90.
Matsuo S, Imai E, Horio M, Yasuda Y, Tomita K, Nitta K, et al. Revised equations for estimated GFR from serum creatinine in Japan. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;53(6):982–92.
Navar LG, Kobori H, Prieto MC, Gonzalez-Villalobos RA. Intratubular renin-angiotensin system in hypertension. Hypertension. 2011;57(3):355–62.
Notohamiprodjo M, Goefert M, Will S, Lorbeer R, Schick F, Rathmann W, et al. Renal sinus fat volumes as quantified by magnetic resonance imaging in subjects with prediabetes, diabetes, and normal glucose tolerance. PLoS ONE. 2020;15(2):e0216635.
Nishiyama A, Seth DM, Navar LG. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor-mediated augmentation of renal interstitial fluid angiotensin II in angiotensin II-induced hypertension. J Hypertens. 2003;21(10):1897–903.
Yamamoto T, Nakagawa T, Suzuki H, Ohashi N, Fukasawa H, Fujigaki Y, et al. Urinary angiotensinogen as a marker of intrarenal angiotensin II activity associated with deterioration of renal function in patients with chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18(5):1558–65.
Kobori H, Ohashi N, Katsurada A, Miyata K, Satou R, Saito T, et al. Urinary angiotensinogen as a potential biomarker of severity of chronic kidney diseases. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2008;2(5):349–54.
Krievina G, Tretjakovs P, Skuja I, Sikina V, Keisa L, Krievina D, et al. Ectopic adipose tissue storage in the left and the right renal sinus is asymmetric and associated with serum kidney injury molecule-1 and fibroblast growth factor-21 levels increase. EBioMedicine. 2016;13:274–83.
Restini CBA, Ismail A, Kumar RK, Burnett R, Garver H, Fink GD, et al. Renal perivascular adipose tissue: Form and function. Vascul Pharmacol. 2018;106:37–45.
Eringa EC, Bakker W, van Hinsbergh VW. Paracrine regulation of vascular tone, inflammation and insulin sensitivity by perivascular adipose tissue. Vascul Pharmacol. 2012;56(5–6):204–9.
Bello AK, de Zeeuw D, El Nahas M, Brantsma AH, Bakker SJL, Jong PE, et al. Impact of weight change on albuminuria in the general population. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 2007;22(6):1619–27.
Saiki A, Nagayama D, Ohhira M, Endoh K, Ohtsuka M, Koide N, et al. Effect of weight loss using formula diet on renal function in obese patients with diabetic nephropathy. Int J Obes (Lond). 2005;29(9):1115–20.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: HF; methodology: HF and TK; formal analysis and investigation: HF, KK and HY; writing—original draft preparation: HF; writing—review and editing: TI and TK; supervision: KK.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by our institutional review board (IRB Approval No. 27-162) and carried out following the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all patients before the inclusion in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Fujioka, H., Koike, T., Imamura, T. et al. Prognostic impact of renal sinus fat accumulation in patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol 27, 613–621 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-023-02350-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-023-02350-0