Abstract
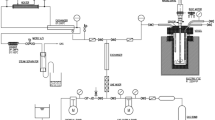
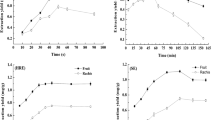
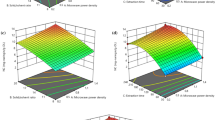
The major compounds of cinnamon are cinnamic acid and cinnamaldehyde, for which the conditions of microwave-assisted extraction (MAE), ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE), and reflux extraction (RE) were optimized using response surface methodology for comparing their efficiencies in terms of extraction yield, consumption of time and energy, and CO2 emission. The results indicated MAE superiority to UAE and RE owing to the highest yield of target compounds (total yield: 0.89%, cinnamic acid: 6.48 mg/100 mL, and cinnamaldehyde: 244.45 mg/100 mL) at optimum MAE conditions: 59% ethanol, 147.5 W microwave power and 3.4 min of extraction time. RE resulted in comparable yields with the highest consumption of time, energy, and solvent, and least CO2 emission. Therefore, it is concluded that MAE is the most efficient method for green extraction of cinnamic acid and cinnamaldehyde from cinnamon powder compared to UAE and RE.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ameer K, Bae SW, Jo Y, Chung N, Gao Y, Kwon JH. Optimization and modeling for heat reflux extraction of total yield, stevioside and rebaudioside-A from Stevia rebaudiana (Bertoni) leaves. Sep. Sci. Technol. 52: 1193–1205 (2017a)
Ameer K, Bae SW, Jo Y, Lee HG, Ameer A, Kwon JH. Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of total extract, stevioside and rebaudioside-A from Stevia rebaudiana (Bertoni) leaves using response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial neural network (ANN) modelling. Food Chem. 229: 198–207 (2017b)
Ameer K, Shahbaz HM, Kwon JH. Green extraction methods for polyphenols from plant matrices and their byproducts: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. F. 16: 295–315 (2017c)
Askari F, Rashidkhani B, Hekmatdoost A. Cinnamon may have therapeutic benefits on lipid profile, liver enzymes, insulin resistance, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients. Nutr. Res. 34: 143–148 (2014)
Cravotto G, Binello A, Orio L. Green extraction techniques. Agro Food Ind. Hi-tech. 22: 57–59 (2011)
Das A, Golder AK, Das C. Enhanced extraction of rebaudioside-A: Experimental, response surface optimization and prediction using artificial neural network. Ind. Crops Prod. 65: 415–421 (2015)
Frydman-Marom A, Levin A, Farfara D, Benromano T, Scherzer-Attali R, Peled S, Vassar R, Segal D, Gazit E, Frenkel D, Ovadia M. Orally administrated cinnamon extract reduces β-amyloid oligomerization and corrects cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease animal models. PLoS One 6: e16564–e16564 (2011)
Ghafoor K, Choi YH, Jeon JY, Jo IH. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds, antioxidants, and anthocyanins from grape (Vitis vinifera) seeds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 57: 4988–4994 (2009)
Ghasemzadeh A, Jaafar HZE. Optimization of reflux conditions for total flavonoid and total phenolic extraction and enhanced antioxidant capacity in Pandan (Pandanus amaryllifolius Roxb.) using response surface methodology. Sci. World J. 2014: 1–10 (2014)
Hamidpour R, Hamidpour M, Hamidpour S, Shahlari M. Cinnamon from the selection of traditional applications to its novel effects on the inhibition of angiogenesis in cancer cells and prevention of Alzheimer’s disease, and a series of functions such as antioxidant, anticholesterol, antidiabetes, antibacterial, antifungal, nematicidal, acaracidal, and repellent activities. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 5: 66–70 (2015)
Hayta M, İşçimen EM. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted antioxidant compounds extraction from germinated chickpea using response surface methodology. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 77: 208–216 (2017)
Kim HK, Do JR, Lim TS, Akram K, Yoon SR, Kwon JH. Optimisation of microwave-assisted extraction for functional properties of Vitis coignetiae extract by response surface methodology. J. Sci. Food Agric. 92: 1780–1785 (2012)
Korea Power Exchange (KPX). http://www.kpx.or.kr/Korean/htdocs/popup/pop_1224.html. Accessed Oct. 2, 2017.
Kwon JH, Belanger JM, Pare JJ, Yaylayan VA. Application of the microwave-assisted process (MAP™) to the fast extraction of ginseng saponins. Food Res. Int. 36: 491–498 (2003)
Maeng JH, Shahbaz HM, Ameer K, Jo Y, Kwon JH. Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of bioactive compounds from Coriolus versicolor mushroom using response surface methodology. J. Food Process. Eng. 40: e12421 (2017)
Martino E, Ramaiola I, Urbano M, Bracco F, Collina S. Microwave-assisted extraction of coumarin and related compounds from Melilotus officinalis (L.) Pallas as an alternative to Soxhlet and ultrasound-assisted extraction. J. Chromatogr. A. 1125: 147–151 (2006)
Mathew S, Abraham TE. Studies on the antioxidant activities of cinnamon (Cinnamomum verum) bark extracts through various in vitro models. Food Chem. 94: 520–528 (2006)
Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS). The Korean Pharmacopoeia. 10th ed. The Society of Korean Official Compendium for Public Health, The Yakup Shinmoon Inc., Seoul, Korea. p. 84 (2013)
Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MTIE). Implementing regulations in energy law, Sejong, Republic of Korea (2011)
Pires RH, Montanari LB, Martins CHG, Zaia JE, Almeida AMF, Matsumoto MT, Mendes-Giannini MJS. Anticandidal efficacy of cinnamon oil against planktonic and biofilm cultures of Candida parapsilosis and Candida orthopsilosis. Mycopathologia 172: 453–464 (2011)
Ranasinghe P, Pigera S, Premakumara GAS, Galappaththy P, Constantine GR, Katulanda P. Medicinal properties of ‘true’ cinnamon (Cinnamomum zeylanicum): a systematic review. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 13: 275 (2013)
SAS Institute, Inc. SAS User’s Guide. Statistical Analysis Systems Institute, Cary, NC, USA (1990)
Seo CS, Kim JH, Shin HK. Simultaneous determination of albiflorin, cinnamaldehyde, cinnamic acid, daidzin, glycyrrhizin, liquiritin, paeoniflorin and puerarin in galgeun-tang by HPLC-PDA. J. Korean Orien. Med. 31: 8–15 (2010)
Xiao W, Han L, Shi B. Microwave-assisted extraction of flavonoids from Radix Astragali. Sep. Purif. Technol. 62: 614–618 (2008)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Kyungpook National University Bokhyeon Research Fund, 2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, HG., Jo, Y., Ameer, K. et al. Optimization of green extraction methods for cinnamic acid and cinnamaldehyde from Cinnamon (Cinnamomum cassia) by response surface methodology. Food Sci Biotechnol 27, 1607–1617 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-0441-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-0441-y