Abstract
Microbead-based point-of-care testing (POCT) has demonstrated great promise in translating detection modalities from bench-side to bed-side. This is due to the ease of visualization, high surface area-to-volume ratio of beads for efficient target binding, and efficient encoding capability for simultaneous detection of multiple analytes. This review (with 112 references) summarizes the progress made in the field of fluorescent microbead-based POCT. Following an introduction into the field, a first large section sums up techniques and materials for preparing microbeads, typically of dye-labelled particles, various kinds of quantum dots and upconversion materials. Further subsections cover the encapsulation of nanoparticles into microbeads, decoration of nanoparticles on microbeads, and in situ embedding of nanoparticles during microbead synthesis. A next large section summarizes microbead-based fluorometric POCT, with subsections on detection of nucleic acids, proteins, circulating tumor cells and bacteria. A further section covers emerging POCT based on the use of smartphones or flexible microchips. The last section gives conclusions and an outlook on current challenges and possible solutions. Aside from giving an overview on the state of the art, we expect this article to boost the further development of POCT technology.

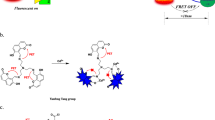
Schematic presentation of the fabrication of microbeads, the detection targets of interest including bacteria, circulating tumor cells (CTCs), protein and nucleic acid, and the emerging point-of-care testing (POCT) platform. The colored wheels of the bus represent the fluorescent materials embedded in (red color) or decorated on the surface of microbeads (green color).











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Quesada-González D, Merkoçi A (2018) Nanomaterial-based devices for point-of-care diagnostic applications. Chem Soc Rev 41(13):4697–4709
Vafajoo A, Rostami A, Parsa SF, Salarian R, Rabiee N, Rabiee G, Rabiee M, Tahriri M, Vashaee D, Tayebi L (2018) Early Diagnosis of Disease Using Microbead Array Technology: A Review. Anal Chim Acta 1032:1–17
Leng Y, Sun K, Chen X, Li W (2015) Suspension arrays based on nanoparticle-encoded microspheres for high-throughput multiplexed detection. Chem Soc Rev 44(15):5552–5595
Shikha S, Salafi T, Cheng JT, Zhang Y (2017) Versatile design and synthesis of nano-barcodes. Chem Soc Rev 46(22):7054–7093
Rödiger S, Liebsch C, Schmidt C, Lehmann W, Resch-Genger U, Schedler U, Schierack P (2014) Nucleic acid detection based on the use of microbeads: a review. Microchim Acta 181(11-12):1151–1168
Zarei M (2017) Portable biosensing devices for point-of-care diagnostics: Recent developments and applications. TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem. 91:26–41
Wang S, Chinnasamy T, Lifson MA, Inci F, Demirci U (2016) Flexible substrate-based devices for point-of-care diagnostics. Trends Biotechnol 34(11):909–921
Wen C-Y, Xie H-Y, Zhang Z-L, Wu L-L, Hu J, Tang M, Wu M, Pang D-W (2016) Fluorescent/magnetic micro/nano-spheres based on quantum dots and/or magnetic nanoparticles: preparation, properties, and their applications in cancer studies. Nanoscale 8(25):12406–12429
Qvortrup K, Nielsen TE, Komnatnyy V (2018) Bead-based screening in chemical biology and drug discovery. Chem Commun 54(50):6759–6771
Fulton RJ, McDade RL, Smith PL, Kienker LJ, Kettman JR (1997) Advanced multiplexed analysis with the FlowMetrixTM system. Clin Chem 43(9):1749–1756
Bradley M, Bruno N, Vincent B (2005) Distribution of CdSe quantum dots within swollen polystyrene microgel particles using confocal microscopy. Langmuir 21(7):2750–2753
Kuang M, Wang D, Bao H, Gao M, Möhwald H, Jiang M (2005) Fabrication of multicolor-encoded microspheres by tagging semiconductor nanocrystals to hydrogel spheres. Adv Mater 17(3):267–270
Han M, Gao X, Su JZ, Nie S (2001) Quantum-dot-tagged microbeads for multiplexed optical coding of biomolecules. Nat Biotechnol 19(7):631–635
Hu SH, Gao X (2010) Stable encapsulation of quantum dot barcodes with silica shells. Adv Funct Mater 20(21):3721–3726
Gao X, Nie S (2004) Quantum dot-encoded mesoporous beads with high brightness and uniformity: rapid readout using flow cytometry. Anal Chem 76(8):2406–2410
Behnke T, Würth C, Hoffmann K, Hübner M, Panne U, Resch-Genger U (2011) Encapsulation of hydrophobic dyes in polystyrene micro-and nanoparticles via swelling procedures. J Fluoresc 21(3):937–944
Zhang F, Shi Q, Zhang Y, Shi Y, Ding K, Zhao D, Stucky GD (2011) Fluorescence upconversion microbarcodes for multiplexed biological detection: nucleic acid encoding. Adv Mater 23(33):3775–3779
Wei Y, Deng X, Xie Z, Cai X, Liang S, Ma P, Hou Z, Cheng Z, Lin J (2017) Enhancing the stability of perovskite quantum dots by encapsulation in crosslinked polystyrene beads via a swelling–shrinking strategy toward superior water resistance. Adv Funct Mater 27(39):1703535
Yang Q, Li Y, Song T, Chang J (2012) Facile single step preparation of high-performance quantum dot barcodes. J Mater Chem 22(14):7043–7049
Wang G, Zhang P, Dou H, Li W, Sun K, He X, Han J, Xiao H, Li Y (2012) Efficient incorporation of quantum dots into porous microspheres through a solvent-evaporation approach. Langmuir 28(14):6141–6150
Song T, Liu J, Li W, Li Y, Yang Q, Gong X, Xuan L, Chang J (2014) Self-healing encapsulation strategy for preparing highly stable, functionalized quantum-dot barcodes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(4):2745–2752
Qu X, Bian F, Guo Q, Ge Q, Sun Q, Huang X (2018) Ligation-Rolling Circle Amplification on Quantum Dot-Encoded Microbeads for Detection of Multiplex G-Quadruplex-Forming Sequences. Anal Chem 90(20):12051–12058
Song T, Zhang Q, Lu C, Gong X, Yang Q, Li Y, Liu J, Chang J (2011) Structural design and preparation of high-performance QD-encoded polymer beads for suspension arrays. J Mater Chem 21(7):2169–2177
Liu Y, Liu L, He Y, He Q, Ma H (2016) Quantum-dots-encoded-microbeads based molecularly imprinted polymer. Biosens Bioelectron 77:886–893
Gong X, Yan H, Yang J, Wu Y, Zhang J, Yao Y, Liu P, Wang H, Hu Z, Chang J (2016) High-performance fluorescence-encoded magnetic microbeads as microfluidic protein chip supports for AFP detection. Anal Chim Acta 939:84–92
Liao Z, Zhang Y, Su L, Chang J, Wang H (2017) Application of upconversion luminescent-magnetic microbeads with weak background noise and facile separation in ochratoxin A detection. J Nanopart Res 19(2):60
Zhang Y, Dong C, Su L, Wang H, Gong X, Wang H, Liu J, Chang J (2015) Multifunctional microspheres encoded with upconverting nanocrystals and magnetic nanoparticles for rapid separation and immunoassays. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(1):745–753
Zhang DSZ, Jiang Y, Yang H, Zhu Y, Zhang S, Zhu Y, Wei D, Lin Y, Wang P, Fu Q (2016) Dual-Encoded Microbeads through a Host–Guest Structure: Enormous, Flexible, and Accurate Barcodes for Multiplexed Assays. Adv Funct Mater 26(34):6146–6157
Gaponik N, Radtchenko IL, Sukhorukov GB, Weller H, Rogach AL (2002) Toward encoding combinatorial libraries: charge-driven microencapsulation of semiconductor nanocrystals luminescing in the visible and near IR. Adv Mater 14(12):879
Gaponik N, Radtchenko IL, Sukhorukov GB, Rogach AL (2004) Luminescent polymer microcapsules addressable by a magnetic field. Langmuir 20(4):1449–1452
Gaponik N, Radtchenko IL, Gerstenberger MR, Fedutik YA, Sukhorukov GB, Rogach AL (2003) Labeling of biocompatible polymer microcapsules with near-infrared emitting nanocrystals. Nano Lett 3(3):369–372
He Q, Guan T, He Y, Lu B, Li D, Chen X, Feng G, Liu S, Ji Y, Xin M (2018) Digital encoding based molecular imprinting suspension array for multiplexed label-free sensing of phenol derivatives. Sensors Actuators B Chem 271:367–373
Brazhnik K, Sokolova Z, Baryshnikova M, Bilan R, Efimov A, Nabiev I, Sukhanova A (2015) Quantum dot-based lab-on-a-bead system for multiplexed detection of free and total prostate-specific antigens in clinical human serum samples. Nanomedicine 11(5):1065–1075
Wang D, Rogach AL, Caruso F (2002) Semiconductor quantum dot-labeled microsphere bioconjugates prepared by stepwise self-assembly. Nano Lett 2(8):857–861
Zhang L, Zhu L, Larson SR, Zhao Y, Wang X (2018) Layer-by-layer assembly of nanorods on a microsphere via electrostatic interactions. Soft Matter 14(22):4541–4550
Radtchenko IL, Sukhorukov GB, Gaponik N, Kornowski A, Rogach AL, Möhwald H (2001) Core–Shell Structures Formed by the Solvent-Controlled Precipitation of Luminescent CdTe Nanocrystals on Latex Spheres. Adv Mater 13(22):1684–1687
Insin N, Tracy JB, Lee H, Zimmer JP, Westervelt RM, Bawendi MG (2008) Incorporation of iron oxide nanoparticles and quantum dots into silica microspheres. ACS Nano 2(2):197–202
Zhu X-X, Cao Y-C, Jin X, Yang J, Hua X-F, Wang H-Q, Liu B, Wang Z, Wang J-H, Yang L (2007) Optical encoding of microbeads based on silica particle encapsulated quantum dots and its applications. Nanotechnology 19(2):025708
Xie M, Hu J, Wen C-Y, Zhang Z-L, Xie H-Y, Pang D-W (2011) Fluorescent–magnetic dual-encoded nanospheres: A promising tool for fast-simultaneous-addressable high-throughput analysis. Nanotechnology 23(3):035602
Rauf S, Glidle A, Cooper JM (2009) Production of Quantum Dot Barcodes Using Biological Self-Assembly. Adv Mater 21(40):4020–4024
Qu X, Jin H, Liu Y, Sun Q (2018) Strand Displacement Amplification Reaction on Quantum Dot-Encoded Silica Bead for Visual Detection of Multiplex MicroRNAs. Anal Chem 90(5):3482–3489
Wilson R, Spiller DG, Prior IA, Veltkamp KJ, Hutchinson A (2007) A simple method for preparing spectrally encoded magnetic beads for multiplexed detection. ACS Nano 1(5):487–493
Allen CN, Lequeux N, Chassenieux C, Tessier G, Dubertret B (2007) Optical analysis of beads encoded with quantum dots coated with a cationic polymer. Adv Mater 19(24):4420–4425
Xiao Q, Ji Y, Xiao Z, Zhang Y, Lin H, Wang Q (2013) Novel multifunctional NaYF4: Er 3+, Yb 3+/PEGDA hybrid microspheres: NIR-light-activated photopolymerization and drug delivery. Chem Commun 49(15):1527–1529
Causa F, Aliberti A, Cusano AM, Battista E, Netti PA (2015) Supramolecular spectrally encoded microgels with double strand probes for absolute and direct miRNA fluorescence detection at high sensitivity. J Am Chem Soc 137(5):1758–1761
Yang X, Zhang Y (2004) Encapsulation of quantum nanodots in polystyrene and silica micro-/nanoparticles. Langmuir 20(14):6071–6073
Vaidya SV, Gilchrist ML, Maldarelli C, Couzis A (2007) Spectral bar coding of polystyrene microbeads using multicolored quantum dots. Anal Chem 79(22):8520–8530
Kage D, Fischer L, Hoffmann K, Thiele T, Schedler U, Resch-Genger U (2018) Close spectroscopic look at dye-stained polymer microbeads. J Phys Chem C 122(24):12782–12791
Janczewski D, Tomczak N, Han M-Y, Vancso GJ (2009) Stimulus responsive PNIPAM/QD hybrid microspheres by copolymerization with surface engineered QDs. Macromolecules 42(6):1801–1804
Tan J, Zhao G, Zeng Z, Winnik MA (2015) PMMA microspheres with embedded lanthanide nanoparticles by photoinitiated dispersion polymerization with a carboxy-functional Macro-RAFT agent. Macromolecules 48(11):3629–3640
Zhang Q, Wang X, Zhu Y (2011) Multicolor upconverted luminescence-encoded superparticles via controlling self-assembly based on hydrophobic lanthanide-doped NaYF4 nanocrystals. J Mater Chem 21(32):12132–12138
Ku KH, Kim MP, Paek K, Shin JM, Chung S, Jang SG, Chae WS, Yi GR, Kim BJ (2013) Multicolor emission of hybrid block copolymer–quantum dot microspheres by controlled spatial isolation of quantum dots. Small 9(16):2667–2672
Shikha S, Zheng X, Zhang Y (2018) Upconversion Nanoparticles-Encoded Hydrogel Microbeads-Based Multiplexed Protein Detection. Nano-Micro Letters 10(2):31
Wang G, Leng Y, Dou H, Wang L, Li W, Wang X, Sun K, Shen L, Yuan X, Li J (2012) Highly efficient preparation of multiscaled quantum dot barcodes for multiplexed hepatitis B detection. ACS Nano 7(1):471–481
Sun L, Yu X, Sun M, Wang H, Xu S, Dixon JD, Wang YA, Li Y, Yang Q, Xu X (2011) Preparation of quantum dots encoded microspheres by electrospray for the detection of biomolecules. J Colloid Interface Sci 358(1):73–80
Vaidya SV, Couzis A, Maldarelli C (2015) Reduction in aggregation and energy transfer of quantum dots incorporated in polystyrene beads by kinetic entrapment due to cross-linking during polymerization. Langmuir 31(10):3167–3179
Yin W, Liu H, Yates M, Du H, Jiang F, Guo L, Krauss T (2007) Fluorescent Quantum Dot− Polymer Nanocomposite Particles by Emulsification/Solvent Evaporation. Chem Mater 19(12):2930–2936
Kim JS, Cho KJ, Tran TH, Nurunnabi M, Moon TH, Hong SM, Lee Y-k (2011) In vivo NIR imaging with CdTe/CdSe quantum dots entrapped in PLGA nanospheres. J Colloid Interface Sci 353(2):363–371
Bian F, Wang H, Sun L, Liu Y, Zhao Y (2018) Quantum-dot-encapsulated core–shell barcode particles from droplet microfluidics. J Mater Chem B 6(44):7257–7262
Liu H, Qian X, Wu Z, Yang R, Sun S, Ma H (2016) Microfluidic synthesis of QD-encoded PEGDA microspheres for suspension assay. J Mater Chem B 4(3):482–488
Yin SN, Wang CF, Yu ZY, Wang J, Liu SS, Chen S (2011) Versatile Bifunctional Magnetic-Fluorescent Responsive Janus Supraballs Towards the Flexible Bead Display. Adv Mater 23(26):2915–2919
Ji X-H, Zhang N-G, Cheng W, Guo F, Liu W, Guo S-S, He Z-K, Zhao X-Z (2011) Integrated parallel microfluidic device for simultaneous preparation of multiplex optical-encoded microbeads with distinct quantum dot barcodes. J Mater Chem 21(35):13380–13387
Leng Y, Wu W, Li L, Lin K, Sun K, Chen X, Li W (2016) Magnetic/fluorescent barcodes based on cadmium-free near-infrared-emitting quantum dots for multiplexed detection. Adv Funct Mater 26(42):7581–7589
Zhang Z, Shikha S, Liu J, Zhang J, Mei Q, Zhang Y (2019) Upconversion nanoprobes: recent advances in sensing applications. Anal Chem 91(1):548–568
Wang XD, Meier RJ, Wolfbeis OS (2013) Fluorescent pH-Sensitive Nanoparticles in an Agarose Matrix for Imaging of Bacterial Growth and Metabolism. Angew Chem Int Ed 52(1):406–409
Kocincová AS, Nagl S, Arain S, Krause C, Borisov SM, Arnold M, Wolfbeis OS (2008) Multiplex bacterial growth monitoring in 24-well microplates using a dual optical sensor for dissolved oxygen and pH. Biotechnol Bioeng 100(3):430–438
Ming K, Kim J, Biondi MJ, Syed A, Chen K, Lam A, Ostrowski M, Rebbapragada A, Feld JJ, Chan WC (2015) Integrated quantum dot barcode smartphone optical device for wireless multiplexed diagnosis of infected patients. ACS Nano 9(3):3060–3074
Dannhauser D, Causa F, Battista E, Cusano AM, Rossi D, Netti PA (2016) In-flow real-time detection of spectrally encoded microgels for miRNA absolute quantification. Biomicrofluidics 10(6):064114
Cai Y, Kang K, Li Q, Wang Y, He X (2018) Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Cardiac Troponin I for Point-of-Care Tests Based on Red Fluorescent Microspheres. Molecules 23(5):1102
Giri S, Sykes EA, Jennings TL, Chan WC (2011) Rapid screening of genetic biomarkers of infectious agents using quantum dot barcodes. ACS Nano 5(3):1580–1587
Gao Y, Stanford WL, Chan WC (2011) Quantum-Dot-Encoded Microbeads for Multiplexed Genetic Detection of Non-amplified DNA Samples. Small 7(1):137–146
Kim J, Biondi MJ, Feld JJ, Chan WC (2016) Clinical validation of quantum dot barcode diagnostic technology. ACS Nano 10(4):4742–4753
Guo Q, Bian F, Liu Y, Qu X, Hu X, Sun Q (2017) Hybridization chain reactions on silica coated Qbeads for the colorimetric detection of multiplex microRNAs. Chem Commun 53(36):4954–4957
Zhao Y, Zhao X, Tang B, Xu W, Li J, Hu J, Gu Z (2010) Quantum-dot-tagged bioresponsive hydrogel suspension array for multiplex label-free DNA detection. Adv Funct Mater 20(6):976–982
Gao Y, Lam AW, Chan WC (2013) Automating quantum dot barcode assays using microfluidics and magnetism for the development of a point-of-care device. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5(8):2853–2860
Magiati M, Sevastou A, Kalogianni DP (2018) A fluorometric lateral flow assay for visual detection of nucleic acids using a digital camera readout. Microchim Acta 185(6):314
Chen GY, Damasco J, Qiu HL, Shao W, Ohulchanskyy TY, Valiev RR, Wu X, Han G, Wang Y, Yang CH, Agren H, Prasad PN (2015) Energy-Cascaded Upconversion in an Organic Dye-Sensitized Core/Shell Fluoride Nanocrystal. Nano Lett 15(11):7400–7407
Wang X, Wang G, Li W, Zhao B, Xing B, Leng Y, Dou H, Sun K, Shen L, Yuan X (2013) NIR-Emitting Quantum Dot-Encoded Microbeads through Membrane Emulsification for Multiplexed Immunoassays. Small 9(19):3327–3335
Ji X-H, Cheng W, Guo F, Liu W, Guo S-S, He Z-K, Zhao X-Z (2011) On-demand preparation of quantum dot-encoded microparticles using a droplet microfluidic system. Lab Chip 11(15):2561–2568
Wu S, Liu L, Li G, Jing F, Mao H, Jin Q, Zhai W, Zhang H, Zhao J, Jia C (2016) Multiplexed detection of lung cancer biomarkers based on quantum dots and microbeads. Talanta 156:48–54
Anfossi L, Di Nardo F, Cavalera S, Giovannoli C, Spano G, Speranskaya ES, Goryacheva IY, Baggiani C (2018) A lateral flow immunoassay for straightforward determination of fumonisin mycotoxins based on the quenching of the fluorescence of CdSe/ZnS quantum dots by gold and silver nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185(2):94
S-j L, Sheng W, Wen W, Gu Y, Wang J-p, Wang S (2018) Three kinds of lateral flow immunochromatographic assays based on the use of nanoparticle labels for fluorometric determination of zearalenone. Microchim Acta 185(4):238
Sheng W, Chang Q, Shi Y, Duan W, Zhang Y, Wang S (2018) Visual and fluorometric lateral flow immunoassay combined with a dual-functional test mode for rapid determination of tetracycline antibiotics. Microchim Acta 185(9):404
Li S, Wang J, Sheng W, Wen W, Gu Y, Wang S (2018) Fluorometric lateral flow immunochromatographic zearalenone assay by exploiting a quencher system composed of carbon dots and silver nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185(8):388
Sheng W, Li S, Liu Y, Wang J, Zhang Y, Wang S (2017) Visual and rapid lateral flow immunochromatographic assay for enrofloxacin using dyed polymer microspheres and quantum dots. Microchim Acta 184(11):4313–4321
Bamrungsap S, Apiwat C, Chantima W, Dharakul T, Wiriyachaiporn N (2014) Rapid and sensitive lateral flow immunoassay for influenza antigen using fluorescently-doped silica nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 181(1-2):223–230
Han SW, Jang E, Koh W-G (2015) Microfluidic-based multiplex immunoassay system integrated with an array of QD-encoded microbeads. Sensors Actuators B Chem 209:242–251
Marx V (2013) Tracking metastasis and tricking cancer. Nature 494:133–138
Pantel K, Brakenhoff RH, Brandt B (2008) Detection, clinical relevance and specific biological properties of disseminating tumour cells. Nat Rev Cancer 8(5):329–340
Stott SL, Hsu C-H, Tsukrov DI, Yu M, Miyamoto DT, Waltman BA, Rothenberg SM, Shah AM, Smas ME, Korir GK (2010) Isolation of circulating tumor cells using a microvortex-generating herringbone-chip. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107(43):18392–18397
Lv S-W, Wang J, Xie M, Lu N-N, Li Z, Yan X-W, Cai S-L, Zhang P-A, Dong W-G, Huang W-H (2015) Photoresponsive immunomagnetic nanocarrier for capture and release of rare circulating tumor cells. Chem Sci 6(11):6432–6438
Rao L, Meng QF, Huang Q, Wang Z, Yu GT, Li A, Ma W, Zhang N, Guo SS, Zhao XZ (2018) Platelet–Leukocyte Hybrid Membrane-Coated Immunomagnetic Beads for Highly Efficient and Highly Specific Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells. Adv Funct Mater 28(34):1803531
Huang Q, Cai B, Chen B, Rao L, He Z, He R, Guo F, Zhao L, Kondamareddy KK, Liu W (2016) Efficient Purification and Release of Circulating Tumor Cells by Synergistic Effect of Biomarker and SiO2@ Gel-Microbead-Based Size Difference Amplification. Advanced Healthcare Materials 5(13):1554–1559
Huang Q, Wang F-B, Yuan C-H, He Z, Rao L, Cai B, Chen B, Jiang S, Li Z, Chen J (2018) Gelatin Nanoparticle-Coated Silicon Beads for Density-Selective Capture and Release of Heterogeneous Circulating Tumor Cells with High Purity. Theranostics 8(6):1624
Zhang H, Zhang Z, Wang Y, Wu C, Li Q, Tang B (2016) Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Cancer Cells Based on the Photothermal Effect of Graphene Functionalized Magnetic Microbeads. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(44):29933–29938
Veli M, Ozcan A (2018) Computational Sensing of Staphylococcus aureus on Contact Lenses Using 3D Imaging of Curved Surfaces and Machine Learning. ACS Nano 12(3):2554–2559
Wang J-C, Chi S-W, Yang T-H, Chuang H-S (2018) Label-Free Monitoring of Microorganisms and Their Responses to Antibiotics based on Self-Powered Microbead Sensors. ACS sensors 3(10):2182–2190
Li P, Müller M, Chang MW, Frettlöh M, Schönherr H (2017) Encapsulation of Autoinducer Sensing Reporter Bacteria in Reinforced Alginate-Based Microbeads. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(27):22321–22331
Min H, Jo SM, Kim HS (2015) Efficient capture and simple quantification of circulating tumor cells using quantum dots and magnetic beads. Small 11(21):2536–2542
Yuan K, Mei Q, Guo X, Xu Y, Yang D, Sánchez B J, Sheng B, Liu C, Hu Z, Yu G (2018) Antimicrobial peptide based magnetic recognition elements and Au@ Ag-GO SERS tags with stable internal standards: a three in one biosensor for isolation, discrimination and killing of multiple bacteria in whole blood. Chem Sci 9(47):8781-8795
Romeo A, Leung T, Sanchez S (2016) Smart biosensors for multiplexed and fully integrated point-of-care diagnostics. Lab Chip 16(11):1957–1961
Quesada-González D, Merkoçi A (2017) Mobile phone-based biosensing: An emerging “diagnostic and communication” technology. Biosens Bioelectron 92:549–562
Mei Q, Jing H, Li Y, Yisibashaer W, Chen J, Li BN, Zhang Y (2016) Smartphone based visual and quantitative assays on upconversional paper sensor. Biosens Bioelectron 75:427–432
Im H, Castro C M, Shao H, Liong M, Song J, Pathania D, Fexon L, Min C, Avila-Wallace M, Zurkiya O (2015) Digital diffraction analysis enables low-cost molecular diagnostics on a smartphone. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences:201501815
Yang M, Zhang Y, Cui M, Tian Y, Zhang S, Peng K, Xu H, Liao Z, Wang H, Chang J (2018) A smartphone-based quantitative detection platform of mycotoxins based on multiple-color upconversion nanoparticles. Nanoscale 10(33):15865–15874
Fraser LA, Kinghorn AB, Dirkzwager RM, Liang S, Cheung Y-W, Lim B, Shiu SC-C, Tang MS, Andrew D, Manitta J (2018) A portable microfluidic Aptamer-Tethered Enzyme Capture (APTEC) biosensor for malaria diagnosis. Biosens Bioelectron 100:591–596
Cui W, He M, Mu L, Lin Z, Wang Y, Pang W, Reed M, Duan X (2018) Cellphone-Enabled Microwell-Based Microbead Aggregation Assay for Portable Biomarker Detection. ACS sensors 3(2):432–440
Yetisen AK, Martinez-Hurtado JL, Ünal B, Khademhosseini A, Butt H (2018) Wearables in Medicine. Adv Mater 30(33):1706910
Gao W, Emaminejad S, Nyein HYY, Challa S, Chen K, Peck A, Fahad HM, Ota H, Shiraki H, Kiriya D (2016) Fully integrated wearable sensor arrays for multiplexed in situ perspiration analysis. Nature 529(7587):509
Tamayol A, Akbari M, Zilberman Y, Comotto M, Lesha E, Serex L, Bagherifard S, Chen Y, Fu G, Ameri SK (2016) Flexible pH-sensing hydrogel fibers for epidermal applications. Advanced Healthcare Materials 5(6):711–719
Zhou L, Fan Y, Wang R, Li X, Fan L, Zhang F (2018) High-Capacity Upconversion Wavelength and Lifetime Binary Encoding for Multiplexed Biodetection. Angew Chem Int Ed 57(39):12824–12829
Lu S, Zhang DS, Wei D, Lin Y, Zhang S, He H, Wei X, Gu H, Xu H (2017) Three-Dimensional Barcodes with Ultrahigh Encoding Capacities: A Flexible, Accurate, and Reproducible Encoding Strategy for Suspension Arrays. Chem Mater 29(24):10398–10408
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the Innovative Research Team of High-level Local Universities in Shanghai, National Natural Science Foundation of China (31671011), and grants from the Ministry of Education of Singapore (MOE2016-T3-1-004, R-397-000-270-114).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Shikha, S., Mei, Q. et al. Fluorescent microbeads for point-of-care testing: a review. Microchim Acta 186, 361 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3449-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3449-y