Abstract
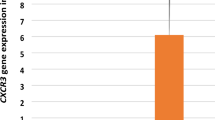
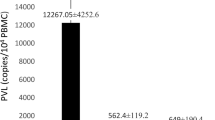
Adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL) is a life-threatening malignancy of HTLV-1 infected Th lymphocytes. In the present study host–virus interactions were investigated by assessment of HTLV-1 proviral load (PVL) and host gene expression. A cross-sectional study was carried out on 18 ATLL, 10 HAM/TSP patients and 18 HTLV-1 asymptomatic carriers (ACs). DNA and mRNA of the peripheral blood mononuclear cells were extracted for PVL and LAT, BIM, c-FOS and RAD51 gene expression measurement using qRT-PCR. The mean PVL in ATLL patients was 11,430 ± 3770 copies/104 which was statistically higher than ACs, 530 ± 119 copies/104, (p < 0.001). The expression of BIM, and c-FOS in ATLL patients were higher than HTLV-1 ACs; however, there were no statistically significant differences. The expression of RAD51 as an essential player on DNA repair showed around 160 times increase in ATLL group (166 ± 95) compared to ACs (1.04 ± 0.34) which is statistically significant (p < 0.001). Interestingly, there was a positive correlation between RAD51 expression and HTLV-PVL. The expression of LAT as a central adaptor in TCR signaling interestingly was around 36 times higher in ATLL group than ACs (ATLL; 41.33 ± 19.91 vs. ACs; 1.15 ± 0.22, p < 0.001). This finding showed that TCR signaling pathway mainly provides the growth factors for transformed cells. Furthermore, the overexpression of RAD51 which has been induced in HTLV-1 infected cells as a consequence of virus replication is not able to overcome the DNA damage toward cell transformation.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACs:
-
Asymptomatic carriers
- AKT:
-
Protein kinase B
- ATLL:
-
Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma
- β2m:
-
β2 microglobulin
- cDNA:
-
Complementary DNA
- CML:
-
Chronic myeloid leukemia
- CREB:
-
c-AMP response element binding protein
- HAM/TSP:
-
HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis
- HBZ:
-
HTLV-1 basic zipper factor of oncogenesis
- HR:
-
Homologous recombination
- HTLV-1:
-
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1
- LAT:
-
Linker for activation of T cells
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- MUMS:
-
Mashhad University of Medical Sciences
- PBMCs:
-
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- PVL:
-
Proviral load
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- TCD4+ cells:
-
CD4 T-lymphocytes
- TCR:
-
T-cell receptor
References
Kannian P, Green PL (2010) Human T lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1): molecular biology and oncogenesis. Viruses 2(9):2037–2077. doi:10.3390/v2092037
Gessain A, Cassar O (2012) Epidemiological aspects and world distribution of HTLV-1 infection. Front Microbiol 3:388. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2012.00388
Shoeibi A, Etemadi M, Moghaddam Ahmadi A, Amini M, Boostani R (2013) “HTLV-1 infection” twenty-year research in neurology department of mashhad university of medical sciences. Iran J Basic Med Sci 16(3):202–207
Farid Hosseni R, Jabbari F, Shabestari M, Rezaee SA, Gharivani Y, Valizadeh N, Sobhani M, Moghiman T, Mozayani F (2013) Human T lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) is a risk factor for coronary artery disease. Iran J Basic Med Sci 16(3):217–220
Hinuma Y, Komoda H, Chosa T, Kondo T, Kohakura M, Takenaka T, Kikuchi M, Ichimaru M, Yunoki K, Sato I, Matsuo R, Takiuchi Y, Uchino H, Hanaoka M (1982) Antibodies to adult T-cell leukemia-virus-associated antigen (ATLA) in sera from patients with ATL and controls in Japan: a nation-wide sero-epidemiologic study. Int J Cancer 29(6):631–635
Rafatpanah H, Hedayati-Moghaddam MR, Fathimoghadam F, Bidkhori HR, Shamsian SK, Ahmadi S, Sohgandi L, Azarpazhooh MR, Rezaee SA, Farid R, Bazarbachi A (2011) High prevalence of HTLV-I infection in Mashhad, Northeast Iran: a population-based seroepidemiology survey. J Clin Virol 52(3):172–176. doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2011.07.004
Azarpazhooh MR, Hasanpour K, Ghanbari M, Rezaee SA, Mashkani B, Hedayati-Moghaddam MR, Valizadeh N, Farid Hosseini R, Foroghipoor M, Soltanifar A, Sahebari M, Azadmanesh K, Hassanshahi G, Rafatpanah H (2012) Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 prevalence in northeastern Iran, Sabzevar: an epidemiologic-based study and phylogenetic analysis. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 28(9):1095–1101. doi:10.1089/aid.2011.0248
Kiadaliri AA, Najafi B, Haghparast-Bidgoli H (2011) Geographic distribution of need and access to health care in rural population: an ecological study in Iran. Int J Equity Health 10(1):39
Hedayati-Moghaddam MR, Fathimoghadam F, Eftekharzadeh Mashhadi I, Soghandi L, Bidkhori HR (2011) Epidemiology of HTLV-1 in Neyshabour, northeast of Iran. Iran red crescent Med J 13(6):424–427
Boostani R, Mellat Ardakani A, Ashrafi H (2011) Khorasan Disease: prevalence of HTLV-I associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP) in west Azarbaijan from 2004 to 2007. Iran red crescent med J 13(6):428–430
Kalavi K, Moradi A, Tabarraei A (2013) Population-based seroprevalence of HTLV-1 infection in Golestan province, south east of Caspian sea, Iran. Iran J Basic Med Sci 16(3):225–228
Ahmadi Ghezeldasht S, Shirdel A, Assarehzadegan MA, Hassannia T, Rahimi H, Miri R, Rezaee SA (2013) Human T lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) oncogenesis: molecular aspects of virus and host interactions in pathogenesis of adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL). Iran J Basic Med Sci 16(3):179–195
Wattel E, Vartanian JP, Pannetier C, Wain-Hobson S (1995) Clonal expansion of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-infected cells in asymptomatic and symptomatic carriers without malignancy. J Virol 69(5):2863–2868
Trevino A, Aguilera A, Caballero E, Benito R, Parra P, Eiros JM, Hernandez A, Calderon E, Rodriguez M, Torres A, Garcia J, Ramos JM, Roc L, Marcaida G, Rodriguez C, Trigo M, Gomez C, de Lejarazu RO, de Mendoza C, Soriano V (2012) Trends in the prevalence and distribution of HTLV-1 and HTLV-2 infections in Spain. Virol J 9:71. doi:10.1186/1743-422x-9-71
Etoh K, Tamiya S, Yamaguchi K, Okayama A, Tsubouchi H, Ideta T, Mueller N, Takatsuki K, Matsuoka M (1997) Persistent clonal proliferation of human T-lymphotropic virus type-1 infected cells in vivo. Cancer Res 57(21):4862–4867
Okayama A, Stuver S, Matsuoka M, Ishizaki J, Tanaka G, Kubuki Y, Mueller N, Hsieh CC, Tachibana N, Tsubouchi H (2004) Role of HTLV-1 proviral DNA load and clonality in the development of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma in asymptomatic carriers. Int J Cancer 110(4):621–625. doi:10.1002/ijc.20144
Mesnard JM, Barbeau B, Devaux C (2006) HBZ, a new important player in the mystery of adult T-cell leukemia. Blood 108(13):3979–3982. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-03-007732
Tabakin-Fix Y, Azran I, Schavinky-Khrapunsky Y, Levy O, Aboud M (2006) Functional inactivation of p53 by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax protein: mechanisms and clinical implications. Carcinogenesis 27(4):673–681. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgi274
Cesarman E, Chadburn A, Inghirami G, Gaidano G, Knowles DM (1992) Structural and functional analysis of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma shows frequent p53 mutations. Blood 80(12):3205–3216
Brauweiler A, Garrus JE, Reed JC, Nyborg JK (1997) Repression of bax gene expression by the HTLV-1 Tax protein: implications for suppression of apoptosis in virally infected cells. Virology 231(1):135–140
Yamada T, Yamaoka S, Goto T, Nakai M, Tsujimoto Y, Hatanaka M (1994) The human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax protein induces apoptosis which is blocked by the Bcl-2 protein. J Virol 68(5):3374–3379
Mulloy JC, Kislyakova T, Cereseto A, Casareto L, LoMonico A, Fullen J, Lorenzi MV, Cara A, Nicot C, Giam C, Franchini G (1998) Human T-cell lymphotropic/leukemia virus type 1 Tax abrogates p53-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through its CREB/ATF functional domain. J Virol 72(11):8852–8860
Kalra N, Kumar V (2004) c-FOS is a mediator of the c-myc-induced apoptotic signaling in serum-deprived hepatoma cells via the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Biol Chem 279(24):25313–25319. doi:10.1074/jbc.M400932200
Harada H, Grant S (2012) Targeting the regulatory machinery of BIM for cancer therapy. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 22(2):117–129
Ward JD, Muzzini DM, Petalcorin MI, Martinez-Perez E, Martin JS, Plevani P, Cassata G, Marini F, Boulton SJ (2010) Overlapping mechanisms promote postsynaptic RAD-51 filament disassembly during meiotic double-strand break repair. Mol Cell 37(2):259–272. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2009.12.026
Martin JS, Winkelmann N, Petalcorin MI, McIlwraith MJ, Boulton SJ (2005) RAD-51-dependent and -independent roles of a Caenorhabditis elegans BRCA2-related protein during DNA double-strand break repair. Mol Cell Biol 25(8):3127–3139. doi:10.1128/mcb.25.8.3127-3139.2005
Rinaldo C, Bazzicalupo P, Ederle S, Hilliard M, La Volpe A (2002) Roles for Caenorhabditis elegans RAD-51 in meiosis and in resistance to ionizing radiation during development. Genetics 160(2):471–479
Fukumoto R, Dundr M, Nicot C, Adams A, Valeri VW, Samelson LE, Franchini G (2007) Inhibition of T-cell receptor signal transduction and viral expression by the linker for activation of T cells-interacting p12(I) protein of human T-cell leukemia/lymphoma virus type 1. J Virol 81(17):9088–9099. doi:10.1128/JVI.02703-06
Salek M, McGowan S, Trudgian DC, Dushek O, de Wet B, Efstathiou G, Acuto O (2013) Quantitative phosphoproteome analysis unveils LAT as a modulator of CD3zeta and ZAP-70 tyrosine phosphorylation. PLoS ONE 8(10):e77423. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0077423
Akbarin MM, Rahimi H, Hassannia T, Shoja Razavi G, Sabet F, Shirdel A (2013) Comparison of HTLV-I proviral load in adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL), HTLV-1 associated myelopathy (HAM-TSP) and healthy carriers. Iran J Basic Med Sci 16(3):208–212
Shuh M, Beilke M (2005) The human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1): new insights into the clinical aspects and molecular pathogenesis of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL) and tropical spastic paraparesis/HTLV-associated myelopathy (TSP/HAM). Microsc Res Tech 68(3–4):176–196. doi:10.1002/jemt.20231
White JD, Zaknoen SL, Kasten-Sportes C, Top LE, Navarro-Roman L, Nelson DL, Waldmann TA (1995) Infectious complications and immunodeficiency in patients with human T-cell lymphotropic virus I-associated adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Cancer 75(7):1598–1607
Cook LB, Melamed A, Niederer H, Valganon M, Laydon D, Foroni L, Taylor GP, Matsuoka M, Bangham CR (2014) The role of HTLV-1 clonality, proviral structure, and genomic integration site in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Blood 123(25):3925–3931. doi:10.1182/blood-2014-02-553602
Boxus M, Willems L (2009) Mechanisms of HTLV-1 persistence and transformation. Br J Cancer 101(9):1497–1501. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6605345
Marriott SJ, Semmes OJ (2005) Impact of HTLV-I Tax on cell cycle progression and the cellular DNA damage repair response. Oncogene 24(39):5986–5995. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208976
Nagata K, Ohtani K, Nakamura M, Sugamura K (1989) Activation of endogenous c-FOS proto-oncogene expression by human T-cell leukemia virus type I-encoded p40tax protein in the human T-cell line. Jurkat. J Virol 63(8):3220–3226
Jeong SJ, Pise-Masison CA, Radonovich MF, Park HU, Brady JN (2005) Activated AKT regulates NF-kappaB activation, p53 inhibition and cell survival in HTLV-1-transformed cells. Oncogene 24(44):6719–6728. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208825
Saggioro D (2011) Anti-apoptotic effect of Tax: an NF-kappaB path or a CREB way? Viruses 3(7):1001–1014. doi:10.3390/v3071001
Piazza R, Magistroni V, Mogavero A, Andreoni F, Ambrogio C, Chiarle R, Mologni L, Bachmann PS, Lock RB, Collini P, Pelosi G, Gambacorti-Passerini C (2013) Epigenetic silencing of the proapoptotic gene BIM in anaplastic large cell lymphoma through an MeCP2/SIN3a deacetylating complex. Neoplasia 15(5):511–522
Soderquist RS, Danilov AV, Eastman A (2014) Gossypol increases expression of the pro-apoptotic BH3-only protein NOXA through a novel mechanism involving phospholipase A2, cytoplasmic calcium, and endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Biol Chem 289(23):16190–16199. doi:10.1074/jbc.M114.562900
Miller AV, Hicks MA, Nakajima W, Richardson AC, Windle JJ, Harada H (2013) Paclitaxel-induced apoptosis is BAK-dependent, but BAX and BIM-independent in breast tumor. PLoS ONE 8(4):e60685. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0060685
Januchowski R, Jagodzinski PP (2007) Trichostatin A down-regulates ZAP-70, LAT and SLP-76 content in Jurkat T cells. Int Immunopharmacol 7(2):198–204. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2006.09.010
Lu SP, Lin Feng MH, Huang HL, Huang YC, Tsou WI, Lai MZ (2007) Reactive oxygen species promote raft formation in T lymphocytes. Free radic biol med 42(7):936–944. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.11.027
Klein HL (2008) The consequences of RAD51 overexpression for normal and tumor cells. DNA repair (Amst) 7(5):686–693. doi:10.1016/j.dnarep.2007.12.008
Zhu J, Zhou L, Wu G, Konig H, Lin X, Li G, Qiu XL, Chen CF, Hu CM, Goldblatt E, Bhatia R, Chamberlin AR, Chen PL, Lee WH (2013) A novel small molecule RAD51 inactivator overcomes imatinib-resistance in chronic myeloid leukaemia. EMBO Mol Med 5(3):353–365. doi:10.1002/emmm.201201760
Banerjee K, Resat H (2016) Constitutive activation of STAT3 in breast cancer cells: a review. Int J Cancer J Int Du Cancer 138(11):2570–2578
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Vice-chancellor for Research, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences (Grant number 911304) and was the subject of a student thesis for Ms Samaneh Ramezani. Great thanks to our colleagues in Inflammation and Inflammatory Research division, Ms N. Valizadeh, Dr. B. Fazeli, Ms S. Ahmadi Ghezeldasht, Dr. A. Mosavat and Ms A. Zeyaee Mehr.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no financial or commercial conflict of interest regarding this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramezani, S., Shirdel, A., Rafatpanah, H. et al. Assessment of HTLV-1 proviral load, LAT, BIM, c-FOS and RAD51 gene expression in adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma. Med Microbiol Immunol 206, 327–335 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-017-0506-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-017-0506-1