Abstract
Objectives
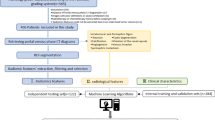
To investigate different radiomics models based on single phase and the different phase combinations of radiomics features from 3D tri-phasic CT to distinguish RO from chRCC.
Methods
A total of 96 patients (30 RO and 66 chRCC) were enrolled in this study. Radiomics features were extracted from unenhanced phase (UP), corticomedullary phase (CMP), and nephrographic phase (NP) CT images. Feature selection was based on the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression (LASSO) method. The selected features were used to develop different radiomics models using logistic regression (LR) analysis, including model 1 (UP), model 2(CMP), model 3(NP), model 4(UP+CMP), model 5(UP+NP), model 6(CMP+NP), and model 7(UP+CMP+NP). The radiomics model demonstrating the highest discrimination performance was utilized to construct the combined model (model 8) with clinical factors. A nomogram based on the model 8 was established. To evaluate the diagnostic performance of the different models, the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and decision curve analysis (DCA) were used. Delong's test was utilized to assess the statistical significance of the AUC improvement across the models.
Results
Among the seven radiomics models, model 7 exhibited the highest AUC of 0.84 (95% CI 0.69, 0.99), and model 7 demonstrated a significantly superior AUC compared to the other radiomics models (all P < 0.05). The AUC values of radiomics models based on two phases (model4, mode5, mode6) were greater than the models based on single phase (model1, mode2, mode3) (all P < 0.05). Model 3 illustrated the best performance of the three radiomics models based on single phase with an AUC of 0.76 (95% CI 0.57, 099). Model 6 illustrated the best performance of the three radiomics models based on two-phases combination with an AUC of 0.83 (0.66, 0.99). Model 8 achieved an AUC of 0.93 (95% CI 0.83, 1.00) which is higher than those all radiomics models.
Conclusion
Radiomics models based on combination of radiomics features from UP, CMP, and NP can be a useful and promising technique to differentiate RO from chRCC. Moreover, the model combining clinical factors and radiomics features showed better classification performance to distinguish them.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hyeok CJ, Won KJ, Yong LJ et al (2015) Comparison of computed tomography findings between renal oncocytomas and chromophobe renal cell carcinomas. Korean Journal of Urology 56:695-702
Kawaguchi S, Fernandes KA, Finelli A, Robinette M, Jewett MAS (2011) Most Renal Oncocytomas Appear to Grow: Observations of Tumor Kinetics With Active Surveillance. The Journal of urology 186:1218-1222
Scialpi M, Martorana E, Rondoni V et al (2017) Value of triphasic MDCT in the differentiation of small renal cell carcinoma and oncocytoma. Urologia 84:244-250
Ljungberg B, Albiges L, Abu-Ghanem Y et al (2019) European Association of Urology Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma: The 2019 Update. European urology 75:799-810
Schieda N, McInnes M, Cao L (2014) Diagnostic accuracy of segmental enhancement inversion for diagnosis of renal oncocytoma at biphasic contrast enhanced CT: systematic review. European radiology 24:1421-9
Demirović A, Cesarec S, Spajić B et al (2010) Can renal oncocytoma be distinguished from chromophobe renal cell carcinoma by the presence of fibrous capsule? Virchows Archiv : an international journal of pathology 456:85-9
Guo K, Ren S, Cao Y et al (2021) Differentiation between renal oncocytomas and chromophobe renal cell carcinomas using dynamic contrast-enhanced computed tomography. Abdominal radiology (New York) 46:3309-3316
Gillies R, Kinahan P, Hricak H (2016) Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 278:563-77
Lambin P, Rios-Velazquez E, Leijenaar R et al (2012) Radiomics: extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. European journal of cancer (Oxford, England : 1990) 48:441-6
Kim J, Cho J, Moon K, Lee H, Kim S (2009) Segmental enhancement inversion at biphasic multidetector CT: characteristic finding of small renal oncocytoma. Radiology 252:441-8
O’Malley ME, Tran P, Hanbidge A, Rogalla P (2012) Small renal oncocytomas: is segmental enhancement inversion a characteristic finding at biphasic MDCT? Ajr American Journal of Roentgenology 199:1312-5
John P, McGahan, Ramit et al (2011) Is segmental enhancement inversion on enhanced biphasic MDCT a reliable sign for the noninvasive diagnosis of renal oncocytomas? AJR. American journal of roentgenology 197: W674-9
Roussel E, Capitanio U, Kutikov A et al (2022) Novel Imaging Methods for Renal Mass Characterization: A Collaborative Review. European urology 81:476-488
Yap FY, Varghese BA, Cen SY et al (2021) Shape and texture-based radiomics signature on CT effectively discriminates benign from malignant renal masses. European radiology 31:1011-1021
Sun X, Feng Q, Xu X et al (2020) Radiologic-Radiomic Machine Learning Models for Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Solid Renal Masses: Comparison With Expert-Level Radiologists. AJR. American journal of roentgenology 214:W44-W54
Luo S, Wei R, Lu S et al (2022) Fuhrman nuclear grade prediction of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: influence of volume of interest delineation strategies on machine learning-based dynamic enhanced CT radiomics analysis. European radiology 32:2340-2350
Nassiri N, Maas M, Cacciamani G et al (2022) A Radiomic-based Machine Learning Algorithm to Reliably Differentiate Benign Renal Masses from Renal Cell Carcinoma. European urology focus 8:988-994
Erdim C, Yardimci A, Bektas C et al (2020) Prediction of Benign and Malignant Solid Renal Masses: Machine Learning-Based CT Texture Analysis. Academic radiology 27:1422-1429
Li X, Ma Q, Tao C, Liu J, Nie P, Dong C (2021) A CT-based radiomics nomogram for differentiation of small masses (< 4 cm) of renal oncocytoma from clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Abdominal radiology (New York) 46:5240-5249
Alhussaini A, Steele J, Nabi G (2022) Comparative Analysis for the Distinction of Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma from Renal Oncocytoma in Computed Tomography Imaging Using Machine Learning Radiomics Analysis. Cancers 14:undefined
Li X, Ma Q, Nie P, Zheng Y, Dong C, Xu W (2022) A CT-based radiomics nomogram for differentiation of renal oncocytoma and chromophobe renal cell carcinoma with a central scar-matched study. The British journal of radiology 95:20210534
Zwanenburg A, Vallières M, Abdalah M et al (2020) The Image Biomarker Standardization Initiative: Standardized Quantitative Radiomics for High-Throughput Image-based Phenotyping. Radiology 295:328-338
Yu Z, Ding J, Pang H et al (2022) A triple-classification for differentiating renal oncocytoma from renal cell carcinoma subtypes and CK7 expression evaluation: a radiomics analysis. BMC urology 22:147-158
Li Y, Huang X, Xia Y, Long L (2020) Value of radiomics in differential diagnosis of chromophobe renal cell carcinoma and renal oncocytoma. Abdominal radiology (New York) 45:3193-3201
Zhou T, Guan J, Feng B et al (2023) Distinguishing common renal cell carcinomas from benign renal tumors based on machine learning: comparing various CT imaging phases, slices, tumor sizes, and ROI segmentation strategies. European radiology 33:4323-4332
Shu J, Tang Y, Cui J et al (2018) Clear cell renal cell carcinoma: CT-based radiomics features for the prediction of Fuhrman grade. European journal of radiology 109:8-12
Yang G, Gong A, Nie P et al (2019) Contrast-Enhanced CT Texture Analysis for Distinguishing Fat-Poor Renal Angiomyolipoma From Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma. Molecular imaging 18:1536012119883161
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, S., Jian, Y., Yang, F. et al. Radiomics analysis based on single phase and different phase combinations of radiomics features from tri-phasic CT to distinguish renal oncocytoma from chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. Abdom Radiol 49, 182–191 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-023-04053-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-023-04053-2