Abstract
Objectives
To use systematic review to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of segmental enhancement inversion (SEI) at contrast-enhanced biphasic multi-detector computed tomography (MDCT) for the diagnosis of renal oncocytoma.
Methods
Several electronic databases were searched through October 2013. Two reviewers independently selected studies that met the inclusion criteria and extracted data. Study quality was assessed with the QUADAS-2 tool. The primary 2 × 2 data were investigated with forest plot and ROC plot of sensitivity and specificity.
Results
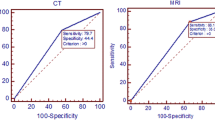
Four studies met the inclusion criteria (307 patients). Considerable heterogeneity between studies precluded meta-analysis. Two studies from the same group of investigators demonstrated reasonable diagnostic accuracy (sensitivity 59-80 % and specificity 87-99 %), while two others did not (sensitivity 0-6 %, specificity 93-100 %). Possible reasons for this include timing of biphasic MDCT and methods of interpretation but not size of lesion.
Conclusions
SEI is a specific imaging finding of renal oncocytoma with highly variable sensitivity. This substantial heterogeneity across studies and between institutions suggests that further validation of this imaging finding is necessary prior to application in clinical practice.
Key Points
• SEI on CT in small renal masses is specific for oncocytoma.
• Sensitivity of SEI varies substantially between studies and across institutions.
• Variability could relate to CT timing or methods of interpretation.
• High accuracy of SEI has only been reported by one group.
• Validation of SEI is needed prior to clinical implementation.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SEI:
-
segmental enhancement inversion
- RCC:
-
renal cell cancer
- PRISMA:
-
preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses
- CCTR:
-
Cochrane central register of controlled trials
- DARE:
-
database of abstracts of reviews of effects
- CSDR:
-
Cochrane database of systematic reviews (CSDR)
- TP:
-
true positive
- TN:
-
true negative
- FP:
-
false positive
- FN:
-
false negative
- ROC:
-
receiver operator curve
- Ch-RCC:
-
chromophobe RCC
- cc-RCC:
-
clear cell RCC
References
Remzi M, Ozsoy M, Klingler HC et al (2006) Are small renal tumors harmless? Analysis of histopathological features according to tumors 4cm or less in diameter. J Urol 176:896–899
Violette P, Abourbih S, Szymanski KM et al (2012) Solitary solid renal mass: can we predict malignancy? BJU Int 110(11 Pt B):E548–E552
Perez-Ordonez B, Hamed G, Campbell S et al (1997) Renal oncocytoma: a clinicopathologic study of 70 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 21:871–883
Lieber MM (1993) Renal oncocytoma. Urol Clin N Am 20:355–359
Quinn MJ, Hartman DS, Friedman AC et al (1984) Renal oncocytoma: new observations. Radiology 153:49–53
Jasinski RW, Amendola MA, Glazer GM, Bree RL, Gikas PW (1985) Computed tomography of renal oncocytomas. Comput Radiol 9:307–314
Davidson AJ, Hayes WS, Hartman DS, McCarthy WF, Davis CJ Jr (1993) Renal oncocytoma and carcinoma: failure of differentiation with CT. Radiology 186:693–696
Kim JI, Cho JY, Moon KC, Lee HJ, Kim SH (2009) Segmental enhancement inversion at biphasic multidetector CT: characteristic finding of small renal oncocytoma. Radiology 252:441–448
Millet I, Doyon FC, Hoa D et al (2011) Characterization of small solid renal lesions: can benign and malignant tumors be differentiated with CT? AJR Am J Roentgenol 197:887–896
McGahan JP, Lamba R, Fisher J et al (2011) Is segmental enhancement inversion on enhanced biphasic MDCT a reliable sign for the noninvasive diagnosis of renal oncocytomas? AJR Am J Roentgenol 197:W674–W679
O'Malley ME, Tran P, Hanbidge A, Rogalla P (2012) Small renal oncocytomas: is segmental enhancement inversion a characteristic finding at biphasic MDCT? AJR Am J Roentgenol 199:1312–1315
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med 151(264–269):W64
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J et al (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ 339:b2700
Staunton M (2007) Evidence-based radiology: steps 1 and 2—asking answerable questions and searching for evidence. Radiology 242:23–31
Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME et al (2011) QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med 155:529–536
Macaskill P GC, Deeks JJ, Harbord RM, Takwoingi Y (2010) Chapter 10: Analysing and Presenting Results. In: Deeks JJ, Bossuyt PM, Gatsonis C (eds) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Version 1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2010. Available from: http://srdta.cochrane.org/
Woo S, Cho JY, Kim SH, Kim SY (2013) Comparison of segmental enhancement inversion on biphasic MDCT between small renal oncocytomas and chromophobe renal cell carcinomas. AJR Am J Roentgenol 201:598–604
Woo S, Cho JY, Kim SH et al (2013) Segmental enhancement inversion of small renal oncocytoma: differences in prevalence according to tumor size. AJR Am J Roentgenol 200:1054–1059
Rosenkrantz AB, Hindman N, Fitzgerald EF, Niver BE, Melamed J, Babb JS (2010) MRI features of renal oncocytoma and chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol 195:W421–W427
He W LJ-Y (2011) Characteristic finding of renal oncocytoma and clear-cell renal cell carcinoma with multiphase CT. Chin J Radiol 45:1203–1206
Acknowledgements
We thank Sascha Davis MLIS, librarian at The Ottawa Hospital for her assistance with the search strategy.
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Matthew DF McInnes. The authors’ institution receives an unrestricted educational grant from GE Medical. The authors state that this work has not received any funding. One of the authors has significant statistical expertise. Institutional Review Board approval was not required because this is a systematic review of published literature. Our IRB waives approval for this type of study. Methodology: systematic review (retrospective).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schieda, N., McInnes, M.D.F. & Cao, L. Diagnostic accuracy of segmental enhancement inversion for diagnosis of renal oncocytoma at biphasic contrast enhanced CT: systematic review. Eur Radiol 24, 1421–1429 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3147-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-014-3147-4