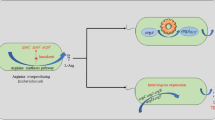
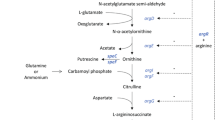
Abstract
L-arginine (L-Arg) is a semi-essential amino acid with many important physiological functions. However, achieving efficient manufacture of L-Arg on an industrial scale using Escherichia coli (E. coli) remains a major challenge. In previous studies, we constructed a strain of E. coli A7, which had good L-Arg production capacity. In this study, E. coli A7 was further modified, and E. coli A21 with more efficient L-Arg production capacity was obtained. Firstly, we reduced the acetate accumulation of strain A7 by weakening the poxB gene and overexpressing acs gene. Secondly, we improved the L-Arg transport efficiency of strains by overexpressing the lysE gene from Corynebacterium glutamicum (C. glutamicum). Finally, we enhanced the supplies of precursors for the synthesis of L-Arg and optimized the supplies of cofactor NADPH and energy ATP in strain. After fermentation in a 5-L bioreactor, the L-Arg titer of strain A21 was found to be 89.7 g/L. The productivity was 1.495 g/(L·h) and the glucose yield was 0.377 g/g. Our study further narrowed the titer gap between E. coli and C. glutamicum in the synthesis of L-Arg. In all recent studies on the L-Arg production by E. coli, this was the highest titer recorded. In conclusion, our study further promotes the efficient mass synthesis of L-Arg by E. coli.
Graphical abstract

Key points
• The acetate accumulation of starting strain A7 was decreased.
• Overexpression of gene lysE of C. glutamicum enhanced L-Arg transport in strain A10.
• Enhance the supplies of precursors for the synthesis of L-Arg and optimize the supplies of cofactor NADPH and energy ATP. Finally, Strain A21 was detected to have an L-Arg titer of 89.7 g/L in a 5-L bioreactor.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in the published article. Construction of recombinant plasmid; primer pairs used in this study; analyzing of L-Arg production by shake-flask fermentation.
Code availability
Not applicable
References
Bellmann A, Vrljic M, Patek M, Sahm H, Kramer R, Eggeling L (2001) Expression control and specificity of the basic amino acid exporter LysE of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Microbiology 147(7):1765–1774. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-147-7-1765
Bormann ER, Eikmanns BJ, Sahm H (1992) Molecular analysis of the Corynebacterium glutamicum gdh gene encoding glutamate dehydrogenase. Mol Microbiol 6(3):317–326. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01474.x
Bouvier J, Stragier P, Morales V, Remy E, Gutierrez C (2008) Lysine represses transcription of the Escherichia coli dapB gene by preventing its activation by the ArgP activator. J Bacteriol 190(15):5224–5229. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01782-07
Celis RE (1999) Repression and activation of arginine transport genes in Escherichia coli K12 by the ArgP protein. J Mol Biol 294(5):1087–1095. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1999.3308
Charlier D, Bervoets I (2019) Regulation of arginine biosynthesis, catabolism and transport in Escherichia coli. Amino Acids 51(8):1103–1127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-019-02757-8
Charlier D, Nguyen Le Minh P, Roovers M (2018) Regulation of carbamoylphosphate synthesis in Escherichia coli: an amazing metabolite at the crossroad of arginine and pyrimidine biosynthesis. Amino Acids 50(12):1647–1661. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-018-2654-z
Deng Y, Ma N, Zhu K, Mao Y, Wei X, Zhao Y (2018) Balancing the carbon flux distributions between the TCA cycle and glyoxylate shunt to produce glycolate at high yield and titer in Escherichia coli. Metab Eng 46:28–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.02.008
Deng C, Lv X, Li J, Zhang H, Liu Y, Du G, Amaro RL, Liu L (2021) Synergistic improvement of N-acetylglucosamine production by engineering transcription factors and balancing redox cofactors. Metab Eng 67:330–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2021.07.012
Dou W, Xu M, Cai D, Zhang X, Rao Z, Xu Z (2011) Improvement of L-arginine production by overexpression of a bifunctional ornithine acetyltransferase in Corynebacterium crenatum. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 165(3-4):845–855. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9302-3
Ginesy M, Belotserkovsky J, Enman J, Isaksson L, Rova U (2015) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for enhanced arginine biosynthesis. Microb Cell Fact 14(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-015-0211-y
Glover G, Voliotis M, Lapinska U, Invergo BM, Soanes D, O’Neill P, Moore K, Nikolic N, Petrov PG, Milner DS, Roy S, Heesom K, Richards TA, Tsaneva-Atanasova K, Pagliara S (2022) Nutrient and salt depletion synergistically boosts glucose metabolism in individual Escherichia coli cells. Commun Bio 5(1):385. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-022-03336-6
Guo J, Man Z, Rao Z, Xu M, Yang T, Zhang X, Xu Z (2017) Improvement of the ammonia assimilation for enhancing L-arginine production of Corynebacterium crenatum. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 44(3):443–451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-017-1900-9
Hadi A, Arab A, Moradi S, Pantovic A, Clark CCT, Ghaedi E (2019) The effect of L-arginine supplementation on lipid profile: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Brit J Nut 122(9):1021–1032. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114519001855
Hasegawa S, Suda M, Uematsu K, Natsuma Y, Hiraga K, Jojima T, Inui M, Yukawa H (2013) Engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for high-yield L-valine production under oxygen deprivation conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 79(4):1250–1257. https://doi.org/10.1128/AΕM.02806-12
Hou Y, Hu S, Jia S, Nawaratna G, Che D, Wang F, Bazer FW, Wu G (2016) Whole-body synthesis of L-homoarginine in pigs and rats supplemented with L-arginine. Amino Acids 48(4):993–1001. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-2145-4
Jiang S, Wang D, Wang R, Zhao C, Ma Q, Wu H, Xie X (2021b) Reconstructing a recycling and nonauxotroph biosynthetic pathway in Escherichia coli toward highly efficient production of L-citrulline. Metab Eng 68:220–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2021.10.009
Jiang Y, Sheng Q, Wu XY, Ye BC, Zhang B (2021a) L-arginine production in Corynebacterium glutamicum: manipulation and optimization of the metabolic process. Crit Rev Biotechnol 41(2):172–185. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2020.1844625
Lee WH, Chin YW, Han NS, Kim MD, Seo JH (2011) Enhanced production of GDP-L-fucose by overexpression of NADPH regenerator in recombinant Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91(4):967–976. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3271-x
Li M, Yao S, Shimizu K (2006) Effect of poxB gene knockout on metabolism in Escherichia coli based on growth characteristics and enzyme activities. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 23(4):573–580. https://doi.org/10.1007/11274-006-9267-5
Li Y, Lin Z, Huang C, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Tang YJ, Chen T, Zhao X (2015) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli using CRISPR-Cas9 meditated genome editing. Metab Eng 31:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2015.06.006
Liao X, Deng T, Zhu Y, Du G, Chen J (2008) Enhancement of glutathione production by altering adenosine metabolism of Escherichia coli in a coupled ATP regeneration system with Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Appl Microbiol 104(2):345–352. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2007.03415.x
Liu J, Li H, Zhao G, Caiyin Q, Qiao J (2018) Redox cofactor engineering in industrial microorganisms: strategies, recent applications and future directions. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 45(5):313–327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-018-2031-7
Long M, Xu M, Ma Z, Pan X, You J, Shao HM, Yang T, Zhang X, Rao Z (2020) Significantly enhancing production of trans -4-hydroxy-L-proline by integrated system engineering in Escherichia coli. Sci Adv 6(21):eaba2383. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aba2383
Majumdar R, Barchi B, Turlapati SA, Gagne M, Minocha R, Long S, Minocha SC (2016) Glutamate, ornithine, arginine, proline, and polyamine metabolic interactions: the pathway is regulated at the post-transcriptional level. Front Plant Sci 7:78. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00078.e
Man Z, Xu M, Rao Z, Guo J, Yang T, Zhang X, Xu Z (2016) Systems pathway engineering of Corynebacterium crenatum for improved L-arginine production. Sci Rep 6:28629. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep28629
Marbaniang CN, Gowrishankar J (2012) Transcriptional cross-regulation between Gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, demonstrated using ArgP-argO of Escherichia coli and LysG-lysE of Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Bacteriol 194(20):5657–5666. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00947-12
Mels CMC, Loots I, Schwedhelm E, Atzler D, Boger RH, Schutte AE (2016) Nitric oxide synthesis capacity, ambulatory blood pressure and end organ damage in a black and white population: the SABPA study. Amino Acids 48(3):801–810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-2128-5
Morrison BA, Shain DH (2008) An AMP nucleosidase gene knockout in Escherichia coli elevates intracellular ATP levels and increases cold tolerance. Biol Lett 4(1):53–56. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2007.0432
Nandineni MR, Gowrishankar J (2004) Evidence for an arginine exporter encoded by yggA (argO) that is regulated by the LysR-type transcriptional regulator ArgP in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 186(11):3539–3546. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.186.11.3539-3546.2004
Park SH, Kim HU, Kim TY, Park JS, Kim SS, Lee SY (2014) Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for L-arginine production. Nat Commun 5:4618. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5618
Peeters E, Nguyen Le Minh P, Foulquie-Moreno M, Charlier D (2009) Competitive activation of the Escherichia coli argO gene coding for an arginine exporter by the transcriptional regulators Lrp and ArgP. Mol Microbiol 74(6):1513–1526. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06950.x
Sander T, Wang CY, Glatter T, Link H (2019) Crispri-based downregulation of transcriptional feedback improves growth and metabolism of arginine overproducing E. coli. ACS Synth Biol 8(9):1983–1990. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.9b00183
Sauer U, Canonaco F, Heri S, Perrenoud A, Fischer E (2004) The soluble and membrane-bound transhydrogenases UdhA and PntAB have divergent functions in NADPH metabolism of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 279(8):6613–6619. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M311657200
Wade M (2015) High-throughput silencing using the crispr-cas9 system: a revie of the benefits and challenges. J Biomol Screen 20(8):1027–1039. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087057115587916
Wang M, Chen B, Fang Y, Tan T (2017) Cofactor engineering for more efficient production of chemicals and biofuels. Biotechnol Adv 35(8):1032–1039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2017.09.008
Wang Q, Jiang A, Tang J, Gao H, Zhang X, Yang T, Xu Z, Xu M, Rao Z (2021) Enhanced production of L-arginine by improving carbamoyl phosphate supply in metabolically engineered Corynebacterium crenatum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105(8):3265–3276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11242-w
Wang HD, Xu JZ, Zhang WG (2022) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for efficient production of L-arginine. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 106(17):5603–5613. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-12109-4
Xu M, Rao Z, Xu H, Lan C, Dou W, Zhang X, Xu H, Jin J, Xu Z (2011) Enhanced production of L-arginine by expression of Vitreoscilla hemoglobin using a novel expression system in Corynebacterium crenatum. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 163(6):707–719. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-010-9076-z
Xu M, Rao Z, Yang J, Dou W, Xu Z (2013) The effect of a LYSE exporter overexpression on L-arginine production in Corynebacterium crenatum. Curr Microbiol 67(3):271–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-013-0358-x
Xu JZ, Yang HK, Zhang WG (2018) NADPH metabolism: a survey of its theoretical characteristics and manipulation strategies in amino acid biosynthesis. Crit Rev Biotechnol 38(7):1061–1076. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2018.1437387
Xu M, Li J, Shu Q, Tang M, Zhang X, Yang T, Xu Z, Rao Z (2019) Enhancement of L-arginine production by increasing ammonium uptake in an AmtR-deficient Corynebacterium crenatum mutant. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 46(8):1155–1166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-019-02204-3
Zhang X, Lai L, Xu G, Zhang X, Shi J, Koffas MAG, Xu Z (2019) Rewiring the central metabolic pathway for high-yield l-serine production in Corynebacterium glutamicum by using glucose. Biotechnol J 14(6):e1800497. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201800497
Zhou J, Liu L, Shi Z, Du G, Chen J (2009) ATP in current biotechnology: regulation, applications and perspectives. Biotechnol Adv 27(1):94–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.10.005
Funding
We acknowledge the financial support from the Class I project of independent innovation of agricultural science and technology in Jiangsu Province (grant numbers CX (22) 1012) and the National Key R&D Program “Green Biological Manufacturing” key special project, the “Important Amino Acid Industrial Strain System Transformation and Industrial Demonstration” project (grant numbers 2021YFC2100900).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H W and J X conceived the experiments. H W and W Z designed and performed the experiments and analyzed the data. H W wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Informed consent
The content of this study was obtained with the informed consent of all participants, whose identified information is included in this article.
Ethics approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1:
Figure S1 and Tables S1 and S2 (PDF 227 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, HD., Xu, JZ. & Zhang, WG. Reduction of acetate synthesis, enhanced arginine export, and supply of precursors, cofactors, and energy for improved synthesis of L-arginine by Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 3593–3603 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12532-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12532-1