Abstract
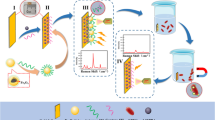
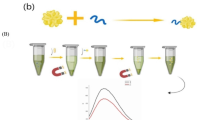
Simple and visual quantitative detection of foodborne pathogens can effectively reduce the outbreaks of foodborne diseases. Herein, we developed a simple and sensitive quantum dot (QD)-based paper device for visual and quantitative detection of Escherichia coli (E. coli) O157:H7 based on immunomagnetic separation and nanoparticle dissolution-triggered signal amplification. In this study, E. coli O157:H7 was magnetically separated and labeled with silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), and the AgNP labels can be converted into millions of Ag ions, which subsequently quench the fluorescence of QDs in the paper strip, which along with the readout can be visualized and quantified by the change in length of fluorescent quenched band. Owing to the high capture efficiency and effective signal amplification, as low as 500 cfu mL−1 of E. coli O157:H7 could be easily detected by naked eyes. Furthermore, this novel platform was successfully applied to detect E. coli O157:H7 in spiked milk samples with good accuracy, indicating its potential in the detection of foodborne pathogens in real samples.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ripp S, Jegier P, Johnson C, Brigati J, Sayler G. Bacteriophage-amplified bioluminescent sensing of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2008;391:507–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-007-1812-z.
Nishikawa K, Matsuoka K, Kita E, Okabe N, Mizuguchi M, Hino K, et al. A therapeutic agent with oriented carbohydrates for treatment of infections by Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157:H7. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2002;99(11):7669–74. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.112058999.
Xu M, Wang R, Li Y. Electrochemical biosensors for rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Talanta. 2017;162:511–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.10.050.
Qiao Z, Lei C, Fu Y, Li Y. An antimicrobial peptide-based colorimetric bioassay for rapid and sensitive detection of E. coli O157:H7. RSC Adv. 2017;7(26):15769–75. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA28362D.
Arora P, Sindhu A, Kaur H, Dilbaghi N, Chaudhury A. An overview of transducers as platform for the rapid detection of foodborne pathogens. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013;97(5):1829–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4692-5.
Riu J, Giussani B. Electrochemical biosensors for the detection of pathogenic bacteria in food. TrAC-Trends Anal Chem. 2020;126:115863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.115863.
Fu K, Zheng Y, Li J, Liu Y, Pang B, Song X, et al. Colorimetric immunoassay for rapid detection of Vibrio parahemolyticus based on Mn2+ mediates the assembly of gold nanoparticles. J Agric Food Chem. 2018;66(36):9516–21. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b02494.
Yang L, Deng W, Cheng C, Tan Y, Xie Q, Yao S. Fluorescent immunoassay for the detection of pathogenic bacteria at the single-cell level using carbon dots-encapsulated breakable organosilica nanocapsule as labels. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(4):3441–8. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b18714.
Wang Z, Cai R, Gao Z, Yuan Y, Yue T. Immunomagnetic separation: an effective pretreatment technology for isolation and enrichment in food microorganisms detection. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2020;19(6):3802–24. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12656.
Park JY, Park K, Ok G, Chang HJ, Park TJ, Choi SW, et al. Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 using automated immunomagnetic separation and enzyme-based colorimetric assay. Sensors. 2020;20(5):1395. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051395.
Liu Y, Zhao C, Song X, Xu K, Wang J, Li J. Colorimetric immunoassay for rapid detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microchim Acta. 2017;184(12):4785–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2523-6.
Mobed A, Baradaran B, Guardia M, Agazadeh M, Hasanzadeh M, Rezaee MA, et al. Advances in detection of fastidious bacteria: from microscopic observation to molecular biosensors. TrAC-Trends Anal Chem. 2019;113:157–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.02.012.
Fu LM, Wang Y-N. Detection methods and applications of microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. TrAC-Trends Anal Chem. 2018;107:196–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.08.018.
Huang JY, Lin HT, Chen TH, Chen CA, Chang HT, Chen CF. Signal amplified gold nanoparticles for cancer diagnosis on paper-based analytical devices. ACS Sens. 2018;3(1):174–82. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.7b00823.
Ozer T, McMahon C, Henry CS. Advances in paper-based analytical devices. Annu Rev Anal Chem. 2020;13(1):85–109. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-anchem-061318-114845.
Adkins JA, Boehle K, Friend C, Chamberlain B, Bisha B, Henry CS. Colorimetric and electrochemical bacteria detection using printed paper- and transparency-based analytic devices. Anal Chem. 2017;89(6):3613–21. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b05009.
Jokerst JC, Adkins JA, Bisha B, Mentele MM, Goodridge LD, Henry CS. Development of a paper-based analytical device for colorimetric detection of select foodborne pathogens. Anal Chem. 2012;84(6):2900–7. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac203466y.
Sun L, Jiang Y, Pan R, Li M, Wang R, Chen S, et al. A novel, simple and low-cost paper-based analytical device for colorimetric detection of Cronobacter spp. Anal Chim Acta. 2018;1036:80–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.05.061.
Ilhan H, Guven B, Dogan U, Torul H, Evran S, Çetin D, et al. The coupling of immunomagnetic enrichment of bacteria with paper-based platform. Talanta. 2019;201:245–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.04.017.
Srisa-Art M, Boehle KE, Geiss BJ, Henry CS. Highly sensitive detection of Salmonella typhimurium using a colorimetric paper-based analytical device coupled with immunomagnetic separation. Anal Chem. 2018;90(1):1035–43. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b04628.
Schaumburg F, Carrell CS, Henry CS. Rapid bacteria detection at low concentrations using sequential immunomagnetic separation and paper-based isotachophoresis. Anal Chem. 2019;91(15):9623–30. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b01002.
Markwalter CF, Kantor AG, Moore CP, Richardson KA, Wright DW. Inorganic complexes and metal-based nanomaterials for infectious disease diagnostics. Chem Rev. 2019;119(2):1456–518. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00136.
Zhao LJ, Yu RJ, Ma W, Han HX, Tian H, Qian RC, et al. Sensitive detection of protein biomarkers using silver nanoparticles enhanced immunofluorescence assay. Theranostics. 2017;7(4):876–83. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.17575.
Gibson LE, Wright DW. Sensitive method for biomolecule detection utilizing signal amplification with porphyrin nanoparticles. Anal Chem. 2016;88(11):5928–33. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b00855.
Tian T, Li J, Song Y, Zhou L, Zhu Z, Yang CJ. Distance-based microfluidic quantitative detection methods for point-of-care testing. Lab Chip. 2016;16(7):1139–51. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5LC01562F.
Alsaeed B, Mansour FR. Distance-based paper microfluidics; principle, technical aspects and applications. Microchem J. 2020;155:104664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.104664.
Povedano E, Valverde A, Montiel VR, Pedrero M, Yáñez-Sedeño P, Barderas R, et al. Rapid electrochemical assessment of tumor suppressor gene methylations in raw human serum and tumor cells and tissues using immunomagnetic beads and selective DNA hybridization. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2018;57(27):8194–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201804339.
Lee PC, Meisel D. Adsorption and surface-enhanced Raman of dyes on silver and gold sols. J Phys Chem. 1982;86(17):3391–5. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100214a025.
Szymanski MS, Porter RA. Preparation and quality control of silver nanoparticle-antibody conjugate for use in electrochemical immunoassays. J Immunol Methods. 2013;387(1):262–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2012.11.003.
Lin Z, Lv S, Zhang K, Tang D. Optical transformation of a CdTe quantum dot-based paper sensor for a visual fluorescence immunoassay induced by dissolved silver ions. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5(4):826–33. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TB03042D.
Yoon SJ, Nam YS, Lee HJ, Lee Y, Lee KB. Colorimetric probe for Ni2+ based on shape transformation of triangular silver nanoprisms upon H2O2 etching. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2019;300:127045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127045.
Yoo SM, Lee SY. Optical biosensors for the detection of pathogenic microorganisms. Trends Biotechnol. 2016;34(1):7–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2015.09.012.
Välimaa AL, Tilsala-Timisjärvi A, Virtanen E. Rapid detection and identification methods for Listeria monocytogenes in the food chain-a review. Food Control. 2015;55:103–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.02.037.
Chen Q, Huang F, Cai G, Wang M, Lin J. An optical biosensor using immunomagnetic separation, urease catalysis and pH indication for rapid and sensitive detection of Listeria monocytogenes. Sensors Actuator B-Chem. 2018;258:447–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.11.087.
Yu J, Su J, Zhang J, Wei X, Guo A. CdTe/CdS quantum dot-labeled fluorescent immunochromatography test strips for rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. RSC Adv. 2017;7(29):17819–23. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra00821j.
Morales-Narvaez E, Naghdi T, Zor E, Merkoci A. Photo luminescent lateral-flow immunoassay revealed by graphene oxide: highly sensitive paper-based pathogen detection. Anal Chem. 2015;87(16):8573–7. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b02383.
Hu J, Jiang Y-Z, Tang M, Wu L-L, Xie H-Y, Zhang Z-L, et al. Colorimetric-fluorescent-magnetic nanosphere-based multimodal assay platform for Salmonella detection. Anal Chem. 2019;91(1):1178–84. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b05154.
Qiao ZH, Lei CY, Fu YC, Li YB. Rapid and sensitive detection of E. coli O157:H7 based on antimicrobial peptide functionalized magnetic nanoparticles and urease-catalyzed signal amplification. Anal Methods. 2017;9:5204–10. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7AY01643C.
Funding
This work was supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. LQ20C200008) and Ningbo civil Public Welfare Technology Application Research Project (Grant No. 202002N3064).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1.20 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiao, Z., Cai, Q., Fu, Y. et al. Visual and quantitative detection of E. coli O157:H7 by coupling immunomagnetic separation and quantum dot-based paper strip. Anal Bioanal Chem 413, 4417–4426 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03395-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03395-4