Abstract
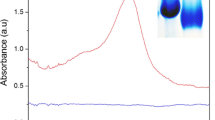
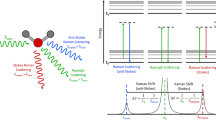
Bisphenol A (BPA) is one of the endocrine-disrupting chemicals which might cause reproductive and endocrine system diseases, and poses a serious threat to the ecosystem and human health. This paper reports an ultrasensitive sensor for trace BPA detection employing fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) between modified upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) and tetramethylrhodamine. To circumvent the problems of low luminous efficiency of FRET and low sensitivity of sensor, the upconversion nanoparticles with very strong fluorescence efficiency were prepared and quantitatively modified. Results showed that the concentrations of amino groups and streptavidin were 43 nmol/mg and 6.12 μg/mg on the surface of the UCNPs, respectively. Under the optimal detection conditions, the peak intensity of UCNPs at 547 nm was linear with the logarithm of the BPA concentration with the detection limit of 0.05 ng/mL. Without complicated pre-processing, the recoveries were in general between 91.0 and 115.0% in tap water, river water, and disposable paper cup water. Therefore, the proposed sensor is suitable for effective sensing of trace BPA in water samples.

ᅟ







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tang JF, Zhang Y, Gou J, Ma ZL, Li GN, Man YH, et al. Sol-gel prepared Yb3+/Er3+ co-doped RE2O3 (RE = La, Gd, Lu) nanocrystals: structural characterization and temperature-dependent upconversion behavior. J Alloys Compd. 2018;740:229–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.01.050.
Du P, Luo LH, Li WP, Yue QY, Chen HB. Optical temperature sensor based on upconversion emission in Er-doped ferroelectric 0.5Ba(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O-3-0.5(Ba0.7Ca0.3)TiO3 ceramic. Appl Phys Lett. 2014;104(15). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4871378.
Du P, Luo LH, Yu JS. Energy back transfer induced color controllable upconversion emissions in La2MoO6:Er3+/Yb3+ nanocrystals for versatile applications. Part Part Syst Charact. 2018;35(3). https://doi.org/10.1002/ppsc.201700416.
Watabe Y, Kondo T, Morita M, Tanaka N, Haginaka J, Hosoya K. Determination of bisphenol A in environmental water at ultra-low level by high-performance liquid chromatography with an effective on-line pretreatment device. J Chromatogr A. 2004;1032(1–2):45–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2003.11.079.
Becerra V, Odermatt J. Detection and quantification of traces of bisphenol A and bisphenol S in paper samples using analytical pyrolysis-GC/MS. Analyst. 2012;137(9):2250–9. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2an15961a.
Motoyama A, Suzuki A, Shirota O, Namba R. Direct determination of bisphenol A and nonylphenol in river water by column-switching semi-microcolumn liquid chromatography/electrospray mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1999;13(21):2204–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-0231(19991115)13:21<2204::aid-rcm776>3.0.co;2-9.
Zhou X, Kramer JP, Calafat AM, Ye X. Automated on-line column-switching high performance liquid chromatography isotope dilution tandem mass spectrometry method for the quantification of bisphenol A, bisphenol F, bisphenol S, and 11 other phenols in urine. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014;944:152–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2013.11.009.
Miao W, Wei B, Yang R, Wu C, Lou D, Jiang W, et al. Highly specific and sensitive detection of bisphenol A in water samples using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay employing a novel synthetic antigen. New J Chem. 2014;38(2):669–75. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NJ01094E.
Moreno MJ, D'Arienzo P, Manclus JJ, Montoya A. Development of monoclonal antibody-based immunoassays for the analysis of bisphenol A in canned vegetables. J Environ Sci Health B. 2011;46(6):509–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2011.583871.
Zhao MP, Li YZ, Guo ZQ, Zhang XX, Chang WB. A new competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for determination of estrogenic bisphenols. Talanta. 2002;57(6):1205–10.
Liang X, Wang H, Wang H, Pei G. Colorimetric detection of bisphenol A using Au-Fe alloy nanoparticle aggregation. Anal Methods. 2015;7(9):3952–7. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5AY00090D.
Ellington AD, Szostak JW. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature. 1990;346(6287):818–22. https://doi.org/10.1038/346818a0.
Tuerk C, Gold L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science (New York, NY). 1990;249(4968):505–10.
Tombelli S, Minunni M, Mascini M. Analytical applications of aptamers. Biosens Bioelectron. 2005;20(12):2424–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2004.11.006.
Xing H, Hwang K, Li J, Torabi S-F, Lu Y. DNA aptamer technology for personalized medicine. Curr Opin Chem Eng. 2014;4:79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coche.2014.01.007.
Guo X, Wu S, Duan N, Wang Z. Mn(2+)-doped NaYF4:Yb/Er upconversion nanoparticle-based electrochemiluminescent aptasensor for bisphenol A. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016;408(14):3823–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9470-7.
Jo M, Ahn J-Y, Lee J, Lee S, Hong SW, Yoo J-W, et al. Development of single-stranded DNA aptamers for specific bisphenol A detection. Oligonucleotides. 2011;21(2):85–91. https://doi.org/10.1089/oli.2010.0267.
Pan D, Gu Y, Lan H, Sun Y, Gao H. Functional graphene-gold nano-composite fabricated electrochemical biosensor for direct and rapid detection of bisphenol A. Anal Chim Acta. 2015;853:297–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2014.11.004.
Xue F, Wu J, Chu H, Mei Z, Ye Y, Liu J, et al. Electrochemical aptasensor for the determination of bisphenol A in drinking water. Microchim Acta. 2013;180(1):109–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-012-0909-z.
Yildirim N, Long F, He M, Shi H-C, Gu AZ. A portable optic fiber aptasensor for sensitive, specific and rapid detection of bisphenol-A in water samples. Environ Sci Process Impacts. 2014;16(6):1379–86. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4EM00046C.
Yu P, Liu Y, Zhang X, Zhou J, Xiong E, Li X, et al. A novel electrochemical aptasensor for bisphenol A assay based on triple-signaling strategy. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;79:22–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.12.007.
Zhou L, Wang J, Li D, Li Y. An electrochemical aptasensor based on gold nanoparticles dotted graphene modified glassy carbon electrode for label-free detection of bisphenol A in milk samples. Food Chem. 2014;162:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.04.058.
Zhong W. Nanomaterials in fluorescence-based biosensing. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2009;394(1):47–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-2643-x.
Zhu Y, Cai Y, Xu L, Zheng L, Wang L, Qi B, et al. Building an aptamer/graphene oxide FRET biosensor for one-step detection of bisphenol A. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(14):7492–6. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b00199.
Kuang R, Kuang X, Pan S, Zheng X, Duan J, Duan Y. Synthesis of cysteamine-coated CdTe quantum dots for the detection of bisphenol A. Microchim Acta. 2010;169(1–2):109–15.
Li Y, Xu J, Wang L, Huang Y, Guo J, Cao X, et al. Aptamer-based fluorescent detection of bisphenol A using nonconjugated gold nanoparticles and CdTe quantum dots. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2016;222:815–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.08.130.
Li DY, Wang YX, Zhang XR, Yang K, Liu L, Song YL. Optical temperature sensor through infrared excited blue upconversion emission in Tm3+/Yb3+ codoped Y2O3. Opt Commun. 2012;285(7):1925–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2011.12.075.
Peng J, Gao W, Gupta BK, Liu Z, Romero-Aburto R, Ge L, et al. Graphene quantum dots derived from carbon fibers. Nano Lett. 2012;12(2):844–9. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl2038979.
Wu S, Duan N, Zhu C, Ma X, Wang M, Wang Z. Magnetic nanobead-based immunoassay for the simultaneous detection of aflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A using upconversion nanoparticles as multicolor labels. Biosens Bioelectron. 2011;30(1):35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2011.08.023.
Yin M, Wu L, Li Z, Ren J, Qu X. Facile in situ fabrication of graphene-upconversion hybrid materials with amplified electrogenerated chemiluminescence. Nanoscale. 2012;4(2):400–4. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1NR11393C.
Wang L, Yan R, Huo Z, Wang L, Zeng J, Bao J, et al. Fluorescence resonant energy transfer biosensor based on upconversion-luminescent nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed Eng. 2005;44(37):6054–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200501907.
Zhang ZLY. An efficient and user-friendly method for the synthesis of hexagonal-phase NaYF4:Yb, Er/Tm nanocrystals with controllable shape and upconversion fluorescence. Nanotechnology. 2008. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/19/34/345606.
Stalder K, Stober W. Haemolytic activity of suspensions of different silica modifications and inert dusts. Nature. 1965;207(4999):874–5.
Wu S, Duan N, Ma X, Xia Y, Wang H, Wang Z, et al. Multiplexed fluorescence resonance energy transfer aptasensor between upconversion nanoparticles and graphene oxide for the simultaneous determination of mycotoxins. Anal Chem. 2012;84(14):6263–70. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac301534w.
Chu C-H, Sarangadharan I, Regmi A, Chen Y-W, Hsu C-P, Chang W-H, et al. Beyond the Debye length in high ionic strength solution: direct protein detection with field-effect transistors (FETs) in human serum. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):5256. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-05426-6.
Stern E, Vacic A, Rajan NK, Criscione JM, Park J, Ilic BR, et al. Label-free biomarker detection from whole blood. Nat Nanotechnol. 2009;5:138. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2009.353 https://www.nature.com/articles/nnano.2009.353#supplementary-information.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 21477162, 81602896, AWS15J006); the Tianjin Research Program of Application Foundation and Advanced Technology (Grant No. 15JCYBJC51200); the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2017YFF0104903) and Natural Science Fund of Tianjin City (Grant No. 17JCQNJC12500).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 5869 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Bai, J., Ren, S. et al. An ultrasensitive sensor based on quantitatively modified upconversion particles for trace bisphenol A detection. Anal Bioanal Chem 411, 171–179 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1425-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1425-8