Abstract
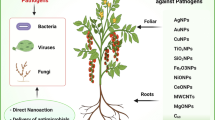
Nanotechnology has been acknowledged recently for its diversified use in the field of science including agriculture, food industry, medicine, and cosmetics. Environment and earth are being constantly exposed to nanomaterials because they are fabricated to be utilized in agribusiness, food, pharmaceuticals, personal care items as well as in biotechnology. Nanoparticle–microbe interaction performs a pivotal role in treatment of various diseases as in case of antimicrobial agents. The potential implementations of nanomaterials are being extensively researched in the field of agriculture, not only as therapeutic options to prevent phytopathogen growth in host plants, but also for early pathogenic symptoms detections and eliciting immune responses. Bacteria, fungi, virus, and other virulent pathogens through their efficient survival strategies and overcoming phyto-defenses confer to overall deterioration of food-crop produce that may sum up to 10–40%. To overcome such challenging situations, there has been constant development and application of engineered agro-nanomaterials. These may affect plant–microbe interactions in different ways. The inhibitory potential of nanoparticles against different microbial growth mainly involves release and interaction of metal ions with cell components that occur through different pathways including reactive oxygen species production, formation of pores in cell-membranes, cell wall and DNA damage, and cell-cycle arrest. The article deals with different plant pathogens, their mechanisms of phyto-pathogenesis followed by detailed responses of nanoparticle interactions with different microbes and their role in phytopathogen suppression.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah Y, Yang M, Zhang M et al (2019) Plant growth promotion and suppression of bacterial leaf blight in rice by Paenibacillus polymyxa Sx3. Lett Appl Microbiol 68:423–429
Abdulkhair WM, Alghuthaymi MA (2016a) Plant pathogens. In: Rigobelo EC (ed) Plant growth. IntechOpen, London
Abdulkhair WM, Alghuthaymi MA (2016b) Plant pathogens. In: Plant growth. IntechOpen, London, p 49
Abdullah AS, Moffat CS, Lopez-Ruiz FJ et al (2017) Host–multi-pathogen warfare: pathogen interactions in co-infected plants. Front Plant Sci 8:1806
Abramovitch RB, Kim YJ, Chen S et al (2003) Pseudomonas type III effector AvrPtoB induces plant disease susceptibility by inhibition of host programmed cell death. EMBO J 22:60–69
Adak T, Kumar J, Dey D, Shakil NA, Walia S (2012) Residue and bio-efficacy evaluation of controlled release formulations of imidacloprid against pests in soybean (Glycine max). J Environ Sci Health B 47:226–231
Agrios GN (1997) Plant pathology, 4th edn. Academic, San Diego
Aleksandrowicz-Trzcińska M, Szaniawski A, Olchowik J, Drozdowski S (2018) Effects of copper and silver nanoparticles on growth of selected species of pathogenic and wood-decay fungi in vitro. For Chron 94:109–116
Ali SH, Ali SA (2019) Nanotechnology is the potential cause of phytotoxicity. J Biomater Dent 3:1–6
Allesen-Holm M, Barken KB, Yang L et al (2006) A characterization of DNA release in Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures and biofilms. Mol Microbiol 59:1114–1128
Amari K, Vazquez F, Heinlein M (2012) Manipulation of plant host susceptibility: an emerging role for viral movement proteins? Front Plant 3:10
An SQ, Allan JH, McCarthy Y et al (2014a) The PAS domain-containing histidine kinase RpfS is a second sensor for the diffusible signal factor of Xanthomonas campestris. Mol Microbiol 92:586–597
An SQ, Caly DL, McCarthy Y et al (2014b) Novel cyclic di-GMP effectors of the YajQ protein family control bacterial virulence. PLoS Pathog 10:e1004429
Aparna G, Chatterjee A, Sonti RV et al (2009) A cell wall-degrading esterase of Xanthomonas oryzae requires a unique substrate recognition module for pathogenesis on rice. Plant Cell 21:1860–1873
Arrebola E, Cazorla FM, Perez-Garcia A et al (2011) Chemical and metabolic aspects of antimetabolite toxins produced by Pseudomonas syringae pathovars. Toxins 3:1089–1110
Aslam SN, Newman MA, Erbs G et al (2008) Bacterial polysaccharides suppress induced innate immunity by calcium chelation. Curr Biol 18:1078–1083
Asselin JAE, Lin J, Perez-Quintero AL et al (2015) Perturbation of maize phenylpropanoid metabolism by an AvrE family type III effector from Pantoea stewartii. Plant Physiol 167:1117–1135
Baker B, Zambryski P, Staskawicz B, Dinesh-Kumar SP (1997) Signaling in plant-microbe interactions. Science 276:726–733
Balasubramaniam M, Kim BS, Hutchens-Williams HM et al (2014) The photosystem II oxygen-evolving complex protein PsbP interacts with the coat protein of Alfalfa mosaic virus and inhibits virus replication. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 27:1107–1118
Bandyopadhyay S, Peralta-Videa JR et al (2012) Comparative toxicity assessment of CeO2 and ZnO nanoparticles towards Sinorhizobium meliloti, a symbiotic alfalfa associated bacterium: Use of advanced microscopic and spectroscopic techniques. J Hazard Mater 241:379–386
Banik S, Luque AP (2017) In vitro effects of copper nanoparticles on plant pathogens, beneficial microbes and crop plants. Span J Agric Res 15:23
Barber CE, Tang JL, Feng JX et al (1997) A novel regulatory system required for pathogenicity of Xanthomonas campestris is mediated by a small diffusible signal molecule. Mol Microbiol 24:555–566
Bartsev AV, Deakin WJ, Boukli NM et al (2004) NopL, an effector protein of Rhizobium sp. NGR234, thwarts activation of plant defense reactions. Plant Physiol 134:871–879
Bender CL, Alarcon-Chaidez F, Gross DC (1999) Pseudomonas syringae phytotoxins: mode of action, regulation, and biosynthesis by peptide and polyketide synthetases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:266–292
Bhargava P, Kumar A, Kumar S, Azad CS (2018) Impact of fungicides and nanoparticles on Ustilaginoidea virens causing false smut disease of rice. J Pharmacogn Phytochem 7:1541–1544
Bhatty M, Laverde GJA, Christie PJ (2013) The expanding bacterial type IV secretion lexicon. Res Microbiol 164:620–639
Bielmyer-Fraser GK, Jarvis TA, Lenihan HS, Miller RJ (2014) Cellular partitioning of nanoparticulate versus dissolved metals in marine phytoplankton. Environ Sci Technol 48:13443–13450
Block A, Guo M, Li G et al (2010) The Pseudomonas syringae type III effector HopG1 targets mitochondria, alters plant development and suppresses plant innate immunity. Cell Microbiol 12:318–330
Bogdanove AJ, Schornack S, Lahaye T (2010) TAL effectors: finding plant genes for disease and defense. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13:394–401
Bouarab K, Melton R, Peart J et al (2002) A saponin-detoxifying enzyme mediates suppression of plant defences. Nature 418:889–892
Boxi SS, Mukherjee K, Paria S (2016) Ag doped hollow TiO2 nanoparticles as an effective green fungicide against Fusarium solani and Venturia inaequalis phytopathogens. Nanotechnology 27:085103
Bramhanwade K, Shende S, Bonde S, Gade A, Rai M (2016) Fungicidal activity of Cu nanoparticles against Fusarium causing crop diseases. Environ Chem Lett 14:229–235
Bretz JR, Mock NM, Charity JC et al (2003) A translocated protein tyrosine phosphatase of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 modulates plant defence response to infection. Mol Microbiol 49:389–400
Brown I, Mansfield J, Bonas U (1995) hrp genes in Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria determine ability to suppress papilla deposition in pepper mesophyll cells. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 8:825–836
Burch AY, Shimada BK, Mullin SW et al (2012) Pseudomonas syringae coordinates production of a motility enabling surfactant with flagellar assembly. J Bacteriol 194:1287–1298
Buttner D, Bonas U (2010) Regulation and secretion of Xanthomonas virulence factors. FEMS Microbiol Rev 34:107–133
Buttner D, Lorenz C, Weber E et al (2006) Targeting of two effector protein classes to the type III secretion system by a HpaC- and HpaB-dependent protein complex from Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria. Mol Microbiol 59:513–527
Chai H, Yao J, Sun J et al (2015) The effect of metal oxide nanoparticles on functional bacteria and metabolic profiles in agricultural soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 94:490–495
Chandra S, Chakraborty N, Dasgupta A et al (2015) Chitosan nanoparticles: a positive modulator of innate immune responses in plants. Sci Rep 5:15195
Chandra S, Chakraborty N, Panda K, Acharya K (2017) Chitosan induced immunity in Camellia sinensis (L.) O, Kuntze against blister blight disease is mediated by nitric-oxide. Plant Physiol Biochem 115:298–307
Chao SHL, Choi HS (2005) Method for providing enhanced photosynthesis. S Korea Bull 11:1–34
Chartuprayoon N, Rheem Y, Ng JC et al (2013) Polypyrrole nanoribbon based chemiresistive immunosensors for viral plant pathogen detection. Anal Methods 5:3497–3502
Chatterjee S, Almeida RP, Lindow S (2008a) Living in two worlds: the plant and insect lifestyles of Xylella fastidiosa. Annu Rev Phytopathol 46:243–271
Chatterjee S, Wistrom C, Lindow SE (2008b) A cell–cell signaling sensor is required for virulence and insect transmission of Xylella fastidiosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:2670–2675
Chavan S, Nadanathangam V (2019) Effects of nanoparticles on plant growth-promoting bacteria in Indian agricultural soil. Agronomy 9:140
Chellappan P, Vanitharani R, Fauquet CM (2005) MicroRNA-binding viral protein interferes with Arabidopsis development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:10381–10386
Chen J, Watanabe Y, Sako N et al (1996) Mapping of host range restriction of the Rakkyo strain of tobacco mosaic virus in Nicotiana tabacum cv. Bright yellow. Virology 226:198–204
Chen J, Wang X, Han H (2013) A new function of graphene oxide emerges: inactivating phytopathogenic bacterium Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. J Nanopart Res 15:1658
Chen J, Peng H, Wang X et al (2014) Graphene oxide exhibits broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against bacterial phytopathogens and fungal conidia by intertwining and membrane perturbation. Nanoscale 6:1879–1889
Chen J, Mao S, Xu Z, Ding W (2019) Various antibacterial mechanisms of biosynthesized copper oxide nanoparticles against soilborne Ralstonia solanacearum. RSC Adv 9:3788–3799
Chhipa H (2017) Nanofertilizers and nanopesticides for agriculture. Environ Chem Lett 15:15–22
Chiang CH, Lee CY, Wang CH et al (2007) Genetic analysis of an attenuated Papaya ringspot virus strain applied for cross-protection. Eur J Plant Pathol 118:333–348
Chikte RG, Paknikar KM, Rajwade JM et al (2019) Nanomaterials for the control of bacterial blight disease in pomegranate: quo vadis? Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103:4605–4621
Chin KH, Lee YC, Tu ZL et al (2010) The cAMP receptor-like protein CLP is a novel c-di-GMP receptor linking cell–cell signaling to virulence gene expression in Xanthomonas campestris. J Mol Biol 396:646–662
Choudhary RC, Kumaraswamy RV, Kumari S et al (2017) Cu-chitosan nanoparticle boost defense responses and plant growth in maize (Zea mays L.). Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08571-0
Chu M, Desvoyes B, Turina M et al (2000) Genetic dissection of tomato bushy stunt virus p19-protein-mediated host-dependent symptom induction and systemic invasion. Virology 266:79–87
Chuan L, He P et al (2013) Establishing a scientific basis for fertilizer recommendations for wheat in China: yield response and agronomic efficiency. Field Crop Res 140:1–8
Cramer HH (1967) Plant protection and crop production. Pflanzenschutz-Nachr, Leverkusen, p 20
Cui F, Wu S, Sun W et al (2013) The Pseudomonas syringae type III effector AvrRpt2 promotes pathogen virulence via stimulating Arabidopsis auxin/indole acetic acid protein turnover. Plant Physiol 162:1018–1029
Dapkekar A, Deshpande P, Oak MD et al (2018) Zinc use efficiency is enhanced in wheat through nanofertilization. Sci Rep 8:6832
Dawson WO, Bubrick P (1988) Modification of the tobacco mosaic virus coat protein gene affecting replication movement and symptomatology. Phytopathology 78:783–789
De Filpo G, Palermo AM, Rachiele F, Nicoletta FP (2013) Preventing fungal growth in wood by titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 85:217–222
De la Rosa-García D, Susana C, Martínez-Torres P et al (2018) Antifungal activity of ZnO and MgO nanomaterials and their mixtures against Colletotrichum gloeosporioides strains from tropical Fruit. J Nanomater 2018:3498527
De la Torre RR, Servin A, Hawthrone J et al (2015) Terrestrial trophic transfer of bulk and nanoparticle La2O3 does not depend on particle size. Environ Sci Technol 49:11866–11874
Dean R, Van Kan JA, Pretorius ZA et al (2012) The top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Mol Plant Pathol 13:414–430
Dejean G, Blanvillain-Baufume S, Boulanger A et al (2013) The xylan utilization system of the plant pathogen Xanthomonas campestris pv campestris controls epiphytic life and reveals common features with oligotrophic bacteria and animal gut symbionts. New Phytol 198:899–915
Delmotte N, Knief C, Chaffron S et al (2009) Community proteogenomics reveals insights into the physiology of phyllosphere bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:16428–16433
Derbalah AS, Elkot GAE, Hamza AM (2012) Laboratory evaluation of botanical extracts microbial culture filtrates and silver nanoparticles against Botrytis cinerea. Ann Microbiol 62:1331–1337
Desbiez C, Gal-On A, Girard M et al (2003) Increase in Zucchini yellow mosaic virus symptom severity in tolerant zucchini cultivars is related to a point mutation in P3 protein and is associated with a loss of relative fitness on susceptible plants. Phytopathology 93:1478–1484
Dimkpa CO, McLean JE, Britt DW, Anderson AJ (2013a) Antifungal activity of ZnO nanoparticles and their interactive effect with a biocontrol bacterium on growth antagonism of the plant pathogen Fusarium graminearum. Biometals 26:913–924
Dimkpa CO, McLean JE, Martineau N et al (2013b) Silver nanoparticles disrupt wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) growth in a sand matrix. Environ Sci Technol 47:1082–1090
Dizaj SM, Lotfipour F, Barzegar-Jalali M et al (2014) Antimicrobial activity of the metals and metal oxide nanoparticles. Mater Sci Eng C 44:278–284
Djonovic S, Urbach JM, Drenkard E et al (2013) Trehalose biosynthesis promotes Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenicity in plants. PLoS Pathog 9:e1003217
Doke N (1975) Prevention of the hypersensitive reaction of potato cells to infection with an incompatible race of Phytophthora infestans by constituents of the zoospores. Physiol Plant Pathol 7:1–7
Dollet M (1984) Plant diseases caused by flagellate protozoa (Phytomonas). Annu Rev Phytopathol 22:115–132
Du Z, Chen A, Chen W et al (2014) Nuclear-cytoplasmic partitioning of cucumber mosaic virus protein 2b determines the balance between its roles as a virulence determinant and an RNA-silencing suppressor. J Virol 88:5228–5241
Dunger G, Relling VM, Tondo ML et al (2007) Xanthan is not essential for pathogenicity in citrus canker but contributes to Xanthomonas epiphytic survival. Arch Microbiol 188:127–135
Dunoyer P, Lecellier CH, Parizotto EA et al (2004) Probing the microRNA and small Interfering RNA pathways with virus-encoded suppressors of RNA silencing. Plant Cell 16:1235–1250
Elbeshehy EKF, Elazzazy AM, Aggelis G (2015) Silver nanoparticles synthesis mediated by new isolates of Bacillus spp.; nanoparticle characterization and their activity against bean yellow mosaic virus and human pathogens. Front Microbiol 6:453
Ellingboe AH (1968) Inoculum production and infection by foliage pathogens. Annu Rev Phytopathol 6:317–330
Elmer WH, White JC (2016) The use of metallic oxide nanoparticles to enhance growth of tomatoes and eggplants in disease infested soil or soilless medium. Environ Sci Nano 3(5):1072–1079
Elmer W, White JC (2018) The future of nanotechnology in plant pathology. Annu Rev Phytopathol 56:111–133
Espinosa A, Guo M, Tam VC et al (2003) The Pseudomonas syringae type III-secreted protein HopPtoD2 possesses protein tyrosine phosphatase activity and suppresses programmed cell death in plants. Mol Microbiol 49:377–387
Fang Y, Ramasamy RP (2015) Current and prospective methods for plant disease detection. Biosensors 5:537–561
Fayaz AM, Balaji K, Girilal M et al (2009) Mycobased synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their incorporation into sodium alginate films for vegetable and fruit preservation. J Agric Food Chem 57:6246–6252
Frampton RA, Pitman AR, Fineran PC (2012) Advances in bacteriophage-mediated control of plant pathogens. Int J Microbiol 2012:326452
Francl LJ (2001) The disease triangle: a plant pathological paradigm revisited. Plant Health Instruct 10:517
Frazer L (2001) Titanium dioxide: environmental white knight. Environ Health Perspect 109:174–177
Freeman BC, Chen C, Beattie GA (2010) Identification of the trehalose biosynthetic loci of Pseudomonas syringae and their contribution to fitness in the phyllosphere. Environ Microbiol 12:1486–1497
Freeman BC, Chen C, Yu X et al (2013) Physiological and transcriptional responses to osmotic stress of two Pseudomonas syringae strains that differ in epiphytic fitness and osmotolerance. J Bacteriol 195:4742–4752
Gahlawat G, Choudhury AR (2019) A review on the biosynthesis of metal and metal salt nanoparticles by microbes. RSC Adv 9:12944–12967
Gaignard JL, Luisetti J (1993) Pseudomonas-syringae, an epiphytic ice nucleation active and phytopathogenic bacterium. Agronomie 13:333–370
Gal M, Preston GM, Massey RC et al (2003) Genes encoding a cellulosic polymer contribute toward the ecological success of Pseudomonas fluorescens SBW25 on plant surfaces. Mol Ecol 12:3109–3121
Galan JE, Lara-Tejero M, Marlovits TC et al (2014) Bacterial type III secretion systems: specialized nanomachines for protein delivery into target cells. Annu Rev Microbiol 68:415–438
Gardea-Torresdey JL, Rico CM, White JC (2014) Trophic transfer, transformation, and impact of engineered nanomaterials in terrestrial environments. Environ Sci Technol 48:2526–2540
Garnham CP, Campbell RL, Walker VK et al (2011) Novel dimeric beta-helical model of an ice nucleation protein with bridged active sites. BMC Struct Biol 11:36
Geri C, Love AJ, Cecchini E et al (2004) Arabidopsis mutants that suppress the phenotype induced by transgene-mediated expression of cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) gene VI are less susceptible to CaMV infection and show reduced ethylene sensitivity. Plant Mol Biol 56:111–124
Gerlach RG, Hensel M (2007) Protein secretion systems and adhesins: the molecular armory of Gram-negative pathogens. Int J Med Microbiol 297(6):401–415
Ghormade V, Deshpande MV, Paknikar KM (2011) Perspectives for nano-biotechnology enabled protection and nutrition of plants. Biotechnol Adv 29:792–803
Giannousi K, Avramidis I, Dendrinou-Samara C (2013) Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of copper based nanoparticles as agrochemicals against Phytophthora infestans. RSC Adv 3:21743–21752
Gilardi P, Garcıa-Luque I, Serra MT (1998) Pepper mild mottle virus coat protein alone can elicit the Capsicum spp. L3 genemediated resistance. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 11:1253–1257
Gilbert GS, Parker IM (2016) The evolutionary ecology of plant disease: a phylogenetic perspective. Annu Rev Phytopathol 54:549–578
Gimenez-Ibanez S, Boter M, Fernandez-Barbero G et al (2014) The bacterial effector HopX1 targets JAZ transcriptional repressors to activate jasmonate signaling and promote infection in Arabidopsis. PLoS Biol 12:e1001792
Glawe DA (1992) Thomas J. Burrill, pioneer in plant pathology. Annu Rev Phytopathol 30:17–25
Gogoi R, Singh PK, Kumar R et al (2013) Suitability of nanosulphur for biorational management of powdery mildew of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus Moench) caused by Erysiphe cichoracearum. J Plant Pathol Microbiol 4:171–175
Gohlke J, Deeken R (2014) Plant responses to Agrobacterium tumefaciens and crown gall development. Front Plant Sci 5:155
Gordon T, Perlstein B, Houbara O et al (2011) Synthesis and characterization of zinc/iron oxide composite nanoparticles and their antibacterial properties. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 374:1–8
Graham JH, Johnson EG, Myers ME et al (2016) Potential of nano-formulated zinc oxide for control of citrus canker on grapefruit trees. Plant Dis 100:2442–2447
Guan H, Chi D, Yu J, Li H (2010) Dynamics of residues from a novel nano-imidacloprid formulation in soyabean fields. Crop Prot 29:942–946
Gudesblat GE, Torres PS, Vojnov AA (2009) Xanthomonas campestris overcomes Arabidopsis stomatal innate immunity through a DSF cell-to-cell signal regulated virulence factor. Plant Physiol 149:1017–1027
Gurian-Sherman D, Lindow SE (1993) Bacterial ice nucleation: significance and molecular basis. FASEB J 7:1338–1343
Haikonen T, Rajamaki ML, Tian YP, Valkonen JP (2013) Mutation of a short variable region in HCpro protein of Potato virus A affects interactions with a microtubule-associated protein and induces necrotic responses in tobacco. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 26:721–733
Hails RS (2000) Genetically modified plants—the debate continues. Trends Ecol Evol 15:14–18
Hajipour MJ, Fromm KM, Ashkarran AA et al (2012) Antibacterial properties of nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol 30:499–511
Han SW, Lee SW, Ronald PC (2011) Secretion, modification, and regulation of Ax21. Curr Opin Microbiol 14:62–67
Hao Y, Cao X, Ma C et al (2017) Potential applications and antifungal activities of engineered nanomaterials against gray mold disease agent Botrytis cinerea on rose petals. Front Plant Sci 8:1332
Hassan SED, Fouda A, Radwan AA et al (2019) Endophytic actinomycetes Streptomyces spp mediated biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles as a promising tool for biotechnological applications. J Biol Inorg Chem 24:377–393
Hauck P, Thilmony R, He SY (2003) A Pseudomonas syringae type III effector suppresses cell wall-based extracellular defense in susceptible Arabidopsis plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:8577–8582
Havelda Z, Hornyik C, Valoczi A, Burgyan J (2005) Defective interfering RNA hinders the activity of a tombusvirus-encoded posttranscriptional gene silencing suppressor. J Virol 79:450–457
He P, Chintamanani S, Chen Z et al (2004) Activation of a COI1-dependent pathway in Arabidopsis by Pseudomonas syringae type III effectors and coronatine. Plant J 37:589–602
He YW, Boon C, Zhou L et al (2009) Co-regulation of Xanthomonas campestris virulence by quorum sensing and a novel two-component regulatory system RavS/RavR. Mol Microbiol 71:1464–1476
He L, Liu Y, Mustapha A, Lin M (2011) Antifungal activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles against Botrytis cinerea and Penicillium expansum. Microbiol Res 166:207–215
Heaton LA, Lee TC, Wei N et al (1991) Point mutations in the turnip crinkle virus capsid protein affect the symptoms expressed by Nicotiana benthamiana. Virology 183:143–150
Hisa Y, Suzuki H, Atsumi G et al (2014) P3NPIPO of Clover yellow vein virus exacerbates symptoms in pea infected with White clover mosaic virus and is implicated in viral synergism. Virology 449:200–206
Horsfall JG, Cowling EB (1980) Plant disease, 3rd edn. Academic, New York
Hossain A, Abdallah Y, Ali MA et al (2019) Lemon-fruit-based green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and titanium dioxide nanoparticles against soft rot bacterial pathogen Dickeyadadantii. Biomol Ther 9:863
Ibrahim E, Zhang M, Zhang Y et al (2020) Green-synthesization of silver nanoparticles using endophytic bacteria isolated from garlic and its antifungal activity against wheat fusarium head blight pathogen Fusarium graminearum. Nano 10:219
Imada K, Sakai S, Kajihara H, Tanaka S, Ito S (2016) Magnesium oxide nanoparticles induce systemic resistance in tomato against bacterial wilt disease. Plant Pathol 65:551–560
Inaba J, Kim BM, Shimura H, Masuta C (2011) Virus-induced necrosis is a consequence of direct protein–protein interaction between a viral RNA-silencing suppressor and a host catalase. Plant Physiol 156:2026–2036
Incarbone M, Dunoyer P (2013) RNA silencing and its suppression: novel insights from in planta analyses. Trends Plant Sci 18:382–392
Ishibashi K, Masuda K, Naito S et al (2007) An inhibitor of viral RNA replication is encoded by a plant resistance gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:13833–13838
Jagana D, Hegde YR, Lella R (2017) Green nanoparticles: a novel approach for the management of banana anthracnose caused by Colletotrichum musae. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 6:1749–1756
Jamir Y, Guo M, Oh HS et al (2004) Identification of Pseudomonas syringae type III effectors that can suppress programmed cell death in plants and yeast. Plant J 37:554–565
Jay F, Wang Y, Yu A et al (2011) Misregulation of auxin response factor 8 underlies the developmental abnormalities caused by three distinct viral silencing suppressors in Arabidopsis. PLoS Pathog 7:e1002035
Jha G, Rajeshwari R, Sonti RV (2005) Bacterial type two secretion system secreted proteins: double-edged swords for plant pathogens. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 18:891–898
Jin T, Sun D, Su JY, Zhang H, Sue HJ (2009) Antimicrobial efficacy of zinc oxide quantum dots against Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella enteritidis, and Escherichia coli O157: H7. J Food Sci 74:46–52
Jo YK, Kim BH, Jung G (2009) Antifungal activity of silver ions and nanoparticles on phytopathogenic fungi. Plant Dis 93:1037–1043
Johnson TL, Abendroth J, Hol WGJ et al (2006) Type II secretion: from structure to function. FEMS Microbiol Lett 255:175–186
Kachroo P, Yoshioka K, Shah J et al (2000) Resistance to turnip crinkle virus in arabidopsis is regulated by two host genes and is salicylic acid dependent but NPR1, ethylene, and jasmonate independent. Plant Cell 12:677–690
Kang Y, Liu H, Genin S et al (2002) Ralstonia solanacearum requires type 4 pili to adhere to multiple surfaces and for natural transformation and virulence. Mol Microbiol 46:427–437
Kang L, Li J, Zhao T et al (2003) Interplay of the Arabidopsis nonhost resistance gene NHO1 with bacterial virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:3519–3524
Kanhed P, Birla S, Gaikwad S et al (2014) In vitro antifungal efficacy of copper nanoparticles against selected crop pathogenic fungi. Mater Lett 115:13–17
Kay S, Hahn S, Marois E et al (2007) A bacterial effector acts as a plant transcription factor and induces a cell size regulator. Science 318:648–651
Khan MR, Haque Z (2013) Morphological and biochemical responses of five tobacco cultivars to simultaneous infection with Pythium aphanidermatum and Meloidogyne incognita. Phytopathol Mediterr 52:98–109
Khan MR, Rizvi TF (2014) Nanotechnology: scope and application in plant disease management. Plant Pathol J 13:214–231
Khater M, de la Escosura-Muñiz A, Merkoçi A (2017) Biosensors for plant pathogen detection. Biosens Bioelectron 93:72–86
Khiyami MA, Almoammar H, Awad YM et al (2014) Plant pathogen nanodiagnostic techniques: forthcoming changes? Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 28:775–785
Kim J, Kim JG, Kang Y et al (2004) Quorum sensing and the LysR-type transcriptional activator ToxR regulate toxoflavin biosynthesis and transport in Burkholderia glumae. Mol Microbiol 54:921–934
Kim H, Kang H, Chu G, Byun G (2008) Antifungal effectiveness of nanosilver colloid against rose powdery mildew in greenhouses. Solid State Phenom 135:15–18
Kim JI, Park HG et al (2016) Trophic transfer of nano-TiO2 in a paddy microcosm: a comparison of single-dose versus sequential multi-dose exposures. Environ Pollut 212:316–324
Klein E, Link D, Schirmer A et al (2007) Sequence variation within Beet necrotic yellow vein virus p25 protein influences its oligomerization and isolate pathogenicity on Tetragonia expansa. Virus Res 126:53–61
Kołodziejczak-Radzimska A, Jesionowski T (2014) Zinc oxide—from synthesis to application: a review. Mater Ther 7:2833–2881
Kong HS, Roberts DP, Patterson CD et al (2012) Effect of overexpressing rsmA from Pseudomonas aeruginosa on virulence of select phytotoxin-producing strains of P. syringae. Phytopathology 102:575–587
Korotkov KV, Sandkvist M, Hol WGJ (2012) The type II secretion system: biogenesis, molecular architecture and mechanism. Nat Rev Microbiol 10:336–351
Krishnaraj C, Ramachandran R, Mohan K, Kalaichelvan PT (2012) Optimization for rapid synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its effect on phytopathogenic fungi. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 93:95–99
Krutyakov YA, Kudrinskiy AA, Zherebin PM et al (2016) Tallow amphopolycarboxyglycinate stabilized silver nanoparticles: new frontiers in development of plant protection products with a broad spectrum of action against phytopathogens. Mater Res Express 3:075403
Kurepa J, Paunesku T, Vogt S et al (2010) Uptake and distribution of ultrasmall anatase TiO2 Alizarin red S nanoconjugates in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nano Lett 10:2296–2302
Lamichhane JR, Osdaghi E, Behlau F et al (2018) Thirteen decades of antimicrobial copper compounds applied in agriculture. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 38:1–18
Lamsal K, Kim SW, Jung JH et al (2011a) Inhibition effects of silver nanoparticles against powdery mildews on cucumber and pumpkin. Mycobiology 39:26–32
Lamsal K, Kim SW, Jung JH et al (2011b) Application of silver nanoparticles for the control of Colletotrichum species in vitro and pepper anthracnose disease in field. Mycobiology 39:194–199
Langston-Unkefer PJ, Robinson AC, Knight TJ et al (1987) Inactivation of pea seed glutamine synthetase by the toxin, tabtoxinine-beta-lactam. J Biol Chem 262:1608–1613
Lara-Tejero M, Kato J, Wagner S et al (2011) A sorting platform determines the order of protein secretion in bacterial type III systems. Science 331:1188–1191
Leduc JL, Roberts GP (2009) Cyclic di-GMP allosterically inhibits the CRP-like protein (Clp) of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri. J Bacteriol 191:7121–7122
Lee J, Teitzel GM, Munkvold K et al (2012) Type III secretion and effectors shape the survival and growth pattern of Pseudomonas syringae on leaf surfaces. Plant Physiol 158:1803–1818
Lee DH, Kim JB, Lim JA et al (2014) Genetic diversity of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliensis isolated in Korea. Plant Pathol J 30:117–124
Lemire JA, Harrison JJ, Turner RJ (2013) Antimicrobial activity of metals: Mechanisms, molecular targets and applications. Nat Rev Microbiol 11:371–384
Lewandowski DJ, Dawson WO (1993) A single amino acid change in tobacco mosaic virus replicase prevents symptom production. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 6:157–160
Li F, Pignatta D, Bendix C et al (2012) MicroRNA regulation of plant innate immune receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:1790–1795
Li J, Sang H, Guo H et al (2017) Antifungal mechanisms of ZnO and Ag nanoparticles to Sclerotinia homoeocarpa. Nanotechnology 28:155101
Liang H, Yao N, Song JT et al (2003) Ceramides modulate programmed cell death in plants. Genes Dev 17:2636–2641
Liang Y, Yang D, Cui J (2017) A graphene oxide/silver nanoparticle composite as a novel agricultural antibacterial agent against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae for crop disease management. New J Chem 41:13692–13699
Liao YY, Strayer-Scherer AL, White J et al (2019) Nano-magnesium oxide: a novel bactericide against coppertolerant Xanthomonas perforans causing tomato bacterial spot. Phytopathology 109:52–62
Lim MTS, Kunkel BN (2004) Mutations in the Pseudomonas syringae avrRpt2 gene that dissociate its virulence and avirulence activities lead to decreased efficiency of AvrRpt2-induced disappearance of RIN4. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 17:313–332
Linsebigler AL, Lu G, Yates JT Jr (1995) Photocatalysis on TiO2 surfaces: principles, mechanisms, and selected results. Chem Rev 95:735–758
Little RH, Grenga L, Saalbach G et al (2016) Adaptive remodeling of the bacterial proteome by specific ribosomal modification regulates Pseudomonas infection and niche colonisation. PLoS Genet 12:e1005837
Lohou D, Lonjon F, Genin S et al (2013) Type III chaperones & Co in bacterial plant pathogens: a set of specialized bodyguards mediating effector delivery. Front Plant Sci 4:435
Lucas WJ (2006) Plant viral movement proteins: agents for cell-to cell trafficking of viral genomes. Virology 344:169–184
Macho AP (2016) Subversion of plant cellular functions by bacterial type-III effectors: beyond suppression of immunity. New Phytol 210:51–57
Macho AP, Zipfel C (2014) Plant PRRs and the activation of innate immune signaling. Mol Cell 54:263–272
Macho AP, Zipfel C (2015) Targeting of plant pattern recognition receptor triggered immunity by bacterial type-III secretion system effectors. Curr Opin Microbiol 23:14–22
Makarovsky D, Fadeev L, Salam BB et al (2018) Silver nanoparticles complexed with bovine submaxillary mucin possess strong antibacterial activity and protect against seedling infection. Appl Environ Microbiol 84(4):e02212
Mala R, Arunachalam P, Sivsankari M (2012) Synergistic bactericidal activity of silver nanoparticles and ciprofloxacin against phytopathogens. J Cell Tissue Res 12:3249–3254
Marco ML, Legac J, Lindow SE (2005) Pseudomonas syringae genes induced during colonization of leaf surfaces. Environ Microbiol 7:1379–1391
Martins PM, Merfa MV, Takita MA et al (2018) Persistence in phytopathogenic bacteria: do we know enough? Front Microbiol 9:1099
Mathioudakis MM, Veiga RS, Canto T et al (2013) Pepino mosaic virus triple gene block protein 1 (TGBp1) interacts with and increases tomato catalase 1 activity to enhance virus accumulation. Mol Plant Pathol 14:589–601
McCarthy Y, Dow JM, Ryan RP (2011) The Ax21 protein is a cell–cell signal that regulates virulence in the nosocomial pathogen Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. J Bacteriol 193:6375–6378
Melotto M, Kunkel BN (2013) Virulence strategies of plant pathogenic bacteria. In: Rosenberg E (ed) The prokaryotes – prokaryotic physiology and biochemistry. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 61–75
Melotto M, Underwood W, Koczan J et al (2006) Plant stomata function in innate immunity against bacterial invasion. Cell 126:969–980
Mise K, Allison RF, Janda M, Ahlquist P (1993) Bromovirus movement protein genes play a crucial role in host specificity. J Virol 67:2815–2823
Mishra S, Singh BR, Singh A et al (2014) Biofabricated silver nanoparticles act as a strong fungicide against Bipolaris sorokiniana causing spot blotch disease in wheat. PLoS One 9(5):e97881
Mochizuki T, Yamazaki R, Wada T et al (2014) Coat protein mutations in an attenuated cucumber mosaic virus encoding mutant 2b protein that lacks RNA silencing suppressor activity induces chlorosis with photosynthesis gene repression and chloroplast abnormalities in infected tobacco plants. Virology 456–457:292–299
Moffett P (2009) Mechanisms of recognition in dominant R gene mediated resistance. Adv Virus Res 75:1–33
Mohmood I, Lopes CB, Lopes I et al (2013) Nanoscale materials and their use in water contaminants removal–a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:1239–1260
Mondal KK, Mani C (2012) Investigation of the antibacterial properties of nanocopper against Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae, the incitant of pomegranate bacterial blight. Ann Microbiol 62:889–893
Mondal KK, Bhar LM, Mani C (2010) Combined efficacy of Pseudomonas fluorescens strain MBPF-01 and nanocopper against bacterial leaf blight in rice. Indian Phytopathol 63:266–268
Morales-Díaz AB, Ortega-Ortíz H (2017) Application of nanoelements in plant nutrition and its impact in ecosystems. Adv Nat Sci Nanosci Nanotechnol 8:013001
Moscoso JA, Mikkelsen H, Heeb S et al (2011) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa sensor RetS switches type III and type VI secretion via cdi-GMP signalling. Environ Microbiol 13:3128–3138
Moscoso JA, Jaeger T, Valentini M et al (2014) The diguanylate cyclase SadC is a central player in Gac/Rsm-mediated biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 196:4081–4088
Moussa SH, Tayel AA, Alsohim AS, Abdallah RR (2013) Botryticidal activity of nanosized silver-chitosan composite and its application for the control of gray mold in strawberry. J Food Sci 78:1589–1594
Mukhopadhyay SS (2014) Nanotechnology in agriculture: prospects and constraints. Nanotechnol Sci Appl 2014:63–71
Nadendla SR, Rani TS, Vaikuntapu PR et al (2018) HarpinPss encapsulation in chitosan nanoparticles for improved bioavailability and disease resistance in tomato. Carbohydr Polym 199:11–19
Nair R, Varghese SH, Nair BG et al (2010) Nanoparticulate material delivery to plants. Plant Sci 179:154–163
Nandini B, Hariprasad P, Prakash HS, Shetty HS, Geetha N (2017) Trichogenic-selenium nanoparticles enhance disease suppressive ability of Trichoderma against downy mildew disease caused by Sclerospora graminicola in pearl millet. Sci Rep 7:2612
Navale GR, Thripuranthaka M, Late DJ, Shinde SS (2015) Antimicrobial activity of ZnO nanoparticles against pathogenic bacteria and fungi. JSM Nanotechnol Nanomed 3:1033–1041
Nguyen LC, Taguchi F, Tran QM et al (2012) Type IV pilin is glycosylated in Pseudomonas syringae pv. tabaci 6605 and is required for surface motility and virulence. Mol Plant Pathol 13:764–774
Nguyen HC, Nguyen TT, Dao TH et al (2016) Preparation of Ag/SiO2 nanocomposite and assessment of its antifungal effect on soybean plant (a Vietnamese species DT-26). Adv Nat Sci Nanosci Nanotechnol 7(4):045014
Ni P, Cheng KC (2013) Non-encapsidation activities of the capsid proteins of positive-strand RNA viruses. Virology 446:123–132
Nisar P, Ali N, Rahman L, Ali M, Shinwari ZK (2019) Antimicrobial activities of biologically synthesized metal nanoparticles: an insight into the mechanism of action. J Biol Inorg Chem 24:929–941
Norman DJ, Chen J (2011) Effect of foliar application of titanium dioxide on bacterial blight of geranium and Xanthomonas leaf spot of poinsettia. HortScience 46:426–428
Ocsoy I, Paret ML, Ocsoy MA et al (2013) Nanotechnology in plant disease management: DNA-directed silver nanoparticles on graphene oxide as an antibacterial against Xanthomonas perforans. ACS Nano 7:8972–8980
Okano Y, Senshu H, Hashimoto M et al (2014) In planta recognition of a double-stranded RNA synthesis protein complex by a potexviral RNA silencing suppressor. Plant Cell 26:2168–2183
Owolade OF, Ogunleti DO, Adenekan MO (2008) Titanium dioxide affects disease development and yield of edible cowpea. EJEAF Chem 7:2942–2947
Pacheco R, Garcıa-Marcos A, Manzano A et al (2012) Comparative analysis of transcriptomic and hormonal responses to compatible and incompatible plant–virus interactions that lead to cell death. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 25:709–723
Padmanabhan MS, Kramer SR, Wang X et al (2008) Tobacco mosaic virus replicase-auxin/indole acetic acid protein interactions: reprogramming the auxin response pathway to enhance virus infection. J Virol 82:2477–2485
Paknikar KM, Nagpal V, Pethkar AV, Rajwade JM (2005) Degradation of lindane from aqueous solutions using iron sulfide nanoparticles stabilized by biopolymers. Sci Technol Adv Mater 6:370–374
Pakrashi S, Jain N, Dalai L et al (2014) In vivo genotoxicity assessment of titanium dioxide nanoparticles by Allium cepa root tip assay at high exposure concentrations. PLoS ONE 9:e87789
Pallas V, Garcıa JA (2011) How do plant viruses induce disease? Interactions and interference with host components. J Gen Virol 92:2691–2705
Pallas V, Genoves A, Sanchez-Pina MA, Navarro JA (2011) Systemic movement of viruses via the plant phloem. In: Caranta C, Aranda MA, Tepfer M, Lopez-Moya JJ (eds) Recent advances in plant virology. Academic, New York
Palza H (2015) Antimicrobial polymers with metal nanoparticles. Int J Mol Sci 16:2099–2116
Paret ML, Palmateer AJ, Knox GW (2013a) Evaluation of a lightactivated nanoparticle formulation of titanium dioxide with zinc for management of bacterial leaf spot on rosa ‘Noare’. HortScience 48:189–192
Paret ML, Vallad GE, Averett DR et al (2013b) Photocatalysis: effect of light-activated nanoscale formulations of TiO2 on Xanthomonas perforans and control of bacterial spot of tomato. Phytopathology 103:228–236
Park HJ, Kim SH, Kim HJ, Choi SH (2006) A new composition of nanosized silica-silver for control of various plant diseases. Plant Pathol J 22:295–302
Peiro A, Canizares MC, Rubio L et al (2014) The movement protein (NSm) of Tomato spotted wilt virus is the avirulence determinant in the tomato Sw-5 gene-based resistance. Mol Plant Pathol 15:802–813
Pel MJ, van Dijken AJ, Bardoel BW et al (2014) Pseudomonas syringae evades host immunity by degrading flagellin monomers with alkaline protease AprA. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 27:603–610
Peng WT, Lee YW, Nester EW (1998) The phenolic recognition profiles of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens VirA protein are broadened by a high level of the sugar binding protein ChvE. J Bacteriol 180:5632–5638
Pepperman AB, Kuan CW, Mc Combs C (1991) Alginate controlled release formulations of metribuzin. J Control Release 17:105–112
Perfileva AI, Tsivileva OM, Koftin OV et al (2018) Selenium-containing nanobiocomposites of fungal origin reduce the viability and biofilm formation of the bacterial phytopathogen Clavibacter michiganensis subsp, sepedonicus. Nanotechnol Russ 13:268–276
Pfeilmeier S, Saur IM, Rathjen JP et al (2016) High levels of cyclic-di-GMP in plant-associated Pseudomonas correlate with evasion of plant immunity. Mol Plant Pathol 17:521–531
Piffanelli P, Zhou F, Casais C et al (2002) The barley MLO modulator of defense and cell death is responsive to biotic and abiotic stress stimuli. Plant Physiol 129:1076–1085
Pingali PL (2012) Green revolution: impacts, limits, and the path ahead. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:12302–12308
Qian G, Zhou Y, Zhao Y et al (2013) Proteomic analysis reveals novel extracellular virulence-associated proteins and functions regulated by the diffusible signal factor (DSF) in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola. J Proteome Res 12:3327–3341
Quinones B, Pujol CJ, Lindow SE (2004) Regulation of AHL production and its contribution to epiphytic fitness in Pseudomonas syringae. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 17:521–531
Quinones B, Dulla G, Lindow SE (2005) Quorum sensing regulates exopolysaccharide production, motility, and virulence in Pseudomonas syringae. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 18:682–693
Rahim MD, Andika IB, Han C (2007) RNA4-encoded p31 of beet necrotic yellow vein virus is involved in efficient vector transmission, symptom severity and silencing suppression in roots. J Gen Virol 88:1611–1619
Rahoutei J, Garcıa-Luque I, Baron M (2000) Inhibition of photosynthesis by viral infection: effect on PSII structure and function. Physiol Plant 110:286–292
Rao ALN, Grantham GL (1996) Molecular studies on bromovirus capsid protein. 2. Functional analysis of the amino-terminal arginine-rich motif and its role in encapsidation, movement, and pathology. Virology 226:294–305
Rao KJ, Paria S (2013) Use of sulfur nanoparticles as a green pesticide on Fusarium solani and Venturia inaequalis phytopathogens. RSC Adv 3:10471–10478
Records AR, Gross DC (2010) Sensor kinases RetS and LadS regulate Pseudomonas syringae type VI secretion and virulence factors. J Bacteriol 192:3584–3596
Ren T, Qu F, Morris TJ (2000) HRT gene function requires interaction between a NAC protein and viral capsid protein to confer resistance to turnip crinkle virus. Plant Cell 12:1917–1926
Ren T, Qu F, Morris TJ (2005) The nuclear localization of the Arabidopsis transcription factor TIP is blocked by its interaction with the coat protein of Turnip crinkle virus. Virology 331:316–324
Renzi M, Copini P, Taddei AR et al (2012) Bacterial canker on kiwifruit in Italy: anatomical changes in the wood and in the primary infection sites. Phytopathology 102:827–840
Ritpitakphong U, Falquet L, Vimoltust A et al (2016) The microbiome of the leaf surface of Arabidopsis protects against a fungal pathogen. New Phytol 210:1033–1043
Robert-Seilaniantz A, Grant M, Jones JD (2011) Hormone crosstalk in plant disease and defense: more than just jasmonate–salicylate antagonism. Annu Rev Phytopathol 49:317–343
Rodrigues S, Dionísio M, Lopez CR, Grenha A (2012) Biocompatibility of chitosan carriers with application in drug delivery. J Funct Biomater 3:615–641
Romling U, Galperin MY, Gomelsky M (2013) Cyclic di-GMP: the first 25 years of a universal bacterial second messenger. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 77:1–52
Ruparelia JP, Chatterjee AK, Duttagupta SP, Mukherji S (2008) Strain specificity in antimicrobial activity of silver and copper nanoparticles. Acta Biomater 4:707–716
Sanzari I, Leone A, Ambrosone A (2019) Nanotechnology in plant science: to make a long story short. Biotechnology 7:120
Sarlak N, Taherifar A, Salehi F (2014) Synthesis of nanopesticides by encapsulating pesticide nanoparticles using functionalized carbon nanotubes and application of new nanocomposite for plant disease treatment. J Agric Food Chem 62:4833–4838
Sathiyabama M, Manikandan A (2016) Chitosan nanoparticle induced defense responses in fingermillet plants against blast disease caused by Pyricularia grisea (Cke.) Sacc. Carbohydr Polym 154:241–246
Sathiyabama M, Parthasarathy R (2016) Biological preparation of chitosan nanoparticles and its in vitro antifungal efficacy against some phytopathogenic fungi. Carbohydr Polym 151:321–325
Sauer AV, Rocha KR, Pedro ED et al (2014) Ice nucleation activity in Pantoea ananatis obtained from maize white spot lesions. Semin-Cienc Agrar 35:1659–1666
Savary S, Ficke A, Aubertot JN, Hollier C (2012) Crop losses due to diseases and their implications for global food production losses and food security. Food Secur 4:519–537
Scholthof KB, Adkins S, Czosnek H et al (2011) Top 10 plant viruses in molecular plant pathology. Mol Plant Pathol 12:938–954
Schuster M, Lostroh CP, Ogi T et al (2003) Identification, timing, and signal specificity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-controlled genes: a transcriptome analysis. J Bacteriol 185:2066–2079
Shanmugam C, Gunasekaran D, Duraisamy N et al (2015) Bioactive bile salt-capped silver nanoparticles activity against destructive plant pathogenic fungi through in vitro system. RSC Adv 5:71174–71182
Shimizu M, Tainaka H et al (2009) Maternal exposure to nanoparticulate titanium dioxide during the prenatal period alters gene expression related to brain development in the mouse. Part Fibre Toxicol 6:20
Shintaku MH, Zhang L, Palukaitis P (1992) A single amino acid substitution in the coat protein of cucumber mosaic virus induces chlorosis in tobacco. Plant Cell 4:751–757
Shivaprasad PV, Chen HM, Patel K et al (2012) A microRNA superfamily regulates nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeats and other mRNAs. Plant Cell 24:859–874
Silva AT, Nguyen A, Ye C et al (2010) Conjugated polymer nanoparticles for effective siRNA delivery to tobacco BY2 protoplasts. BMC Plant Biol 10:1–14
Simonin M, Richaume A (2015) Impact of engineered nanoparticles on the activity, abundance, and diversity of soil microbial communities: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:13710–13723
Singh S, Singh M, Agrawal VV, Kumar A (2010) An attempt to develop surface plasmon resonance based immunosensor for Karnal bunt (Tilletia indica) diagnosis based on the experience of nano-gold based lateral flow immuno-dipstick test. Thin Solid Films 519:1156–1159
Slater H, Alvarez-Morales A, Barber CE et al (2000) A two-component system involving an HD-GYP domain protein links cell-cell signalling to pathogenicity gene expression in Xanthomonas campestris. Mol Microbiol 38:986–1003
Soenen S, Rivera-Gil P, Montenegro JM et al (2011) Cellular toxicity of inorganic nanoparticles: common aspects and guidelines for improved nanotoxicity evaluation. Nano Today 6:446–465
Spetz C, Valkonen JPT (2004) Potyviral 6K2 protein long-distance movement and symptom-induction functions are independent and host-specific. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 17:502–510
Strayer A, Ocsoy I, Tan W (2016) Low concentrations of a silver-based nanocomposite to manage bacterial spot of tomato in the greenhouse. Plant Dis 100:1460–1465
Strayer-Scherer AL, Liao YY, Young M et al (2018) Advanced copper composites against copper-tolerant Xanthomonas perforans and tomato bacterial spot. Phytopathology 108:196–205
Streubel J, Pesce C, Hutin M et al (2013) Five phylogenetically close rice SWEET genes confer TAL effector-mediated susceptibility to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. New Phytol 200:808–819
Sugawara K, Shiraishi T, Yoshida T et al (2013) A replicase of Potato virus X acts as the resistance breaking determinant for JAX1-mediated resistance. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 26:1106–1112
Sun Q, Greve LC, Labavitch JM (2011) Polysaccharide compositions of intervessel pit membranes contribute to Pierce’s disease resistance of grapevines. Plant Physiol 155:1976–1987
Tamir-Ariel D, Rosenberg T, Navon N et al (2012) A secreted lipolytic enzyme from Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria is expressed in planta and contributes to its virulence. Mol Plant Pathol 13:556–567
Tans-Kersten J, Huang H, Allen C (2001) Ralstonia solanacearum needs motility for invasive virulence on tomato. J Bacteriol 183:3597–3605
Tilman D, Balzer C, Hill J et al (2011) Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture. PNAS 108:20260–20264
Toth IK, Bell KS, Holeva MC et al (2003) Soft rot erwiniae: from genes to genomes. Mol Plant Pathol 4:17–30
Trampari E, Stevenson CE, Little RH et al (2015) Bacterial rotary export ATPases are allosterically regulated by the nucleotide second messenger cyclic-di-GMP. J Biol Chem 290:24470–24483
Udalova ZV, Folmanis GE, Khasanov FK, Zinovieva SV (2018) Selenium nanoparticles—an inducer of tomato resistance to the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita (Kofoid et White 1919) Chitwood 1949. Dokl Biochem Biophys 482:264–267
Vadlapudi V, Naidu KC (2011) Fungal pathogenicity of plants. Molecular approach. Eur J Exp Biol 1:38–42
Vankar PS, Shukla D (2012) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using lemon leaves extract and its application for antimicrobial finish on fabric. Appl Nanosci 2:163–168
Wang ZL (2004) Nanostructures of zinc oxide. Mater Today 7:26–33
Wang LH, He Y, Gao Y et al (2004) A bacterial cell–cell communication signal with cross-kingdom structural analogues. Mol Microbiol 51:903–912
Wang Z, Wei F, Liu SY et al (2010) Electrocatalytic oxidation of phytohormone salicylic acid at copper nanoparticles-modified gold electrode and its detection in oilseed rape infected with fungal pathogen Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Talanta 80:1277–1281
Wang MB, Masuta C, Smith NA, Shimura H (2012) RNA silencing and plant viral diseases. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 25:1275–1285
Wu Z, Kan FW, She YM et al (2012) Biofilm, ice recrystallization inhibition and freeze–thaw protection in an epiphyte community. Prikl Biokhim Mikrobiol 48:403–410
Xia ZK, Ma QH, Li SY et al (2016) The antifungal effect of silver nanoparticles on Trichosporon asahii. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 49:182–188
Xin XF, He SY (2013) Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000: a model pathogen for probing disease susceptibility and hormone signaling in plants. Annu Rev Phytopathol 51:473–498
Xu L, Liu Y, Bai R, Chen C (2010) Applications and toxicological issues surrounding nanotechnology in the food industry. Pure Appl Chem 82:349–372
Xu C, Peng C, Sun L et al (2015) Distinctive effects of TiO2 and CuO nanoparticles on soil microbes and their community structures in flooded paddy soil. Soil Biol Biochem 86:24–33
Yadeta K, Thomma B (2013) The xylem as battleground for plant hosts and vascular wilt pathogens. Front Plant Sci 4:97
Yang J, Hsiang T, Bhadauria V et al (2017) Plant fungal pathogenesis. Biomed Res Int 2017:9724283. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9724283
Yao KS, Li SJ, Tzeng KC et al (2009) Fluorescence silica nanoprobe as a biomarker for rapid detection of plant pathogens. Adv Mater Res 79:513–516
Yaryura PM, Conforte VP, Malamud F et al (2015) XbmR, a new transcription factor involved in the regulation of chemotaxis, biofilm formation and virulence in Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri. Environ Microbiol 17:4164–4176
Ye CM, Chen S, Payton M et al (2013) TGBp3 triggers the unfolded protein response and SKP1-dependent programmed cell death. Mol Plant Pathol 14:241–255
Yoon JY, Ahn HI, Kim M et al (2006) Pepper mild mottle virus pathogenicity determinants and cross protection effect of attenuated mutants in pepper. Virus Res 118:23–30
Yoshioka H, Shiraishi T, Yamada K et al (1990) Suppression of pisatin production and ATPase activity in pea plasma membranes by orthovanadate, verapamil and a suppressor from Mycosphaerella pinodes. Plant Cell Physiol 31:1139–1146
You T, Liu D, Chen J et al (2018) Effects of metal oxide nanoparticles on soil enzyme activities and bacterial communities in two different soil types. J Soils Sediments 18:211–221
Yu J, Penaloza-Vazquez A, Chakrabarty AM et al (1999) Involvement of the exopolysaccharide alginate in the virulence and epiphytic fitness of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae. Mol Microbiol 33:712–720
Yu X, Lund SP, Scott RA et al (2013) Transcriptional responses of Pseudomonas syringae to growth in epiphytic versus apoplastic leaf sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:E425–E434
Zeng W, He SY (2010) A prominent role of the flagellin receptor FLAGELLINSENSING2 in mediating stomatal response to Pseudomonas syringae pv tomato DC3000 in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 153:1188–1198
Zhang X, Yuan Y-R, Pei Y et al (2006) Cucumber mosaic virus-encoded 2b suppressor inhibits Arabidopsis Argonaute1 cleavage activity to counter plant defense. Genes Dev 20:3255–3268
Zhang CZ, Liu YY, Sun XC et al (2008) Characterization of a specific interaction between IP-L, a tobacco protein localized in the thylakoid membranes, and tomato mosaic virus coat protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 374:253–257
Zhu SF, Gao F, Cao XS et al (2005) The rice dwarf virus P2 protein interacts with ent-kaurene oxidases in vivo, leading to reduced biosynthesis of gibberellins and rice dwarf symptoms. Plant Physiol 139:1935–1945
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Pattanayak, S.P., Bose, P., Sunita, P. (2023). Interaction Between Nanoparticles and Phytopathogens. In: Fernandez-Luqueno, F., Patra, J.K. (eds) Agricultural and Environmental Nanotechnology. Interdisciplinary Biotechnological Advances. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5454-2_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5454-2_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-5453-5
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-5454-2
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)