Abstract
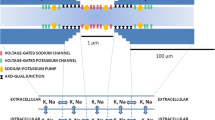
The aim of this study is to investigate the membrane properties (potentials and axonal excitability indices) in the case of myelin wrap reduction (96%) in one, two and three consecutive internodes along the length of human motor nerve fibre. The internodally focally demyelinated cases (termed as IFD1, IFD2 and IFD3, respectively, with one, two and three demyelinated internodes are simulated using our previous double cable model of the fibre. The progressively greater increase of focal loss of myelin lamellae blocks the invasion of the intracellular potentials into the demyelinated zones. For all investigated cases, the radial decline of the extracellular potential amplitudes increases with the increase of the radial distance and demyelination, whereas the electrotonic potentials show a decrease in the slow part of the depolarizing and hyperpolarizing responses. The time constants are shorter and the rheobases higher for the IFD2 and IFD3 cases than for the normal case. In the recovery cycles, the same cases have less refractoriness, greater supernormality and less late subnormality than the normal case. The simulated membrane abnormalities can be observed in vivo in patients with demyelinating forms of Guillain-Barré syndrome. The study provides new information about the pathophysiology of acquired demyelinating neuropathies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birouk, N., Gouider, R., Le Guern, E., Gugenheim, M., Tardieu, S., Maisonobe, T., Le Forestier, N., Agid, Y., Brice, A. and Bouche, P.: Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Type 1A with 17p11.2 Duplication. Clinical and Electrophysiological Phenotype Study and Factors Influencing Disease Severity in 119 Cases, Brain 120 (1997), 813–823.
Dyck, P.J., Chance, P., Lebo, R. and Camey, A.J.: Hereditary Motor and Sensory Neuropathies. In: Dyck P.J., Thomas, P.K., Griffin, J.W., Low P.A., Poduslo, J.F. (eds.) Peripheral Neuropathy, 3rd edn. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, 1993, pp.1094–1136.
Choudhury, D. and Arora: Axonal Guillain-Barré Syndrome: A Critical Review, Acta Neurol. Scan. 103 (2001), 267–277.
Feasby, T.E., Gilbert, J.J., Brown, W.F., Bolton, C.F., Hahn, A.F., Koopman, W.F. and Zochodne, D.W.: An Acute Axonal form of Guillain-Barré Polyneuropathy, Brain 109 (1986), 1115–1126.
Griffin, J.W., Li, C.Y., Ho, T.W., Xue, P., Macko, C., Gao, C.Y., Yang, C., Tian, M., Mishu, B. and Cornblath, D.R.: Guillain-Barré Syndrome in Northern China. The Spectrum of Neuropathological Changes in Clinically Defined Cases, Brain 118 (1995), 575–595.
Kaji, R.: Physiology of Conduction Block in Multifocal Motor Neurophathy and Other Demyelinating Neuropathies, Muscle Nerve 27 (2003), 285–296.
Priori, A., Bossi, B., Ardolino, G., Bertolasi, L., Carpo, M., Nobile-Orazio, E. and Barbieri, S.: Pathophysiological Heterogeneity of Conduction Blocks in Multifocal Motor Neuropathy, Brain 128 (2005), 1642–1648.
Kiernan, M.C., Guglielmi, J.M., Kaji, R., Murray, N. M.F. and Bostock, H.: Evidence for Axonal Membrane Hyperpolarization in Multifocal Motor Neuropathy with Conduction Block, Brain 125 (2002), 664–675.
Kuwabara, S., Bostock, H., Ogawara, K., Sung, J.Y., Kanai, K., Mori, M., Hattori, T. and Burke, D.: The Refractory Period of Transmission is Impaired in Axonal Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Muscle Nerve 28 (2003), 683–689.
Kuwabara, S., Ogawara, K., Sung, J.Y., Mori, M., Kanai, K., Hattori, T., Yuki, N., Lin, C.S., Burke, D. and Bostock, H.: Differences in Membrane Properties of Axonal and Demyelinating Guillain-Barré Syndromes, Ann. Neurol. 52 (2002), 180–187.
Nodera, H., Bostock, H., Kuwabara, S., Sakamoto, T., Asanuma, K., Sung, J.Y., Ogawara, K., Hattori, N., Hirayama, M., Sobue, G. and Kaji, R.: Nerve Excitability Properties in Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Type A1, Brain 127 (2004), 203–211.
Sung, J.Y., Kuwabara, S., Kaji, R., Ogawara, K., Mori, M., Kanai, K., Nodera, H., Hattori, T. and Bostock, H.: Threshold Electrotonus in Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy: Correlation with Clinical Profiles, Muscle Nerve 29 (2004), 28–37.
Stephanova, D.I. and Daskalova, M.: Extracellular Potentials of Human Motor Myelinated Nerve Fibers in Normal Case and in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, Electromyogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 42 (2002), 443–448.
Stephanova, D.I. and Daskalova, M.: Differences in Potentials and Excitability Properties in Simulated Cases of Demyelinating Neuropathies. Part II. Paranodal demyelination. Clin. Neurophysiol, 116 (2005), 1159–1166.
Stephanova, D.I. and Daskalova, M.: Differences in Potentials and Excitability Properties in Simulated Cases of Demyelinating Neuropathies. Part III. Paranodal Internodal Demyelination, Clin. Neurophysiol. 116 (2005), 2334–2341.
Stephanova, D.I., Daskalova, M. and Alexandrov, A.S.: Differences in Potentials and Excitability Properties in Simulated Cases of Demyelinating Neuropathies. Part I, Clin. Neurophysiol. 116 (2005),1153–1158.
Stephanova, D.I., Daskalova, M. and Alexandrov, A.S.: Differences in Membrane Properties in Simulated Cases of Demyelinating Neuropathies: Internodal Focal Demyelinations Without Conduction Block, J. Biol. Phys. (2006), DOI: 10.1007/s10867-006-9001-9.
Stephanova, D.I. and Bostock, H.: A Distributed-Parameter Model of the Myelinated Human Motor Nerve Fibre: Temporal and Spatial Distributions of Action Potentials and Ionic Currents. Biol. Cybern. 73 (1995), 275–280.
Stephanova, D.I. and Bostock, H.: A Distributed-Parameter Model of the Myelinated Human Motor Nerve Fibre: Temporal and Spatial Distributions of Electrotonic Potentials and Ionic Currents, Biol. Cybern, 74 (1996), 543–547.
Stephanova, D.I. and Mileva, K.: Different Effects of Blocked Potassium Channels on Action Potentials, Accommodations, Adaptation and Anode Break Excitation in Human Motor and Sensory Myelinated Nerve Fibres: Computer Simulations, Biol. Cybern. 83 (2000), 161–167.
Bostock, H., Baker, M. and Reid, G.: Changes in Excitability of Human Motor Axons Underlying Post-Ischaemic Fasciculations: Evidence for Two Stable States, J. Physiol. (Lond.) 441 (1991), 537–557.
Scholz, A., Reid, G., Vogel, W. and Bostock H.: Ion Channels in Human Axons, J. Neurophysiol, 70 (1993), 1274–1279.
Schwarz, J.R., Reid, G. and Bostock, H.: Action Potentials and Membrane Currents in the Human Node of Ranvier, Pflügers Arch. 430 (1995), 283–292.
Chiu, S.Y., Ritchie, J.M., Rogart, R. B. and Stagg, D.: A Quantitative Description of Membrane Current in Rabbit Myelinated Nerve, J. Physiol. (Lond.) 292 (1979), 149–166.
Brismar T.: Potential Clamp Analysis of Membrane Currents in Rat Myelinated Nerve Fibres, J. Physiol. (Lond) 298 (1980), 171–184.
Neumcke, B. and Stämpftly, R.: Sodium Currents and Sodium Current Fluctuation in Rat Myelinated Nerve Fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond) 329 (1982), 163–184.
Schwarz, J.R. and Eikhof, G.: Na Currents and Action Potentials in Rat Myelinated Nerve Fibres at 20 and 37 ∘C, Pflügers Arch. 409 (1987), 569–577.
Stephanova, D.I., Trayanova, N., Gydikov, A. and Kossev, A.: Extracellular Potentials of a Single Myelinated Nerve Fiber in An Unbounded Volume Conductor, Biol. Cybern. 61 (1989), 205–210.
Bostock, H. and Rothwell, J.C.: Latent Addition in Motor and Sensory Fibres of Human Peripheral Nerve, J. Physiol. (Lond) 498 (1997), 277–294.
Dimitrov, A.G.: Internodal Sodium Channels Ensure Active Processes Under Myelin Manifesting in Depolarizing Afterpotentials. J. Theor. Biol 235 (2005), 451–462.
Halter, J. and Clark, J.: A Distributed-Parameter Model of the Myelinated Nerve Fibre, J. Theor. Biol. 148 (1991), 345–382.
Stephanova, D. and Kossev, A.: Action Potentials and Ionic Currents Through Internodally Demyelinated Human Motor Nerve Fibres: I. Computer Simulations, Comp. Rend. l'Acad. Bulg. Sci. 50(3) (1997), 107–110.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stephanova, D.I., Daskalova, M.S. & Alexandrov, A.S. Differences in Membrane Properties in Simulated Cases of Demyelinating Neuropathies: Internodal Focal Demyelinations with Conduction Block. J Biol Phys 32, 129–144 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-006-9008-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-006-9008-x