Abstract
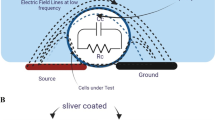
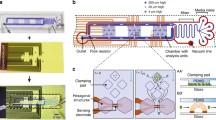
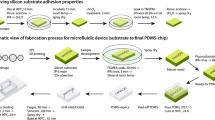
This paper describes the design, modeling, fabrication and characterization MEMS Coulter counter that can detect and monitor the dynamic cell impedance changes in situ as a function of time after mixing isolated cell populations with different extracellular media within 0.3 s from the start of mixing. The novelty of this design is the use of multi-electrodes with vertical sidewalls to enable the measurements of time sensitive cells with significantly enhanced sensitivity as well as the integration of passive mixing, focusing of cells in line and impedance detection using the vertical electrodes on a single chip that is made mainly using multilayer of SU-8, which has not been reported before. The devices were tested with both fluidic and electrical functionality using yeast cells in cryoprotectant agent (diluted dimethyl sulfoxide), red blood cells, microbeads with different dimensions, and dyed fluids. The results demonstrate rapid changes of cell volume within the first 0.6 s after mixing followed by a stable and a fixed cell volume. The micromixer was initially simulated using COMSOL finite element tool. Image processing technique was used to quantitatively evaluate mixing efficiency by analyzing color intensities variation of captured images of 2 dyed fluids mixed in the channel at flow rates between 0.1–0.4 μl/min, the mixing efficiencies were between 87 %–95 %, respectively.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.A. Ateya, J.S. Erickson, P.B. Howell Jr., L.R. Hilliard, J.P. Golden, F.S. Ligler, The good, the bad, and the tiny: a review of micro flow cytometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 391, 1485–1498 (2008)
R. Bernini, E.D. Nuccio, F. Brescia, A. Minardo, L. Zeni, P.M. Sarro, R. Palumbo, M.R. Scarfi, Development and characterization of integrated silicon micro flow cytometer. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 386, 1267–1272 (2006)
C.C. Chang, Z.X. Huang, R.J. Yang, Three-dimensional hydrodynamic focusing in two-layer polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) microchannels. J. Micromech. Microeng. 17, 1479–1486 (2007)
H.T. Chen, Y.N. Wang, Fluorescence detection in a micro flow cytometer without on-chip fibers. Microfluid Nanofluid 4, 689–694 (2008)
H.T. Chen, Y.N. Wang, Optical microflow cytometer for particle counting, sizing and fluorescence detection. Microfluid Nanofluid 6, 529–537 (2009)
W.H. Coulter, US Patent 2,656,508 (1953)
L. Du, J. Zhe, J.E. Carletta, R.J. Veillette, Inductive Coulter counting: detection and differentiation of metal wear particles in lubricant. Smart Mater. Struct. 19, 057001 (2010)
J.M. England, M.C. Down, Measurement of the mean cell volume using electronic particle counters. Br. J. Haematol. 32, 403–410 (1975)
F.U. Gast, P.S. Dittrich, P. Schwille, M. Weigel, M. Mertig, J. Opitz, U. Queitsch, S. Diez, B. Lincoln, F. Wottawah, S. Schinkinger, J. Guck, J. Kas, J. Smolinski, K. Salchert, C. Werner, C. Duschl, M.S. Jager, K. Uhlig, P. Geggier, S. Howitz, The microscopy cell (MicCell), a versatile modular flow through system for cell biology, biomaterial research, and nanotechnology. Microfluid Nanofluid 2, 21–36 (2006)
S. Gawad, L. Schild, P. Renaud, Micromachined impedance spectroscopy flow cytometer for cell analysis and particle sizing. Lab-on-a-Chip 1, 76–82 (2001)
S. Gawad, K. Cheung, U. Seger, A. Bertsch, P. Renaud, Lab Chip 4, 241–251 (2004)
D. Holmes, H. Morgan, N.G. Green, High throughput particle analysis: combining dielectrophoretic particle focusing with confocal optical detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 21, 1621–1630 (2006)
F. Jiang, K.S. Drese, S. Hardt, M. Kupper, F. Schonfeld, Helical flows and chaotic mixing in curved micro channels. A.I.Ch.E. J 50, 2297 (2004)
M. Koch, A.G.R. Evans, A. Brunnschweiler, Design and fabrication of a micromachined Coulter counter. J. Micromech. Microeng. 9, 159–161 (1999)
D. Larsen, G.B. Lankenstein, J. Branebjerg, Microchip coulter particle counter. Transducers’97, 1319–1322 (1997)
S.W. Levin, R.L. Levin, A.K. Solomon, A. Pandiscio, D.H. Kirkwood, Improved stop-flow apparatus to measure permeability of human red cells and ghosts. J. Biochem. Biophys. Meth. 3, 255–272 (1980)
C. Lin, G. Lee, L. Fu, B. Hwey, Vertical focusing device utilizing dielectrophoretic force and its application on microflow cytometer. IEEE Trans. J. MEMS 13, 923–932 (2004)
A.D.C. Macknight, A. Leaf, Regulation of cellular volume. J. Physiology 57, 510–73 (1977)
X. Mao, J.R. Waldeisena, T.J. Huang, Microfluidic drifting implementing three-dimensional hydrodynamic focusing with a single-layer planar microfluidic device. Lab-on-a-Chip 7, 1260–1262 (2007)
J.H. Milgram, A.K. Solomon, Membrane-permeability equations and their solutions for red-cells. J. Membr. Biol. 34, 103–144 (1977)
S. Murali, X. Xia, A.V. Jagtiani, J. Carletta, J. Zhe, Capacitive Coulter counting: detection of metal wear particles in lubricant using a microfluidic device. Smart Mater. Struct. 18, 037001 (2008)
T.N.T. Nguyen, M.C. Kimb, J.S. Park, N.E. Lee, An effective passive microfluidic mixer utilizing chaotic advection. Sensor Actuator B Chem. 132, 172–181 (2008)
J.H. Nieuwenhuis, F. Kohl, J. Bastemeijer, P.M. Sarro, M.J. Vellekoop, Integrated Coulter counter based on 2-dimensional liquid aperture control. Sensor Actuator B Chem. 102, 44–50 (2004)
T. Papanek, The water permeability of the human erythrocyte in the temperature range +25 C to −10 C, PhD thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (1978)
O.A. Saleh, L.L. Sohn, An artificial nanopore for molecular sensing. Nano Lett. 3, 37–38 (2003)
R. Scott, P. Sethu, C.K. Harnett, Three-dimensional hydrodynamic focusing in a microfluidic Coulter counter. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 79, 046104 (2008)
M. Sridhar, D. Xu, Y. Kang, A.B. Hmelo, L.C. Feldman, D. Li, D. Li, Experimental characterization of a metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor-based Coulter counter. J. Appl. Phys. 103, 104701 (2008)
N. Sundararajan, M.S. Pio, L.P. Lee, A. Berlin, Three-dimensional hydrodynamic focusing in Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) microchannels. IEEE Trans. J. MEMS. 13, 559–567 (2004)
C. Tsai, H. Hou, L. Fu, An optimal three-dimensional focusing technique for micro-flow cytometers. Microfluid Nanofluid 5, 827–836 (2008)
Z. Wang, O. Hansen, P.K. Petersen, A. Rogeberg, J.P. Kutter, D.D. Bang, A. Wolff, Dielectrophoresis microsystem with integrated flow cytometers for on-line monitoring of sorting efficiency. Electrophoresis 27, 5081–5092 (2006)
J. Zhe, A. Jagtiani, P. Dutta, H. Jun, J. Carletta, A micromachined high throughput Coulter counter for bioparticle detection and counting. J. Micromech. Microeng. 17, 304 (2007)
S. Zheng, Y.C. Tai, Design and fabrication of a micro coulter counter with thin film electrodes. Proceedings of 2006 International Conference on Microtechnologies in Medicine and Biology. 16–19 (2006)
S. Zheng, M. Liu, Y.C. Tai, Micro coulter counters with platinum black electroplated electrodes for human blood cell sensing. Biomed. Microdev. 10, 221–231 (2008a)
S. Zheng, M.S. Nandra, C.Y. Shih, W. Li, Y.C. Tai, Resonance impedance sensing of human blood cells. Sensor Actuator Phys. 145, 29–36 (2008b)
S. Zheng, Y.C. Tai, Design and fabrication of amicro coulter counter with thin film electrodes. Proceedings of 2006 International Conference on Microtechnologies in Medicine and Biology. 16–19 (2006c)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Benson, J.D. & Almasri, M. Micromachined Coulter counter for dynamic impedance study of time sensitive cells. Biomed Microdevices 14, 739–750 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-012-9655-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-012-9655-6