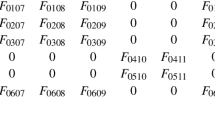Abstract
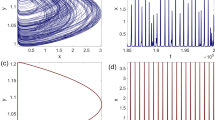
A simple mathematical model for the dynamics of network-bundle transitions in actin filaments has been previously proposed and some of its mathematical properties have been described. Other models in this class have since been considered and investigated mathematically. In this paper, we have made the first steps in connecting parameters in the model with biologically measurable quantities such as published values of rate constants for filament-crosslinker association. We describe how this connection was made, and give some preliminary numerical simulation results for the behavior of the model under biologically realistic parameter regimes. A key result is that filament length influences the bundle-network transition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberts, B, D. Bray, J. Lewis, M. Raff, M. Roberts and J. D. Watson (1989). Molecular Biology of the Cell. New York: Garland.
Bray, D. (1992). Cell Movements. New York: Garland.
Burridge K. and J. R. Feramisco (1981). Non-muscle α-actinins are Calcium-sensitive Actin-binding Proteins. Nature 294, 565–567.
Civelekoglu, G. and L. Edelstein-Keshet (1994). Models for the formation of actin structures. Bull. Math. Biol. 56, 587–616.
Colombo, R., I. DalleDonne and A. Milzani (1993) α-Actinin Increases Actin Filament End Concentration by Inhibiting Annealing. J. Mol. Biol. 230, 1151–1158.
Coppin, C. M. and P. Leavis (1992). Quantitation of liquid-crystaline ordering in F-actin solutions. Biophys J. 63, 794–807.
Doi, M. and S. F. Edwards (1986). The Theory of Polymer Dynamics, Oxford: Clarendon Press.
Edelstein-Keshet, L. and G. B. Ermentrout (1990). Models for contact-mediated pattern formation: cells that form parallel arrays. J. Math. Biol. 29, 33–58.
Edelstein-Keshet, L. and G. B. Ermentrout (1998). Models for the length distribution of actin filaments: I Simple polymerization and fragmentation acting alone. Bull. Math. Biol., in press.
Ermentrout, G. B. and L. Edelstein-Keshet (1998). Models for the length distribution of actin filaments: II: Polymerization and Fragmentation by Gelsolin acting together. Bull. Math. Biol., in press.
Furukawa, R., R. Kundra and M. Fechheimer (1993). Formation of liquid crystals from actin filaments. Biochemistry 32, 12346–12352.
Geigant, E., K. Ladizhansky and A. Mogilner (1997). Integro-differential model for orientational distribution of F-actin in cells. SIAM J. Appl. Math., in press.
Geigant, E. and M. Stoll, (1996). A non-local model for alignment of oriented particles. Research Summary. Bonn University.
Giuliano, K. A. and D. L. Taylor (1995). Measurement and manipulation of cytoskeletal dynamics in living cells. Current Opinion Cell Biol. 7, 4–12.
Gorlin, J. B., R. Yamin, S. Eagen, M. Stewart, T. P. Stossel, D. J. Kwiatkowski and J. H. Hartwig (1990). Human endothelial actin-binding protein (ABP-280, nonmuscle filamin): a molecular leaf spring. J. Cell. Biol. 111, 1089–1105.
Hartwig, J. H. and D. J. Kwiatkowski (1991). Actin binding proteins. Current Opinion Cell Biol. 3, 87–97.
Hartwig, J. H., J. Tyler and T. P. Stossel (1980). Actin-binding protein promotes the bipolar and perpendicular branching of actin filaments. J. Cell. Biol. 87, 841–848.
Jacquez J. A. (1972). Compartmental Analysis in Biology and Medicine, Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Janmey, P. A., S. Hvidt, J. Käs, D. Lerche, A. Maggs, E. Sackmann, M. Schliwa and T. P. Stossel (1994). The Mechanical Properties of Actin Gels. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 32503–32513.
Janmey, P. A., J. Peetermans, K. S. Zaner, T. P. Stossel and T. Tanaka (1986). Structure and Mobility of actin filaments as measured by quasielectric light scattering, viscometry and electron microscopy. J. Biol. Chem. 261, 8357–8362.
Janson, L. W. and D. L. Taylor (1994). Actin-crosslinking protein regulation of filament movement in motility assays: a theoretical model. Biophys. J. 67, 973–982.
Jockusch, B. M. and G. Isenberg (1981). Interaction of α-Actinin and Vinculin with Actin: Opposite effects on Filament Network Formation. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA. 78, 3005–3009.
Ladizhansky, K. (1994). Distribution of generalized aspect with applications to actin fibers and social interactions, Technical Report, MSc thesis Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, Israel.
Luby-Phelps, K. (1994). Physical Properites of Cytoplasm. Current Opinion Cell Biol. 6, 3–9.
Lumsden, C. J. and P. A. Dufort (1993). Cellular Automaton Model of the Actin Cytoskeleton. Cell Motil. Cytoskel. 25, 87–104.
McGough, A. (1997). Structural Studies of Gelsolin: Actin Interactions, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, http://dali.bcm.tmc.edu/amy/Gelsolin.html.
Maciver, S. K., D. H. Wachsstock, W. H. Schwarz and T. D. Pollard (1991). The actin filament severing protein acotophorin promotes the formation of rigid bundles of actin filaments crosslinked with α-actinin. J. Cell Biol. 115, 1621–1628.
Meyer, R. K. and U. Aebi (1990). Bundling of actin filaments by α-actinin depends on its molecular length. J. Cell Biol. 110, 2013–2024.
Mogilner, A. and L. Edelstein-Keshet (1995). Selecting a common direction I. How orientational order can arise from simple contact responses between interacting cells. J. Math. Biol. 33, 619–660.
Mogilner, A. and L. Edelstein-Keshet (1996). Spatio-angular order in populations of self-aligning objects: formation of oriented patches. Physica D89, 346–367.
Niederman, R. R., P. C. Amrein and J. Hartwig (1983). Three-dimensional structure of actin filaments and of an actin gel made with actin-binding protein. J. Cell. Biol. 96, 1400–1413.
Oster, G. F. (1994). Biophysics of Cell Motility, Lecture Notes, University of California Berkeley.
Otto, J. J. (1994). Actin-bundling proteins. Current Opinion Cell Biol. 6, 105–109.
Parfenov, V. N., D. S. Davis, G. N. Pochukalina, C. E. Sample, E. A. Bugaeva and K. G. Murti (1995). Nuclear actin filaments and their topological changes in frog oocytes. Exp. Cell Res. 217, 385–394.
Suzuki, A., T. Maeda and T. Ito (1991). Formation of liquid crystalline phase of actin filament solutions and its dependence on filament length as studied by optical birefringence. Biophys. J. 59, 25–30.
Taylor, K. A. and D. W. Taylor (1994). Formation of two-dimensional complexes of F-Actin and crosslinking proteins on Lipid monolayers: demonstration of unipolar α-actinin—F-actin crosslinking. Biophys. J. 67, 1976–1983.
Wachsstock, D. H., W. H. Schwarz and T. D. Pollard (1993). Affinity of α—Actinin for actin determines the structure and mechanical properties of actin filament gels. Biophys. J., 65, 205–214.
Wachsstock, D. H., W. H. Schwarz and T. D. Pollard (1994). Cross—linker dynamics determine the mechanical properties of actin gels. Biophys. J. 66, 801–809.
Zaner, K. S. (1995). Physics of actin networks. I. Rheology of semi-dilute F-Actin. Biophys. J. 68, 1019–1026.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spiros, A., Edelstein-Keshet, L. Testing a model for the dynamics of actin structures with biological parameter values. Bull. Math. Biol. 60, 275–305 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1006/bulm.1997.0022
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/bulm.1997.0022