Abstract
The undoped and iron doped tin oxide thin films were deposited on glass substrates by sol-gel dip coating technique, using tin chloride and iron III chloride as the starting materials. The effect of method conditions and Fe doping on the structural, morphological and optical properties of applied thin films have been studied by X-ray diffraction (XRD), and UV–vis spectroscopy. Surface topography of thin films was examined by atomic force microscopy (AFM).
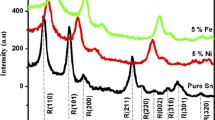
XRD patterns showed an increase in peak intensities of the rutile and cubic crystalline phases of SnO2 by increasing the Fe content. SnO2 nanoparticles in the range of 9–20 nm size were obtained by the Scherrer equation using FWHM (Full Width at Half Maximum) values of the main peaks in the XRD diffraction pattern when calcined at 500 °C.
The UV–Vis–spectroscopy analyses have shown that all the thin films were transparent in the visible region with an average transmittance ranging from 70% to 87%. And showed a direct band gap reducing with increase in Fe3+ doping from 3.82 to 3.72 eV.
AFM images shown thin films with different contents of Fe. The effect of Fe concentration has been discussed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Demichelis, F., Minetti-Mezzetti, E., Tagliaferro, A., Tresso, E.: Determination of optical properties of SnO2 films. In: II Nuovo Cimento D, vol. 4, pp. 68–78 (1984)
Kotz, R., Stucki, S., Carcer, B.: Electrochemical waste water treatment using high overvoltage anodes. Part1: Physical and electrochemical properties of SnO2 anodes. J. Appl. Electrochem. 21, 14–20 (1991)
Takahata, K.: Tin dioxide sensors development and applications. Chem. Sens. Technol. 1, 39–55 (1988)
Shang, G., Wu, J., Huang, M., Lin, J., Lan, Z., Huang, Y., Fan, L.: Facile synthesis of mesoporous tin oxide spheres and their applications in dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 116(38), 20140–20145 (2012)
Fukano, T., Motohiro, T., Ida, T., Hashizume, H.: Ionization potentials of transparent conductive indium tin oxide films covered with a single layer of fluorine-doped tin oxide nanoparticles grown by spray pyrolysis deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 084314 (2005)
Patil, G.E., Kajale, D.D., Gaikwad, V.B., Jain, G.H.: Preparation and characterization of SnO2 nanoparticles by hydrothermal route. Int. Nano Lett. 2, 17 (2012)
Haines, J., Leger, J.M.: X-ray diffraction study of the phase transitions and structural evolution of tin dioxide at high pressure: relationships between structure types and implications for other rutile-type dioxides. Phys. Rev. B 55, 11144 (1997)
Junbo, W., Ming, Y., Yingmin, L., Licheng, C., Yan, Z., Bingjun, D.: Synthesis of Fe-doped nanosized SnO2 powders by chemical co-precipitation method. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 351, 228–232 (2005)
Sakuma, J., Nomura, K., Barrero, C., Takeda, M.: Mössbauer studies and magnetic properties of SnO2 doped with 57Fe. Thin Solid Films 515, 8653–8655 (2007)
Khodja, S., Touam, T., Chelouche, A., Boudjouan, F.: Effects of stabilizer ratio on structural, morphological, optical and waveguide properties of ZnO nano-structured thin films by a sol–gel process. Superlattices Microstruct. 75, 485–495 (2014)
Martinez, D.Y.T., Perez, R.C., Delgado, G.T., Angel, O.Z.: Structural, morphological, optical and photocatalytic characterization of ZnO–SnO2 thin films prepared by the sol–gel technique. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 235, 49–55 (2012)
Pankove, J.I.: Optical Processes in Semiconductors. Prentice-Hall Inc., Englewoord Cliffs (1971)
Shajira, P.S., Junaid Bushiri, M., Nair, B.B., Ganesh Chandra, P.V.: Energy band structure investigation of blue and green light emitting Mg doped SnO2 nanostructures synthesized by combustion method. J. Lumin. 145, 425–429 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Benkara, S., Ghamri, H., Zaabat, M. (2018). Study of Structural, Morphological and Optical, Properties of Fe Doped SnO2 Semiconductor Thin Films Prepared by Sol-Gel Technique. In: Abdelbaki, B., Safi, B., Saidi, M. (eds) Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on Materials and Sustainable Development. SMSD 2017. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-89707-3_71
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-89707-3_71
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-89706-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-89707-3
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)