Abstract
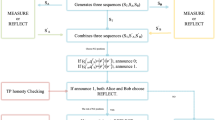
A quantum private comparison is a primitive protocol of secure multiparty quantum computation that enables two parties to privately decide whether x = y or not, given two integers x and y, that are held as private inputs by the two parties, respectively. However, many existing quantum private comparison schemes may not be efficient enough, especially applied in big-data and large-scale network environments, because of low efficiency bit-by-bit comparisons. In this paper, we present a novel and efficient quantum private comparison scheme. The proposed scheme provides higher communication efficiency because a secret-by-secret comparison instead of a bit-by-bit comparison is used.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. C. Yao, in Proceedings of 23rd Annual IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (Washington, DC, USA, Nov. 3–5, 1982), p. 160.
C. H. Bennett and G. Brassard, in Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems, and Signal Processing (Bangalore, India, 1984), p. 175.
H. K. Lo, Phys. Rev. A 56, 1154 (1997).
R. Colbeck, Phys. Rev. A 76, 062308 (2007).
H. Buhrman, M. Christandl and C. Schaffner, Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 160501 (2012).
Y. G. Yang and Q. Y. Wen, J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 42, 055305 (2009).
W. W. Zhang, D. Li, K. J. Zhang and H. J. Zuo, Quantum Inf. Process 12, 2241 (2013).
Y. J. Chang, C. W. Tsai and T. Hwang, Quantum Inf. Process 12, 1077 (2013).
Y. B. Li et al., Quantum Inf. Process 12, 2191 (2013).
Y. B. Li et al., Int. J. Theor. Phys. 52, 2818 (2013).
W. W. Zhang, D. Li, T. T. Song and Y. B. Li, Int. J. Theor. Phys. 52, 1466 (2013).
Z. W. Sun and D. Y. Long, Int. J. Theor. Phys. 52, 212 (2013).
S. Lin, Y. Sun, X. F. Liu and Z. Q. Yao, Quantum Inf. Process 12, 559 (2013).
Q. B. Luo et al., Quantum Inf. Process 13, 2343 (2014).
Q. L. Wang, H. X. Sun and W. Huang, Quantum Inf. Process 13, 2375 (2014).
J. Lin, C. W. Yang and T. Hwang, Quantum Inf. Process 13, 239 (2014).
Z. W. Sun et al., Quantum Inf. Process 14, 2125 (2015).
G. P. He, Int. J. Quantum Inf. 15, 1750014 (2017).
H. M. Pan, Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57, 3389 (2018).
G. P. He, Int. J. Quantum Inf. 11, 1350025 (2013).
Z. J. Diao, C. F. Huang and K. Wang, Acta Appl. Math. 118, 147 (2012).
W. Yang, L. S. Huang, R. H. Shi and L. B. He, Quantum Inf. Process 12, 2465 (2013).
H. Barnum et al., in Proceedings of the 43rd Annual IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (FOCS), edited by C. M. Danielle (Vancouver, BC, Canada, Nov. 19, 2002).
D. Aharonov, M. Ben-Or and E. Eban, https://arxiv.org/abs/0810.5375v2.
K. F. Yu et al., Quantum Inf. Process 13, 1457 (2014).
D. J. Guan, Y. J. Wang and E. S. Zhuang, Quantum Inf. Process 13, 2355 (2014).
A. Farouk et al., Sci. Rep. 5, 16080 (2015).
R. H. Shi et al., Sci. Rep. 5, 15914 (2015).
R. H. Shi, Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56, 1208 (2017).
H. F. Wang et al., New J. Phys. 13, 013021 (2011).
X. B. Song et al., Sci. Rep. 5, 14113 (2015).
N. Bent et al., Phys. Rev. X 5, 041006 (2015).
A. Majumder, S. Mohapatra and A. Kumar, https://arxiv.org/pdf/1707.07460.pdf.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61772001), Natural Science Key Fund of Education Department of Anhui Province (No. KJ2018A0823), and Research Project of Hefei Technology College (No. 201814KJB001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Shi, Rh. A Novel and Efficient Quantum Private Comparison Scheme. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 75, 15–21 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.75.15
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.75.15