Abstract
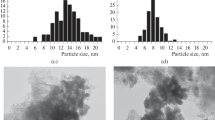
The effect of temperature of calcination of Co catalysts reduced at 400°C on their characteristics (the surface area, degree of reduction, particle size, and average crystallite diameter), was investigated. It was found that an increase in the calcination temperature from 400 to 500°C significantly affects the size of cobalt crystallites. Based on these data, a method for predicting the catalyst stability is proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lapidus, A.L., Izv. Akad. Nauk, Ser. Khim., 1991, no. 12, p. 2681.
Budtsov, V.S., Kuli, T.E., Lapidus, A.L., and Eliseev, O.L., Khim. Tverd. Topliva, 2006, no. 1, p. 65.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.L. Lapidus, V.S. Budtsov, O.L. Eliseev, A.B. Erofeev, 2007, published in Khimiya Tverdogo Topliva, 2007, No. 6, pp. 12–15.
About this article
Cite this article
Lapidus, A.L., Budtsov, V.S., Eliseev, O.L. et al. Prediction of stability of cobalt catalysts for hydrocarbon synthesis from CO and H2 in terms of resistance of cobalt crystallites against high-temperature agglomeration. Soil Fuel Chem. 41, 331–334 (2007). https://doi.org/10.3103/S036152190706002X
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S036152190706002X