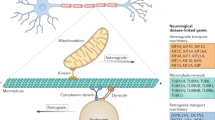
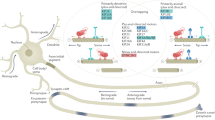
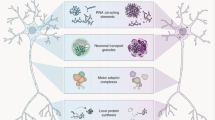
Abstract
Gene products such as organelles, proteins and RNAs are actively transported to synaptic terminals for the remodeling of pre-existing neuronal connections and formation of new ones. Proteins described as molecular motors mediate this transport and utilize specialized cytoskeletal proteins that function as molecular tracks for the motor based transport of cargos. Molecular motors such as kinesins and dynein’s move along microtubule tracks formed by tubulins whereas myosin motors utilize tracks formed by actin. Deficits in active transport of gene products have been implicated in a number of neurological disorders. We describe such disorders collectively as “transportopathies”. Here we review current knowledge of critical components of active transport and their relevance to neurodegenerative diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hirokawa N., Niwa S., Tanaka Y., Molecular motors in neurons: transport mechanisms and roles in brain function, development, and disease, Neuron, 2010, 68, 610–638
Chao M. V., Retrograde transport redux, Neuron, 2003, 39, 1–2
Ikenaka K., Katsuno M., Kawai K., Ishigaki S., Tanaka F., Sobue G., Disruption of axonal transport in motor neuron diseases, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2012, 13, 1225–1238
Hollenbeck P. J., Saxton W. M., The axonal transport of mitochondria, J. Cell Sci., 2005, 118, 5411–5419
Caviston J. P., Holzbaur E. L., Microtubule motors at the intersection of trafficking and transport, Trends Cell Biol., 2006, 16, 530–537
Hirokawa N., Takemura R., Molecular motors and mechanisms of directional transport in neurons, Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 2005, 6, 201–214
Verhey K. J., Rapoport T. A., Kinesin carries the signal, Trends Biochem. Sci., 2001, 26, 545–550
Gunawardena S., Goldstein L. S., Cargo-carrying motor vehicles on the neuronal highway: transport pathways and neurodegenerative disease, J. Neurobiol., 2004, 58, 258–271
Kardon J. R., Vale R. D., Regulators of the cytoplasmic dynein motor, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol., 2009, 10, 854–865
Kapitein L. C., Hoogenraad C. C., Which way to go? Cytoskeletal organization and polarized transport in neurons, Mol. Cell. Neurosci., 2011, 46, 9–20
Conde C., Caceres A., Microtubule assembly, organization and dynamics in axons and dendrites, Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 2009, 10, 319–332
Signor D., Scholey J. M., Microtubule-based transport along axons, dendrites and axonemes, Essays Biochem., 2000, 35, 89–102
Black M. M., Baas P. W., The basis of polarity in neurons, Trends Neurosci., 1989, 12, 211–214
Zheng Y., Wong M. L., Alberts B., Mitchison T., Nucleation of microtubule assembly by a gamma-tubulin-containing ring complex, Nature, 1995, 378, 578–583
Schuyler S. C., Pellman D., Microtubule “plus-end-tracking proteins”: The end is just the beginning, Cell, 2001, 105, 421–424
Galjart N., Plus-end-tracking proteins and their interactions at microtubule ends, Curr. Biol., 2010, 20, R528–537
Dehmelt L., Halpain S., The MAP2/Tau family of microtubuleassociated proteins, Genome Biol., 2005, 6, 204
Halpain S., Dehmelt L., The MAP1 family of microtubule-associated proteins, Genome Biol., 2006, 7, 224
Caceres A., Kosik K. S., Inhibition of neurite polarity by tau antisense oligonucleotides in primary cerebellar neurons, Nature, 1990, 343, 461–463
Caceres A., Mautino J., Kosik K. S., Suppression of MAP2 in cultured cerebellar macroneurons inhibits minor neurite formation, Neuron, 1992, 9, 607–618
Harada A., Oguchi K., Okabe S., Kuno J., Terada S., Ohshima T., et al., Altered microtubule organization in small-calibre axons of mice lacking tau protein, Nature, 1994, 369, 488–491
Hirokawa N., Kinesin and dynein superfamily proteins and the mechanism of organelle transport, Science, 1998, 279, 519–526
Brady S. T., A novel brain ATPase with properties expected for the fast axonal transport motor, Nature, 1985, 317, 73–75
Vale R. D., Reese T. S., Sheetz M. P., Identification of a novel forcegenerating protein, kinesin, involved in microtubule-based motility, Cell, 1985, 42, 39–50
Aizawa H., Sekine Y., Takemura R., Zhang Z., Nangaku M., Hirokawa N., Kinesin family in murine central nervous system, J. Cell Biol., 1992, 119, 1287–1296
Lawrence C. J., Dawe R. K., Christie K. R., Cleveland D. W., Dawson S. C., Endow S. A., et al., A standardized kinesin nomenclature, J. Cell Biol., 2004, 167, 19–22
Brady S. T., Molecular motors in the nervous system, Neuron, 1991, 7, 521–533
Goldstein L. S., Yang Z., Microtubule-based transport systems in neurons: the roles of kinesins and dyneins, Annu. Rev. Neurosci., 2000, 23, 39–71
Goldstein L. S., Molecular motors: from one motor many tails to one motor many tales, Trends Cell Biol., 2001, 11, 477–482
Goldstein L. S., Kinesin molecular motors: transport pathways, receptors, and human disease, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2001, 98, 6999–7003
Hirokawa N., mRNA transport in dendrites: RNA granules, motors, and tracks, J. Neurosci., 2006, 26, 7139–7142
Goldstein A. Y., Wang X., Schwarz T. L., Axonal transport and the delivery of pre-synaptic components, Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 2008, 18, 495–503
Puthanveettil S. V., Monje F. J., Miniaci M. C., Choi Y. B., Karl K. A., Khandros E., et al., A new component in synaptic plasticity: upregulation of kinesin in the neurons of the gill-withdrawal reflex, Cell, 2008, 135, 960–973
Gibbons I. R., Rowe A. J., Dynein: a protein with adenosine triphosphatase activity from cilia, Science, 1965, 149, 424–426
Burns R. G., Pollard T. D., A dynein-like protein from brain, FEBS Lett., 1974, 40, 274–280
Vallee R. B., Shpetner H. S., Paschal B. M., The role of dynein in retrograde axonal transport, Trends Neurosci., 1989, 12, 66–70
Vale R. D., The molecular motor toolbox for intracellular transport, Cell, 2003, 112, 467–480
McGrath J. L., Dynein motility: four heads are better than two, Curr. Biol., 2005, 15, R970–972
King S. J., Schroer T. A., Dynactin increases the processivity of the cytoplasmic dynein motor, Nat. Cell Biol., 2000, 2, 20–24
Susalka S. J., Pfister K. K., Cytoplasmic dynein subunit heterogeneity: implications for axonal transport, J. Neurocytol., 2000, 29, 819–829
Vallee R. B., Williams J. C., Varma D., Barnhart L. E., Dynein: An ancient motor protein involved in multiple modes of transport, J. Neurobiol., 2004, 58, 189–200
Fifkova E., Delay R. J., Cytoplasmic actin in neuronal processes as a possible mediator of synaptic plasticity, J. Cell Biol., 1982, 95, 345–350
Luo L., Actin cytoskeleton regulation in neuronal morphogenesis and structural plasticity, Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol., 2002, 18, 601–635
Hotulainen P., Hoogenraad C. C., Actin in dendritic spines: connecting dynamics to function, J. Cell Biol., 2010, 189, 619–629
dos Remedios C. G., Chhabra D., Kekic M., Dedova I. V., Tsubakihara M., Berry D. A., et al., Actin binding proteins: regulation of cytoskeletal microfilaments, Physiol. Rev., 2003, 83, 433–473
Puszkin S., Berl S., Puszkin E., Clarke D. D., Actomyosin-like protein isolated from mammalian brain, Science, 1968, 161, 170–171
Puszkin S., Nicklas W. J., Berl S., Actomyosin-like protein in brain: subcellular distribution, J. Neurochem., 1972, 19, 1319–1333
Bridgman P. C., Myosin-dependent transport in neurons, J. Neurobiol., 2004, 58, 164–174
Bridgman P.C., Elkin L. L., Axonal myosins, J. Neurocytol., 2000, 29, 831–841
Sellers J. R., Myosins: a diverse superfamily, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2000, 1496, 3–22
Titus M. A., Myosins, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 1993, 5, 77–81
Foth B. J., Goedecke M. C., Soldati D., New insights into myosin evolution and classification, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2006, 103, 3681–3686
Dunn B. D., Sakamoto T., Hong M. S., Sellers J. R., Takizawa P. A., Myo4p is a monomeric myosin with motility uniquely adapted to transport mRNA, J. Cell Biol., 2007, 178, 1193–1206
Harrington W. F., Burke M., Geometry of the myosin dimer in highsalt media. I. Association behavior of rod segments from myosin, Biochemistry, 1972, 11, 1448–1455
Saitoh T., Takemura S., Ueda K., Hosoya H., Nagayama M., Haga H., et al., Differential localization of non-muscle myosin II isoforms and phosphorylated regulatory light chains in human MRC-5 fibroblasts, FEBS Lett., 2001, 509, 365–369
Vibert P., Cohen C., Domains, motions and regulation in the myosin head, J. Muscle Res. Cell. Motil., 1988, 9, 296–305
Krendel M., Mooseker M.S., Myosins: tails (and heads) of functional diversity, Physiology (Bethesda), 2005, 20, 239–251
Syamaladevi D. P., Spudich J. A., Sowdhamini R., Structural and functional insights on the Myosin superfamily, Bioinform. Biol. Insights, 2012, 6, 11–21
Wang Z., Edwards J. G., Riley N., Provance D. W. Jr., Karcher R., Li X. D., et al., Myosin Vb mobilizes recycling endosomes and AMPA receptors for postsynaptic plasticity, Cell, 2008, 135, 535–548
Wagner W., Brenowitz S. D., Hammer J. A. 3rd, Myosin-Va transports the endoplasmic reticulum into the dendritic spines of Purkinje neurons, Nat. Cell Biol., 2011, 13, 40–48
Phichith D., Travaglia M., Yang Z., Liu X., Zong A. B., Safer D., et al., Cargo binding induces dimerization of myosin VI, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2009, 106, 17320–17324
Seabrooke S., Qiu X., Stewart B. A., Nonmuscle Myosin II helps regulate synaptic vesicle mobility at the Drosophila neuromuscular junction, BMC Neurosci., 2010, 11, 37
Gavin C. F., Rubio M. D., Young E., Miller C., Rumbaugh G., Myosin II motor activity in the lateral amygdala is required for fear memory consolidation, Learn. Mem., 2011, 19, 9–14
Rex C. S., Gavin C. F., Rubio M. D., Kramar E. A., Chen L. Y., Jia Y., et al., Myosin IIb regulates actin dynamics during synaptic plasticity and memory formation, Neuron, 2010, 67, 603–617
Hu X., Viesselmann C., Nam S., Merriam E., Dent E. W., Activitydependent dynamic microtubule invasion of dendritic spines, J. Neurosci., 2008, 28, 13094–13105
Maas C., Belgardt D., Lee H. K., Heisler F. F., Lappe-Siefke C., Magiera M. M., et al., Synaptic activation modifies microtubules underlying transport of postsynaptic cargo, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2009, 106, 8731–8736
Hoogenraad C. C., Bradke F., Control of neuronal polarity and plasticity—a renaissance for microtubules?, Trends Cell Biol., 2009, 19, 669–676
Holzbaur E. L., Scherer S. S., Microtubules, axonal transport, and neuropathy, N. Engl. J. Med., 2011, 365, 2330–2332
Cambray-Deakin M. A., Burgoyne R. D., Posttranslational modifications of alpha-tubulin: acetylated and detyrosinated forms in axons of rat cerebellum, J. Cell Biol., 1987, 104, 1569–1574
Audebert S., Koulakoff A., Berwald-Netter Y., Gros F., Denoulet P., Edde B., Developmental regulation of polyglutamylated alpha- and betatubulin in mouse brain neurons, J. Cell Sci., 1994, 107, 2313–2322
Mansfield S. G., Gordon-Weeks P. R., Dynamic post-translational modification of tubulin in rat cerebral cortical neurons extending neurites in culture: effects of taxol, J. Neurocytol., 1991, 20, 654–666
Billingsley M. L., Kincaid R. L., Regulated phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of tau protein: effects on microtubule interaction, intracellular trafficking and neurodegeneration, Biochem. J., 1997, 323, 577–591
Perdiz D., Mackeh R., Pous C., Baillet A., The ins and outs of tubulin acetylation: more than just a post-translational modification?, Cell. Signal., 2011, 23, 763–771
Janke C., Kneussel M., Tubulin post-translational modifications: encoding functions on the neuronal microtubule cytoskeleton, Trends Neurosci., 2010, 33, 362–372
Fukushima N., Furuta D., Hidaka Y., Moriyama R., Tsujiuchi T., Posttranslational modifications of tubulin in the nervous system, J. Neurochem., 2009, 109, 683–693
Reed N. A., Cai D., Blasius T. L., Jih G. T., Meyhofer E., Gaertig J., et al., Microtubule acetylation promotes kinesin-1 binding and transport, Curr. Biol., 2006, 16, 2166–2172
Westermann S., Weber K., Post-translational modifications regulate microtubule function, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 2003, 4, 938–947
Konishi Y., Setou M., Tubulin tyrosination navigates the kinesin-1 motor domain to axons, Nat. Neurosci., 2009, 12, 559–567
Bettencourt da Cruz A., Schwarzel M., Schulze S., Niyyati M., Heisenberg M., Kretzschmar D., Disruption of the MAP1B-related protein FUTSCH leads to changes in the neuronal cytoskeleton, axonal transport defects, and progressive neurodegeneration in Drosophila, Mol. Biol. Cell, 2005, 16, 2433–2442
Fischer M., Kaech S., Knutti D., Matus A., Rapid actin-based plasticity in dendritic spines, Neuron, 1998, 20, 847–854
Matsuzaki M., Honkura N., Ellis-Davies G. C., Kasai H., Structural basis of long-term potentiation in single dendritic spines, Nature, 2004, 429, 761–766
Luo L., Hensch T. K., Ackerman L., Barbel S., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Differential effects of the Rac GTPase on Purkinje cell axons and dendritic trunks and spines, Nature, 1996, 379, 837–840
McIlvain J. M. Jr., Burkhardt J. K., Hamm-Alvarez S., Argon Y., Sheetz M. P., Regulation of kinesin activity by phosphorylation of kinesinassociated proteins, J. Biol. Chem., 1994, 269, 19176–19182
Lindesmith L., McIlvain J. M. Jr., Argon Y., Sheetz M. P., Phosphotransferases associated with the regulation of kinesin motor activity, J. Biol. Chem., 1997, 272, 22929–22933
Sheetz M. P., Motor and cargo interactions, Eur. J. Biochem., 1999, 262, 19–25
Morfini G., Pigino G., Szebenyi G., You Y., Pollema S., Brady S. T., JNK mediates pathogenic effects of polyglutamine-expanded androgen receptor on fast axonal transport, Nat. Neurosci., 2006, 9, 907–916
Stagi M., Gorlovoy P., Larionov S., Takahashi K., Neumann H., Unloading kinesin transported cargoes from the tubulin track via the inflammatory c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway, FASEB J., 2006, 20, 2573–2575
Koushika S. P., “JIP”ing along the axon: the complex roles of JIPs in axonal transport, Bioessays, 2008, 30, 10–14
Blasius T. L., Cai D., Jih G. T., Toret C. P., Verhey K. J., Two binding partners cooperate to activate the molecular motor Kinesin-1, J. Cell Biol., 2007, 176, 11–17
Horiuchi D., Collins C. A., Bhat P., Barkus R. V., Diantonio A., Saxton W. M., Control of a kinesin-cargo linkage mechanism by JNK pathway kinases, Curr. Biol., 2007, 17, 1313–1317
Chang L., Jones Y., Ellisman M. H., Goldstein L. S., Karin M., JNK1 is required for maintenance of neuronal microtubules and controls phosphorylation of microtubule-associated proteins, Dev. Cell, 2003, 4, 521–533
Reynolds C. H., Utton M. A., Gibb G. M., Yates A., Anderton B. H., Stress-activated protein kinase/c-jun N-terminal kinase phosphorylates tau protein, J. Neurochem., 1997, 68, 1736–1744
Tararuk T., Ostman N., Li W., Bjorkblom B., Padzik A., Zdrojewska J., et al., JNK1 phosphorylation of SCG10 determines microtubule dynamics and axodendritic length, J. Cell Biol., 2006, 173, 265–277
Colin E., Zala D., Liot G., Rangone H., Borrell-Pages M., Li X. J., et al., Huntingtin phosphorylation acts as a molecular switch for anterograde/retrograde transport in neurons, EMBO J., 2008, 27, 2124–2134
Schaefer A. W., Schoonderwoert V. T., Ji L., Mederios N., Danuser G., Forscher P., Coordination of actin filament and microtubule dynamics during neurite outgrowth, Dev. Cell, 2008, 15, 146–162
Burnette D. T., Ji L., Schaefer A. W., Medeiros N. A., Danuser G., Forscher P., Myosin II activity facilitates microtubule bundling in the neuronal growth cone neck, Dev. Cell, 2008, pp15, 163–169
Arimura N., Kaibuchi K., Neuronal polarity: from extracellular signals to intracellular mechanisms, Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 2007, 8, 194–205
Dent E. W., Gertler F. B., Cytoskeletal dynamics and transport in growth cone motility and axon guidance, Neuron, 2003, 40, 209–227
Mufson E. J., Kroin J. S., Sendera T. J., Sobreviela T., Distribution and retrograde transport of trophic factors in the central nervous system: functional implications for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, Prog. Neurobiol., 1999, 57, 451–484
Hirokawa N., Noda Y., Intracellular transport and kinesin superfamily proteins, KIFs: structure, function, and dynamics, Physiol. Rev., 2008, 88, 1089–1118
Kandel E. R., The molecular biology of memory storage: a dialogue between genes and synapses, Science, 2001, 294, 1030–1038
Kiebler M. A., DesGroseillers L., Molecular insights into mRNA transport and local translation in the mammalian nervous system, Neuron, 2000, 25, 19–28
Martin K. C., Casadio A., Zhu H., Yaping E., Rose J. C., Chen M., et al., Synapse-specific, long-term facilitation of aplysia sensory to motor synapses: a function for local protein synthesis in memory storage, Cell, 1997, 91, 927–938
Si K., Giustetto M., Etkin A., Hsu R., Janisiewicz A. M., Miniaci M. C., et al., A neuronal isoform of CPEB regulates local protein synthesis and stabilizes synapse-specific long-term facilitation in aplysia, Cell, 2003, 115, 893–904
Martin K. C., Ephrussi A., mRNA localization: gene expression in the spatial dimension, Cell, 2009, 136, 719–730
Tubing F., Vendra G., Mikl M., Macchi P., Thomas S., Kiebler M. A., Dendritically localized transcripts are sorted into distinct ribonucleoprotein particles that display fast directional motility along dendrites of hippocampal neurons, J. Neurosci., 2010, 30, 4160–4170
Lyles V., Zhao Y., Martin K. C., Synapse formation and mRNA localization in cultured Aplysia neurons, Neuron, 2006, 49, 349–356
Raymond C. R., Thompson V. L., Tate W. P., Abraham W. C., Metabotropic glutamate receptors trigger homosynaptic protein synthesis to prolong long-term potentiation, J. Neurosci., 2000, 20, 969–976
Miki H., Okada Y., Hirokawa N., Analysis of the kinesin superfamily: insights into structure and function, Trends Cell Biol., 2005, 15, 467–476
Kanai Y., Dohmae N., Hirokawa N., Kinesin transports RNA: isolation and characterization of an RNA-transporting granule, Neuron, 2004, 43, 513–525
De Vos K. J., Grierson A. J., Ackerley S., Miller C. C., Role of axonal transport in neurodegenerative diseases, Annu. Rev. Neurosci., 2008, 31, 151–173
Pack-Chung E., Kurshan P. T., Dickman D. K., Schwarz T. L., A Drosophila kinesin required for synaptic bouton formation and synaptic vesicle transport, Nat. Neurosci., 2007, 10, 980–989
Horiuchi D., Barkus R. V., Pilling A. D., Gassman A., Saxton W. M., APLIP1, a kinesin binding JIP-1/JNK scaffold protein, influences the axonal transport of both vesicles and mitochondria in Drosophila, Curr. Biol., 2005, 15, 2137–2141
Miller K. E., DeProto J., Kaufmann N., Patel B. N., Duckworth A., Van Vactor D., Direct observation demonstrates that Liprin-alpha is required for trafficking of synaptic vesicles, Curr. Biol., 2005, 15, 684–689
Gindhart J. G., Chen J., Faulkner M., Gandhi R., Doerner K., Wisniewski T., et al., The kinesin-associated protein UNC-76 is required for axonal transport in the Drosophila nervous system, Mol. Biol. Cell, 2003, 14, 3356–3365
Glater E. E., Megeath L. J., Stowers R. S., Schwarz T. L., Axonal transport of mitochondria requires milton to recruit kinesin heavy chain and is light chain independent, J. Cell Biol., 2006, 173, 545–557
Hafezparast M., Klocke R., Ruhrberg C., Marquardt A., Ahmad-Annuar A., Bowen S., et al., Mutations in dynein link motor neuron degeneration to defects in retrograde transport, Science, 2003, 300, 808–812
Ori-McKenney K. M., Xu J., Gross S. P., Vallee R. B., A cytoplasmic dynein tail mutation impairs motor processivity, Nat. Cell Biol., 2010, 12, 1228–1234
Courchesne S. L., Pazyra-Murphy M. F., Lee D. J., Segal R. A., Neuromuscular junction defects in mice with mutation of dynein heavy chain 1, PLoS One, 2011, 6, e16753
Ilieva H. S. Yamanaka K., Malkmus S., Kakinohana O., Yaksh T., Marsala M., et al., Mutant dynein (Loa) triggers proprioceptive axon loss that extends survival only in the SOD1 ALS model with highest motor neuron death, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2008, 105, 12599–12604
Braunstein K. E., Eschbach J., Rona-Voros K., Soylu R., Mikrouli E., Larmet Y., et al., A point mutation in the dynein heavy chain gene leads to striatal atrophy and compromises neurite outgrowth of striatal neurons, Hum. Mol. Genet., 2010, 19, 4385–4398
Jiang Y. M., Yamamoto M., Kobayashi Y., Yoshihara T., Liang Y., Terao S., et al., Gene expression profile of spinal motor neurons in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Ann. Neurol., 2005, 57, 236–251
Riviere J. B., Ramalingam S., Lavastre V., Shekarabi M., Holbert S., Lafontaine J., et al., KIF1A, an axonal transporter of synaptic vesicles, is mutated in hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type 2, Am. J. Hum. Genet., 2011, 89, 219–230
Erlich Y., Edvardson S., Hodges E., Zenvirt S., Thekkat P., Shaag A., et al., Exome sequencing and disease-network analysis of a single family implicate a mutation in KIF1A in hereditary spastic paraparesis, Genome Res., 2011, 21, 658–664
Blair M. A., Ma S., Hedera P., Mutation in KIF5A can also cause adultonset hereditary spastic paraplegia, Neurogenetics, 2006, 7, 47–50
Dafinger C., Liebau M. C., Elsayed S. M., Hellenbroich Y., Boltshauser E., Korenke G. C., et al., Mutations in KIF7 link Joubert syndrome with Sonic Hedgehog signaling and microtubule dynamics, J. Clin. Invest., 2011, 121, 2662–2667
Tarabeux J., Champagne N., Brustein E., Hamdan F. F., Gauthier J., Lapointe M., et al., De novo truncating mutation in Kinesin 17 associated with schizophrenia, Biol. Psychiatry, 2010, 68, 649–656
Lu S., Zhao C., Zhao K., Li N., Larsson C., Novel and recurrent KIF21A mutations in congenital fibrosis of the extraocular muscles type 1 and 3, Arch. Ophthalmol., 2008, 126, 388–394
Khan A. O., Khalil D. S., Al Sharif L. J., Al-Ghadhfan F. E., Al Tassan N. A., Germline mosaicism for KIF21A mutation (p.R954L) mimicking recessive inheritance for congenital fibrosis of the extraocular muscles, Ophthalmology, 2010, 117, 154–158
Zhao C., Takita J., Tanaka Y., Setou M., Nakagawa T., Takeda S., et al., Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2A caused by mutation in a microtubule motor KIF1Bbeta, Cell, 2001, 105, 587–597
Sharma R., Buras E., Terashima T., Serrano F., Massaad C. A., Hu L., et al., Hyperglycemia induces oxidative stress and impairs axonal transport rates in mice, PLoS One, 2010, 5, e13463
Haider L., Fischer M. T., Frischer J. M., Bauer J., Hoftberger R., Botond G., et al., Oxidative damage in multiple sclerosis lesions, Brain, 2011, 134, 1914–1924
Wilkinson A. E., Bridges L. R., Sivaloganathan S., Correlation of survival time with size of axonal swellings in diffuse axonal injury, Acta Neuropathol., 1999, 98, 197–202
Roediger B., Armati P. J., Oxidative stress induces axonal beading in cultured human brain tissue, Neurobiol. Dis., 2003, 13, 222–229
Stamer K., Vogel R., Thies E., Mandelkow E., Mandelkow E. M., Tau blocks traffic of organelles, neurofilaments, and APP vesicles in neurons and enhances oxidative stress, J. Cell Biol., 2002, 156, 1051–1063
Hirai K., Aliev G., Nunomura A., Fujioka H., Russell R. L., Atwood C. S., et al., Mitochondrial abnormalities in Alzheimer’s disease, J. Neurosci., 2001, 21, 3017–3023
Massaad C. A., Amin S. K., Hu L., Mei Y., Klann E., Pautler R. G., Mitochondrial superoxide contributes to blood flow and axonal transport deficits in the Tg2576 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease, PLoS One, 2010, 5, e10561
Shidara Y., Hollenbeck P. J., Defects in mitochondrial axonal transport and membrane potential without increased reactive oxygen species production in a Drosophila model of Friedreich ataxia, J. Neurosci., 2010, 30, 11369–11378
Green D. R., Reed J. C., Mitochondria and apoptosis, Science, 1998, 281, 1309–1312
Magrané J, Manfredi G., Mitochondrial function, morphology, and axonal transport in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Antioxid. Redox Signal., 2009, 11, 1615–1626
Sasaki S., Iwata M., Impairment of fast axonal transport in the proximal axons of anterior horn neurons in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Neurology, 1996, 47, 535–540
Sasaki S., Iwata M., Mitochondrial alterations in the spinal cord of patients with sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol., 2007, 66, 10–16
Yue Z., Wang Q. J., Komatsu M., Neuronal autophagy: going the distance to the axon, Autophagy, 2008, 4, 94–96
Katsumata K., Nishiyama J., Inoue T., Mizushima N., Takeda J., Yuzaki M., Dynein- and activity-dependent retrograde transport of autophagosomes in neuronal axons, Autophagy, 2010, 6, 378–385
Harris H., Rubinsztein D. C., Control of autophagy as a therapy for neurodegenerative disease, Nat. Rev. Neurol., 2012, 8, 108–117
Nixon R. A., Autophagy in neurodegenerative disease: friend, foe or turncoat?, Trends Neurosci., 2006, 29, 528–535
Yu W. H., Cuervo A. M., Kumar A., Peterhoff C. M., Schmidt S. D., Lee J. H., et al., Macroautophagy — a novel beta-amyloid peptidegenerating pathway activated in Alzheimer’s disease, J. Cell Biol., 2005, 171, 87–98
Nixon R. A., Autophagy, amyloidogenesis and Alzheimer disease, J. Cell Sci., 2007, 120, 4081–4091
Chu C. T., Tickled PINK1: mitochondrial homeostasis and autophagy in recessive Parkinsonism, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2010, 1802, 20–28
Sapp E., Schwarz C., Chase K., Bhide P. G., Young A. B., Penney J., et al., Huntingtin localization in brains of normal and Huntington’s disease patients, Ann. Neurol., 1997, 42, 604–612
Martinez-Vicente M., Talloczy Z., Wong E., Tang G., Koga H., Kaushik S., et al., Cargo recognition failure is responsible for inefficient autophagy in Huntington’s disease, Nat. Neurosci., 2010, 13, 567–576
Sasaki S., Autophagy in spinal cord motor neurons in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol., 2011, 70, 349–359
Ravikumar B., Acevedo-Arozena A., Imarisio S., Berger Z., Vacher C., O’Kane C.J., et al., Dynein mutations impair autophagic clearance of aggregate-prone proteins, Nat. Genet., 2005, 37, 771–776
Laird F. M., Farah M. H., Ackerley S., Hoke A., Maragakis N., Rothstein J. D., et al., Motor neuron disease occurring in a mutant dynactin mouse model is characterized by defects in vesicular trafficking, J. Neurosci., 2008, 28, 1997–2005
Mattson M. P., Pathways towards and away from Alzheimer’s disease, Nature, 2004, 430, 631–639
Lee V.M., Goedert M., Trojanowski J. Q., Neurodegenerative tauopathies, Annu. Rev. Neurosci., 2001, 24, 1121–1159
Morris M., Maeda S., Vossel K., Mucke L., The many faces of tau, Neuron, 2011, 70, 410–426
Wang J. Z., Liu F., Microtubule-associated protein tau in development, degeneration and protection of neurons, Prog. Neurobiol., 2008, 85, 148–175
Hardy J., Selkoe D. J., The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics, Science, 2002, 297, 353–356
Vossel K. A., Zhang K., Brodbeck J., Daub A. C., Sharma P., Finkbeiner S., et al., Tau reduction prevents amyloid beta-induced defects in axonal transport, Science, 2010, 330, 198
Ittner L. M., Gotz J., Amyloid-beta and tau — a toxic pas de deux in Alzheimer’s disease, Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 2011, 12, 65–72
Reddy P. H., Abnormal tau, mitochondrial dysfunction, impaired axonal transport of mitochondria, and synaptic deprivation in Alzheimer’s disease, Brain. Res., 2011, 1415, 136–148
Spillantini M. G., Murrell J. R., Goedert M., Farlow M. R., Klug A., Ghetti B., Mutation in the tau gene in familial multiple system tauopathy with presenile dementia, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1998, 95, 7737–7741
Cash A. D., Aliev G., Siedlak S. L., Nunomura A., Fujioka H., Zhu X., et al., Microtubule reduction in Alzheimer’s disease and aging is independent of tau filament formation, Am. J. Pathol., 2003, 162, 1623–1627
Khatoon S., Grundke-Iqbal I., Iqbal K., Brain levels of microtubuleassociated protein tau are elevated in Alzheimer’s disease: a radioimmuno-slot-blot assay for nanograms of the protein, J. Neurochem., 1992, 59, 750–753
Ebneth A., Godemann R., Stamer K., Illenberger S., Trinczek B., Mandelkow E., Overexpression of tau protein inhibits kinesindependent trafficking of vesicles, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum: implications for Alzheimer’s disease, J. Cell Biol., 1998, 143, 777–794
Ishihara T., Hong M., Zhang B., Nakagawa Y., Lee M. K., Trojanowski J. Q., et al., Age-dependent emergence and progression of a tauopathy in transgenic mice overexpressing the shortest human tau isoform, Neuron, 1999, 24, 751–762
Ittner L. M., Fath T., Ke Y. D., Bi M., van Eersel J., Li K. M., et al., Parkinsonism and impaired axonal transport in a mouse model of frontotemporal dementia, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2008, 105, 15997–16002
Probst A., Gotz J., Wiederhold K. H., Tolnay M., Mistl C., Jaton A. L., et al., Axonopathy and amyotrophy in mice transgenic for human four-repeat tau protein, Acta Neuropathol., 2000, 99, 469–481
Spittaels K., Van den Haute C., Van Dorpe J., Bruynseels K., Vandezande K., Laenen I., et al., Prominent axonopathy in the brain and spinal cord of transgenic mice overexpressing four-repeat human tau protein, Am. J. Pathol., 1999, 155, 2153–2165
Cote F., Collard J. F., Julien J. P., Progressive neuronopathy in transgenic mice expressing the human neurofilament heavy gene: a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Cell, 1993, 73, 35–46
Xu Z., Cork L. C., Griffin J. W., Cleveland D. W., Increased expression of neurofilament subunit NF-L produces morphological alterations that resemble the pathology of human motor neuron disease, Cell, 1993, 73, 23–33
Zhang B., Higuchi M., Yoshiyama Y., Ishihara T., Forman M. S., Martinez D., et al., Retarded axonal transport of R406W mutant tau in transgenic mice with a neurodegenerative tauopathy, J. Neurosci., 2004, 24, 4657–4667
Higuchi M., Zhang B., Forman M. S., Yoshiyama Y., Trojanowski J. Q., Lee V. M., Axonal degeneration induced by targeted expression of mutant human tau in oligodendrocytes of transgenic mice that model glial tauopathies, J. Neurosci., 2005, 25, 9434–9443
Bull N. D., Guidi A., Goedert M., Martin K. R., Spillantini M. G., Reduced axonal transport and increased excitotoxic retinal ganglion cell degeneration in mice transgenic for human mutant P301S tau, PLoS One, 2012, 7, e34724
Dixit R., Ross J. L., Goldman Y. E., Holzbaur E. L., Differential regulation of dynein and kinesin motor proteins by tau, Science, 2008, 319, 1086–1089
Falzone T. L., Stokin G. B., Lillo C., Rodrigues E. M., Westerman E. L., Williams D. S., et al., Axonal stress kinase activation and tau misbehavior induced by kinesin-1 transport defects, J. Neurosci., 2009, 29, 5758–5767
Santacruz K., Lewis J., Spires T., Paulson J., Kotilinek L., Ingelsson M., et al., Tau suppression in a neurodegenerative mouse model improves memory function, Science, 2005, 309, 476–481
Lewis J., Dickson D. W., Lin W. L., Chisholm L., Corral A., Jones G., et al., Enhanced neurofibrillary degeneration in transgenic mice expressing mutant tau and APP, Science, 2001, 293, 1487–1491
Roberson E. D., Scearce-Levie K., Palop J. J., Yan F., Cheng I. H., Wu T., et al., Reducing endogenous tau ameliorates amyloid beta-induced deficits in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model, Science, 2007, 316, 750–754
Falzone T. L., Gunawardena S., McCleary D., Reis G. F., Goldstein L. S., Kinesin-1 transport reductions enhance human tau hyperphosphorylation, aggregation and neurodegeneration in animal models of tauopathies, Hum. Mol. Genet., 2010, 19, 4399–4408
Yuan A., Kumar A., Peterhoff C., Duff K., Nixon R. A., Axonal transport rates in vivo are unaffected by tau deletion or overexpression in mice, J. Neurosci., 2008, 28, 1682–1687
Kamal A., Stokin G. B., Yang Z, Xia C. H., Goldstein L. S., Axonal transport of amyloid precursor protein is mediated by direct binding to the kinesin light chain subunit of kinesin-I, Neuron, 2000, 28, 449–459
Stokin G. B., Lillo C., Falzone T. L., Brusch R. G., Rockenstein E., Mount S. L., et al., Axonopathy and transport deficits early in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease, Science, 2005, 307, 1282–1288
Wirths O., Weis J., Szczygielski J., Multhaup G., Bayer T. A., Axonopathy in an APP/PS1 transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease, Acta Neuropathol., 2006, 111, 312–319
Hiruma H., Katakura T., Takahashi S., Ichikawa T., Kawakami T., Glutamate and amyloid beta-protein rapidly inhibit fast axonal transport in cultured rat hippocampal neurons by different mechanisms, J. Neurosci., 2003, 23, 8967–8977
Rui Y., Tiwari P., Xie Z., Zheng J. Q., Acute impairment of mitochondrial trafficking by beta-amyloid peptides in hippocampal neurons, J. Neurosci., 2006, 26, 10480–10487
Decker H., Lo K. Y., Unger S. M., Ferreira S. T., Silverman M. A., Amyloid-beta peptide oligomers disrupt axonal transport through an NMDA receptor-dependent mechanism that is mediated by glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in primary cultured hippocampal neurons, J. Neurosci., 2010, 30, 9166–9171
Pigino G., Morfini G., Atagi Y., Deshpande A., Yu C., Jungbauer L., et al., Disruption of fast axonal transport is a pathogenic mechanism for intraneuronal amyloid beta, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2009, 106, 5907–5912
Pigino G., Morfini G., Pelsman A., Mattson M. P., Brady S. T., Busciglio J., Alzheimer’s presenilin 1 mutations impair kinesin-based axonal transport, J. Neurosci., 2003, 23, 4499–4508
Lazarov O., Morfini G. A., Pigino G., Gadadhar A., Chen X., Robinson J., et al., Impairments in fast axonal transport and motor neuron deficits in transgenic mice expressing familial Alzheimer’s diseaselinked mutant presenilin 1, J. Neurosci., 2007, 27, 7011–7020
Cai D., Leem J. Y., Greenfield J. P., Wang P., Kim B. S., Wang R., et al., Presenilin-1 regulates intracellular trafficking and cell surface delivery of beta-amyloid precursor protein, J. Biol. Chem., 2003, 278, 3446–3454
Tesseur I., Van Dorpe J., Bruynseels K., Bronfman F., Sciot R., Van Lommel A., et al., Prominent axonopathy and disruption of axonal transport in transgenic mice expressing human apolipoprotein E4 in neurons of brain and spinal cord, Am. J. Pathol., 2000, 157, 1495–1510
Haberland C., Frontotemporal dementia or frontotemporal lobar degeneration -overview of a group of proteinopathies, Ideggyogy Sz., 2010, 63, 87–93
Fujioka S., Wszolek Z. K., Clinical aspects of familial forms of frontotemporal dementia associated with parkinsonism, J. Mol. Neurosci., 2011, 45, 359–365
Ghazi-Noori S., Froud K. E., Mizielinska S., Powell C., Smidak M., Fernandez de Marco M., et al., Progressive neuronal inclusion formation and axonal degeneration in CHMP2B mutant transgenic mice, Brain, 2012, 135, 819–832
Urwin H., Authier A., Nielsen J. E., Metcalf D., Powell C., Froud K., et al., Disruption of endocytic trafficking in frontotemporal dementia with CHMP2B mutations, Hum. Mol. Genet., 2010, 19, 2228–2238
Ittner L. M., Ke Y. D., Gotz J., Phosphorylated Tau interacts with c-Jun N-terminal kinase-interacting protein 1 (JIP1) in Alzheimer disease, J. Biol. Chem., 2009, 284, 20909–20916
Magnani E., Fan J., Gasparini L., Golding M., Williams M., Schiavo G., et al., Interaction of tau protein with the dynactin complex, EMBO J., 2007, 26, 4546–4554
Hong M., Zhukareva V., Vogelsberg-Ragaglia V., Wszolek Z., Reed L., Miller B. I., et al., Mutation-specific functional impairments in distinct tau isoforms of hereditary FTDP-17, Science, 1998, 282, 1914–1917
Stoothoff W., Jones P. B., Spires-Jones T. L., Joyner D., Chhabra E., Bercury K., et al., Differential effect of three-repeat and four-repeat tau on mitochondrial axonal transport, J. Neurochem., 2009, 111, 417–427
Tien N. W., Wu G. H., Hsu C. C., Chang C. Y., Wagner O. I., Tau/PTL-1 associates with kinesin-3 KIF1A/UNC-104 and affects the motor’s motility characteristics in C. elegans neurons, Neurobiol. Dis., 2011, 43, 495–506
Gilley J., Seereeram A., Ando K., Mosely S., Andrews S., Kerschensteiner M., et al., Age-dependent axonal transport and locomotor changes and tau hypophosphorylation in a “P301L” tau knockin mouse, Neurobiol. Aging, 2012, 33, 621.e1–621.e15
Mulder D. W., Clinical limits of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Adv. Neurol., 1982, 36, 15–22
Rowland L. P., Shneider N. A., Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, N. Engl. J. Med., 2001, 344, 1688–1700
Rosen D. R., Siddique T., Patterson D., Figlewicz D. A., Sapp P., Hentati A., et al., Mutations in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene are associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Nature, 1993, 362, 59–62
Zhang B., Tu P., Abtahian F., Trojanowski J. Q., Lee V. M., Neurofilaments and orthograde transport are reduced in ventral root axons of transgenic mice that express human SOD1 with a G93A mutation, J. Cell Biol., 1997, 139, 1307–1315
Williamson T. L., Cleveland D. W., Slowing of axonal transport is a very early event in the toxicity of ALS-linked SOD1 mutants to motor neurons, Nat. Neurosci., 1999, 2, 50–56
Borchelt D. R., Wong P. C., Becher M. W., Pardo C. A., Lee M. K., Xu Z. S., et al., Axonal transport of mutant superoxide dismutase 1 and focal axonal abnormalities in the proximal axons of transgenic mice, Neurobiol. Dis., 1998, 5, 27–35
Tateno M., Kato S., Sakurai T., Nukina N., Takahashi R., Araki T., Mutant SOD1 impairs axonal transport of choline acetyltransferase and acetylcholine release by sequestering KAP3, Hum. Mol. Genet., 2009, 18, 942–955
Landers J. E., Melki J., Meininger V., Glass J. D., van den Berg L. H., van Es M. A., et al., Reduced expression of the Kinesin-Associated Protein 3 (KIFAP3) gene increases survival in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2009, 106, 9004–9009
Dupuis L., de Tapia M., Rene F., Lutz-Bucher B., Gordon J. W., Mercken L., et al., Differential screening of mutated SOD1 transgenic mice reveals early up-regulation of a fast axonal transport component in spinal cord motor neurons, Neurobiol. Dis., 2000, 7, 274–285
Murakami T., Nagano I., Hayashi T., Manabe Y., Shoji M., Setoguchi Y., et al., Impaired retrograde axonal transport of adenovirusmediated E. coli LacZ gene in the mice carrying mutant SOD1 gene, Neurosci. Lett., 2001, 308, 149–152
Ligon L. A., LaMonte B. H., Wallace K. E., Weber N., Kalb R. G., Holzbaur E. L., Mutant superoxide dismutase disrupts cytoplasmic dynein in motor neurons, Neuroreport, 2005, 16, 533–536
Bilsland L. G., Sahai E., Kelly G., Golding M., Greensmith L., Schiavo G., Deficits in axonal transport precede ALS symptoms in vivo, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2010, 107, 20523–20528
Munch C., Sedlmeier R., Meyer T., Homberg V., Sperfeld A. D., Kurt A., et al., Point mutations of the p150 subunit of dynactin (DCTN1) gene in ALS, Neurology, 2004, 63, 724–726
Moore J. K., Sept D., Cooper J. A., Neurodegeneration mutations in dynactin impair dynein-dependent nuclear migration, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2009, 106, 5147–5152
Pasinelli P., Brown R. H., Molecular biology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: insights from genetics, Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 2006, 7, 710–723
Puls I., Jonnakuty C., LaMonte B. H., Holzbaur E. L., Tokito M., Mann E., et al., Mutant dynactin in motor neuron disease, Nat. Genet., 2003, 33, 455–456
Teuchert M., Fischer D., Schwalenstoecker B., Habisch H. J., Bockers T. M., Ludolph A. C., A dynein mutation attenuates motor neuron degeneration in SOD1(G93A) mice, Exp. Neurol., 2006, 198, 271–274
Kieran D., Hafezparast M., Bohnert S., Dick J. R., Martin J., Schiavo G., et al., A mutation in dynein rescues axonal transport defects and extends the life span of ALS mice, J. Cell Biol., 2005, 169, 561–567
Teuling E., van Dis V., Wulf P. S., Haasdijk E. D., Akhmanova A., Hoogenraad C. C., et al., A novel mouse model with impaired dynein/dynactin function develops amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)-like features in motor neurons and improves lifespan in SOD1-ALS mice, Hum. Mol. Genet., 2008, 17, 2849–2862
LaMonte B. H., Wallace K. E., Holloway B. A., Shelly S. S., Ascano J., Tokito M., et al., Disruption of dynein/dynactin inhibits axonal transport in motor neurons causing late-onset progressive degeneration, Neuron, 2002, 34, 715–727
Gepner J., Li M., Ludmann S., Kortas C., Boylan K., Iyadurai S. J., et al., Cytoplasmic dynein function is essential in Drosophila melanogaster, Genetics, 1996, 142, 865–878
Chevalier-Larsen E. S., Wallace K. E., Pennise C. R., Holzbaur E. L., Lysosomal proliferation and distal degeneration in motor neurons expressing the G59S mutation in the p150Glued subunit of dynactin, Hum. Mol. Genet., 2008, 17, 1946–1955
Robertson J., Doroudchi M. M., Nguyen M. D., Durham H. D., Strong M. J., Shaw G., et al., A neurotoxic peripherin splice variant in a mouse model of ALS, J. Cell Biol., 2003, 160, 939–949
Kong J., Xu Z., Massive mitochondrial degeneration in motor neurons triggers the onset of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in mice expressing a mutant SOD1, J. Neurosci., 1998, 18, 3241–3250
Marinkovic P., Reuter M. S., Brill M. S., Godinho L., Kerschensteiner M., Misgeld T., Axonal transport deficits and degeneration can evolve independently in mouse models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2012, 109, 4296–4301
Bendotti C., Atzori C., Piva R., Tortarolo M., Strong M. J., DeBiasi S., Migheli A., Activated p38MAPK is a novel component of the intracellular inclusions found in human amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and mutant SOD1 transgenic mice, J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol., 2004, 63, 113–119
Tortarolo M., Veglianese P., Calvaresi N., Botturi A., Rossi C., Giorgini A., et al., Persistent activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in a mouse model of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis correlates with disease progression, Mol. Cell. Neurosci., 2003, 23, 180–192
Morfini G. A., Burns M., Binder L. I., Kanaan N. M., LaPointe N., Bosco D. A., et al., Axonal transport defects in neurodegenerative diseases, J. Neurosci., 2009, 29, 12776–12786
Pizzuti A., Petrucci S., Mitochondrial disfunction as a cause of ALS, Arch. Ital. Biol., 2011, 149, 113–119
Rothstein J. D., Excitotoxicity hypothesis, Neurology, 1996, 47, S19–25; discussion S26
Wiedau-Pazos M., Goto J. J., Rabizadeh S., Gralla E. B., Roe J. A., Lee M. K., et al., Altered reactivity of superoxide dismutase in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Science, 1996, 271, 515–518
Zhang Y., Marcillat O., Giulivi C., Ernster L., Davies K. J., The oxidative inactivation of mitochondrial electron transport chain components and ATPase, J. Biol. Chem., 1990, 265, 16330–16336
Salinas S., Proukakis C., Crosby A., Warner T. T., Hereditary spastic paraplegia: clinical features and pathogenetic mechanisms, Lancet Neurol., 2008, 7, 1127–1138
Blackstone C., O’Kane C. J., Reid E., Hereditary spastic paraplegias: membrane traffic and the motor pathway, Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 2011, 12, 31–42
Reid E., Kloos M., Ashley-Koch A., Hughes L., Bevan S., Svenson I. K., et al., A kinesin heavy chain (KIF5A) mutation in hereditary spastic paraplegia (SPG10), Am. J. Hum. Genet., 2002, 71, 1189–1194
Fichera M., Lo Giudice M., Falco M., Sturnio M., Amata S., Calabrese O., et al., Evidence of kinesin heavy chain (KIF5A) involvement in pure hereditary spastic paraplegia, Neurology, 2004, 63, 1108–1110
Ebbing B., Mann K., Starosta A., Jaud J., Schols L., Schule R., et al., Effect of spastic paraplegia mutations in KIF5A kinesin on transport activity, Hum. Mol. Genet., 2008, 17, 1245–1252
Ferreirinha F., Quattrini A., Pirozzi M., Valsecchi V., Dina G., Broccoli V., et al., Axonal degeneration in paraplegin-deficient mice is associated with abnormal mitochondria and impairment of axonal transport, J. Clin. Invest., 2004, 113, 231–242
Baas P. W., Karabay A., Qiang L., Microtubules cut and run, Trends Cell Biol., 2005, 15, 518–524
Zhao X., Alvarado D., Rainier S., Lemons R., Hedera P., Weber C. H., et al., Mutations in a newly identified GTPase gene cause autosomal dominant hereditary spastic paraplegia, Nat. Genet., 2001, 29, 326–331
Hazan J., Fonknechten N., Mavel D., Paternotte C., Samson D., Artiguenave F., et al., Spastin, a new AAA protein, is altered in the most frequent form of autosomal dominant spastic paraplegia, Nat. Genet., 1999, 23, 296–303
Goizet C., Depienne C., Benard G., Boukhris A., Mundwiller E., Sole G., et al., REEP1 mutations in SPG31: frequency, mutational spectrum, and potential association with mitochondrial morphofunctional dysfunction, Hum. Mutat., 2011, 32, 1118–1127
Kasher P. R., De Vos K. J., Wharton S. B., Manser C., Bennett E. J., Bingley M., et al., Direct evidence for axonal transport defects in a novel mouse model of mutant spastin-induced hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP) and human HSP patients, J. Neurochem., 2009, 110, 34–44
Tarrade A., Fassier C., Courageot S., Charvin D., Vitte J., Peris L., et al., A mutation of spastin is responsible for swellings and impairment of transport in a region of axon characterized by changes in microtubule composition, Hum. Mol. Genet., 2006, 15, 3544–3558
Zuchner S., Vance J. M., Mechanisms of disease: a molecular genetic update on hereditary axonal neuropathies, Nat. Clin. Pract. Neurol., 2006, 2, 45–53
Crimella C., Baschirotto C., Arnoldi A., Tonelli A., Tenderini E., Airoldi G., et al., Mutations in the motor and stalk domains of KIF5A in spastic paraplegia type 10 and in axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 2, Clin. Genet., 2011
Willemsen M. H., Vissers L. E., Willemsen M. A., van Bon B. W., Kroes T., de Ligt J., et al., Mutations in DYNC1H1 cause severe intellectual disability with neuronal migration defects, J. Med. Genet., 2012, 49, 179–183
d’Ydewalle C., Krishnan J., Chiheb D.M., Van Damme P., Irobi J., Kozikowski A.P., et al., HDAC6 inhibitors reverse axonal loss in a mouse model of mutant HSPB1-induced Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, Nat. Med., 2011, 17, 968–974
Estela A., Pla-Martin D., Sanchez-Piris M., Sesaki H., Palau F., Charcot-Marie-Tooth-related gene GDAP1 complements cell cycle delay at G2/M phase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae fis1 gene-defective cells, J. Biol. Chem., 2011, 286, 36777–36786
Cassereau J., Chevrollier A., Gueguen N., Desquiret V., Verny C., Nicolas G., et al., Mitochondrial dysfunction and pathophysiology of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease involving GDAP1 mutations, Exp. Neurol., 2011, 227, 31–41
Warren G., Wickner W., Organelle inheritance, Cell, 1996, 84, 395–400
Kabzinska D., Niemann A., Drac H., Huber N., Potulska-Chromik A., Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz I., et al., A new missense GDAP1 mutation disturbing targeting to the mitochondrial membrane causes a severe form of AR-CMT2C disease, Neurogenetics, 2011, 12, 145–153
Baxter R. V., Ben Othmane K., Rochelle J. M., Stajich J. E., Hulette C., Dew-Knight S., et al., Ganglioside-induced differentiationassociated protein-1 is mutant in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 4A/8q21, Nat. Genet., 2002, 30, 21–22
Misko A., Jiang, S., Wegorzewska, I., Milbrandt, J., Baloh, R. H., Mitofusin 2 is necessary for transport of axonal mitochondria and interacts with the Miro/Milton complex, J. Neurosci., 2010, 30, 4232–4240
Davies S. W., Turmaine M., Cozens B. A., DiFiglia M., Sharp A. H., Ross C. A., et al., Formation of neuronal intranuclear inclusions underlies the neurological dysfunction in mice transgenic for the HD mutation, Cell, 1997, 90, 537–548
Shirendeb U. P., Calkins M. J., Manczak M., Anekonda V., Dufour B., McBride J. L., et al., Mutant huntingtin’s interaction with mitochondrial protein Drp1 impairs mitochondrial biogenesis and causes defective axonal transport and synaptic degeneration in Huntington’s disease, Hum. Mol. Genet., 2012, 21, 406–420
Morfini G. A., You Y. M., Pollema S. L., Kaminska A., Liu K., Yoshioka K., et al., Pathogenic huntingtin inhibits fast axonal transport by activating JNK3 and phosphorylating kinesin, Nat. Neurosci., 2009, 12, 864–871
Gunawardena S., Her L. S., Brusch R. G., Laymon R. A., Niesman I. R., Gordesky-Gold B., et al., Disruption of axonal transport by loss of huntingtin or expression of pathogenic polyQ proteins in Drosophila, Neuron, 2003, 40, 25–40
Hurd D. D., Saxton W. M., Kinesin mutations cause motor neuron disease phenotypes by disrupting fast axonal transport in Drosophila, Genetics, 1996, 144, 1075–1085
Ticozzi N., Ratti A., Silani V., Protein aggregation and defective RNA metabolism as mechanisms for motor neuron damage, CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets, 2010, 9, 285–296
Weedon M. N., Hastings R., Caswell R., Xie W., Paszkiewicz K., Antoniadi T., et al., Exome sequencing identifies a DYNC1H1 mutation in a large pedigree with dominant axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, Am. J. Hum. Genet., 2011, 89, 308–312
Piccioni F., Pinton P., Simeoni S., Pozzi P., Fascio U., Vismara G., et al., Androgen receptor with elongated polyglutamine tract forms aggregates that alter axonal trafficking and mitochondrial distribution in motor neuronal processes, FASEB J., 2002, 16, 1418–1420
Kemp M. Q., Poort J. L., Baqri R. M., Lieberman A. P., Breedlove S. M., Miller K. E., et al., Impaired motoneuronal retrograde transport in two models of SBMA implicates two sites of androgen action, Hum. Mol. Genet., 2011, 20, 4475–4490
La Spada A. R., Wilson E. M., Lubahn D. B., Harding A. E., Fischbeck K. H., Androgen receptor gene mutations in X-linked spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy, Nature, 1991, 352, 77–79
Saha A. R., Hill J., Utton M. A., Asuni A. A., Ackerley S., Grierson A. J., et al., Parkinson’s disease alpha-synuclein mutations exhibit defective axonal transport in cultured neurons, J. Cell Sci., 2004, 117, 1017–1024
Abou-Sleiman P. M., Muqit M. M., Wood N. W., Expanding insights of mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease, Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 2006, 7, 207–219
Miller K. E., Sheetz M. P., Axonal mitochondrial transport and potential are correlated, J. Cell Sci., 2004, 117, 2791–2804
Morfini G., Pigino G., Opalach K., Serulle Y., Moreira J. E., Sugimori M., et al., 1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium affects fast axonal transport by activation of caspase and protein kinase C, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2007, 104, 2442–2447
Su K. G., Banker G., Bourdette D., Forte M., Axonal degeneration in multiple sclerosis: the mitochondrial hypothesis, Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep., 2009, 9, 411–417
Pagliardini S., Giavazzi A., Setola V., Lizier C., Di Luca M., DeBiasi S., et al., Subcellular localization and axonal transport of the survival motor neuron (SMN) protein in the developing rat spinal cord, Hum. Mol. Genet., 2000, 9, 47–56
Fallini C., Bassell G. J., Rossoll W., Spinal muscular atrophy: The role of SMN in axonal mRNA regulation, Brain Res., 2012, 1462, 81–92
Morfini G., Pigino G., Brady S. T., Polyglutamine expansion diseases: failing to deliver, Trends Mol. Med., 2005, 11, 64–70
Takahashi T., Katada S., Onodera O., Polyglutamine diseases: where does toxicity come from? What is toxicity? Where are we going?, J. Mol. Cell. Biol., 2010, 2, 180–191
Feany M. B., La Spada A. R., Polyglutamines stop traffic: axonal transport as a common target in neurodegenerative diseases, Neuron, 2003, 40, 1–2
Ermolayev V., Cathomen T., Merk J., Friedrich M., Hartig W., Harms G. S., et al., Impaired axonal transport in motor neurons correlates with clinical prion disease, PLoS Pathog., 2009, 5, e1000558
Almasieh M., Wilson A. M., Morquette B., Cueva Vargas J. L., Di Polo A., The molecular basis of retinal ganglion cell death in glaucoma, Prog. Retin. Eye Res., 2012, 31, 152–181
Lorenzo D. N., Li M. G., Mische S. E., Armbrust K. R., Ranum L. P., Hays T. S., Spectrin mutations that cause spinocerebellar ataxia type 5 impair axonal transport and induce neurodegeneration in Drosophila, J. Cell Biol., 2010, 189, 143–158
Smith D. H., Uryu K., Saatman K. E., Trojanowski J. Q., McIntosh T. K., Protein accumulation in traumatic brain injury, Neuromolecular Med., 2003, 4, 59–72
Bernier G., Kothary R., Prenatal onset of axonopathy in Dystonia musculorum mice, Dev. Genet., 1998, 22, 160–168
Furlong R. A., Zhou C. Y., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Affara N. A., Characterization of a kinesin-related gene ATSV, within the tuberous sclerosis locus (TSC1) candidate region on chromosome 9Q34, Genomics, 1996, 33, 421–429
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, XA., Rizzo, V. & Puthanveettil, S.V. Pathologies of axonal transport in neurodegenerative diseases. Translat.Neurosci. 3, 355–372 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2478/s13380-012-0044-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s13380-012-0044-7