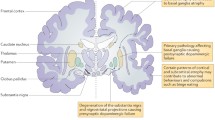
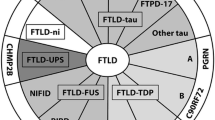
Abstract
Frontotemporal dementia is the second most common dementia among people under the age of 65. Fifty percent of affected patients have an associated family history. Several pathogenic genes have been identified for frontotemporal dementia associated with parkinsonism, including microtubule-associated protein tau, progranulin, and chromatin modifying protein 2B, and fused in sarcoma. It has also been reported that frontotemporal dementia associated with parkinsonism can be linked to chromosome 9p. In addition, there are families with frontotemporal dementia associated with a parkinsonian phenotype but unknown genetic status. Some of these kindreds have been diagnosed clinically as familial progressive supranuclear palsy, hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids, “overlap” syndrome, and others. Clinical presentation of frontotemporal dementia associated with parkinsonism is variable at age of symptomatic disease onset, disease duration, symptoms, and their occurrence during the disease course. Clinically, it is often difficult to sort out the different genetic forms of frontotemporal dementia associated with parkinsonism. However, with available clinical genetic testing for known genes, the precise diagnosis can be accomplished in some cases.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
AD&FTD Mutation Database 2011. Available from: http://www.molgen.ua.ac.be/FTDMutations. 03 Mar 2011
Alter M, Schaumann B (1976) A family with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Parkinsonism. J Neurol 212(3):281–284
Ashworth A, Lloyd S, Brown J et al (1999) Molecular genetic characterisation of frontotemporal dementia on chromosome 3. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 10(Suppl 1):93–101
Axelsson R, Roytta M, Sourander P, Akesson HO, Andersen O (1984) Hereditary diffuse leucoencephalopathy with spheroids. Acta Psychiatr Scand 314:1–65
Baba Y, Ghetti B, Baker MC et al (2006) Hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids: clinical, pathologic and genetic studies of a new kindred. Acta Neuropathol 111(4):300–311
Baker M, Mackenzie IR, Pickering-Brown SM et al (2006) Mutations in progranulin cause tau-negative frontotemporal dementia linked to chromosome 17. Nature 442(7105):916–919
Boxer AL, Mackenzie IR, Boeve BF et al (2011) Clinical, neuroimaging and neuropathological features of a new chromosome 9p-linked FTD-ALS family. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 82(2):196–203
Brown J (1998) Chromosome 3-linked frontotemporal dementia. Cell Mol Life Sci 54(9):925–927
Brown J, Lantos P, Stratton M, Roques P, Rossor M (1993) Familial progressive supranuclear palsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 56(5):473–476
Brown J, Gydesen S, Johannsen P et al (2004) Frontotemporal dementia linked to chromosome 3. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 17(4):274–276
Chow TW, Miller BL, Hayashi VN, Geschwind DH (1999) Inheritance of frontotemporal dementia. Arch Neurol 56(7):817–822
Cruts M, Gijselinck I, van der Zee J et al (2006) Null mutations in progranulin cause ubiquitin-positive frontotemporal dementia linked to chromosome 17q21. Nature 442(7105):920–924
David NJ, Mackey EA, Smith JL (1968) Further observations in progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurology 18(4):349–356
Davis PH, Golbe LI, Duvoisin RC, Schoenberg BS (1988) Risk factors for progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurology 38(10):1546–1552
de Yebenes JG, Sarasa JL, Daniel SE, Lees AJ (1995) Familial progressive supranuclear palsy. Description of a pedigree and review of the literature. Brain 118(Pt 5):1095–1103
Desai J, Swash M (1999) Extrapyramidal involvement in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: backward falls and retropulsion. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 67(2):214–216
Donker Kaat L, Boon AJ, Azmani A et al (2009) Familial aggregation of parkinsonism in progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurology 73(2):98–105
Eisen A, Calne D (1992) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease: phylogenetic disorders of the human neocortex sharing many characteristics. Can J Neurol Sci 19(1 Suppl):117–123
Gazeley S, Maguire JA (1996) Familial progressive supranuclear palsy. Clin Neuropathol 15(4):215–220
Ghanim M, Guillot-Noel L, Pasquier F et al (2010) CHMP2B mutations are rare in French families with frontotemporal lobar degeneration. J Neurol 257(12):2032–2036
Gilbert JJ, Kish SJ, Chang LJ, Morito C, Shannak K, Hornykiewicz O (1988) Dementia, parkinsonism, and motor neuron disease: neurochemical and neuropathological correlates. Ann Neurol 24(5):688–691
Gilbert RM, Fahn S, Mitsumoto H, Rowland LP (2010) Parkinsonism and motor neuron diseases: twenty-seven patients with diverse overlap syndromes. Mov Disord 25(12):1868–1875
Gydesen S, Hagen S, Klinken L, Abelskov J, Sorensen SA (1987) Neuropsychiatric studies in a family with presenile dementia different from Alzheimer and Pick disease. Acta Psychiatr Scand 76(3):276–284
Gydesen S, Brown JM, Brun A et al (2002) Chromosome 3 linked frontotemporal dementia (FTD-3). Neurology 59(10):1585–1594
Hancock N, Poon M, Taylor B, McLean C (2003) Hereditary diffuse leucoencephalopathy with spheroids. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74(9):1345–1347
Hirano A, Malamud N, Elizan TS, Kurland LT (1966) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Parkinsonism-dementia complex on Guam. Further pathologic studies. Arch Neurol 15(1):35–51
Holm IE, Englund E, Mackenzie IR, Johannsen P, Isaacs AM (2007) A reassessment of the neuropathology of frontotemporal dementia linked to chromosome 3. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66(10):884–891
Hutton M, Lendon CL, Rizzu P et al (1998) Association of missense and 5'-splice-site mutations in tau with the inherited dementia FTDP-17. Nature 393(6686):702–705
Imamura A, Wszolek Z, Uitti R (2007) Neurodegenerative overlap syndrome: Parkinsonism and motor neuron disorder. Mov Disord 22(1):151–152
Itoh K, Shiga K, Shimizu K, Muranishi M, Nakagawa M, Fushiki S (2006) Autosomal dominant leukodystrophy with axonal spheroids and pigmented glia: clinical and neuropathological characteristics. Acta Neuropathol 111(1):39–45
Konagaya M, Kato T, Sakai M et al (2003) A clinical and pathological study of a Japanese case of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/Parkinsonism-dementia complex with family history. J Neurol 250(2):164–170
Kovacs GG, Murrell JR, Horvath S et al (2009) TARDBP variation associated with frontotemporal dementia, supranuclear gaze palsy, and chorea. Mov Disord 24(12):1843–1847
Kuzuhara S, Kokubo Y (2005) Atypical parkinsonism of Japan: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-parkinsonism-dementia complex of the Kii peninsula of Japan (Muro disease): an update. Mov Disord 20(Suppl 12):S108–S113
Kwiatkowski TJ Jr, Bosco DA, Leclerc AL et al (2009) Mutations in the FUS/TLS gene on chromosome 16 cause familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 323(5918):1205–1208
Le Ber I, Camuzat A, Berger E et al (2009) Chromosome 9p-linked families with frontotemporal dementia associated with motor neuron disease. Neurology 72(19):1669–1676
Luty AA, Kwok JB, Thompson EM et al (2008) Pedigree with frontotemporal lobar degeneration—motor neuron disease and Tar DNA binding protein-43 positive neuropathology: genetic linkage to chromosome 9. BMC Neurol 8:32
Marotti JD, Tobias S, Fratkin JD, Powers JM, Rhodes CH (2004) Adult onset leukodystrophy with neuroaxonal spheroids and pigmented glia: report of a family, historical perspective, and review of the literature. Acta Neuropathol 107(6):481–488
Mata M, Dorovini-Zis K, Wilson M, Young AB (1983) New form of familial Parkinson-dementia syndrome: clinical and pathologic findings. Neurology 33(11):1439–1443
Mayer B, Oelschlaeger C, Keyvani K, Niederstadt T (2007) Two cases of LENAS: diagnosis by MRI and biopsy. J Neurol 254:1453–1454
McCluskey LF, Elman LB, Martinez-Lage M et al (2009) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-plus syndrome with TAR DNA-binding protein-43 pathology. Arch Neurol 66(1):121–124
Mendes A, Pinto M, Vieira S, Castro L, Carpenter S (2010) Adult-onset leukodystrophy with axonal spheroids. J Neurol Sci 297(1-2):40–45
Mochizuki A, Komatsuzaki Y, Iwamoto H, Shoji S (2004) Frontotemporal dementia with ubiquitinated neuronal inclusions presenting with primary lateral sclerosis and parkinsonism: clinicopathological report of an autopsy case. Acta Neuropathol 107(4):377–380
Momeni P, Schymick J, Jain S et al (2006) Analysis of IFT74 as a candidate gene for chromosome 9p-linked ALS-FTD. BMC Neurol 6:44
Morimoto S, Kuzuhara S, Kokubo Y (2009) Increased oxidative stress in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/Parkinsonism-dementia complex in the Kii peninsula, Japan. Mov Disord 24(1):123–126
Morita M, Al-Chalabi A, Andersen PM et al (2006) A locus on chromosome 9p confers susceptibility to ALS and frontotemporal dementia. Neurology 66(6):839–844
Ohara S, Kondo K, Morita H, Maruyama K, Ikeda S, Yanagisawa N (1992) Progressive supranuclear palsy-like syndrome in two siblings of a consanguineous marriage. Neurology 42(5):1009–1014
Pearson JP, Williams NM, Majounie E et al (2011) Familial frontotemporal dementia with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and a shared haplotype on chromosome 9p. J Neurol 258(4):647–655
Poorkaj P, Bird TD, Wijsman E et al (1998) Tau is a candidate gene for chromosome 17 frontotemporal dementia. Ann Neurol 43(6):815–825
Portera-Cailliau C, Russ C, Brown RH Jr et al (2007) A familial form of pallidoluysionigral degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with divergent clinical presentations. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66(7):650–659
Qureshi AI, Wilmot G, Dihenia B, Schneider JA, Krendel DA (1996) Motor neuron disease with parkinsonism. Arch Neurol 53(10):987–991
Schweitzer KJ, Boylan KB, Christian WW (2009) Parkinsonism (P), motor neuron disease (M), and dementia (D): clinical and pathological studies. Ann Neurol 66(Suppl 13):S51–S52
Sercle M, Kovarik J (1963) On the familial incident of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand 39:169–176
Spillantini MG, Murrell JR, Goedert M, Farlow MR, Klug A, Ghetti B (1998) Mutation in the tau gene in familial multiple system tauopathy with presenile dementia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(13):7737–7741
Terada S, Ishizu H, Yokota O et al (2004) An autopsy case of hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids, clinically suspected of Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 108(6):538–545
Tetrud JW, Golbe LI, Forno LS, Farmer PM (1996) Autopsy-proven progressive supranuclear palsy in two siblings. Neurology 46(4):931–934
Uitti RJ, Berry K, Yasuhara O et al (1995) Neurodegenerative 'overlap' syndrome: clinical and pathological features of Parkinson's disease, motor neuron disease, and Alzheimer's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 1(1):21–34
Valdmanis PN, Dupre N, Bouchard JP et al (2007) Three families with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia with evidence of linkage to chromosome 9p. Arch Neurol 64(2):240–245
van der Knaap MS, Naidu S, Kleinschmidt-Demasters BK, Kamphorst W, Weinstein HC (2000) Autosomal dominant diffuse leukoencephalopathy with neuroaxonal spheroids. Neurology 54(2):463–468
Van Gerpen JA, Wider C, Broderick DF, Dickson DW, Brown LA, Wszolek ZK (2008) Insights into the dynamics of hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids. Neurology 71(12):925–929
Van Langenhove T, van der Zee J, Sleegers K et al (2010) Genetic contribution of FUS to frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Neurology 74(5):366–371
Vance C, Al-Chalabi A, Ruddy D et al (2006) Familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with frontotemporal dementia is linked to a locus on chromosome 9p13.2-21.3. Brain 129(Pt 4):868–876
Vance C, Rogelj B, Hortobagyi T et al (2009) Mutations in FUS, an RNA processing protein, cause familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis type 6. Science 323(5918):1208–1211
Wider C, Van Gerpen JA, DeArmond S, Shuster EA, Dickson DW, Wszolek ZK (2009) Leukoencephalopathy with spheroids (HDLS) and pigmentary leukodystrophy (POLD): a single entity? Neurology 72(22):1953–1959
Yan J, Deng HX, Siddique N et al (2010) Frameshift and novel mutations in FUS in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and ALS/dementia. Neurology 75(9):807–814
Yazawa I, Nakano I, Yamada H, Oda M (1997) Long tract degeneration in familial sudanophilic leukodystrophy with prominent spheroids. J Neurol Sci 147(2):185–191
Yvonneau M, Vital C, Belly C, Coquet M (1971) Familial syndrome of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with dementia. Encephale 60(6):449–462
Zoccolella S, Palagano G, Fraddosio A et al (2002) ALS-plus: 5 cases of concomitant amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and parkinsonism. Neurol Sci 23(Suppl 2):S123–S124
Acknowledgments
SF is partially funded by Mayo Clinic Florida (MCF) Research Committee CR program (MCF no. 90052018). ZKW is partially supported by the NIH/NINDS 1RC2NS070276, NS057567, P50NS072187, Mayo Clinic Florida (MCF) Research Committee CR programs (MCF no. 90052018 and MCF no. 90052030), and the gift from Carl Edward Bolch, Jr., and Susan Bass Bolch (MCF no. 90052031/PAU no. 90052).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujioka, S., Wszolek, Z.K. Clinical Aspects of Familial Forms of Frontotemporal Dementia Associated with Parkinsonism. J Mol Neurosci 45, 359–365 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-011-9568-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-011-9568-5