Abstract
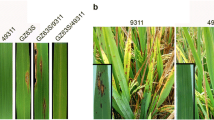
Hybrid rice has contributed greatly to the self-sufficiency of the food supply in China. However, bacterial blight is a major disease that limits hybrid rice production in China. The study was conducted to develop an efficient breeding technique to improve the bacterial blight resistance in hybrid rice. A marker-assisted backcross breeding technique was adopted to improve HN189, an elite restorer line containing the Pi1 gene. This breeding technique was simplified to foreground selection with only one generation of backcrossing and background selection based on phenotypic selection. A novel bacterial blight resistance gene, Xa23, was introgressed into HN189. Two improved restorer lines, HBH145 (with one generation of backcrossing) and HBH146 (with two generations of backcrossing), were obtained that had a significant bacterial blight resistance advantage over HN189. The corresponding hybrid combination Tianyou H145 (Tianfeng A / HBH145) was certified one year earlier than Qianyou H146 (Qianjiang 1A / HBH146). The use of the marker-assisted backcross breeding technique with one generation of backcrossing and without background selection in rice breeding programs shortened the breeding period of the rice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basavaraj S., Singh V.K., Singh A., Singh A., Singh A., Anand D., Yadav S., Ellur R.K., Singh D. & Krishnan S.G. 2010. Marker-assisted improvement of bacterial blight resistance in parental lines of Pusa RH10, a superfine grain aromatic rice hybrid. Mol. Breed. 26: 293–305.
Bhasin H., Bhatia D., Raghuvanshi S., Lore J.S., Sahi G.K., Kaur B., Vikal Y. & Singh K. 2011. New PCR-based sequencetagged site marker for bacterial blight resistance gene Xa38 of rice. Mol. Breed. 30: 607–611.
Cheng S.H., Cao L.Y., Zhuang J.Y., Chen S.G., Zhan X.D., Fan Y.Y., Zhu D.F. & Min S.K. 2007. Super hybrid rice breeding in China: achievements and prospects. J. Integ. Plant Biol. 49: 805–810.
Chevalet C. & Mulsant P. 1992. Using markers in gene introgression breeding programs. Genetics 132: 1199–1210.
Garris A.J., McCouch S.R. & Kresovich S. 2003. Population structure and its effect on haplotype diversity and linkage disequilibrium surrounding the xa5 locus of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genetics 165: 759–769.
Huang B., Xu J.Y., Hou M.S., Ali J. & Mou T.M. 2012. Introgression of bacterial blight resistance genes Xa7, Xa21, Xa22 and Xa23 into hybrid rice restorer lines by molecular markerassisted selection. Euphytica 187: 449–459.
Huang N., Angeles E., Domingo J., Magpantay G., Singh S., Zhang G., Kumaravadivel N., Bennett J. & Khush G. 1997. Pyramiding of bacterial blight resistance genes in rice: marker-assisted selection using RFLP and PCR. Theor. Appl. Genet. 95: 313–320.
Kumar P.N., Sujatha K., Laha G.S., Rao K.S., Mishra B., Viraktamath B.C., Hari Y., Reddy C.S., Balachandran S.M., Ram T. et al. 2012. Identification and fine-mapping of Xa33, a novel gene for resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Phytopathol. 102: 222–228.
Luo Y., Sangha J.S., Wang S., Li Z., Yang J. & Yin Z. 2012. Marker-assisted breeding of Xa4, Xa21 and Xa27 in the restorer lines of hybrid rice for broad-spectrum and enhanced disease resistance to bacterial blight. Mol. Breed. 30: 1601–1610.
Mew T., Alvarez A., Leach J. & Swings J. 1993. Focus on bacterial blight of rice. Plant Dis. 77: 5–12.
Prasad M.S., Kanthi B.A., Balachandran S., Seshumadhav M., Mohan K.M. & Viraktamath B. 2009. Molecular mapping of rice blast resistance gene Pi-1 (t) in the elite indica variety Samba mahsuri. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 25: 1765–1769.
Singh S., Sidhu J., Huang N., Vikal Y., Li Z., Brar D., Dhaliwal H. & Khush G. 2001. Pyramiding three bacterial blight resistance genes (xa5, xa13 and Xa21) using marker-assisted selection into indica rice cultivar PR106. Theor. Appl. Genet. 102: 1011–1015.
Singh V.K., Singh A., Singh S.P., Ellur R.K., Choudhary V., Sarkel S., Singh D., Krishnan S.G., Nagarajan M., Vinod K.K. et al. 2012. Incorporation of blast resistance into “PRR78”, an elite Basmati rice restorer line, through marker assisted backcross breeding. Field Crops Res. 128: 8–16.
Sundaram R.M., Vishnupriya M.R., Biradar S.K., Laha G.S., Reddy G.A., Rani N.S., Sarma N.P. & Sonti, R.V. 2007. Marker assisted introgression of bacterial blight resistance in Samba Mahsuri, an elite indica rice variety. Euphytica 160: 411–422.
Tao R., Chen J. & Liao Q. 2006. Field manual of diseases and pests in rice identification and resistance evaluation for the diseases and pests. China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, Beijing, pp 118–122.
Wang C., Qi H., Pan H., Li J., Fan Y. Zhang G. & Zhao K. 2005: EST-Markers flanking the rice bacterial blight resistance gene Xa23 and their application in marker-assisted selection. Sci Agri Sin. 38: 1996–2001. (In Chinese with English abstract)
Zhai W., Wang W., Zhou Y., Li X., Zheng X., Zhang Q., Wang G. & Zhu L. 2002. Breeding bacterial blight-resistant hybrid rice with the cloned bacterial blight resistance gene Xa21. Mol. Breed. 8: 285–293.
Zhang Q. 1995. Utilization and strategy of genes for resistance to rice bacterial blight in China. Acta Phytophyl. Sin. 22: 241–245.
Zhang Q. 2009. Genetics and improvement of bacterial blight resistance of hybrid rice in China. Rice Science 16: 83–92.
Zhang Q., Lin S., Zhao B., Wang C., Yang W., Zhou Y., Li D., Chen C. & Zhu L. 1998. Identification and tagging a new gene for resistance to bacterial blight (Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae) from O. rufipogon. Rice Genet. Newsl. 15: 138–142.
Zhang Q., Wang C., Zhao K., Zhao Y., Caslana V., Zhu X., Li D. & Jiang Q. 2001. Rice Genetics Newsletter, Vol. 18, 71 pp.
Zhou Y.-L., Uzokwe V.N.E., Zhang C.-H., Cheng L.-R., Wang L., Chen K., Gao, X.-Q., Sun Y., Chen J.-J., Zhu L.-H. et al. 2011. Improvement of bacterial blight resistance of hybrid rice in China using the Xa23 gene derived from wild rice (Oryza rufipogon). Crop Protect. 30: 637–644.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, Z., Shi, J., Zeng, Y. et al. Application of a simplified marker-assisted backcross technique for hybrid breeding in rice. Biologia 69, 463–468 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-014-0335-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-014-0335-2