Abstract
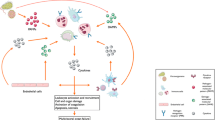
Cell adhesion molecules (CAM) have a key role in the inflammatory response. Selectins, integrins and immunoglobulin (Ig) gene superfamily adhesion receptors mediate the different steps of the migration of leucocytes from the bloodstream towards inflammatory foci. The activation of endothelial cells (EC) upregulates the expression of several CAM and triggers the interaction of these cells with leucocytes. Selectins are involved in the initial interactions (tethering/rolling) of leucocytes with activated endothelium, whereas integrins and Ig superfamily CAM mediate the firm adhesion of these cells and their subsequent extravasation. During rolling, leucocytes are activated through the intracellular signals generated by CAM and chemokine receptors. Blockade of the function or expression of CAM has emerged as a new therapeutic target in inflammatory diseases. Different drugs are able to interfere with cell adhesion phenomena. In addition, new antiadhesion therapeutic approaches (blocking monoclonal antibodies, soluble receptors, synthetic peptides, peptidomimetics, etc.) are currently in development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Springer TA. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature 1990; 346: 425–34
Frenette PS, Wagner DD. Adhesion molecules —part I. N Engl J Med 1996; 334: 1526–9
Frenette PS, Wagner DD. Adhesion molecules —part II: blood vessels and blood cells. N Engl J Med 1996; 335: 43–5
Carlos TM, Harlan JM. Leukocyte-endothelial adhesion molecules. Blood 1994; 84: 2068–101
Kansas GS. Selectins and their ligands: current concepts and controversies. Blood 1996; 88: 3259–3287
Rosen SD, Bertozzi CR. The selectins and their ligands. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1994; 6: 663–73
SteegmaierM, Levinovitz A, Isenmman S, et al. The E-selectinligand ESL-1 is a variant of a receptor for fibroblast growth factor. Nature 1995; 373: 615–20
Brenner G, Gulbins E, Schlottman K, et al. L-selectin activates the Ras pathway via the tyrosine kinase p561ck. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1996; 93: 15376–81
Lo SK, Golenbock DT, Sass PM, et al. Engagement of the Lewis X antigen (CD15) results in monocyte activation. Blood 1997; 89: 307–14
Corbl AL. Leukocyte integrins, structure, expression and function. Heidelberg: Springer Verlag, 1996
Postigo AA, Teixidó J, Sánchez-Madrid F. The α4βl/VCAM-1 adhesion pathway in physiology and disease. Res Immunol 1993; 144: 723–35
Altevogt P, Hubbe M, Ruppert M, et al. The α4 integrin chain is a ligand for α4β7 and α4β1. J Exp Med 1995; 182: 345–55
Phillips DR, Charo FI, Parise L, et al. The platelet membrane glycoprotein lib-Ilia complex. Blood 1988; 71: 831–43
Gawaz M, Neumann FJ, Dickfeld T, et al. Vitronectin receptor (alpha(v)beta3) mediates platelet adhesion to the luminal aspect of endothelial cells: implications for reperfusion in acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 1997; 96: 1809–18
Sánchez-Mateos P, Cabañas C, Sánchez-Madrid F. Regulation of integrin function. Semin Cancer Biol 1996; 7: 99–109
Clark EA, Brugge JS. Integrins and signal transduction pathways: the road taken. Science 1995; 268: 233–8
Juliano RL, Haskill S. Signal transduction from the extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol 1993; 120: 577–85
Takeichi M. The cadherins: cell-cell adhesion molecules controlling animal morphogenesis. Development 1988; 102: 639–55
Bianchi E, Bender JR, Biasi F, et al. Through and beyond the wall: late steps in leukocyte transendothelial migration. Immunol Today 1997; 18: 586–91
Imai T, Hieshima K, Haskell C, et al. Identification and molecular characterization of fractalkine receptor CX3CR1, which mediates both leukocyte migration and adhesion. Cell 1997; 91: 521–30
Rollins BJ. Chemokines. Blood 1997; 90: 909–28
Bach FH, Hancock WW, Ferran C. Protective genes expressed in endothelial cells: a regulatory response to injury. Immunol Today 1997; 18: 483–6
Vassalli P. The pathophysiology of tumor necrosis factor. Annu Rev Immunol 1992; 10: 411–43
Heller RA, Krönke M. Tumor necrosis factor receptor mediated signaling pathways. J Cell Biol 1994; 126: 5–9
Baggiolini M, Dewald B, Moser B. Human chemokines: an update. Annu Rev Immunol 1997; 15: 675–705
Luster AD. Chemokines: chemotactic cytokines that mediate inflammation. N Engl J Med 1998; 338: 436–45
Nieto M, Frade JMR, Sancho D, et al. Polarization of chemokine receptors to the leading edge during lymphocyte chemotaxis. J Exp Med 1997; 18: 153–8
Ernofsson M, Siegbahn A. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB, and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 induce human peripheral blood monocytes to express tissue factor. Thromb Res 1996; 83: 307–20
Schecter AD, Rollins BJ, Zhang YJ, et al. Tissue factor is induced by monocyte chemotactic protein-1 in human aortic smooth muscle and THP-1 cells. J Biol Chem 1997: 272: 28568–73
Berlin C, Bargatze RF, Campbell JJ, et al. α4 Integrins mediate lymphocyte attachment and rolling under physiologic flow. Cell 1995; 80: 413–22
Johnston B, Issekutz TB, Kubes P. The alpha 4-integrin supports leukocyte rolling and adhesion in chronically inflamed postcapillary venules in vivo. J Exp Med 1996; 183: 1995–2006
Feng D, Nagy JA, Pyne K, et al. Neutrophils emigrate from venules by a transendothelial cell pathway in response to fMLP. J Exp Med 1998; 187: 903–15
Piali L, Hammel P, Uherek C, et al. CD31/PECAM-1 is a ligand for αvβ3 integrin involved in adhesion of leukocytes to endothelium. J Cell Biol 1995; 130: 451–560
Dustin ML, Springer TA. Role of lymphocyte adhesion receptors in transient interactions and cell locomotion. Annu Rev Immunol 1991; 9: 27–66
Savage B, Saldivar E, Ruggeri ZM. Initiation of platelet adhesion by arrest onto fibrinogen or translocation on von Willebrand factor. Cell 1996; 84: 289–97
Henn V, Slupsky JR, Grafe M, et al. CD40 ligand on activated platelets triggers an inflammatory reaction of endothelial cells. Nature 1998; 391: 591–4
Diasio RB, Lo Buglio AR Immunomodulators: immunosup-pressive agents and immunostimulants. In: Hardman JG, Limbird LE, editors. Goodman & Gilman: the pharmacological basis of therapeutics. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1996: 1291–308
Cronstein BN, Eberle MA, Gruber HE, et al. Methotrexate inhibits neutrophil function by stimulating adenosine release from connective tissue cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1991; 18: 2441–52
Cronstein BN, Nalme D, Ostud E, et al. The antiinflammatory mechanism of methotrexate; increased adenosine release at inflamed sites disminishes leukocyte accumulation in an in vivo model of inflammation. J Clin Invest 1993; 92: 2675–89
Servitje O, Bordas X, Seron D, et al. Changes in T-cell pheno-type and adhesion molecules expression in psoriatic lesions after low-dose cyclosporin therapy. J Cutan Pathol 1996; 23: 431–6
Wheller SK, Perretti M. Dexamethasone inhibits cytokine-induced intercellular adhesion molecule-1 up-regulation on endothelial cell lines. Eur J Pharmacol 1997; 331: 65–71
Farsky SP, Sannomiya P, Garcia-Leme J. Secreted glucorticoids regulate leukocyte-endothelial interactions in inflammation: a direct vital microscopic study. J Leukoc Biol 1995; 57: 379–86
Dimitrijevic M, Bartlett RR. Leflunomide, a novel immuno-modulating drug, inhibits homotypic adhesion of peripheral blood and synovial fluid mononuclear cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Inflamm Res 1996; 45: 550–5
Sekido N, Mukaida N, Harada A, et al. Prevention of lung reperfusion injury in rabbits by a monoclonal antibody against interleukin-8. Nature 1993; 365: 654–57
Eigler A, Sinha B, Hartmann G, et al. Taming TNF: strategies to restrain this proinflammatory cytokine. Immunol Today 1997; 18: 487–91
Osborn L, Vassallo C, Browning BG, et al. Arrangement of domains, and amino acid residues required for binding of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 to its counter-receptor VLA-4 (alpha 4 beta 1). J Cell Biol 1994; 124: 601–8
Lee JO, Rieu P, Arnaout MA, et al. Crystal structure of the A domain from the alpha subunit of integrin CR3(CDllb/CD18). Cell 1995; 80: 631–8
Gahmberg CG, Tolvanen M, Nortamo P, et al. The intercellular adhesion molecules (ICAMs). In: Horton MA, editor. Adhesion receptors as therapeutic targets. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1996: 37–58
Buckley CD, Simmons DL. Cell adhesion: a new target for theraphy. Mol Med Today 1997; 3: 449–56
Archelos JJ, Hartung HP. The role of adhesion molecules in multiple sclerosis: biology, pathogenesis and therapeutic implications. Mol Med Today 1997; 3: 310–21
Cornejo CJ, Winn RK, Harlan JM. Anti-adhesion therapy. Adv Pharmacol 1997; 39: 99–142
Liao F, Ali J, Greene T, et al. Soluble domain 1 of platelet-endothelial cell adhesion molecule (PECAM) is sufficient to block transendothelial migration in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Med 1997; 185: 1349–57
Verstraete M, Zoldhelyi P. Novel antithrombotic drugs in development. Drugs 1995; 49: 856–84
Alig L, Edenhofer A, Hadvary P, et al. Low molecular weight, non-peptide fibrinogen receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 1992; 35: 4393–407
Bernabei A, Gikakis N, Kowalska MA, et al. Iloprost and echistatin protect platelets during simulated extracorporeal circulation. Ann Thorac Surg 1995; 59: 149–53
Mausa SA, Bozarth JM, Forsythe MS, et al. Antiplatelet and antithrombotic efficacy of DMP 728, a novel platelet GPIIb/IIIa receptor antagonist. Circulation 1994; 89: 3–12
Higashi H, Suzuki Y, Mukaida N, et al. Intervention in endotoxin shock by sulfatide (I3SO3-GalCer) with a concomitant reduction in tumor necrosis factor alpha production. Infect Immun 1997; 65: 1223–7
Shjmaoka M, Ikeda M, Iida T, et al. Fucoidin, a potent inhibitor of leukocyte rolling, prevents neutrophil influx into phorbolester-induced inflammatory sites in rabbit lungs. Am J Resp Crit Care Med 1996; 153; 307–11
Dlaz-González F, González-Alvaro I, Campanero MR, et al. Prevention of in vitro neutrophil-endothelial attachment through shedding of L-selectin by nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. J Clin Invest 1995; 95: 1756–65
González-Alvaro I, Carmona L, Díaz-González F, et al. Aceclofenac, a new nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug, decreases the expression and function of some adhesion molecules on human neutrophils. J Rheumatol 1996; 23: 723–9
García-Vicuña R, Diaz-González F, González-Alvaro I, et al. Prevention of cytokine-induced changes in leukocyte adhesion receptors by nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs from oxicam family. Arthritis Rheum 1997; 40: 143–53
Dlaz-González F, Sánchez-Madrid F. Inhibition of leukocyte adhesion: an alternative mechanism of action for antiinflammatory drugs. Immunol Today 1998; 19: 169–72
Koike R, Miki I, Otoshi M, et al. Gold sodium thiomalate down-regulates intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression on vascular endothelial cells. Mol Pharmacol 1994; 46: 599–604
Gadangi P, Longaker M, Naime D, et al. The antiinflammatory mechanisms of sulfasalazine is related to adenosine release at inflamed sites. J Immunol 1996; 156: 1937–41
Cronstein BN, Molad Y, Reibman J, et al. Colchicine alters the quantitative and qualitative display of selectins on endothelial cells and neutrophils. J Clin Invest 1995; 96: 994–1002
Zhou L, Pope BL, Chourmouzis E, et al. Tepoxalin blocks neutrophil migration into cutaneous inflammatory sites by inhibiting Mac-1 and E-selectin expression. Eur J Immunol 1996; 26: 120–9
Panes J, Russell JM, Wolf RE, et al. Effects of tenidap on leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion in mesenteric venules. J Rheumatol 1995; 22: 444–9
Kopp E, Ghosh S. Inhibition of NF-kappa B by sodium salicylate and aspirin. Science 1994; 265: 956–9
Khachigian LM, Collins T, Fries JW. N-acetyl cysteine blocks mesangial VCAM-1 and NF-kappa B expression in. vivo. Am J Pathol 1997; 151: 1225–9
Read MA, Neish AS, Luscinskas FW, et al. The proteasome pathway is required for cytokine-induced endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule expression. Immunity 1995; 2: 493–506
Mazzone A, Mazzucchelli I, Fossati G, et al. Iloprost effects on phagocytes in patients suffering from ischaemic diseases: in vivo evidence for down-regulation of alpha M beta 2 integrin. Eur J Clin Invest 1996; 26: 860–6
Weber C, Erl W, Weber KS, et al. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors decrease CDllb expression and CDllb-dependent adhesion of monocytes to endothelium and reduce increased adhesiveness of monocytes isolated from patients with hyper-cholesterolemia. J Am Coll Cardiol 1997; 30: 1212–7
Cominacini L, Garbin U, Pasini AF, et al. Antioxidants inhibit the expression of intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 induced by oxidized LDL on human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Free Radic Biol Med 1997; 22: 117–27
Torphy TJ, Barnette MS, Hay DW, et al. Phosphodiesterase IV inhibitors as therapy for eosinophil-induced lung injury in asthma. Environ Health Perspect 1994; 102 Suppl.: 79–84
Ciprandi G, Buscaglia S, Pesce G, et al. Cetirizine reduces inflammatory cell recruitment and ICAM-1 (or CD54) expression on conjunctival epithelium in both early-and late-phase reactions after allergen-specific challenge. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1995; 95: 612–21
Hamilton GS, Mewshaw RE, Bryant CM, et al. Fluorenyalkanoic and benzoic acids as novel inhibitors of cell adhesion processes in leukocytes. J Med Chem 1995; 38: 1650–6
Endemann G, Feng Y, Bryant CM, et al. Novel anti-inflammatory compounds prevent CD11b/CD18, alpha M beta 2 (Mac-1)-dependent neutrophil adhesion without blocking activation-induced changes in Mac-1. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1996; 276: 5–12
González-Amaro R, Portales-Pérez D, Baranda L, et al. Pentoxifylline inhibits adhesion and activation of human T lymphocytes. J Immunol 1998 1 Jul; 161: 65–72
Kovach NL, Lindgren CG, Fefer A, et al. Pentoxifylline inhibits integrin-mediated adherence of interleukin-2-activated human peripheral blood lymphocytes to human umbilical vein endothelial cells, matrix components, and cultured tumor cells. Blood 1994; 84: 2234–42
Agrawal S. Antisense oligonucleotides: towards clinical trials. Trends Biotechnol 1996; 14: 376–87
Bennett CF, Kornbrust D, Henry S, et al. An ICAM-1 antisense oligonucleotide prevents and reverses dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1997; 280: 988–1000
Stepkowski SM, Tu Y, Condon TP, et al. Blocking of heart allograft rejection by intercellular adhesion molecule-1 antisense aligonucleotides alone or in combination with other immunosuppressive modalities. J Immunol 1994; 153: 5336–46
Glover JM, Leeds JM, Mant TG, et al. Phase I safety and pharmacokinetics profile of an intercellular adhesion molecule-1 antisense oligonucleotide (ISIS 2302). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1997; 282: 1173–80
Agrawal S, Iyer RP. Perspectives in antisense therapeutics. Pharmacol Ther 1997; 76: 151–60
Morishita R, Sugimoto T, Aoki M, et al. In. vivo transfection of cis element ‘decoy’ against nuclear factor-kappaB binding site prevents myocardial infarction. Nat Med 1997; 3: 894–9
Claude H. The anti-gene strategy: control of gene expression by triplex-forming oligonucleotides. Anticancer Drug Des 1991; 6: 569–84
Suitters AJ, Foulkes R, Opal SM, et al. Differential effect of isotype on efficacy of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha chimeric antibodies in experimental septic shock. J Exp Med 1994; 179: 849–56
Abraham E, Wunderink R, Silverman H, et al. Efficacy and safety of monoclonal antibody to human tumor necrosis factor α in patients with sepsis syndrome: a randomized, controlled, double-blind, multicenter clinical trial. JAMA 1995; 273: 934–41
Fisher Jr CJ, Agosti JM, Opal SM, et al. Treatment of septic shock with the tumor necrosis factor receptor: Fc fusion protein. N Engl J Med 1996; 334: 1697–702
Fisher Jr CJ, Dhainaut JF, Opal SM, et al. Recombinant human interleukin 1 receptor antagonist in the treatment of patients with sepsis syndrome: results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. JAMA 1994; 271: 1836–43
Ikeda N, Mukaida N, Kaneko S, et al. Prevention of endotoxin-induced acute lethality in Propionibacterium acnes-primed rabbits by an antibody to leukocyte integrin β2 with concomitant reduction of cytokine production. Infect Immun 1995; 63: 4812–7
Watanabe S, Mukaida N, Ikeda N, et al. Prevention of endotoxin shock by an antibody against leukocyte integrin beta 2 through inhibiting production and action of TNF. Int Immunol 1995; 7: 1037–46
Targan SR, Hanauer SB, van Deventer SJ, et al. A short-term study of chimeric monoclonal antibody cA2 to tumor necrosis factor alpha for Crohn’s disease: Crohn’s disease study group. N Engl J Med 1997; 337: 1029–35
Stack WA, Mann SD, Roy AJ, et al. Randomised controlled trial of CDP571 antibody to tumor necrosis factor-alpha in Crohn’s disease. Lancet 1997; 349: 521–4
Moreland LW, Baumgartner SW, Schiff MH, et al. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with a recombinant human tumor necrosis factor receptor (p75)-Fc fusion protein. N Engl J Med 1997; 337: 141–7
Elliot MJ, Maini RN, Feldmann M, et al. Repeated therapy with monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor a (cA2) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 1994; 344: 1125–7
Tak PP, Taylor PC, Breedveld FC, et al. Decrease in cellularity and expression of adhesion molecules by anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1996; 39: 1077–81
Paleolog EM, Hunt M, Elliot MJ, et al. Deactivation of vascular endothelium bymonoclonal anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha antibody in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1996; 39: 1082–91
Kavanaugh AF, Schulze-Koops H, Davis LS, et al. Repeat treatment of rheumatoid arthritis patients with a murine anti-intercellular adhesion molecule 1 monoclonal antibody. Arthritis Rheum 1997; 40: 849–53
Davis LS, Kavanaugh AF, Nichols LA, et al. Induction of persistent T cell hyporesponsiveness in. vivo by monoclonal antibody to ICAM-1 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol 1995; 154: 3525–37
Jasin HE, Lightfoot E, Davis LS, et al. Amelioration of antigen-induced arthritis in rabbits treated with monoclonal antibodies to leukocyte adhesion molecules. Arthritis Rheum 1992; 35: 541–49
Barbadillo C, G-Arroyo A, Salas C, et al. Anti-integrin immuno-therapy in rheumatoid arthritis: protective effect of anti-alpha 4 antibody in adjuvant arthritis. Springer Semin Immunopathol 1995; 16: 427–36
Issekutz AC, Ayer L, Miyasaka M, et al. Treatment of stablished adjuvant arthritis in rats with monoclonal antibody to CD18 and very late activation antigen-4 integrins suppresses neutro-phil and T-lymphocyte migration to the joints and improves clinical disease. Immunology 1996; 88: 569–76
McFadden Jr ER, Gilbert IA. Asthma. N Engl J Med 1992; 327: 1928–37
Wardlaw AJ, Walsh GM, Symon FA. Adhesion interactions involved in eosinophil migration through vascular endothelium. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1996; 796: 124–37
Takafuji S, Ohtoshi T, Takizawa H, et al. Eosinophil degranulation in the presence of epithelial cells. Effect of cytokines and role of adhesion. J Immunol 1996; 156: 3980–5
Wegner CD, Gundel RH, Reoly P, et al. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in the pathogenesis of asthma. Science 1990; 247: 456–9
Gundel RH, Wegner CD, Torcellini CA, et al. Endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 mediates antigen-induced acute airway inflammation and late-phase airway obstruction in monkeys. J Clin Invest 1991; 88: 1407–11
Abraham WM, Sielczak MW, Ahmed A, et al. Alpha-4 integrins mediate antigen-induced late bronchial responses and prolonged airway hyperresponsiveness in sheep. J Clin Invest 1994; 93: 776–87
Pretolani M, Ruffe C, Lapa-e-Silva JR, et al. Antibody to very late activation antigen-4 prevents antigen-induced bronchial hyperreactivity and cellular infiltration in guinea pig airways. J Exp Med 1994; 180: 795–805
Featherstone C. Anti-integrin drugs developed to treat inflammation. Lancet 1996; 347: 1106
Herstenberg PE, Winsor-Hines D, Briskin MJ, et al. Rapid resolution of chronic colitis in the cotton-top tamarin with an antibody to a gut-homing integrin alpha 4 beta 7. Gastroenterology 1996; 111: 1373–80
Picarella D, Hurlbut P, Rottman J, et al. Monoclonal antibodies specific for beta 7 integrin and mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule-1 (MadCAM-1) reduce inflammation in the colon of scid mice reconstituted with CD45RBhigh CD4+ T cells. J Immunol 1997; 158: 2099–106
del Zoppo GJ, Wagner S, Tagaya M. Trends and future developments in the pharmacological treatment of acute ischemie stroke. Drugs 1997; 54: 9–38
Birnbaum Y, Patterson M, Kloner RA. The effect of CY1503, a sialyl Lewisx analog blocker of the selectin adhesion molecules, on infarct size and ’no-reflow’ in the rabbit model of acute myocardial infarction/reperfusion. J Mol Cell Cardiol 1997; 29: 2013–25
Buerke M, Weyrich AS, Zheng Z, et al. Sialyl Lewisx-containing oligosaccharide attenuates myocardial reperfusion injury in cats. J Clin Invest 1994; 93: 1140–8
Silver MJ, Sutton JM, Hook S, et al. Adjunctive selectin blockade succesfully reduces infarct size beyond thrombolysis in the electrolytic canine coronary artery model. Circulation 1995; 92: 492–9
Flynn DM, Buda AJ, Jeffords PR, et al. A sialyl Lewisx-containing carbohydrate reduces infarct size: role of selectins in myocardial reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol 1996; 271: H2086–96
Weiser MR, Gibbs SA, Valeri CR, et al. Anti-selectin therapy modifies skeletal muscle ischemia and reperfusion injury. Shock 1996; 5: 402–7
Takada M, Nadeau KC, Shaw GD, et al. Prevention of late renal changes after initial ischemia/reperfusion injury by blocking early selectin binding. Transplantation 1997; 64: 1520–5
Simoons ML, Rutsch W, Vahanian A, et al. Randomised placebo-controlled trial of abciximab before and during coronary intervention in refractory unstable angina: the CAPTURE study. Lancet 1997; 349: 1429–35
Zhao ZQ, Lefer DJ, Sato H, et al. Monoclonal antibody to ICAM-1 preserves postischemic blood flow and reduces infarct size after ischemia/reperfusion in rabbit. J Leukoc Biol 1997; 62: 292–300
Anderson DC, Springer TA. Leukocyte adhesion deficiency: an inherited defect in the Mac-1, LFA-1 and p150/95 glycoproteins. Annu Rev Med 1987; 38: 175–94
Etzioni A, Phillips LM, Paulson JC, et al. Leukocyte adhesion deficiency (LAD) II. Ciba Found Symp 1995; 189: 51–8
Kuijpers TW, van Lier RAW, Hamann D, et al. Leukocyte adhesion deficiency type 1 (LAD-1)/variant. J Clin Invest 1997; 100: 1725–33
Sharar S, Sasaki SS, Flaherty LC, et al. P-selectin blockade does not impair leukocyte host defense against bacterial peritonitis and soft tissue infection in rabbits. J Immunol 1993; 151: 4982–8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
González-Amaro, R., Diaz-González, F. & Sánchez-Madrid, F. Adhesion Molecules in Inflammatory Diseases. Drugs 56, 977–988 (1998). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-199856060-00003
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-199856060-00003