Abstract
Objectives
The objectives of the study were to characterise the pharmacokinetics and assess the tolerability of duloxetine in healthy Chinese subjects after single and multiple oral 60mg dosing.
Methods
This was a single-centre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, single-period study in healthy native Chinese subjects. A total of 32 subjects, 19 men (14 on duloxetine, 5 on placebo) and 13 women (10 on duloxetine, 3 on placebo) between the ages of 20 and 39 years, participated in the study. Duloxetine 60mg (enteric-coated pellets in a capsule) was given orally once on day 1 and once daily on days 4 to 9. Sequential blood samples were collected over 72 hours after the dose on days 1 and 9, and a predose sample was obtained on days 7 and 8. Duloxetine concentrations in plasma were determined by a validated liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method. The tolerability evaluation included a physical examination, vital signs, adverse event monitoring and clinical laboratory evaluations.
Results
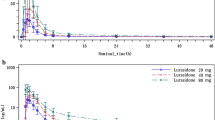
Duloxetine disposition on oral administration is characterised by a one-compartment pharmacokinetic model. Duloxetine is well absorbed, with a median time of maximum plasma concentration at 6 and 4 hours following single and multiple dosing, respectively. At steady state, the mean apparent oral clearance (CLss/F), mean apparent volume of distribution (Vss/F) and mean terminal elimination half-life (t½) were 86.8 L/h, 1570L and 11 hours, respectively. CL/F and Vss/F on single dosing were not statistically significantly different (p > 0.05) compared with multiple dosing. The linearity index, calculated as the ratio of the area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) during the dosing interval τ at steady state (AUCτ,ss) to the AUC from time zero to infinity after single dosing (AUC∞single dose) was 1.15 (coefficient of variation 35.7%). The accumulation in duloxetine exposure was estimated to be 50% on multiple dosing compared with single dosing, consistent with the t½ and dosing interval (24 hours). The pharmacokinetic parameters of duloxetine in Chinese subjects were not statistically significantly different from those reported previously in Caucasian and Japanese subjects. There were no clinically significant adverse events, abnormal safety laboratory data or vital sign changes reported.
Conclusion
Duloxetine pharmacokinetics in healthy Chinese subjects given a 60mg once-daily dosing regimen were well characterised and consistent with known duloxetine pharmacokinetics in healthy Caucasian and Japanese subjects. Both single dosing and multiple once-daily dosing of duloxetine 60mg were well tolerated by healthy Chinese subjects in this study.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hunziker ME, Suehs BT, Bettinger TL, et al. Duloxetine hydrochloride: a new dual-acting medication for the treatment of major depressive disorder. Clin Ther 2005; 27(8): 1126–43
Bymaster FP, Lee TC, Knadler MP, et al. The dual transporter inhibitor duloxetine: a review of its preclinical pharmacology, pharmacokinetic profile, and clinical results in depression. Curr Pharm Des 2005; 11(12): 1475–93
Detke MJ, Wiltse CG, Mallinckrodt CH, et al. Duloxetine in the acute and long-term treatment of major depressive disorder: a placebo- and paroxetine-controlled trial. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2004; 14(6): 457–70
Dmochowski RR, Miklos JR, Norton PA, et al. Duloxetine versus placebo for the treatment of North American women with stress urinary incontinence. J Urol 2003; 170(4 Pt 1): 1259–63
Raskin J, Pritchett YL, Wang F, et al. A double-blind, randomized multicenter trial comparing duloxetine with placebo in the management of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. Pain Med 2005; 6(5): 346–56
Eli Lilly and Company. Cymbalta® (duloxetine hydrochloride) delayed-release capsules [US package insert; online]. Available from URL: http://www.fda.gov/cder/foi/label/2007/021427s009s011s0131bl.pdf [Accessed 2007 Jul 19]
Arnold LM, Rosen A, Pritchett YL, et al. A randomized, doubleblind, placebo-controlled trial of duloxetine in the treatment of women with fibromyalgia with or without major depressive disorder. Pain 2005; 119(1–3): 5–15
Lantz RJ, Gillespie TA, Rash TJ, et al. Metabolism, excretion, and pharmacokinetics of duloxetine in healthy human subjects. Drug Metab Dispos 2003; 31(9): 1142–50
Kuo F, Gillespie TA, Kulanthaivel P, et al. Synthesis and biological activity of some known and putative duloxetine metabolites. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2004; 14(13): 3481–6
Skinner MH, Kuan HY, Pan A, et al. Duloxetine is both an inhibitor and a substrate of cytochrome P4502D6 in healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2003; 73(3): 170–7
Hua TC, Pan A, Chan C, et al. Effect of duloxetine on tolterodine pharmacokinetics in healthy volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2004; 57(5): 652–6
Bradford LD, Kirlin WG. Polymorphism of CYP2D6 in Black populations: implications for psychopharmacology. Int J Neuropsychopharmcol 1998; 1(2): 173–85
Kitada M. Genetic polymorphism of cytochrome P450 enzymes in Asian populations: focus on CYP2D6. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res 2003; 23(1): 31–5
Landi MT, Sinha R, Lang NP, et al. Human cytochrome P4501A2. IARC Sci Publ 1999; (148): 173–95
Chan C, Yeo KP, Pan AX, et al. Duloxetine pharmacokinetics are similar in Japanese and Caucasian subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2007; 63(3): 310–4
Ma N, Zhang B, Li H, et al. Determination of duloxetine in human plasma via LC/MS and subsequent application to a pharmacokinetic study in healthy Chinese volunteers. Clinica Chimica Acta 2007; 380: 100–5
Sharma A, Goldberg MJ, Cerimele BJ. Pharmacokinetics and safety of duloxetine, a dual-serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. J Clin Pharmacol 2000; 40(2): 161–7
Bartoli A, Xiaodong S, Gatti G, et al. The influence of ethnic factors and gender on CYP1A2-mediated drug disposition: a comparative study in Caucasian and Chinese subjects using phenacetin as a marker substrate. Ther Drug Monit 1996; 18(5): 586–91
Eli Lilly and Company. Cymbalta (duloxetine hydrochloride) capsules. Clinical pharmacology biopharmaceutics review, part 2: 20 [online]. Available from URL: http://www.fda.gov/cder/foi/nda/2004/021427_s000_Cymbalta.htm [Accessed 2007 Aug 9]
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the subjects for their participation in the study and Richard F. Bergstrom, PhD, and Stephen Wise, MD, for their valuable guidance on the study design.
This study was presented in part at the American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists Annual Meeting in San Antonio, TX, USA, October 2006. The work was funded by Eli Lilly and Company. All of the authors, except for Shu Liang, MD, Professor of Psychiatry, and Si Tianmei, PhD, are employees of Eli Lilly and Company. Dr Liang was the primary investigator and Dr Tianmei was the co-investigator for the study. Drs Liang and Tianmei have no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tianmei, S., Knadler, M.P., Lim, M.T. et al. Pharmacokinetics and Tolerability of Duloxetine following Oral Administration to Healthy Chinese Subjects. Clin Pharmacokinet 46, 767–775 (2007). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-200746090-00004
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-200746090-00004