Summary
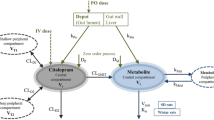
A steady-state model is here developed as a framework for the analysis of blood concentrations of clomipramine, obtained during routine drug monitoring. A model is proposed to account for its major metabolic pathways, hydroxylation and demethylation, including first-pass effect. Impaired hydroxylation capacity is shown to lead to a dramatic increase in the concentration of demethyl-clomipramine, with a concomitant moderate increase in that of the parent drug. Deficient demethylation capacity is associated with a reduced ratio of demethyl metabolite to parent drug. A nomogram is provided to allow easy determination of hydroxylation and demethylation capacities from routinely measured blood concentrations.
Data from 150 patients are analysed in order to identify interindividual variability factors. Average pseudo-clearances, calculated from trough blood concentrations at steadystate, are 17 L/h for hydroxylation, 23 L/h for demethylation and 40 L/h for elimination of hydroxylated metabolites. Maximum to minimum ratios are 8, 27 and 11, respectively. The metabolising capacity through either process significantly decreases with increasing age, clearance estimates being 40 to 50% lower for patients 75 years or older than for those 40 years or younger. Tobacco smoking and chronic alcohol consumption induce and reduce the demethylation clearance, respectively. Inhibition of hydroxylation in the presence of phenothiazine comedication is also shown. Finally, small but significant differences according to sex are observed.
Potential implications of the proposed model-based approach include adaptation of the dosage regimen to individual characteristics at the very beginning of antidepressant therapy, and early detection of patients with impaired metabolising capacities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åsberg M, Sjöqvist F. Therapeutic monitoring of tricyclic antidepressants — clinical aspects. In Richens & Marks (Eds) Therapeutic drug monitoring, pp. 225–254, Churchill Livingstone, New York, 1981
Balant-Gorgia AE, Balant LP, Garrone G. High blood concentrations of imipramine or clomipramine and therapeutic failure: a case report study using drug monitoring data. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring 11: 415–420, 1989
Balant-Gorgia AE, Balant LP, Genet C, Dayer P, Aeschlimann JM. et al. Importance of oxidative polymorphism and levomepromazine treatment on the steady-state blood concentrations of clomipramine and its major metabolites. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 31: 449–455, 1986
Balant-Gorgia AE, Schulz P, Dayer P, Balant L, Kübli A. et al. Role of oxidation polymorphism on blood and urine concentrations of amitriptyline and its metabolites in man. Archiv für Psychiatrie und Nervenkrankenheiten 232: 215–222, 1982
Benítez J, Llerena A, Cobaleda J. Debrisoquine oxidation polymorphism in a Spanish population. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 44: 74–77, 1988
Bertilsson L, Åberg-Wistedt A, Dumont E, Lundström J. Rapid conjugation in an extremely rapid hydroxylator of debrisoquine: a case report supporting a coregulation of certain phase I and II metabolic reactions. Therapeutic Drue Monitoring 10 242–244, 1988
Broadhurst AD, James HD, Delia Corte L, Heeley AF. Clomipramine plasma level and clinical response. Postgraduate Medical Journal 53: 139–145, 1977
Brøsen K. The relationship between imipramine metabolism and the sparteine oxidation polymorphism, Laegeforeningens For1ag, Copenhagen, 1988
Brøsen K, Gram LF, Kjysner R, Bech P. Steady-state levels of imipramine and its metabolites: significance of dose-dependent kinetics. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 30: 43–49, 1986
Burch JE, Shaw DM, Michalakeas A, Karajgi B, Roberts SG. et al. Time course of plasma drug levels during once-daily oral administration of clomipramine. Psychopharmacology 77: 344–347, 1982
Conrad CD, Küdler HS. Symptom exacerbation in psychotically depressed adolescents due to high desipramine plasma concentrations. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 6: 161–164, 1986
De Cuyper HJA, van Praag HM, Mulder-Hajonides WREM, Westenberg HGM, de Zeeuw RA. Pharmacokinetics of clomipramine in depressive patients. Psychiatry Research 4: 147–156, 1981
Delia Corte L, Broadhurst AD, Sgaragli GP, Filippini S, Heeley AF. et al. Clinical response and tricyclic plasma levels during treatment with clomipramine. British Journal of Psychiatry 134: 390–400, 1979
Dencker SJ, Nagy A. Single versus divided daily dosages of clomipramine. Plasma concentration and clinical effect. Acta Psych iatnca Scandinavica 59: 326–333, 1979
Dubois JP, Kueng W, Theobald W, Wirz B. Measurement of clomipramine, N-desmethyl-clomipramine, imipramine, and dehydroimipramine in biological fluids by selective ion monitoring, and pharmacokinetics of clomipramine. Clinical Chemistry 22: 892–897, 1976
Evans LEJ, Bett JHN, Cox JR, Dubois JP, Van Hees T. The bioavailability of oral and paremeral chlorimipramine (Anafranil). Progress in Neuropsychopharmacology 4: 293–302, 1980
Faravelli C, Ballerini A, Ambonetti A, Broadhurst AD, Das M. Plasma levels and clinical response during treatment with clomipramine. Journal of Affective Disorders 6: 95–107, 1984
Faravelli C, Ballerini A, Broadhurst AD, Das M. Relevance of plasma levels during clomipramine treatment of primary depression. Journal of Affective Disorders 4: 163–165, 1982
Garvey MJ, Tuason VB, Johnson RA, Valentine RH, Cooper TB. Elevated plasma tricyclic levels with therapeutic doses of imipramine. American Journal of Psychiatry 141: 853–856, 1984
Gibaldi M, Perrier D. Pharmacokinetics, Marcel Dekker, New York, 1982
Hrdina PD, Rovei V, Henry JF, Hervy MP, Gomeni R. et al. Comparison of single-dose pharmacokinetics of imipramine and maprotiline in the elderly. Psychopharmacology 70: 29–34, 1980
John VA, Luscombe DK, Kemp H. Effects of age, cigarette smoking and the oral contraceptive on the pharmacokinetics of clomipramine and its desmethyl metabolite during chronic dosing. Journal of International Medical Research 8: 88–95, 1980
Kuss HJ, Jungkunz G. Nonlinear pharmacokinetics of chlorimipramine after infusion and oral administration in patients. Progress in Neuropsychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry 10: 739–748, 1986
Lane EA, Guthrie S, Linnoila M. Effects of ethanol on drug and metabolite pharmacokinetics. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 10: 228–247, 1985
Loo H, Benyacoub AK, Rovei V, Altamura CA, Vadrot M. et al. Long-term monitoring of tricyclic antidepressant plasma concentrations. British Journal of Psychiatry 137: 444–451, 1980
Luscombe DK. Pharmacokinetics of clomipramine. British Journal of Clinical Practice 3 (Suppl.): 35–50, 1979
Malauzat D, Léger JM, Tharaud M, Herrmann C, Clément JP. et al. Intérêts et limites des dosages plasmatiques dans la prescription courante des antidépresseurs. Annales Médico-Psychologiques 142: 1110–1117, 1984
Mårtensson E, Axelsson R, Nyberg G, Svensson C. Pharmacokinetic properties of the antidepressant drugs amitriptyline, clomipramine and imipramine: a clinical study. Current Therapeutic Research 36: 228–238, 1984
Martin E, Moll W, Schmid P, Dettli L. Problems and pitfalls in estimating average pharmacokinetic parameters. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 26: 595–602, 1984
Miller LG. Recent developments in the study of the effects of cigarette smoking on clinical pharmacokinetics and clinical pharmacodynamics. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 17: 90–108, 1989
Nies A, Robinson DS, Friedman MJ, Green R, Cooper TB. et al. Relationship between age and tricyclic antidepressant plasma levels. American Journal of Psychiatry 134: 790–793, 1977
O’Malley K, Stevenson IH, Crooks J. Impairment of human drug metabolism by oral contraceptive steroids. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 13: 552–557, 1972
Perry PJ, Pfohl BM, Holstad SG. The relationship between antidepressant response and tricyclic antidepressant plasma concentrations: a retrospective analysis of the literature using logistic regression analysis. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 13: 381–392, 1987
Reisby N, Gram LF, Bech P, Sihm F, Krautwald O. et al. Clomipramine: plasma levels and clinical effects. Communications in Psychopharmacology 3: 341–351, 1979
Schneider LS, Cooper TB, Severson JA, Zempleni T, Sloane RB. Electrocardiographic changes with nortriptyline and 10-hydroxynortriptyline in elderly depressed outpatients. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 8: 402–408, 1988
Sheiner LB, Benet LZ. Premarketing observational studies of population pharmacokinetics of new drugs. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 38: 481–487, 1985
Sheiner LB, Rosenberg B, Marathe VV. Estimation of population characteristics of pharmacokinetic parameters from routine clinical data. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 5: 445–479, 1977
Spina E, Birgersson C, Von Bahr C, Ericsson Ö, Mellström B. et al. Phenotypic consistency in hydroxylation of desmethylimipramine and debrisoquine in healthy subjects and in human liver microsomes. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 36: 677–682, 1984
Suckow RF, Cooper TB. Simultaneous determination of imipramine, desipramine and their 2-hydroxymetabolites in plasma by ion-pair reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography with amperometric detection. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 70: 257–261, 1981
Sutfin TA, Perini GI, Molnar G, Jusko WJ. Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of imipramine and its major active and conjugated metabolites in depressed patients. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 8: 48–53, 1988
Vandel B, Vandel S, Jounet JM, Allers G, Volmat R. Relationship between the plasma concentration of clomipramine and desmethylclomipramine in depressive patients and the clinical response. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 22: 15–20, 1982
Vandel S, Sandoz M, Vandel B, Bertschy G, Allers G. et al. Interaction pharmacocinétique éentre la clomipramine et les phénothiazines. Thérapie 42: 67–68, 1987
Vandel S, Vandel B, Sandoz M, Allers G, Bechtel P. et al. Clinical response and plasma concentration of amitriptyline and its metabolite nortriptyline. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 14: 185–190, 1978
Von Bahr C, Birgersson C, Morgan ET, Eriksson Ö, Göransson M. et al. Oxidation of tricyclic antidepressant drugs, debrisoquine and 7-ethoxyresorufin, by human liver preparations. Xenobiotica 16: 391–400, 1986
Walle T, Walle UK, Cowart TD, Conradi EC. Pathway-selective sex differences in the metabolic clearance of propranolol in human subjects. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapuetics 46: 257–263, 1989
Whiting B, Kelman AW, Grevel J. Population pharmacokinetics, theory and clinical application. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 11: 387–401, 1986
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gex-Fabry, M., Balant-Gorgia, A.E., Balant, L.P. et al. Clomipramine Metabolism Model-Based Analysis of Variability Factors from Drug Monitoring Data. Clin Pharmacokinet 19, 241–255 (1990). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199019030-00007
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199019030-00007