Abstract
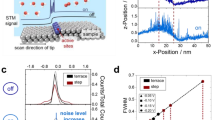
We demonstrated the imaging of local electron transfer-rate differences on a flat conductive carbon substrate, attributed to only surface functional groups, by using a scanning electrochemical microscopy (SECM) technique. These differences were clearly imaged by using a redox mediator with surface state sensitive electron transfer rates, even if the conductivity of each imaging area were almost identical. The carbon electrode surface was masked with a patterned photoresist, and selectively introduced oxygen functional groups using an oxygen plasma treatment. This patterned surface exhibited hardly any topographical features when observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and a height difference of only 1.0 nm was observed with atomic force microscopy (AFM). However, the SECM feedback mode and substrate generation-tip collection (SG-TC) mode are able to distinguish these interfaces with an almost micrometer order resolution by utilizing the difference in the electron transfer rate for the Fe2+/3+ mediator, and the current ratios for regions rich and poor in oxygen containing groups were 1.5 and 2.0, respectively. This technique could be employed for imaging and monitoring the electron transfer rates on various electrode surfaces, including fluorine and nitrogen terminated surfaces and a monolayer film patterned with micro or nano contact printing techniques.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. L. McCreery, Chem. Rev., 2008, 108, 2646.
K. Honda, T. Noda, A. Yoshimura, K. Nakagawa, and A. Fujishima, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108, 16117.
P. Sun, F. O. Laforge, and M. V. Mirkin, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2007, 9, 802.
A. Kueng, C. Kranz, A. Lugstein, E. Bertagnolli, and B. Mizaikoff, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2003, 42, 3238.
K. B. Holt, A. J. Bard, Y. Show, and G. M. Swain, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108, 15117.
S. H. Wang and G. M. Swain, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111, 3986.
N. R. Wilson, S. L. Clewes, M. E. Newton, P. R. Unwin, and J. V. Macpherson, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110, 5639.
G. Janssen, W. J. P. Vanenckevort, W. Vollenberg, and L. J. Giling, Diamond Relat. Mater., 1992, 1, 789.
P. H. Chen and R. L. McCreery, Anal. Chem., 1996, 68, 3958.
P. H. Chen, M. A. Fryling, and R. L. Mccreery, Anal. Chem., 1995, 67, 3115.
I. Yagi, H. Notsu, T. Kondo, D. A. Tryk, and A. Fujishima, J. Electroanal. Chem., 1999, 473, 173.
M. C. Granger and G. M. Swain, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1999, 146, 4551.
R. J. Bowling, R. T. Packard, and R. L. Mccreery, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1989, 111, 1217.
R. C. Tenent and D. O. Wipf, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2003, 150, E131.
O. Niwa, J. Jia, Y. Sato, D. Kato, R. Kurita, K. Maruyama, K. Suzuki, and S. Hirono, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 7144.
S. Hirono, S. Umemura, M. Tomita, and R. Kaneko, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2002, 80, 425.
J. B. Jia, D. Kato, R. Kurita, Y. Sato, K. Maruyama, K. Suzuki, S. Hirono, T. Ando, and O. Niwa, Anal. Chem., 2007, 79, 98.
D. Kato, N. Sekioka, A. Ueda, R. Kurita, S. Hirono, K. Suzuki, and O. Niwa, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 3716.
N. Sekioka, D. Kato, A. Ueda, T. Kamata, R. Kurita, S. Umemura, S. Hirono, and O. Niwa, Carbon, 2008, 46, 1918.
A. Ueda, O. Niwa, K. Maruyama, Y. Shindo, K. Oka, and K. Suzuki, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2007, 46, 8238.
Y. Kobayashi, M. Sakai, A. Ueda, K. Maruyama, T. Saiki, and K. Suzuki, Anal. Sci., 2008, 24, 571.
A. J. Bard, F. R. F. Fan, J. Kwak, and O. Lev, Anal. Chem., 1989, 61, 132.
J. Kwak and A. J. Bard, Anal. Chem., 1989, 61, 1221.
C. E. Nebel, H. Uetsuka, B. Rezek, D. Shin, N. Tokuda, and T. Nakamura, Diamond Relat. Mater., 2007, 16, 1648.
Y. Lee, Z. F. Ding, and A. J. Bard, Anal. Chem., 2002, 74, 3634.
Y. Takahashi, Y. Hirano, T. Yasukawa, H. Shiku, H. Yamada, and T. Matsue, Langmuir, 2006, 22, 10299.
A. Kueng, C. Kranz, B. Mizaikoff, A. Lugstein, and E. Bertagnolli, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2003, 82, 1592.
H. Shin, P. J. Hesketh, B. Mizaikoff, and C. Kranz, Anal. Chem., 2007, 79, 4769.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ueda, A., Kato, D., Sekioka, N. et al. Local Imaging of an Electrochemical Active/Inactive Region on a Conductive Carbon Surface by Using Scanning Electrochemical Microscopy. ANAL. SCI. 25, 645–651 (2009). https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.25.645
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.25.645