Abstract
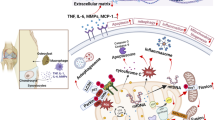
Osteoarthritis (OA), characterized by cartilage degeneration, synovial inflammation, and subchondral bone remodeling, is among the most common musculoskeletal disorders globally in people over 60 years of age. The initiation and progression of OA involves the abnormal metabolism of chondrocytes as an important pathogenic process. Cartilage degeneration features mitochondrial dysfunction as one of the important causative factors of abnormal chondrocyte metabolism. Therefore, maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis is an important strategy to mitigate OA. Mitophagy is a vital process for autophagosomes to target, engulf, and remove damaged and dysfunctional mitochondria, thereby maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis. Cumulative studies have revealed a strong association between mitophagy and OA, suggesting that the regulation of mitophagy may be a novel therapeutic direction for OA. By reviewing the literature on mitophagy and OA published in recent years, this paper elaborates the potential mechanism of mitophagy regulating OA, thus providing a theoretical basis for studies related to mitophagy to develop new treatment options for OA.
摘要
骨关节炎是一种以关节内软骨损伤退变、软骨下骨异常重塑、骨赘生成、滑膜炎症反应和广泛血管生成为特征的慢性退行性关节疾病,是全球60岁以上人群最常见的肌肉骨骼疾病。在骨关节炎的发生发展过程中,软骨细胞的异 常代谢发挥了重要致病作用。线粒体功能障碍作为软骨细胞代谢异常的重要诱因,参与了骨关节炎的发生和发展。因此,维持线粒体稳态是一种避免骨关节炎发生的重要方式。线粒体自噬是自噬体靶向吞噬损伤线粒体,以清除受损或 功能失调的线粒体,维持线粒体稳态的一种方式。越来越多的研究发现线粒体自噬与骨关节炎密切相关,这提示线粒体自噬功能的调节可以作为一种治疗骨关节炎的新方法。本文通过对近年来线粒体自噬在骨关节炎中的研究进行综述, 进一步阐述了线粒体自噬调控骨关节炎的潜在机制,为线粒体自噬治疗骨关节炎的相关研究提供理论依据。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akasaki Y, Alvarez-Garcia O, Saito M, et al., 2014. FoxO transcription factors support oxidative stress resistance in human chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheumatol, 66(12):3349–3358. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.38868
Almonte-Becerril M, Navarro-Garcia F, Gonzalez-Robles A, et al., 2010. Cell death of chondrocytes is a combination between apoptosis and autophagy during the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis within an experimental model. Apoptosis, 15(5):631–638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-010-0458-z
Anding AL, Baehrecke EH, 2017. Cleaning house: selective autophagy of organelles. Dev Cell, 41(1):10–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2017.02.016
Ansari MY, Khan NM, Ahmad I, et al., 2018. Parkin clearance of dysfunctional mitochondria regulates ROS levels and increases survival of human chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 26(8):1087–1097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2017.07.020
Ansari MY, Ahmad N, Haqqi TM, 2020. Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: role of polyphenols. Biomed Pharmacother, 129:110452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110452
Arra M, Swarnkar G, Ke K, et al., 2020. LDHA-mediated ROS generation in chondrocytes is a potential therapeutic target for osteoarthritis. Nat Commun, 11:3427. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-17242-0
Bellot G, Garcia-Medina R, Gounon P, et al., 2009. Hypoxia-induced autophagy is mediated through hypoxia-inducible factor induction of BNIP3 and BNIP3L via their BH3 domains. Mol Cell Biol, 29(10):2570–2581. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.00166-09
Bernardini JP, Brouwer JM, Tan IKL, et al., 2019. Parkin inhibits BAK and BAX apoptotic function by distinct mechanisms during mitophagy. EMBO J, 38(2):e99916. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201899916
Bhujabal Z, Birgisdottir ÅB, Sjøttem E, et al., 2017. FKBP8 recruits LC3A to mediate parkin-independent mitophagy. EMBO Rep, 18(6):947–961. https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.201643147
Bingol B, Tea JS, Phu L, et al., 2014. The mitochondrial deubiquitinase USP30 opposes parkin-mediated mitophagy. Nature, 510(7505):370–375. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13418
Birgisdottir ÅB, Mouilleron S, Bhujabal Z, et al., 2019. Members of the autophagy class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex I interact with GABARAP and GABARAPL1 via LIR motifs. Autophagy, 15(8):1333–1355. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2019.1581009
Blanco FJ, Rego-Pérez I, 2018. Mitochondria and mitophagy: biosensors for cartilage degradation and osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 26(8):989–991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2018.05.018
Blanco FJ, Rego I, Ruiz-Romero C, 2011. The role of mitochondria in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 7(3):161–169. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2010.213
Bulua AC, Simon A, Maddipati R, et al., 2011. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species promote production of proinflammatory cytokines and are elevated in TNFR1-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS). J Exp Med, 208(3):519–533. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20102049
Cao ST, Wang CC, Yan JT, et al., 2020. Curcumin ameliorates oxidative stress-induced intestinal barrier injury and mitochondrial damage by promoting Parkin dependent mitophagy through AMPK-TFEB signal pathway. Free Radical Biol Med, 147:8–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.12.004
Charlier E, Deroyer C, Ciregia F, et al., 2019. Chondrocyte dedifferentiation and osteoarthritis (OA). Biochem Pharmacol, 165:49–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2019.02.036
Chen G, Han Z, Feng D, et al., 2014. A regulatory signaling loop comprising the PGAM5 phosphatase and CK2 controls receptor-mediated mitophagy. Mol Cell, 54(3):362–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.02.034
Chen M, Chen ZH, Wang YY, et al., 2016. Mitophagy receptor FUNDC1 regulates mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy. Autophagy, 12(4):689–702. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2016.1151580
Cheong H, Nair U, Geng JF, et al., 2008. The Atg1 kinase complex is involved in the regulation of protein recruitment to initiate sequestering vesicle formation for nonspecific autophagy in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Cell, 19(2):668–681. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e07-08-0826
Collins JA, Wood ST, Nelson KJ, et al., 2016. Oxidative stress promotes peroxiredoxin hyperoxidation and attenuates pro-survival signaling in aging chondrocytes. J Biol Chem, 291(13):6641–6654. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.693523
Coryell PR, Diekman BO, Loeser RF, 2021. Mechanisms and therapeutic implications of cellular senescence in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 17(1):47–57. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41584-020-00533-7
Cuervo AM, Bergamini E, Brunk UT, et al., 2005. Autophagy and aging: the importance of maintaining “clean” cells. Autophagy, 1(3):131–140. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.1.3.2017
Cui AY, Li HZ, Wang DW, et al., 2020. Global, regional prevalence, incidence and risk factors of knee osteoarthritis in population-based studies. EClinicalMedicine, 29:100587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100587
D’Adamo S, Cetrullo S, Guidotti S, et al., 2020. Spermidine rescues the deregulated autophagic response to oxidative stress of osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Free Radic Biol Med, 153:159–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.03.029
Dai SH, Chen T, Wang YH, et al., 2014. Sirt3 protects cortical neurons against oxidative stress via regulating mitochondrial Ca2+ and mitochondrial biogenesis. Int J Mol Sci, 15(8):14591–14609. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150814591
D’Amico D, Olmer M, Fouassier AM, et al., 2022. Urolithin A improves mitochondrial health, reduces cartilage degeneration, and alleviates pain in osteoarthritis. Aging Cell, 21(8):e13662. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.13662
Davis JE, Price LL, Lo GH, et al., 2017. A single recent injury is a potent risk factor for the development of accelerated knee osteoarthritis: data from the osteoarthritis initiative. Rheumatol Int, 37(10):1759–1764. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-017-3802-6
Dawson TM, Dawson VL, 2017. Mitochondrial mechanisms of neuronal cell death: potential therapeutics. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol, 57:437–454. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010716-105001
Deng R, Wang Y, Bu YH, et al., 2022. BNIP3 mediates the different adaptive responses of fibroblast-like synovial cells to hypoxia in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Med, 28:64. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10020-022-00490-9
Duan R, Xie H, Liu ZZ, 2020. The role of autophagy in osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol, 8:608388. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.608388
Duan YM, Fang HB, 2016. RecQL4 regulates autophagy and apoptosis in U2OS cells. Biochem Cell Biol, 94(6):551–559. https://doi.org/10.1139/bcb-2016-0005
Edgar RS, Green EW, Zhao YW, et al., 2012. Peroxiredoxins are conserved markers of circadian rhythms. Nature, 485(7399):459–464. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11088
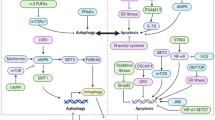
Egan DF, Shackelford DB, Mihaylova MM, et al., 2011. Phosphorylation of ULK1 (hATG1) by AMP-activated protein kinase connects energy sensing to mitophagy. Science, 331(6016):456–461. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1196371
Eyre D, 2002. Articular cartilage and changes in Arthritis: collagen of articular cartilage. Arthritis Res Ther, 4:30. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar380
Feng XF, Pan JY, Li JY, et al., 2020. Metformin attenuates cartilage degeneration in an experimental osteoarthritis model by regulating AMPK/mTOR. Aging (Albany NY), 12(2):1087–1103. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102635
Fernández-Moreno M, Rego-Pérez I, Blanco FJ, 2022. Is osteoarthritis a mitochondrial disease? What is the evidence? Curr Opin Rheumatol, 34(1):46–53. https://doi.org/10.1097/bor.0000000000000855
Fivenson EM, Lautrup S, Sun N, et al., 2017. Mitophagy in neurodegeneration and aging. Neurochem Int, 109:202–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2017.02.007
Friedman JR, Nunnari J, 2014. Mitochondrial form and function. Nature, 505(7483):335–343. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12985
Furuya N, Kakuta S, Sumiyoshi K, et al., 2018. NDP52 interacts with mitochondrial RNA poly(A) polymerase to promote mitophagy. EMBO Rep, 19(12):e46363. https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.201846363
Glick D, Barth S, Macleod KF, 2010. Autophagy: cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol, 221(1):3–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.2697
Glyn-Jones S, Palmer AJR, Agricola R, et al., 2015. Osteoarthritis. Lancet, 386(9991):376–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(14)60802-3
Hanna RA, Quinsay MN, Orogo AM, et al., 2012. Microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (LC3) interacts with Bnip3 protein to selectively remove endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria via autophagy. J Biol Chem, 287(23): 19094–19104. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.322933
Hardie DG, 2014. AMP-activated protein kinase: maintaining energy homeostasis at the cellular and whole-body levels. Annu Rev Nutr, 34:31–55. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-nutr-071812-161148
He J, He J, 2023. Baicalin mitigated IL-1β -induced osteoarthritis chondrocytes damage through activating mitophagy. Chem Biol Drug Des, 101(6):1322–1334. https://doi.org/10.1111/cbdd.14215
He YZ, Wu ZP, Xu LH, et al., 2020. The role of SIRT3-mediated mitochondrial homeostasis in osteoarthritis. Cell Mol Life Sci, 77(19):3729–3743. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-020-03497-9
Herzig S, Shaw RJ, 2018. AMPK: guardian of metabolism and mitochondrial homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 19(2):121–135. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2017.95
Higuchi-Sanabria R, Frankino PA, Paul JWIII, et al., 2018. A futile battle? Protein quality control and the stress of aging. Dev Cell, 44(2):139–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2017.12.020
Hu SL, Zhang CW, Ni LB, et al., 2020. Stabilization of HIF-1α alleviates osteoarthritis via enhancing mitophagy. Cell Death Dis, 11(6):481. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2680-0
Huang LW, Huang TC, Hu YC, et al., 2020. Zinc protects chondrocytes from monosodium iodoacetate-induced damage by enhancing ATP and mitophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 521(1):50–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.10.066
Hunter W, 1995. Of the structure and disease of articulating cartilages. Clin Orthop Relat Res, (317):3–6.
Ibrahim BA, Alenazi FSH, Briski KP, 2015. Energy status determines hindbrain signal transduction pathway transcriptional reactivity to AMPK in the estradiol-treated ovariectomized female rat. Neuroscience, 284:888–899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.10.068
Imhof H, Sulzbacher I, Grampp S, et al., 2000. Subchondral bone and cartilage disease: a rediscovered functional unit. Invest Radiol, 35(10):581–588. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004424-200010000-00004
Jiang N, Xing BZ, Peng R, et al., 2022. Inhibition of Cpt1a alleviates oxidative stress-induced chondrocyte senescence via regulating mitochondrial dysfunction and activating mitophagy. Mech Ageing Dev, 205:111688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2022.111688
Jin ZZ, Chang BH, Wei YL, et al., 2022. Curcumin exerts chondroprotective effects against osteoarthritis by promoting AMPK/PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Biomed Pharmacother, 151:113092. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113092
Jones DP, 2015. Redox theory of aging. Redox Biol, 5:71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2015.03.004
Kawamata T, Kamada Y, Kabeya Y, et al., 2008. Organization of the pre-autophagosomal structure responsible for autophagosome formation. Mol Biol Cell, 19(5):2039–2050. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e07-10-1048
Kerr JS, Adriaanse BA, Greig NH, et al., 2017. Mitophagy and Alzheimer’s disease: cellular and molecular mechanisms. Trends Neurosci, 40(3):151–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2017.01.002
Kiaer T, Grønlund J, Sørensen KH, 1988. Subchondral pO2, pCO2, pressure, pH, and lactate in human osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res, (229):149–155.
Kiani C, Chen LW, Wu YJ, et al., 2002. Structure and function of aggrecan. Cell Res, 12(1):19–32. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cr.7290106
Kim C, Nevitt M, Guermazi A, et al., 2018. Brief report: leg length inequality and hip osteoarthritis in the multicenter osteoarthritis study and the osteoarthritis initiative. Arthritis Rheumatol, 70(10):1572–1576. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.40537
Kim D, Song J, Jin EJ, 2021. BNIP3-dependent mitophagy via PGC1α promotes cartilage degradation. Cells, 10(7): 1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10071839
Kim HA, Suh DI, Song YW, 2001. Relationship between chondrocyte apoptosis and matrix depletion in human articular cartilage. J Rheumatol, 28(9):2038–2045.
Kimura S, Noda T, Yoshimori T, 2008. Dynein-dependent movement of autophagosomes mediates efficient encounters with lysosomes. Cell Struct Funct, 33(1):109–122. https://doi.org/10.1247/csf.08005
Kop’eva TN, Bel’skaia OB, Astapenko MG, et al., 1986. Morphology of articular cartilage in osteoarthrosis. Arkh Patol, 48(12):40–46 (in Russian).
Koyano F, Okatsu K, Kosako H, et al., 2014. Ubiquitin is phosphorylated by PINK1 to activate parkin. Nature, 510(7503):162–166. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13392
Lazarou M, Sliter DA, Kane LA, et al., 2015. The ubiquitin kinase PINK1 recruits autophagy receptors to induce mitophagy. Nature, 524(7565):309–314. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14893
Lei QY, Tan J, Yi SQ, et al., 2018. Mitochonic acid 5 activates the MAPK–ERK–yap signaling pathways to protect mouse microglial BV-2 cells against TNFα-induced apoptosis via increased Bnip3-related mitophagy. Cell Mol Biol Lett, 23:14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-018-0081-5
Liu D, Cai ZJ, Yang YT, et al., 2022. Mitochondrial quality control in cartilage damage and osteoarthritis: new insights and potential therapeutic targets. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 30(3):395–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2021.10.009
Liu L, Feng D, Chen G, et al., 2012. Mitochondrial outermembrane protein FUNDC1 mediates hypoxia-induced mitophagy in mammalian cells. Nat Cell Biol, 14(2):177–185. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2422
Liu L, Zhang WY, Liu TH, et al., 2023. The physiological metabolite α-ketoglutarate ameliorates osteoarthritis by regulating mitophagy and oxidative stress. Redox Biol, 62: 102663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2023.102663
Lombard DB, Alt FW, Cheng HL, et al., 2007. Mammalian Sir2 homolog SIRT3 regulates global mitochondrial lysine acetylation. Mol Cell Biol, 27(24):8807–8814. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.01636-07
Lu JR, Peng Y, Zou JP, et al., 2021. Hypoxia inducible factor-1α is a regulator of autophagy in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Cartilage, 13(2_suppl):1030s–1040s. https://doi.org/10.1177/19476035211035434
Ma ZT, Wang DL, Weng J, et al., 2020. BNIP3 decreases the LPS-induced inflammation and apoptosis of chondrocytes by promoting the development of autophagy. J Orthop Surg Res, 15:284. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-020-01791-7
Maimaitijuma T, Yu JH, Ren YL, et al., 2020. PHF23 negatively regulates the autophagy of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis. Life Sci, 253:117750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117750
Matsuhashi T, Sato T, Kanno SI, et al., 2017. Mitochonic acid 5 (MA-5) facilitates ATP synthase oligomerization and cell survival in various mitochondrial diseases. eBioMedicine, 20:27–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.05.016
Mei RH, Lou P, You GC, et al., 2021. 17β-Estradiol induces mitophagy upregulation to protect chondrocytes via the SIRT1-mediated AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 11:615250. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2020.615250
Miwa S, Kashyap S, Chini E, et al., 2022. Mitochondrial dysfunction in cell senescence and aging. J Clin Invest, 132(13):e158447. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci158447
Najafipour H, Ferrell WR, 1995. Comparison of synovial PO2 and sympathetic vasoconstrictor responses in normal and acutely inflamed rabbit knee joints. Exp Physiol, 80(2): 209–220. https://doi.org/10.1113/expphysiol.1995.sp003841
Nguyen TN, Padman BS, Lazarou M, 2016. Deciphering the molecular signals of PINK1/Parkin mitophagy. Trends Cell Biol, 26(10):733–744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2016.05.008
Novak I, Kirkin V, McEwan DG, et al., 2010. Nix is a selective autophagy receptor for mitochondrial clearance. EMBO Rep, 11(1):45–51. https://doi.org/10.1038/embor.2009.256
Paulsson M, Heinegård D, 1979. Matrix proteins bound to associatively prepared proteoglycans from bovine cartilage. Biochem J, 183(3):539–545. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj1830539
Pedro JMBS, Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, 2017. Autophagy and mitophagy in cardiovascular disease. Circ Res, 120(11): 1812–1824. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.117.311082
Petursson F, Husa M, June R, et al., 2013. Linked decreases in liver kinase B1 and AMP-activated protein kinase activity modulate matrix catabolic responses to biomechanical injury in chondrocytes. Arthritis Res Ther, 15(4):R77. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar4254
Pfander D, Gelse K, 2007. Hypoxia and osteoarthritis: how chondrocytes survive hypoxic environments. Curr Opin Rheumatol, 19(5):457–462. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOR.0b013e3282ba5693
Qin N, Wei LW, Li WY, et al., 2017. Local intra-articular injection of resveratrol delays cartilage degeneration in C57BL/6 mice by inducing autophagy via AMPK/mTOR pathway. J Pharmacol Sci, 134(3):166–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphs.2017.06.002
Reed KN, Wilson G, Pearsall A, et al., 2014. The role of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in cartilage matrix destruction. Mol Cell Biochem, 397(1–2):195–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2187-z
Russell EM, Miller RH, Umberger BR, et al., 2013. Lateral wedges alter mediolateral load distributions at the knee joint in obese individuals. J Orthop Res, 31(5):665–671. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.22248
Salucci S, Falcieri E, Battistelli M, 2022. Chondrocyte death involvement in osteoarthritis. Cell Tissue Res, 389(2): 159–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-022-03639-4
Sarraf SA, Raman M, Guarani-Pereira V, et al., 2013. Landscape of the PARKIN-dependent ubiquitylome in response to mitochondrial depolarization. Nature, 496(7445): 372–376. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12043
Scherz-Shouval R, Shvets E, Fass E, et al., 2007. Reactive oxygen species are essential for autophagy and specifically regulate the activity of Atg4. EMBO J, 26(7):1749–1760. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601623
Schulz RM, Bader A, 2007. Cartilage tissue engineering and bioreactor systems for the cultivation and stimulation of chondrocytes. Eur Biophys J, 36(4–5):539–568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-007-0139-1
Shang J, Lin N, Peng R, et al., 2023. Inhibition of Klf10 attenuates oxidative stress-induced senescence of chondrocytes via modulating mitophagy. Molecules, 28(3):924. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28030924
Shin HJ, Park H, Shin N, et al., 2019. Pink1-mediated chondrocytic mitophagy contributes to cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis. J Clin Med, 8(11):1849. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8111849
Sowter HM, Ratcliffe PJ, Watson P, et al., 2001. HIF-1-dependent regulation of hypoxic induction of the cell death factors BNIP3 and NIX in human tumors. Cancer Res, 61(18): 6669–6673.
Stolz A, Ernst A, Dikic I, 2014. Cargo recognition and trafficking in selective autophagy. Nat Cell Biol, 16(6):495–501. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2979
Sun K, Jing XZ, Guo JC, et al., 2021. Mitophagy in degenerative joint diseases. Autophagy, 17(9):2082–2092. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2020.1822097
Suzuki K, Kirisako T, Kamada Y, et al., 2001. The preautophagosomal structure organized by concerted functions of APG genes is essential for autophagosome formation. EMBO J, 20(21):5971–5981. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/20.21.5971
Suzuki K, Akioka M, Kondo-Kakuta C, et al., 2013. Fine mapping of autophagy-related proteins during autophagosome formation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Sci, 126(Pt 11):2534–2544. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.122960
Tahrir FG, Langford D, Amini S, et al., 2019. Mitochondrial quality control in cardiac cells: mechanisms and role in cardiac cell injury and disease. J Cell Physiol, 234(6): 8122–8133. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27597
Tamrakar P, Ibrahim BA, Gujar AD, et al., 2015. Estrogen regulates energy metabolic pathway and upstream adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase and phosphatase enzyme expression in dorsal vagal complex metabolosensory neurons during glucostasis and hypoglycemia. J Neurosci Res, 93(2):321–332. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.23481
Tang Q, Zheng G, Feng ZH, et al., 2017. Trehalose ameliorates oxidative stress-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and ER stress via selective autophagy stimulation and autophagic flux restoration in osteoarthritis development. Cell Death Dis, 8(10):e3081. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.453
Tian WL, Li W, Chen YQ, et al., 2015. Phosphorylation of ULK1 by AMPK regulates translocation of ULK1 to mitochondria and mitophagy. FEBS Lett, 589(15):1847–1854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2015.05.020
Vadalà G, di Giacomo G, Ambrosio L, et al., 2020. Irisin recovers osteoarthritic chondrocytes in vitro. Cells, 9(6): 1478. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061478
Vina ER, Kwoh CK, 2018. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: literature update. Curr Opin Rheumatol, 30(2):160–167. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOR.0000000000000479
Wang CZ, Yang Y, Zhang YQ, et al., 2018. Protective effects of metformin against osteoarthritis through upregulation of SIRT3-mediated PINK1/Parkin-dependent mitophagy in primary chondrocytes. BioSci Trends, 12(6):605–612. https://doi.org/10.5582/bst.2018.01263
Wang FS, Kuo CW, Ko JY, et al., 2020. Irisin mitigates oxidative stress, chondrocyte dysfunction and osteoarthritis development through regulating mitochondrial integrity and autophagy. Antioxidants (Basel), 9(9):810. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9090810
Wang JL, Wang K, Huang CA, et al., 2018. SIRT3 activation by dihydromyricetin suppresses chondrocytes degeneration via maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis. Int J Biol Sci, 14(13):1873–1882. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.27746
Wang S, Deng ZT, Ma YC, et al., 2020. The role of autophagy and mitophagy in bone metabolic disorders. Int J Biol Sci, 16(14):2675–2691. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.46627
Wang WF, Liu SY, Qi ZF, et al., 2020. MiR-145 targeting BNIP3 reduces apoptosis of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis through notch signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 24(16):8263–8272. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202008_22622
Wang YQ, Serricchio M, Jauregui M, et al., 2015. Deubiquitinating enzymes regulate PARK2-mediated mitophagy. Autophagy, 11(4):595–606. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2015.1034408
Williams JA, Zhao K, Jin SK, et al., 2017. New methods for monitoring mitochondrial biogenesis and mitophagy in vitro and in vivo. Exp Biol Med (Maywood), 242(8): 781–787. https://doi.org/10.1177/1535370216688802
Wu LH, Liu HQ, Li LF, et al., 2014. Mitochondrial pathology in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Curr Drug Targets, 15(7): 710–719. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389450115666140417120305
Wu WX, Tian WL, Hu Z, et al., 2014. ULK1 translocates to mitochondria and phosphorylates FUNDC1 to regulate mitophagy. EMBO Rep, 15(5):566–575. https://doi.org/10.1002/embr.201438501
Xian HX, Watari K, Sanchez-Lopez E, et al., 2022. Oxidized DNA fragments exit mitochondria via mPTP- and VDAC-dependent channels to activate NLRP3 inflammasome and interferon signaling. Immunity, 55(8): 1370–1385.e8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2022.06.007
Xin RB, Xu YY, Long DB, et al., 2022. Mitochonic acid-5 inhibits reactive oxygen species production and improves human chondrocyte survival by upregulating SIRT3-mediated, Parkin-dependent mitophagy. Front Pharmacol, 13:911716. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.911716
Xu L, Wu Z, He Y, et al., 2020. MFN2 contributes to metabolic disorders and inflammation in the aging of rat chondrocytes and osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 28(8): 1079–1091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2019.11.011
Xu WN, Yang RZ, Zheng HL, et al., 2019. PGC-1α acts as an mediator of Sirtuin2 to protect annulus fibrosus from apoptosis induced by oxidative stress through restraining mitophagy. Int J Biol Macromol, 136:1007–1017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.06.163
Yamamoto H, Fujioka Y, Suzuki SW, et al., 2016. The intrinsically disordered protein Atg13 mediates supramolecular assembly of autophagy initiation complexes. Dev Cell, 38(1):86–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2016.06.015
Yu WJ, Gao BL, Li N, et al., 2017. Sirt3 deficiency exacerbates diabetic cardiac dysfunction: role of Foxo3A-Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Mol Basis Dis, 1863(8):1973–1983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.10.021
Yu XB, Chen GY, Zhou L, et al., 2022. Chondroprotective effects of Gubitong recipe via inhibiting excessive mitophagy of chondrocytes. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2022:8922021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8922021
Zhang XJ, Chen S, Song L, et al., 2014. MTOR-independent, autophagic enhancer trehalose prolongs motor neuron survival and ameliorates the autophagic flux defect in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Autophagy, 10(4):588–602. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.27710
Zhang YJ, Liu Y, Hou MZ, et al., 2023. Reprogramming of mitochondrial respiratory chain complex by targeting SIRT3-COX4I2 axis attenuates osteoarthritis progression. Adv Sci (Weinh), 10(10):2206144. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202206144
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82071762), the Shanghai Key Lab of Human Performance (Shanghai University of Sport) (No. 11DZ2261100), and the 2021 Capacity Building of Shanghai Universities (No. 21010503600), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Hong CAO and Xuchang ZHOU; Methodology: Jianming GUO; Validation: Hong CAO; Resources: Miao WANG; Writing–original draft preparation: Hong CAO and Xuchang ZHOU; Writing–review and editing: Bowen XU and Han HU; Funding acquisition: Jun ZOU and Nan LI. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Hong CAO, Xuchang ZHOU, Bowen XU, Han HU, Jianming GUO, Miao WANG, Nan LI, and Jun ZOU declare that they have no conflict of interest.
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, H., Zhou, X., Xu, B. et al. Advances in the study of mitophagy in osteoarthritis. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 25, 197–211 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2300402
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2300402