Abstract
Background
Osteoporosis (OP) has become a major public health issue, threatening the bone health of middle-aged and elderly people from all around the world. Changes in the gut microbiota (GM) are correlated with the maintenance of bone mass and bone quality. However, research results in this field remain highly controversial, and no systematic review or meta-analysis of the relationship between GM and OP has been conducted. This paper addresses this shortcoming, focusing on the difference in the GM abundance between OP patients and healthy controls based on previous 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene sequencing results, in order to provide new clinical reference information for future customized prevention and treatment options of OP.
Methods
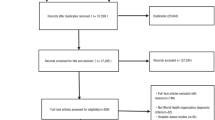
According to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA), we comprehensively searched the databases of PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, Cochrane Library, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI). In addition, we applied the R programming language version 4.0.3 and Stata 15.1 software for data analysis. We also implemented the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS), funnel plot analysis, sensitivity analysis, Egger’s test, and Begg’s test to assess the risk of bias.
Results
This research ultimately considered 12 studies, which included the fecal GM data of 2033 people (604 with OP and 1429 healthy controls). In the included research papers, it was observed that the relative abundance of Lactobacillus and Ruminococcus increased in the OP group, while the relative abundance for Bacteroides of Bacteroidetes increased (except for Ireland). Meanwhile, Firmicutes, Blautia, Alistipes, Megamonas, and Anaerostipes showed reduced relative abundance in Chinese studies. In the linear discriminant analysis Effect Size (LEfSe) analysis, certain bacteria showed statistically significant results consistently across different studies.
Conclusions
This observational meta-analysis revealed that changes in the GM were correlated with OP, and variations in some advantageous GM might involve regional differences.
概要
骨质疏松症(osteoporosis,OP)已成为严重威胁全球中老年人骨健康的重大公共卫生问题。肠道菌群(gut microbiota,GM)的改变与维持骨量和骨质量有关。然而,相关研究结果仍存在很大争议,目前尚没有研究对肠道菌群和骨质疏松间关系进行过系统评价和荟萃分析。本研究通过对骨质疏松症患者和健康人群之间肠道菌群差异的既往16S rRNA基因测序结果进行系统评价和荟萃分析,以期为未来个体化预防和治疗骨质疏松症提供新的临床参考。这项观察性的荟萃分析显示,肠道菌群的改变与骨质疏松症之间存在关联,并且一些优势菌群的变化可能存在地域差异。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbari S, Rasouli-Ghahroudi AA, 2018. Vitamin K and bone metabolism: a review of the latest evidence in preclinical studies. Biomed Res Int, 2018:4629383. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4629383
Anonymous, 1993. Consensus development conference: diagnosis, prophylaxis, and treatment of osteoporosis. Am J Med, 94(6):646–650. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9343(93)90218-e
Atkins GJ, Welldon KJ, Wijenayaka AR, et al., 2009. Vitamin K promotes mineralization, osteoblast-to-osteocyte transition, and an anticatabolic phenotype by γ-carboxylation-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol, 297(6):C1358–C1367. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00216.2009
Baker RG, Hayden MS, Ghosh S, 2011. NF-κB, inflammation, and metabolic disease. Cell Metab, 13(1):11–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2010.12.008
Britton RA, Irwin R, Quach D, et al., 2014. Probiotic L. reuteri treatment prevents bone loss in a menopausal ovariectomized mouse model. J Cell Physiol, 229(11):1822–1830. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.24636
Bui TPN, Mannerås-Holm L, Puschmann R, et al., 2021. Conversion of dietary inositol into propionate and acetate by commensal Anaerostipes associates with host health. Nat Commun, 12:4798. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25081-w
Crespo-Piazuelo D, Lawlor PG, Ranjitkar S, et al., 2021. Intestinal microbiota modulation and improved growth in pigs with post-weaning antibiotic and ZnO supplementation but only subtle microbiota effects with Bacillus altitudinis. Sci Rep, 11:23304. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-01826-x
Danne C, Ryzhakov G, Martínez-López M, et al., 2017. A large polysaccharide produced by Helicobacter hepaticus induces an anti-inflammatory gene signature in macrophages. Cell Host Microbe, 22(6):733–745.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2017.11.002
Das M, Cronin O, Keohane DM, et al., 2019. Gut microbiota alterations associated with reduced bone mineral density in older adults. Rheumatology (Oxford), 58(12):2295–2304. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kez302
Ding C, 2017. The Effects of LPS on the Proliferation and Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells and the Study on the Related Mechanisms. MS Thesis, Naval Medical University, Shanghai, China (in Chinese).
Duvallet C, 2018. Meta-analysis generates and prioritizes hypotheses for translational microbiome research. Microb Biotechnol, 11(2):273–276. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.13047
Gupta VK, Paul S, Dutta C, 2017. Geography, ethnicity or subsistence-specific variations in human microbiome composition and diversity. Front Microbiol, 8:1162. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01162
He JQ, Xu SB, Zhang BZ, et al., 2020. Gut microbiota and metabolite alterations associated with reduced bone mineral density or bone metabolic indexes in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Aging (Albany NY), 12(9):8583–8604. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103168
Hou M, Xu GL, Ran MS, et al., 2021. APOE-ε4 carrier status and gut microbiota dysbiosis in patients with alzheimer disease. Front Neurosci, 15:619051. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.619051
Jafarnejad S, Djafarian K, Fazeli MR, et al., 2017. Effects of a multispecies probiotic supplement on bone health in osteopenic postmenopausal women: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. J Am Coll Nutr, 36(7):497–506. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2017.1318724
Jansson PA, Curiac D, Lazou Ahrén I, et al., 2019. Probiotic treatment using a mix of three Lactobacillus strains for lumbar spine bone loss in postmenopausal women: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial. Lancet Rheumatol, 1(3):e154–e162. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2665-9913(19)30068-2
Juanola O, Piñero P, Gómez-Hurtado I, et al., 2018. Regulatory T cells restrict permeability to bacterial antigen trans-location and preserve short-chain fatty acids in experimental cirrhosis. Hepatol Commun, 2(12):1610–1623. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep4.1268
Juárez-Fernández M, Porras D, García-Mediavilla MV, et al., 2020. Aging, gut microbiota and metabolic diseases: management through physical exercise and nutritional interventions. Nutrients, 13(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13010016
Khokhlova EV, Smeianov VV, Efimov BA, et al., 2012. Anti-inflammatory properties of intestinal Bifidobacterium strains isolated from healthy infants. Microbiol Immunol, 56(1):27–39. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1348-0421.2011.00398.x
Lambert MNT, Thybo CB, Lykkeboe S, et al., 2017. Combined bioavailable isoflavones and probiotics improve bone status and estrogen metabolism in postmenopausal osteopenic women: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr, 106(3):909–920. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.117.153353
Li C, Huang Q, Yang R, et al., 2019. Gut microbiota composition and bone mineral loss-epidemiologic evidence from individuals in Wuhan, China. Osteoporos Int, 30(5):1003–1013. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-019-04855-5
Li LS, 2019. Study of Correlation Between Structural Characteristics of Gut Microbiota and TH17/Treg Ratio in Osteoporosis. MS Thesis, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China (in Chinese).
Li SY, Wang ZL, Yang Y, et al., 2017. Lachnospiraceae shift in the microbial community of mice faecal sample effects on water immersion restraint stress. AMB Express, 7:82. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-017-0383-4
Liang C, Peng SL, Li J, et al., 2018. Inhibition of osteoblastic Smurf1 promotes bone formation in mouse models of distinctive age-related osteoporosis. Nat Commun, 9:3428. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05974-z
Ling CW, Miao ZL, Xiao ML, et al., 2021. The association of gut microbiota with osteoporosis is mediated by amino acid metabolism: multiomics in a large cohort. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 106(10):e3852–e3864. https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgab492
Liu XM, Mao BY, Gu JY, et al., 2021. Blautia—a new functional genus with potential probiotic properties? Gut Microbes, 13(1):1875796. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2021.1875796
Liu ZJ, Xu C, Tian R, et al., 2021. Screening beneficial bacteriostatic lactic acid bacteria in the intestine and studies of bacteriostatic substances. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 22(7):533–547. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000602
Lyu J, Zhao HP, Yu Y, et al., 2021a. Composition and gene function of intestinal microbiota in male osteoporotic patients. Chin J Osteoporosis Bone Miner Res, 14(5):457–469 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1674-2591.2021.05.003.
Lyu J, Zhao HP, Yu Y, et al., 2021b. Profile and gene functional analysis of gut microbiota in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis. Chin J Microbiol Immunol, 41(11):867–874 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.cn112309-20210425-00134
Mandatori D, Pelusi L, Schiavone V, et al., 2021. The dual role of vitamin K2 in “bone-vascular crosstalk”: opposite effects on bone loss and vascular calcification. Nutrients, 13(4):1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041222
Mccabe LR, Irwin R, Schaefer L, et al., 2013. Probiotic use decreases intestinal inflammation and increases bone density in healthy male but not female mice. J Cell Physiol, 228(8):1793–1798. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.24340
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, et al., 2009. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ, 339:b2535. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b2535
Nagura N, Komatsu J, Iwase H, et al., 2015. Effects of the combination of vitamin K and teriparatide on the bone metabolism in ovariectomized rats. Biomed Rep, 3(3):295–300. https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2015.431
Nilsson AG, Sundh D, Bäckhed F, et al., 2018. Lactobacillus reuteri reduces bone loss in older women with low bone mineral density: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, clinical trial. J Intern Med, 284(3):307–317. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.12805
Palacios-González B, Ramírez-Salazar EG, Rivera-Paredez B, et al., 2020. A multi-omic analysis for low bone mineral density in postmenopausal women suggests a relationship between diet, metabolites, and microbiota. Microorganisms, 8(11):1630. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8111630
Ravi A, Avershina E, Angell IL, et al., 2018. Comparison of reduced metagenome and 16S rRNA gene sequencing for determination of genetic diversity and mother-child overlap of the gut associated microbiota. J Microbiol Methods, 149:44–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2018.02.016
Rettedal EA, Ilesanmi-Oyelere BL, Roy NC, et al., 2021. The gut microbiome is altered in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis and osteopenia. JBMR Plus, 5(3):e10452. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm4.10452
Rey FE, Faith JJ, Bain J, et al., 2010. Dissecting the in vivo metabolic potential of two human gut acetogens. J Biol Chem, 285(29):22082–22090. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.117713
Rinaldi E, Consonni A, Cordiglieri C, et al., 2019. Therapeutic effect of bifidobacterium administration on experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis in Lewis rats. Front Immunol, 10:2949. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02949
Salari N, Ghasemi H, Mohammadi L, et al., 2021. The global prevalence of osteoporosis in the world: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res, 16:609. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-021-02772-0
Shi HL, Yu YH, Lin DH, et al., 2020. β-Glucan attenuates cognitive impairment via the gut-brain axis in diet-induced obese mice. Microbiome, 8:143. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-020-00920-y
Sjögren K, Engdahl C, Henning P, et al., 2012. The gut microbiota regulates bone mass in mice. J Bone Miner Res, 27(6):1357–1367. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.1588
Smets W, Leff JW, Bradford MA, et al., 2016. A method for simultaneous measurement of soil bacterial abundances and community composition via 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Soil Biol Biochem, 96:145–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.02.003
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, et al., 2000. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. JAMA, 283(15):2008–2012. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.283.15.2008
Suzuki TA, Ley RE, 2020. The role of the microbiota in human genetic adaptation. Science, 370(6521):eaaz6827. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaz6827
Takimoto T, Hatanaka M, Hoshino T, et al., 2018. Effect of Bacillus subtilis C-3102 on bone mineral density in healthy postmenopausal Japanese women: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial. Biosci Microbiota Food Health, 37(4):87–96. https://doi.org/10.12938/bmfh.18-006
Tett A, Pasolli E, Masetti G, et al., 2021. Prevotella diversity, niches and interactions with the human host. Nat Rev Microbiol, 19(9):585–599. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-021-00559-y
Tousen Y, Matsumoto Y, Nagahata Y, et al., 2019. Resistant starch attenuates bone loss in ovariectomised mice by regulating the intestinal microbiota and bone-marrow inflammation. Nutrients, 11(2):297. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11020297
Tyagi AM, Yu MC, Darby TM, et al., 2018. The microbial metabolite butyrate stimulates bone formation via T regulatory cell-mediated regulation of WNT10B expression. Immunity, 49(6):1116–1131.e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2018.10.013
Vangay P, Johnson AJ, Ward TL, et al., 2018. US immigration westernizes the human gut microbiome. Cell, 175(4):962–972.e10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.10.029
Wan XY, Eguchi A, Fujita Y, et al., 2022. Effects of (R)-ketamine on reduced bone mineral density in ovariectomized mice: a role of gut microbiota. Neuropharmacology, 213:109139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2022.109139
Wang BK, Zhou YH, Mao YL, et al., 2021. Dietary supplementation with Lactobacillus plantarum ameliorates compromise of growth performance by modulating short-chain fatty acids and intestinal dysbiosis in broilers under Clostridium perfringens challenge. Front Nutr, 8:706148. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2021.706148
Wang ZX, Chen K, Wu CC, et al., 2021. An emerging role of Prevotella histicola on estrogen deficiency-induced bone loss through the gut microbiota-bone axis in postmenopausal women and in ovariectomized mice. Am J Clin Nutr, 114(4):1304–1313. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/nqab194
Wei MH, Li C, Dai Y, et al., 2021. High-throughput absolute quantification sequencing revealed osteoporosis-related gut microbiota alterations in Han Chinese elderly. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 11:630372. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2021.630372
Wei MY, Shi S, Liang C, et al., 2019. The microbiota and microbiome in pancreatic cancer: more influential than expected. Mol Cancer, 18:97. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1008-0
Xu L, Wu ZF, Wang Y, et al., 2021. High-throughput sequencing identifies salivary microbiota in Chinese caries-free preschool children with primary dentition. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 22(4):285–294. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000554
Xu ZM, Xie Z, Sun JG, et al., 2020. Gut microbiome reveals specific dysbiosis in primary osteoporosis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 10:160. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2020.00160
Yachida S, Mizutani S, Shiroma H, et al., 2019. Metagenomic and metabolomic analyses reveal distinct stage-specific phenotypes of the gut microbiota in colorectal cancer. Nat Med, 25(6):968–976. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-019-0458-7
Zhao ZH, Shi AM, Wang Q, et al., 2019. High oleic acid peanut oil and extra virgin olive oil supplementation attenuate metabolic syndrome in rats by modulating the gut microbiota. Nutrients, 11(12):3005. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11123005
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81860391), the Guangxi Medical High-level Backbone Talents Training “139” Program Training Project (No. [2020]15), and the Guangxi Hundred Thousand Talents Project (No. [2019]32), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Gaofeng ZENG and Shaohui ZONG; Methodology: Jieqiong HUANG; Formal analysis: Rui HUANG and Huihua LI; Resources: Yeping SU; Writing — original draft preparation: Rui HUANG and Pan LIU; Writing — review and editing: Rui HUANG, Ruixin MA, and Quan ZHOU; Visualization: Rui HUANG and Yiguang BAI; Project administration: Rui PAN; Funding acquisition: Gaofeng ZENG and Shaohui ZONG. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript, and therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Materials and methods
Detailed methods are provided in the electronic supplementary materials of this paper.
Compliance with ethics guidelines
Rui HUANG, Pan LIU, Yiguang BAI, Jieqiong HUANG, Rui PAN, Huihua LI, Yeping SU, Quan ZHOU, Ruixin MA, Shaohui ZONG, and Gaofeng ZENG declare that they have no conflict of interest.
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Supplementary information
Tables S1 and S2; Figs. S1 and S2; Materials and methods
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, R., Liu, P., Bai, Y. et al. Changes in the gut microbiota of osteoporosis patients based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 23, 1002–1013 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2200344
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2200344