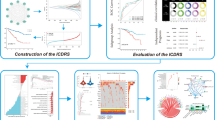
Abstract
Due to the low specificity and sensitivity of biomarkers in sepsis diagnostics, the prognosis of sepsis patient outcomes still relies on the assessment of clinical symptoms. Inflammatory response is crucial to sepsis onset and progression; however, the significance of inflammatory response-related genes (IRRGs) in sepsis prognosis is uncertain. This study developed an IRRG-based signature for sepsis prognosis and immunological function. The Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database was retrieved for two sepsis microarray datasets, GSE64457 and GSE69528, followed by gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) comparing sepsis and healthy samples. A predictive signature for IRRGs was created using least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO). To confirm the efficacy and reliability of the new prognostic signature, Cox regression, Kaplan-Meier (K-M) survival, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analyses were performed. Subsequently, we employed the GSE95233 dataset to independently validate the prognostic signature. A single-sample GSEA (ssGSEA) was conducted to quantify the immune cell enrichment score and immune-related pathway activity. We found that more gene sets were enriched in the inflammatory response in sepsis patient samples than in healthy patient samples, as determined by GSEA. The signature of nine IRRGs permitted the patients to be classified into two risk categories. Patients in the low-risk group showed significantly better 28-d survival than those in the high-risk group. ROC curve analysis corroborated the predictive capacity of the signature, with the area under the curve (AUC) for 28-d survival reaching 0.866. Meanwhile, the ssGSEA showed that the two risk groups had different immune states. The validation set and external dataset showed that the signature was clinically predictive. In conclusion, a signature consisting of nine IRRGs can be utilized to predict prognosis and influence the immunological status of sepsis patients. Thus, intervention based on these IRRGs may become a therapeutic option in the future.
概要
目的
探讨免疫反应相关的基因(inflammatory response-related genes,IRRGs)在预测脓毒症患者生存预后中的作用。
创新点
鉴定与脓毒症生存预后密切相关的IRRGs,构建风险评分模型。
方法
对Gene Expression Omnibus(GEO)数据库中478例脓毒症患者的微阵列芯片数据进行综合生物信息学分析,利用least absolute shrinkage and selection operator(LASSO)-Cox回归分析筛选与脓毒症28天生存率密切相关的IRRGs,并以此构建脓毒症预后风险评分模型。使用受试者工作特征曲线(ROC)及生存曲线(基于Kaplan-Meier法)评估预后风险评分模型的预测效能及区分度,并用GSE95233数据集进行验证。
结论
利用9个IRRGs构建了与脓毒症28天生存预后有关的风险评估模型,且在GSE95233数据集中进行验证,证实这些IRRGs可作为脓毒症患者的预后生物标志物。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andaluz-Ojeda D, Bobillo F, Iglesias V, et al., 2012. A combined score of pro- and anti-inflammatory interleukins improves mortality prediction in severe sepsis. Cytokine, 57(3):332–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2011.12.002
Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P, et al., 2013. NCBI GEO: archive for functional genomics data sets—update. Nucleic Acids Res, 41(D1):D991–D995. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1193
Bauer JW, Bilgic H, Baechler EC, 2009. Gene-expression profiling in rheumatic disease: tools and therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 5(5):257–265. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2009.50
Bosmann M, Ward PA, 2013. The inflammatory response in sepsis. Trends Immunol, 34(3):129–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2012.09.004
Bouras M, Asehnoune K, Roquilly A, 2018. Contribution of dendritic cell responses to sepsis-induced immunosuppression and to susceptibility to secondary pneumonia. Front Immunol, 9:2590. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.02590
Cuocolo R, Caruso M, Perillo T, et al., 2020. Machine learning in oncology: a clinical appraisal. Cancer Lett, 481:55–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2020.03.032
Darash-Yahana M, Gillespie JW, Hewitt SM, et al., 2009. The chemokine CXCL16 and its receptor, CXCR6, as markers and promoters of inflammation-associated cancers. PLoS ONE, 4(8):e6695. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0006695
Delano MJ, Ward PA, 2016. The immune system’s role in sepsis progression, resolution, and long-term outcome. Immunol Rev, 274(1):330–353. https://doi.org/10.1111/imr.12499
Demaret J, Venet F, Friggeri A, et al., 2015. Marked alterations of neutrophil functions during sepsis-induced immunosuppression. J Leukoc Biol, 98(6):1081–1090. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.4A0415-168RR
Deng ZL, Zhou DZ, Cao SJ, et al., 2022. Development and validation of an inflammatory response-related gene signature for predicting the prognosis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Inflammation, 45(4):1732–1751. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-022-01657-6
Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, et al., 2021. Executive summary: Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for the Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock 2021. Crit Care Med, 49(11):1974–1982. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.jzus005357
Feng AL, Ma WL, Faraj R, et al., 2021. Identification of S1PR3 gene signature involved in survival of sepsis patients. BMC Med Genomics, 14:43. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12920-021-00886-2
Fleischmann C, Scherag A, Adhikari NKJ, et al., 2016. Assessment of global incidence and mortality of hospital-treated sepsis. Current estimates and limitations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 193(3):259–272. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201504-0781OC
Fleischmann-Struzek C, Mellhammar L, Rose N, et al., 2020. Incidence and mortality of hospital- and ICU-treated sepsis: results from an updated and expanded systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med, 46(8):1552–1562. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-020-06151-x
Gotts JE, Matthay MA, 2016. Sepsis: pathophysiology and clinical management. BMJ, 353:i1585. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.i1585
Hanna MOF, Abdelhameed AM, Abou-Elalla AA, et al., 2019. Neutrophil and monocyte receptor expression in patients with sepsis: implications for diagnosis and prognosis of sepsis. Pathog Dis, 77(6):ftz055. https://doi.org/10.1093/femspd/ftz055
Hänzelmann S, Castelo R, Guinney J, 2013. GSVA: gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-Seq data. BMC Bioinformatics, 14:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-7
He WX, Xiao K, Fang M, et al., 2021. Immune cell number, phenotype, and function in the elderly with sepsis. Aging Dis, 12(1):277–296. https://doi.org/10.14336/Ad.2020.0627
Helmke A, Nordlohne J, Balzer MS, et al., 2019. CX3CL1—CX3CR1 interaction mediates macrophage-mesothelial cross talk and promotes peritoneal fibrosis. Kidney Int, 95(6):1405–1417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2018.12.030
Hotchkiss RS, Monneret G, Payen D, 2013. Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: from cellular dysfunctions to immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol, 13(12):862–874. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3552
Itagaki K, Kaczmarek E, Kwon WY, et al., 2020. Formyl peptide receptor-1 blockade prevents receptor regulation by mitochondrial danger-associated molecular patterns and preserves neutrophil function after trauma. Crit Care Med, 48(2):e123–e132. https://doi.org/10.1097/Ccm.jzus004094
Jensen IJ, Winborn CS, Fosdick MG, et al., 2018. Polymicrobial sepsis influences NK-cell-mediated immunity by diminishing NK-cell-intrinsic receptor-mediated effector responses to viral ligands or infections. PLoS Pathog, 14(10):e1007405. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1007405
Ju AJ, Tang JZ, Chen SH, et al., 2021. Pyroptosis-related gene signatures can robustly diagnose skin cutaneous melanoma and predict the prognosis. Front Oncol, 11:709077. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.709077
Kolaczkowska E, Kubes P, 2013. Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol, 13(3):159–175. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3399
Korbecki J, Simińska D, Kojder K, et al., 2020. Fractalkine/CX3CL1 in neoplastic processes. Int J Mol Sci, 21(10):3723. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103723
Kriplani A, Pandit S, Chawla A, et al., 2022. Neutrophillymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) and lymphocyte-monocyte ratio (LMR) in predicting systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and sepsis after percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PNL). Urolithiasis, 50(3):341–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-022-01319-0
Levy MM, Evans LE, Rhodes A, 2018. The surviving sepsis campaign bundle: 2018 update. Crit Care Med, 46(6):997–1000. https://doi.org/10.1097/Ccm.jzus003119
Liberzon A, Birger C, Thorvaldsdóttir H, et al., 2015. The molecular signatures database (MSigDB) hallmark gene set collection. Cell Syst, 1(6):417–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cels.2015.12.004
Lu JQ, Liu JY, Li A, 2022. Roles of neutrophil reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation in organ function impairment in sepsis. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 23(6):437–450. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2101075
Markwart R, Saito H, Harder T, et al., 2020. Epidemiology and burden of sepsis acquired in hospitals and intensive care units: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med, 46(8):1536–1551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-020-06106-2
Miyata K, Yotsumoto F, Nam SO, et al., 2012. Regulatory mechanisms of the HB-EGF autocrine loop in inflammation, homeostasis, development and cancer. Anticancer Res, 32(6):2347–2352.
Ni CM, Ling BY, Xu X, et al., 2020. CX3CR1 contributes to streptozotocin-induced mechanical allodynia in the mouse spinal cord. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 21(2):166–171. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1900439
Pankla R, Buddhisa S, Berry M, et al., 2009. Genomic transcriptional profiling identifies a candidate blood biomarker signature for the diagnosis of septicemic melioidosis. Genome Biol, 10(11):R127. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2009-10-11-r127
Patten M, Bünemann J, Thoma B, et al., 2002. Endotoxin induces desensitization of cardiac endothelin-1 receptor signaling by increased expression of RGS4 and RGS16. Cardiovasc Res, 53(1):156–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6363(01)00443-6
Raspé C, Höcherl K, Rath S, et al., 2013. NF-κB-mediated inverse regulation of fractalkine and CX3CR1 during CLP-induced sepsis. Cytokine, 61(1):97–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2012.08.034
Reinhart K, Bauer M, Riedemann NC, et al., 2012. New approaches to sepsis: molecular diagnostics and biomarkers. Clin Microbiol Rev, 25(4):609–634. https://doi.org/10.1128/Cmr.00016-12
Rhee C, Dantes R, Epstein L, et al., 2017. Incidence and trends of sepsis in US hospitals using clinical vs claims data, 2009–2014. JAMA, 318(13):1241–1249. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2017.13836
Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, et al., 2017. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Intensive Care Med, 43(3):304–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-017-4683-6
Rich JT, Neely JG, Paniello RC, et al., 2010. A practical guide to understanding Kaplan-Meier curves. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 143(3):331–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2010.05.007
Robin X, Turck N, Hainard A, et al., 2011. pROC: an open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinformatics, 12:77. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-12-77
Ruan L, Chen GY, Liu Z, et al., 2018. The combination of procalcitonin and C-reactive protein or presepsin alone improves the accuracy of diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Crit Care, 22:316. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-018-2236-1
Schlatterer K, Beck C, Schoppmeier U, et al., 2021a. Acetate sensing by GPR43 alarms neutrophils and protects from severe sepsis. Commun Biol, 4:928. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-021-02427-0
Schlatterer K, Peschel A, Kretschmer D, 2021b. Short-chain fatty acid and FFAR2 activation—a new option for treating infections? Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 11:785833. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2021.785833
Scicluna BP, Klouwenberg PMCK, van Vught LA, et al., 2015. A molecular biomarker to diagnose community-acquired pneumonia on intensive care unit admission. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 192(7):826–835. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201502-0355OC
Silwal P, Kim JK, Kim YJ, et al., 2020. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species: double-edged weapon in host defense and pathological inflammation during infection. Front Immunol, 11:1649. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.01649
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, et al., 2016. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA, 315(8):801–810. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.0287
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, et al., 2005. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 102(43):15545–15550. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0506580102
van der Poll T, van de Veerdonk FL, Scicluna BP, et al., 2017. The immunopathology of sepsis and potential therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Immunol, 17(7):407–420. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2017.36
Venet F, Monneret G, 2018. Advances in the understanding and treatment of sepsis-induced immunosuppression. Nat Rev Nephrol, 14(2):121–137. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2017.165
Venet F, Schilling J, Cazalis MA, et al., 2017. Modulation of LILRB2 protein and mRNA expressions in septic shock patients and after ex vivo lipopolysaccharide stimulation. Hum Immunol, 78(5–6):441–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humimm.2017.03.010
Watanabe N, Suzuki Y, Inokuchi S, et al., 2016. Sepsis induces incomplete M2 phenotype polarization in peritoneal exu-date cells in mice. J Intensive Care, 4:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40560-015-0124-1
Wedepohl S, Beceren-Braun F, Riese S, et al., 2012. L-Selectin — a dynamic regulator of leukocyte migration. Eur J Cell Biol, 91(4):257–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcb.2011.02.007
Winters BD, Eberlein M, Leung J, et al., 2010. Long-term mortality and quality of life in sepsis: a systematic review. Crit Care Med, 38(5):1276–1283. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181d8cc1d
Xiao ZJ, Li JY, Yu Q, et al., 2021. An inflammatory response related gene signature associated with survival outcome and gemcitabine response in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Front Pharmacol, 12:778294. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.778294
Xu F, Zhou FC, 2020. Inhibition of microRNA-92a ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced endothelial barrier dysfunction by targeting ITGA5 through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells. Int Immunopharmacol, 78:106060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2019.106060
Zhong WW, Wang DJ, Yao B, et al., 2021. Integrative analysis of prognostic long non-coding RNAs with copy number variation in bladder cancer. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol), 22(8):664–681. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2000494
Zou WJ, Chen L, Mao WW, et al., 2021. Identification of inflammatory response-related gene signature associated with immune status and prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 9:772206. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.772206
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Key Research and Development Program of Zhejiang Province (No. 2019C03076) and the Opening Foundation of the State Key Laboratory for Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases (No. 2018KF02), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shuai JIANG and Wenyuan ZHANG conceived the idea and performed data analyses, wrote and edited the manuscript. Yuanqiang LU contributed to the study design, data analysis, and writing and editing of the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript, and therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Compliance with ethics guidelines
Shuai JIANG, Wenyuan ZHANG, and Yuanqiang LU declare that they have no conflict of interest.
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Supplementary information
Tables S1–S5
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, S., Zhang, W. & Lu, Y. Development and validation of novel inflammatory response-related gene signature for sepsis prognosis. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 23, 1028–1041 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2200285
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2200285