Abstract
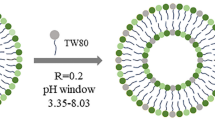
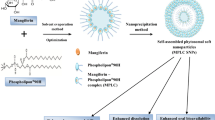
Hesperetin, an abundant bioactive component of citrus fruits, is poorly water-soluble, resulting in low oral bioavailability. We developed new formulations to improve the water solubility, antioxidant activity, and oral absorption of hesperetin. Two nano-based formulations were developed, namely hesperetin-TPGS (D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate) micelles and hesperetin-phosphatidylcholine (PC) complexes. These two formulations were prepared by a simple technique called solvent dispersion, using US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved excipients for drugs. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and dynamic light scattering (DLS) were used to characterize the formulations’ physical properties. Cytotoxicity analysis, cellular antioxidant activity assay, and a pharmacokinetic study were performed to evaluate the biological properties of these two formulations. The final weight ratios of both hesperetin to TPGS and hesperetin to PC were 1:12 based on their water solubility, which increased to 21.5- and 20.7-fold, respectively. The hesperetin-TPGS micelles had a small particle size of 26.19 nm, whereas the hesperetin-PC complexes exhibited a larger particle size of 219.15 nm. In addition, the cellular antioxidant activity assay indicated that both hesperetin-TPGS micelles and hesperetin-PC complexes increased the antioxidant activity of hesperetin to 4.2- and 3.9-fold, respectively. Importantly, the in vivo oral absorption study on rats indicated that the micelles and complexes significantly increased the peak plasma concentration (Cmax) from 2.64 μg/mL to 20.67 and 33.09 μg/mL and also increased the area under the concentration–time curve of hesperetin after oral administration to 16.2- and 18.0-fold, respectively. The micelles and complexes increased the solubility and remarkably improved the in vitro antioxidant activity and in vivo oral absorption of hesperetin, indicating these formulations’ potential applications in drugs and healthcare products.
概要
目的
橙皮素拥有抗氧化、抗炎和降脂等多种生理活性, 但由于其水溶性差、代谢快, 导致其口服生物利 用度很低。 因此, 本研究制备了橙皮素-维生素E 聚乙二醇琥珀酸酯(TPGS)胶束和橙皮素-磷脂 酰胆碱(PC)复合物, 来提高橙皮素的水溶性、 抗氧化活性和口服吸收率。
创新点
本研究使用美国食品药品监督管理局(US FDA) 批准的辅料制备了两种纳米制剂:橙皮素-TPGS 胶束和橙皮素-PC 复合物。 不仅制备方法简单, 而且能显著提高橙皮素的水溶性、抗氧化活性和 口服吸收率。
方法
本研究使用溶剂分散法制备纳米制剂。 将橙皮素 与分散剂溶于有机溶剂中, 在40 °C下搅拌30 min, 然后旋转蒸发除去溶剂, 用水复溶即得橙皮素- TPGS 胶束和橙皮素-PC 复合物。 本研究使用差 示扫描量热法表征纳米制剂的热效应;用动态光 散射法测定纳米制剂的粒径;用噻唑蓝(MTT) 法检测纳米制剂的细胞毒性;用细胞抗氧化活性 测定法对比纳米制剂与橙皮素本身的抗氧化活 性;使用灌胃法评估纳米制剂的口服吸收效果。
结论
研究结果发现:以质量比1:12 制备的橙皮素- TPGS 胶束和橙皮素-PC 复合物, 其粒径分别为 26.19 和219.15 nm, 没有明显的细胞毒性, 同时 能够将橙皮素的水溶性分别提高到21.5和20.7倍, 抗氧化活性分别提高到4.2 和3.9 倍,口服生物利 用分别提高到16.2 和18.0 倍。 因此, 这两种纳米 制剂在药剂和保健品制造方面具有重要的应用 价值。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attili–Qadri S, Karra N, Nemirovski A, et al., 2013. Oral delivery system prolongs blood circulation of docetaxel nanocapsules via lymphatic absorption. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 110(43):17498–17503. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1313839110
Brand W, van der Wel PAI, Rein MJ, et al., 2008. Metabolism and transport of the citrus flavonoid hesperetin in Caco–2 cell monolayers. Drug Metab Dispos, 36(9):1794–1802. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.107.019943
Choudhury H, Gorain B, Pandey M, et al., 2017. Recent advances in TPGS–based nanoparticles of docetaxel for improved chemotherapy. Int J Pharm, 529(1–2): 506–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.07.018
de Souza VT, de Franco ÉPD, de Araújo MEMB, et al., 2016. Characterization of the antioxidant activity of aglycone and glycosylated derivatives of hesperetin:an in vitro and in vivo study. J Mol Recognit, 29(2):80–87. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmr.2509
Dintaman JM, Silverman JA, 1999. Inhibition of P–glycoprotein by D–a–tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS). Pharm Res, 16(10):1550–1556. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015000503629
Kanaze FI, Bounartzi MI, Georgarakis M, et al., 2007. Pharmacokinetics of the citrus flavanone aglycones hesperetin and naringenin after single oral administration in human subjects. Eur J Clin Nutr, 61(4):472–477. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602543
Khan J, Alexander A Ajazuddin, et al., 2013. Recent advances and future prospects of phyto–phospholipid complexation technique for improving pharmacokinetic profile of plant actives. J Control Release, 168(1):50–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.02.025
Kim HJ, Jeon SM, Lee MK, et al., 2010. Comparison of hesperetin and its metabolites for cholesterol–lowering and antioxidative efficacy in hypercholesterolemic hamsters. J Med Food, 13(4):808–814. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2009.1320
Krasavage WJ, Terhaar CJ, 1977. d–a–Tocopheryl poly(ethylene glycol) 1000 succinate. Acute toxicity, subchronic feeding, reproduction, and teratologic studies in the rat. J Agric Food Chem, 25(2):273–278. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf60210a002
Li Y, Yang DJ, Chen SL, et al., 2008. Process parameters and morphology in puerarin, phospholipids and their complex microparticles generation by supercritical antisolvent precipitation. Int J Pharm, 359(1–2): 35–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2008.03.022
Liu LX, Chen J, 2008. Solubility of hesperetin in various solvents from (288.2 to 323.2) K. J Chem Eng Data, 53(7):1649–1650. https://doi.org/10.1021/je800078j
Maiti K, Mukherjee K, Murugan V, et al., 2009. Exploring the effect of hesperetin–HSPC complex—a novel drug delivery system on the in vitro release, therapeutic efficacy and pharmacokinetics. AAPS PharmSciTech, 10(3):943–950. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-009-9282-6
Németh K, Plumb GW, Berrin JG, et al., 2003. Deglycosylation by small intestinal epithelial cell ß–glucosidases is a critical step in the absorption and metabolism of dietary flavonoid glycosides in humans. Eur J Nutr, 42(1):29–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-003-0397-3
Parhiz H, Roohbakhsh A, Soltani F, et al., 2015. Antioxidant and anti–inflammatory properties of the citrus flavonoids hesperidin and hesperetin:an updated review of their molecular mechanisms and experimental models. Phytother Res, 29(3):323–331. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.5256
Qin LH, Niu YW, Wang YM, et al., 2018. Combination of phospholipid complex and submicron emulsion techniques for improving oral bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy of water–insoluble drug. Mol Pharm, 15(3):1238–1247. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.7b01061
Roohbakhsh A, Parhiz H, Soltani F, et al., 2014. Neuropharmacological properties and pharmacokinetics of the citrus flavonoids hesperidin and hesperetin—a mini–review. Life Sci, 113(1–2): 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2014.07.029
Shete G, Pawar YB, Thanki K, et al., 2015. Oral bioavailability and pharmacodynamic activity of hesperetin nanocrystals generated using a novel bottom–up technology. Mol Pharm, 12(4):1158–1170. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp5008647
Shin GH, Li JL, Cho JH, et al., 2016. Enhancement of curcumin solubility by phase change from crystalline to amorphous in cur–TPGS nanosuspension. J Food Sci, 81(2): N494–N501. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.13208
Singh H, Narang JK, Singla YP, et al., 2017. TPGS stabilized sublingual films of frovatriptan for the management of menstrual migraine:formulation, design and antioxidant activity. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol, 41:144–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2017.07.008
Testai L, Calderone V, 2017. Nutraceutical value of citrus flavanones and their implications in cardiovascular disease. Nutrients, 9(5):502. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9050502
Varma MVS, Panchagnula R, 2005. Enhanced oral paclitaxel absorption with vitamin E–TPGS:effect on solubility and permeability in vitro, in situ and in vivo. Eur J Pharm Sci, 25(4–5): 445–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2005.04.003
Wang JN, Wang LL, Zhang L, et al., 2018. Studies on the curcumin phospholipid complex solidified with Soluplus®. J Pharm Pharmacol, 70(2):242–249. https://doi.org/10.1111/jphp.12857
Wolfe KL, Liu RH, 2007. Cellular antioxidant activity (CAA) assay for assessing antioxidants, foods, and dietary supplements. J Agric Food Chem, 55(22):8896–8907. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0715166
Zhang ZP, Tan SW, Feng SS, 2012. Vitamin E TPGS as a molecular biomaterial for drug delivery. Biomaterials, 33(19):4889–4906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.03.046
Zhao BX, Gu SF, Du Y, et al., 2018. Solid lipid nanoparticles as carriers for oral delivery of hydroxysafflor yellow A. Int J Pharm, 535(1–2): 164–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.10.040.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51773176, 51522304, and U1501243) and the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No. LY17H300002), China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, SF., Wang, LY., Tian, YJ. et al. Enhanced water solubility, antioxidant activity, and oral absorption of hesperetin by D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate and phosphatidylcholine. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 20, 273–281 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1800346
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1800346
Key words
- Hesperetin
- D-α-Tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS)
- Phosphatidylcholine
- Antioxidant activity
- Oral absorption