Abstract
Objective
To investigate the role of iptakalim, an ATP-sensitive potassium channel opener, in transient cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury and its involved mechanisms.
Methods
Intraluminal occlusion of middle cerebral artery (MCAO) in a rat model was used to investigate the effect of iptakalim at different time points. Infarct volume was measured by staining with 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride, and immunohistochemistry was used to evaluate the expressions of Bcl-2 and Bax. In vitro, neurovascular unit (NVU) cells, including rat primary cortical neurons, astrocytes, and cerebral microvascular endothelial cells, were cultured and underwent oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD). The protective effect of iptakalim on NVU cells was investigated by cell viability and injury assessments, which were measured by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide and release of lactate dehydrogenase. Caspase-3, Bcl-2 and Bax mRNA expressions were evaluated by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Results
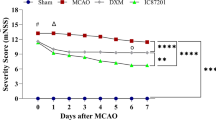
Administration of iptakalim 0 or 1 h after reperfusion significantly reduced infarct volumes, improved neurological scores, and attenuated brain edema after cerebral I/R injury. Iptakalim treatment (0 h after reperfusion) also reduced caspase-3 expression and increased the ratio of Bcl-2 to Bax by immunohistochemistry. Iptakalim inhibited OGD-induced cell death in cultured neurons and astrocytes, and lactate dehydrogenase release from cerebral microvascular endothelial cells. Iptakalim reduced mRNA expression of caspase-3 and increased the ratio of Bcl-2 to Bax in NVU cells.
Conclusions
Iptakalim confers neuroprotection against cerebral I/R injury by protecting NVU cells via inhibiting of apoptosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Hamid, K.M., Baimbridge, K.G., 1997. The effects of artificial calcium buffers on calcium responses and glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity in cultured hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience, 81(3):673–687. [doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(97)00162-0]
Chan, P.H., 1996. Role of oxidants in ischemic brain damage. Stroke, 27(6):1124–1129. [doi:10.1161/01.STR.27.6.1124]
Chen, Y.P., Qiu, C.R., Wang, H., 2004. Cardiovascular pharmacological characterization of novel 2,3-dimethyl-2-butylamine derivatives in rats. Life Sci., 75(17): 2131–2142. [doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2004.06.003]
Chen, Y.P., Cui, W.Y., Wang, H., 2006. Selective actions of iptakalim on the subtypes of KATP channels. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull, 22(3):278–284.
Diarra, A., Sheldon, C., Brett, C.L., Baimbridge, K.G., Church, J., 1999. Anoxia-evoked intracellular pH and Ca2+ concentration changes in cultured postnatal rat hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience, 93(3):1003–1016. [doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(99)00230-4]
Domoki, F., Kis, B., Nagy, K., Farkas, E., Busija, D.W., Bari, F., 2005. Diazoxide preserves hypercapnia-induced arteriolar vasodilation after global cerebral ischemia in piglets. Am. J. Physiol., 289(1):H368–H373. [doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00887.2004]
Dunn-Meynell, A.A., Rawson, N.E., Levin, B.E., 1998. Distribution and phenotype of neurons containing the ATP-sensitive K+ channel in rat brain. Brain Res., 814(1–2):41–54. [doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(98)00956-1]
Girn, H.R., Ahilathirunayagam, S., Mavor, A.I., Homer-Vanniasinkam, S., 2007. Reperfusion syndrome: cellular mechanisms of microvascular dysfunction and potential therapeutic strategies. Vasc. Endovascular Surg., 41(4): 277–293. [doi:10.1177/1538574407304510]
Graham, S.H., Chen, J., 2001. Programmed cell death in cerebral ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab., 21(2): 99–109. [doi:10.1097/00004647-200102000-00001]
Green, D.R., Reed, J.C., 1998. Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science, 281(5381):1309–1312. [doi:10.1126/science.281.5381.1309]
Hamprecht, B., Löffler, F., 1985. Primary glial cultures as a model for studying hormone action. Methods Enzymol., 109:341–345. [doi:10.1016/0076-6879(85)09097-8]
Hu, X.L., Olsson, T., Johansson, I.M., Brannstrom, T., Wester, P., 2004. Dynamic changes of the anti- and pro-apoptotic proteins Bcl-w, Bcl-2, and Bax with Smac/Diablo mitochondrial release after photothrombotic ring stroke in rats. Eur. J. Neurosci., 20(5):1177–1188. [doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03554.x]
Janigro, D., West, G.A., Gordon, E.L., Winn, H.R., 1993. ATP-sensitive K+ channels in rat aorta and brain microvascular endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol., 265(3 Pt 1): C812–C821.
Kis, B., Kaiya, H., Nishi, R., Deli, M.A., Abraham, C.S., Yanagita, T., Isse, T., Gotoh, S., Kobayashi, H., Wada, A., et al., 2002. Cerebral endothelial cells are a major source of adrenomedullin. J. Neuroendocrinol., 14(4):283–293. [doi:10.1046/j.1365-2826.2002.00778.x]
Kis, B., Snipes, J.A., Simandle, S.A., Busija, D.W., 2005. Acetaminophen-sensitive prostaglandin production in rat cerebral endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol., 288(4): R897–R902. [doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00613.2004]
Kowaltowski, A.J., Castilho, R.F., Vercesi, A.E., 2001. Mitochondrial permeability transition and oxidative stress. FEBS Lett., 495(1–2):12–15. [doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(01)02316-X]
Kroemer, G., 2003. Mitochondrial control of apoptosis: an introduction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 304(3): 433–435. [doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(03)00614-4]
Li, P., Nijhawan, D., Budihardjo, I., Srinivasula, S.M., Ahmad, M., Alnemri, E.S., Wang, X., 1997. Cytochrome C and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell, 91(4): 479–489. [doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80434-1]
Li, Y., Chopp, M., Jiang, N., Yao, F., Zaloga, C., 1995. Temporal profile of in situ DNA fragmentation after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab., 15(3):389–397. [doi:10.1038/jcbfm.1995.49]
Linnik, M.D., Zobrist, R.H., Hatfield, M.D., 1993. Evidence supporting a role for programmed cell death in focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke, 24(12):2002–2008; discussion 2008–2009. [doi:10.1161/01.STR.24.12.2002]
Liss, B., Bruns, R., Roeper, J., 1999. Alternative sulfonylurea receptor expression defines metabolic sensitivity of KATP channels in dopaminergic midbrain neurons. EMBO J., 18(4):833–846. [doi:10.1093/emboj/18.4.833]
Lo, E.H., Rosenberg, G.A., 2009. The neurovascular unit in health and disease: introduction. Stroke, 40(3):S2–S3. [doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.534404]
Makins, R., Ballinger, A., 2003. Gastrointestinal side effects of drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Saf., 2(4):421–429. [doi:10.1517/14740338.2.4.421]
Mattson, M.P., Duan, W., Pedersen, W.A., Culmsee, C., 2001. Neurodegenerative disorders and ischemic brain diseases. Apoptosis, 6(1–2):69–81. [doi:10.1023/A:1009676112184]
Mederos y Schnitzler, M., Derst, C., Daut, J., Preisig-Müller, R., 2000. ATP-sensitive potassium channels in capillaries isolated from guinea-pig heart. J. Physiol., 525(2): 307–317. [doi:10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.t01-1-00307.x]
Roof, R.L., Schielke, G.P., Ren, X., Hall, E.D., 2001. A comparison of long-term functional outcome after 2 middle cerebral artery occlusion models in rats. Stroke, 32(11):2648–2657. [doi:10.1161/hs1101.097397]
Sato, T., Sasaki, N., O’Rourke, B., Marban, E., 2000. Nicorandil, a potent cardioprotective agent, acts by opening mitochondrial ATP-dependent potassium channels. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., 35(2):514–518. [doi:10.1016/S0735-1097(99)00552-5]
Seino, S., Miki, T., 2004. Gene targeting approach to clarification of ion channel function: studies of Kir6.x null mice. J. Physiol., 554(2):295–300. [doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2003.047175]
Shimizu, K., Lacza, Z., Rajapakse, N., Horiguchi, T., Snipes, J., Busija, D.W., 2002. MitoKATP opener, diazoxide, reduces neuronal damage after middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. Am. J. Physiol., 283(3):H1005–H1011. [doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00054.2002]
Simard, J.M., Chen, M., 2004. Regulation by sulfanylurea receptor type 1 of a non-selective cation channel involved in cytotoxic edema of reactive astrocytes. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol., 16(1):98–99. [doi:10.1097/00008506-200401000-00021]
Swanson, R.A., Sharp, F.R., 1994. Infarct measurement methodology. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab., 14(4): 697–698. [doi:10.1038/jcbfm.1994.88]
Tsuchiya, D., Hong, S., Matsumori, Y., Shiina, H., Kayama, T., Swanson, R.A., Dillman, W.H., Liu, J., Panter, S.S., Weinstein, P.R., 2003. Overexpression of rat heat shock protein 70 is associated with reduction of early mitochondrial cytochrome C release and subsequent DNA fragmentation after permanent focal ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab., 23(6):718–727. [doi:10.1097/01.WCB.0000054756.97390.F7]
Wang, H., Zhang, Y.L., Tang, X.C., Feng, H.S., Hu, G., 2004. Targeting ischemic stroke with a novel opener of ATP-sensitive potassium channels in the brain. Mol. Pharmacol., 66(5):1160–1168. [doi:10.1124/mol.104.003178]
Wang, H., Tang, Y., Wang, L., Long, C.L., Zhang, Y.L., 2007. ATP-sensitive potassium channel openers and 2,3-dimethyl-2-butylamine derivatives. Curr. Med. Chem., 14(2):133–155. [doi:10.2174/092986707779313390]
Yamada, K., Ji, J.J., Yuan, H., Miki, T., Sato, S., Horimoto, N., Shimizu, T., Seino, S., Inagaki, N., 2001. Protective role of ATP-sensitive potassium channels in hypoxia-induced generalized seizure. Science, 292(5521):1543–1546. [doi: 10.1126/science.1059829]
Yanamoto, H., Nagata, I., Hashimoto, N., Kikuchi, H., 1998. Three-vessel occlusion using a micro-clip for the proximal left middle cerebral artery produces a reliable neocortical infarct in rats. Brain Res. Brain Res. Protoc., 3(2): 209–220. [doi:10.1016/S1385-299X(98)00042-7]
Yang, G.Y., Betz, A.L., 1994. Reperfusion-induced injury to the blood-brain barrier after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Stroke, 25(8):1658–1664; discussion 1664–1655. [doi:10.1161/01.STR.25.8.1658]
Yoshida, H., Feig, J.E., Morrissey, A., Ghiu, I.A., Artman, M., Coetzee, W.A., 2004. KATP channels of primary human coronary artery endothelial cells consist of a heteromultimeric complex of Kir6.1, Kir6.2, and SUR2B subunits. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol., 37(4):857–869. [doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2004.05.022]
Zhang, S., Zhou, F., Ding, J.H., Zhou, X.Q., Sun, X.L., Hu, G., 2007. ATP-sensitive potassium channel opener iptakalim protects against MPP-induced astrocytic apoptosis via mitochondria and mitogen-activated protein kinase signal pathways. J. Neurochem., 103(2):569–579. [doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04775.x]
Zhu, H.L., Luo, W.Q., Wang, H., 2008. Iptakalim protects against hypoxic brain injury through multiple pathways associated with ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Neuroscience, 157(4):884–894. [doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.09.033]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ran, Yh., Wang, H. Iptakalim, an ATP-sensitive potassium channel opener, confers neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by protecting neurovascular unit cells. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 12, 835–845 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1100067
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1100067
Key words
- Neurovascular unit
- Cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury
- ATP-sensitive potassium channel opener
- Neuroprotection
- Apoptosis