Abstract
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-dependent excitotoxicity is one of the most important mechanisms underlying stroke injury and the resulting neuronal death. In the present study, in order to reduce post-stroke brain injury and improve behavioral performance, a new molecule named IC87201, which acts as an inhibitor of PSD95/nNOS interaction in the intracellular signaling pathway of NMDA receptors, was administered. Using the middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) technique, 24 adult male rats were subjected to one hour of cerebral ischemia. Animals were randomly divided into sham, MCAO, MCAO + DXM, and MCAO + IC87201 groups, and in the last two groups, intraperitoneal injection of dextromethorphan hydrobromide monohydrate (DXM), as an NMDA antagonist, and IC87201 was performed after ischemia. Neurobehavioral scores were evaluated for seven days, and on the last two days, the rats’ memory performance was appraised using the passive avoidance test. On seventh day, the brain tissue was properly prepared for stereological analysis. Stereological studies of the hippocampus CA1 and CA3 regions revealed that changes in the total and infarcted volumes, total number of neurons, non-neurons, and dead neurons are the consequences of cerebral ischemia. Also, following cerebral ischemia, neurobehavioral and memory function impairments which were assessed by modified neurological severity scores (mNSS) and passive avoidance test, were observed. The aforementioned impairments were recovered after administration of IC87201 significantly and more potently than DXM. Based on our findings, IC87201 successfully attenuated post-ischemia damages. Therefore, this molecule can be considered as a new therapeutic approach in future research.
Highlights
-
• Ischemic stroke severely destroys hippocampus neurons and causes memory impairment.
-
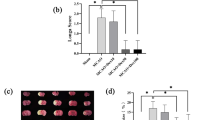
• IC87201 improved hippocampal histological injury following brain ischemia.
-
• IC87201 improved memory impairment resulting from brain ischemia.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy or ethical restrictions.
References
Mukherjee D, Patil CG (2011) Epidemiology and the global burden of stroke. World Neurosurg 76:S85–S90
Bingham D, Martin SJ, Macrae IM, Carswell HV (2012) Watermaze performance after middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat: the role of sensorimotor versus memory impairments. J Cereb Blood Flow Metabolism 32:989–999
Dahlqvist P, Rönnbäck A, Bergström SA, Söderström I, Olsson T (2004) Environmental enrichment reverses learning impairment in the Morris water maze after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Eur J Neurosci 19:2288–2298
Ottani A, Saltini S, Bartiromo M, Zaffe D, Botticelli AR, Ferrari A, Bertolini A, Genedani S (2003) Effect of γ-hydroxybutyrate in two rat models of focal cerebral damage. Brain Res 986:181–190
Otmakhova NA, Otmakhov N, Lisman JE (2002) Pathway-specific properties of AMPA and NMDA-mediated transmission in CA1 hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Neurosci 22:1199–1207
Neumann T, Cohan JH, Dave CR, Wright KB, Perez-Pinzon CA M (2013) Global cerebral ischemia: synaptic and cognitive dysfunction. Curr Drug Targets 14:20–35
Wu QJ, Tymianski M (2018) Targeting NMDA receptors in stroke: new hope in neuroprotection. Mol Brain 11:1–14
Willing AE, Jiang L, Nowicki P, Poulos S, Milliken M, Cahill DW, Sanberg PR (2002) Effects of middle cerebral artery occlusion on spontaneous activity and cognitive function in rats. Int J Neurosci 112:503–516
Florio S, Loh C, Huang S, Iwamaye A, Kitto K, Fowler K, Treiberg J, Hayflick J, Walker J, Fairbanks C (2009) Disruption of nNOS-PSD95 protein–protein interaction inhibits acute thermal hyperalgesia and chronic mechanical allodynia in rodents. Br J Pharmacol 158:494–506
Bokesch PM, Marchand JE, Connelly CS, Wurm WH, Kream RM (1994) Dextromethorphan inhibits ischemia-induced c-fos expression and delayed neuronal death in hippocampal neurons. Anesthesiology 81:470–477
Smith AE, Xu Z, Lai YY, Kulkarni PM, Thakur GA, Hohmann AG, Crystal JD (2016) Source memory in rats is impaired by an NMDA receptor antagonist but not by PSD95-nNOS protein–protein interaction inhibitors. Behav Brain Res 305:23–29
Owjfard M, Bigdeli MR, Safari A, Namavar MR (2020) Effects of Nicorandil on neurobehavioral function, BBB integrity, edema and stereological parameters of the brain in the sub-acute phase of stroke in a rat model. J Biosci 45:1–16
Chen J, Li Y, Wang L, Zhang Z, Lu D, Lu M, Chopp M (2001) Therapeutic benefit of intravenous administration of bone marrow stromal cells after cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 32:1005–1011
Dolatabadi LK, Emamghoreishi M, Namavar MR, Sarkala HB (2019) Curcumin effects on memory impairment and restoration of irregular neuronal distribution in the hippocampal CA1 region after global cerebral ischemia in male rats. Basic Clin Neurosci 10:527
Ebrahimian Z, Karimi Z, Khoshnoud MJ, Namavar MR, Daraei B, Haidari MR (2017) Behavioral and stereological analysis of the effects of intermittent feeding diet on the orally administrated MDMA (ecstasy) in mice. Innovations Clin Neurosci 14:40
Fluri F, Schuhmann MK, Kleinschnitz C (2015) Animal models of ischemic stroke and their application in clinical research. Drug Des Devel Ther 9:3445
Hattori K, Lee H, Hurn PD, Crain BJ, Traystman RJ, DeVries AC (2000) Cognitive deficits after focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Stroke 31:1939–1944
Kondo T, Yoshida S, Nagai H, Takeshita A, Mino M, Morioka H, Nakajima T, Kusakabe KT, Okada T (2018) Transient forebrain ischemia induces impairment in cognitive performance prior to extensive neuronal cell death in Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus). J Vet Sci 19:505–511
Li Y, Yu Q, Fu J, Li Y, Peng B, Huang G, Xiao Z (2018) Learning-dependent LTP and synaptic ultrastructural modification after physical exercise in rats with middle cerebral artery occlusion: relevance for learning and memory. Int J Clin Exp Med 11:13042–13054
Onufriev MV, Moiseeva YV, Zhanina MY, Lazareva NA, Gulyaeva NV (2021) A comparative study of Koizumi and longa methods of intraluminal filament middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats: early corticosterone and inflammatory response in the hippocampus and frontal cortex. Int J Mol Sci 22:13544
Izquierdo I, Bevilaqua LR, Rossato JI, Bonini JS, Medina JH, Cammarota M (2006) Different molecular cascades in different sites of the brain control memory consolidation. Trends Neurosci 29:496–505
Shipton OA, Paulsen O (2014) GluN2A and GluN2B subunit-containing NMDA receptors in hippocampal plasticity. Philosophical Trans Royal Soc B: Biol Sci 369:20130163
Pittenger C, Huang YY, Paletzki RF, Bourtchouladze R, Scanlin H, Vronskaya S, Kandel ER (2002) Reversible inhibition of CREB/ATF transcription factors in region CA1 of the dorsal hippocampus disrupts hippocampus-dependent spatial memory. Neuron 34:447–462
de Lima MNM, Laranja DC, Bromberg E, Roesler R, Schröder N (2005) Pre-or post-training administration of the NMDA receptor blocker MK-801 impairs object recognition memory in rats. Behav Brain Res 156:139–143
Jafari-Sabet M (2006) NMDA receptor blockers prevents the facilitatory effects of post-training intra-dorsal hippocampal NMDA and physostigmine on memory retention of passive avoidance learning in rats. Behav Brain Res 169:120–127
Chen S, Yin Z-J, Jiang C, Ma Z-Q, Fu Q, Qu R, Ma S-P (2014) Asiaticoside attenuates memory impairment induced by transient cerebral ischemia–reperfusion in mice through anti-inflammatory mechanism. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 122:7–15
Hori E, Uwano T, Tamura R, Miyake N, Nishijo H, Ono T (2002) Effects of a novel arginine-vasopressin derivative, NC-1900, on the spatial memory impairment of rats with transient forebrain ischemia. Cogn Brain Res 13:1–15
Xu X, Li Z, Yang Z, Zhang T (2012) Decrease of synaptic plasticity associated with alteration of information flow in a rat model of vascular dementia. Neuroscience 206:136–143
Calabresi P, Centonze D, Pisani A, Cupini LM, Bernardi G (2003) Synaptic plasticity in the ischaemic brain. Lancet Neurol 2:622–629
Doucet MV, Levine H, Dev KK, Harkin A (2013) Small-molecule inhibitors at the PSD-95/nNOS interface have antidepressant-like properties in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 38:1575–1584
Bouët V, Freret T, Toutain J, Divoux D, Boulouard M, Schumann-Bard P (2007) Sensorimotor and cognitive deficits after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in the mouse. Exp Neurol 203:555–567
De Butte M, Fortin T, Pappas B (2002) Pinealectomy: behavioral and neuropathological consequences in a chronic cerebral hypoperfusion model. Neurobiol Aging 23:309–317
Atlasi MA, Naderian H, Noureddini M, Fakharian E, Azami A (2013) Morphology of rat hippocampal CA1 neurons following modified two and four-vessels global ischemia models
Ritchie LJ, De Butte M, Pappas BA (2004) Chronic mild stress exacerbates the effects of permanent bilateral common carotid artery occlusion on CA1 neurons. Brain Res 1014:228–235
Hoyte L, Barber P, Buchan A, Hill M (2004) The rise and fall of NMDA antagonists for ischemic stroke. Curr Mol Med 4:131–136
Hu W, Guan L-S, Dang X-B, Ren P-Y, Zhang Y-L (2014) Small-molecule inhibitors at the PSD-95/nNOS interface attenuate MPP+-induced neuronal injury through Sirt3 mediated inhibition of mitochondrial dysfunction. Neurochem Int 79:57–64
Zhou L, Li F, Xu H-B, Luo C-X, Wu H-Y, Zhu M-M, Lu W, Ji X, Zhou Q-G, Zhu D-Y (2010) Treatment of cerebral ischemia by disrupting ischemia-induced interaction of nNOS with PSD-95. Nat Med 16:1439–1443
Dzamba D, Honsa P, Anderova M (2013) NMDA receptors in glial cells: pending questions. Curr Neuropharmacol 11:250–262
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran (Grant number: SU9531466), which was extracted from Maryam Mohammadian’s Ph.D. thesis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MM: Designing the study, performing laboratory work, graphical design, data collection, and writing the manuscript draft. AB: Supervising laboratory works, conceptualization, methodology, and data analysis. MRN: Conceptualization, methodology editing, and revising the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All procedures were performed based on the National Institutes of Health?s Guidelines for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and Animal Research: Reporting in Vivo Experiments (ARRIVE) and approved by the local Ethical Committee of Shiraz University (SU-9531466).
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammadian, M., Bahaoddini, A. & Namavar, M.R. The IC87201 (a PSD95/nNOS Inhibitor) Attenuates Post- Stroke Injuries. Neurochem Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-024-04140-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-024-04140-w