Abstract
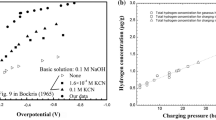
We studied the behavior of several heavy metals implanted into 4H-SiC during high-temperature annealing. We evaluated the diffusion of Iron, Nickel, and Titanium in 4H-SiC after Al+ and Ge+ implantation in detail. The diffusion of these metals depends on the existence of ion species in 4H-SiC and implantation damage. Furthermore, implantation temperature of Al+ and Ge+ that has a large impact on defects generation plays an important role for the diffusion of heavy metals in 4H-SiC. It should be noted that the implantation damages such as vacancy and interstitial atom enhance the diffusion of heavy metals in 4H-SiC. The diffusion coefficient in SiC becomes larger in the order of Ti, Fe, and Ni. It is found that this order does not change depending on the implanted ion species and implantation temperature, although the diffusion coefficient significantly changes.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
T. Kimoto, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 54, 040103 (2015)
Y.A. Vodakov, E.N. Mokhov, Silicon Carbide 1973 (University of South Carolina Press, Columbia, 1974), p.508
L. Baldi et al., J. Electr. Soc. 127, 164 (1980)
F.C. Beyer et al., J. Appl. Phys. 110, 123701 (2011)
T. Dalibor et al., Phys. Rev. B 55, 13618 (1997)
K. Danno et al., Appl. Phys. Express 5, 031301 (2012)
Y. Negoro et al., J. Appl. Phys. 96, 224 (2004)
A.V. Suvorov et al., Symposium A—ion-solid interactions for materials modification and processing. J. Appl. Phys. 396, 239 (1995)
G. Lim, A. Kar, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 176, 660 (2011)
M. Miyake, S. Aoyama, J. Appl. Phys. 63, 1754 (1988)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their sincere thanks to Dr. N. Tokoro of Nissin Ion Equipment Co.,Ltd. for helpful discussion throughout this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wada, R., Hamamoto, N., Nagayama, T. et al. The diffusion analysis of implanted heavy metals in 4H-SiC. MRS Advances 7, 1331–1337 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43580-022-00393-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43580-022-00393-1