Abstract
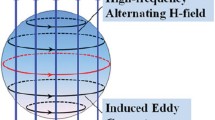
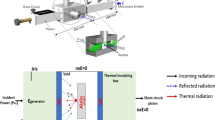
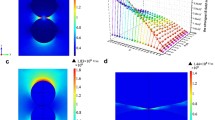
Ultra-rapid microwave sintering of ceramics has been recently demonstrated by the authors. In the experiments with oxide ceramic samples carried out in a 24 GHz gyrotron system for microwave processing of materials, full density was achieved in the sintering processes with a duration of the high-temperature stage of one to several minutes and zero hold at the maximum temperature. The implementation of the ultra-rapid microwave sintering processes was made possible due to fast and efficient control over the temperature of the materials and the supplied microwave power. The absorbed microwave power density was typically in the range of 10–100 W/cm3, which is within the same order of magnitude as the power of Joule heat in the DC electric field–assisted flash sintering processes. At this power level, a thermal instability is triggered by the volumetric heating, which results in a drastic enhancement of mass transport. In addition, possibility of ultra-rapid microwave sintering of powder metals has been demonstrated within a model accounting for the effective electromagnetic properties and resonant absorption effects.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.R. Tinga and W.A.G. Voss: Microwave Power Engineering (Academic Press, New York, New York, 1968).
A.J. Berteaud and J.C. Badot: High temperature microwave heating in refractory materials. J. Microwave Power 11, 315 (1976).
J.M. Osepchuk: A history of microwave heating applications. IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 32, 1200 (1984).
T.T. Meek, C.E. Holcombe, and N. Dykes: Microwave sintering of some oxide materials using sintering aids. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 6, 1060 (1987).
D.L. Johnson: Microwave and plasma sintering of ceramics. Ceram. Int. 17, 295 (1991).
W.H. Sutton: Microwave processing of ceramics—An overview. In Microwave Processing of Materials III, R.L. Beatty, W.H. Sutton, and M.F. Iskander, eds.; Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol. 269 (Materials Research Society, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, 1994); p. 3.
J.D. Katz: Microwave sintering of ceramics. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 22, 153 (1992).
D.K. Agrawal: Microwave processing of ceramics: A review. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 3, 480 (1998).
Y.V. Bykov, K.I. Rybakov, and V.E. Semenov: High-temperature microwave processing of materials. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 34, R55 (2001).
J.G.P. Binner and B. Vaidhyanathan: Microwave sintering of ceramics: What does it offer? Key Eng. Mater. 264–268, 725 (2004).
K.I. Rybakov, E.A. Olevsky, and E.V. Krikun: Microwave sintering—Fundamentals and modeling. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96, 1003 (2013).
J.A. Eastmen, K.E. Sickafus, J.D. Katz, S.G. Boeke, R.D. Blake, C.R. Evans, R.B. Schwarz, and Y.X. Liao: Microwave sintering of nanocrystalline TiO2. In Microwave Processing of Materials II, W.B. Snyder, Jr., W.H. Sutter, M.F. Iskander, and D.L. Johnson, eds.; Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol. 189 (Materials Research Society, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, 1990); p. 273.
J. Freim, J. McKittrick, J. Katz, and K. Sickafus: Microwave sintering of nanocrystalline γ-Al2O3. Nanostruct. Mater. 4, 371 (1994).
Y. Bykov, A. Eremeev, S. Egorov, V. Ivanov, Y. Kotov, V. Khrustov, and A. Sorokin: Sintering of nanostructural titanium oxide using millimeter-wave radiation. Nanostruct. Mater. 12, 115 (1999).
G. Roussy and J. Mercier: Temperature runaway of microwave heated materials: Study and control. J. Microwave Power 20, 47 (1985).
P.E. Parris and V.M. Kenkre: Thermal runaway in ceramics arising from the temperature dependence of the thermal conductivity. Phys. Status Solidi B 200, 39 (1997).
E.B. Kulumbaev, V.E. Semenov, and K.I. Rybakov: Stability of microwave heating of ceramic materials in a cylindrical cavity. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 40, 6809 (2007).
M.S. Spotz, D.J. Skamser, and D.L. Johnson: Thermal-stability of ceramic materials in microwave-heating. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 78, 1041 (1995).
M. Alliouat, Y. Lecluse, J. Massieu, and L. Mazo: Control algorithm for microwave sintering in a resonant system. J. Microwave Power Electromagn. Energy 25, 25 (1990).
G.O. Beale, F.J. Arteaga, and W.M. Black: Design and evaluation of a controller for the process of microwave joining of ceramics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 39, 301 (1992).
V.E. Semenov and N.A. Zharova: Thermal runaway and hot spots under controlled microwave heating. In Advances in Microwave and Radio Frequency Processing, M. Willert-Porada, ed. (Springer, Berlin, Germany, 2006); p. 482.
Z.A. Munir, D.V. Quach, and M. Ohyanagi: Electric current activation of sintering: A review of the pulsed electric current sintering process. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 1 (2011).
R. Raj, M. Cologna, and J.S.C. Francis: Influence of externally imposed and internally generated electrical fields on grain growth, diffusional creep, sintering and related phenomena in ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 1941 (2011).
O. Guillon, J. Gonzales-Julian, B. Dargatz, T. Kessel, G. Schierning, J. Rathel, and M. Herrmann: Field-assisted sintering technology/spark plasma sintering: Mechanisms, materials, and technology developments. Adv. Eng. Mater. 16, 830 (2014).
E.A. Olevsky and D.V. Dudina: Field-assisted Sintering: Science and Applications (Springer International Publishing, Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018).
M. Cologna, B. Rashkova, and R. Raj: Flash sintering of nanograin zirconia in <5 s at 850 °C. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93, 3556 (2010).
C.E.J. Dancer: Flash sintering of ceramic materials. Mater. Res. Express 3, 102001 (2016).
M. Yu, S. Grasso, R. Mckinnon, T. Saunders, and M.J. Reece: Review of flash sintering: Materials, mechanisms and modelling. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 116, 24 (2017).
R.I. Todd, E. Zapata-Solvas, R.S. Bonilla, T. Sneddon, and P.R. Wilshaw: Electrical characteristics of flash sintering: Thermal runaway of Joule heating. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 35, 1865 (2015).
K.I. Rybakov, Y.V. Bykov, A.G. Eremeev, S.V. Egorov, V.V. Kholoptsev, A.A. Sorokin, and V.E. Semenov: Microwave ultra-rapid sintering of oxide ceramics. In Processing and Properties of Advanced Ceramics and Composites VII, M.M. Mahmoud, A.S. Bhalla, N.P. Bansal, J.P. Singh, R. Castro, N.J. Manjooran, G. Pickrell, S. Johnson, G. Brennecka, G. Singh, and D. Zhu, eds.; Ceramic Transactions, Vol. 252 (Wiley, Hoboken, New Jersey, 2015); p. 57.
Y.V. Bykov, S.V. Egorov, A.G. Eremeev, V.V. Kholoptsev, K.I. Rybakov, and A.A. Sorokin: Flash microwave sintering of transparent Yb:(LaY)2O3 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 98, 3518 (2015).
Y.V. Bykov, S.V. Egorov, A.G. Eremeev, V.V. Kholoptsev, I.V. Plotnikov, K.I. Rybakov, and A.A. Sorokin: Sintering of oxide ceramics under rapid microwave heating. In Processing, Properties and Design of Advanced Ceramics and Composites, G. Singh, A. Bhalla, M.M. Mahmoud, R.H.R. Castro, N.P. Bansal, D. Zhu, J.P. Singh, and Y. Wu, eds.; Ceramic Transactions, Vol. 259 (Wiley, Hoboken, New Jersey, 2016); p. 233.
Y.V. Bykov, S.V. Egorov, A.G. Eremeev, V.V. Kholoptsev, I.V. Plotnikov, K.I. Rybakov, and A.A. Sorokin: On the mechanism of microwave flash sintering of ceramics. Materials 9, 684 (2016).
Y.V. Bykov, S.V. Egorov, A.G. Eremeev, I.V. Plotnikov, K.I. Rybakov, A.A. Sorokin, and V.V. Kholoptsev: Effect of specific absorbed power on microwave sintering of 3YSZ ceramics. IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 218, 012001 (2017).
Y.V. Bykov, S.V. Egorov, A.G. Eremeev, I.V. Plotnikov, K.I. Rybakov, A.A. Sorokin, and V.V. Kholoptsev: Flash sintering of oxide ceramics under microwave heating. Tech. Phys. 63, 391 (2018).
Y.V. Bykov, A.G. Eremeev, S.V. Egorov, V.V. Kholoptsev, I.V. Plotnikov, K.I. Rybakov, and A.A. Sorokin: Ultra-rapid microwave sintering. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1115, 042005 (2018).
Y.V. Bykov, S.V. Egorov, A.G. Eremeev, V.V. Kholoptsev, I.V. Plotnikov, K.I. Rybakov, A.A. Sorokin, S.S. Balabanov, and A.V. Belyaev: Ultra-rapid microwave sintering of pure and Y2O3-doped MgAl2O4. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 102, 559 (2019).
F. Trombin and R. Raj: Developing processing maps for implementing flash sintering into manufacture of whiteware ceramics. Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull. 93, 32 (2014).
E. Sortino, J-M. Lebrun, A. Sansone, and R. Raj: Continuous flash sintering. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 101, 1432 (2018).
Y.V. Bykov, S.V. Egorov, A.G. Eremeev, V.V. Kholoptsev, I.V. Plotnikov, K.I. Rybakov, and A.A. Sorokin: Additive manufacturing of ceramic products based on millimeter-wave heating. In Abstract Book of the International Conference on High-Performance Ceramics (CICC-11) (Kunming, China, 2019); p. 27.
R. Raj: Analysis of the power density at the onset of flash sintering. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 99, 3226 (2016).
F. Kremer and J.R. Izatt: Millimeter-wave absorption measurements in low-loss dielectric using an untuned cavity resonator. Int. J. Infrared Millimeter Waves 2, 675 (1981).
H.D. Kimrey and M.A. Janney: Design principles for high-frequency microwave cavities. In Microwave Processing of Materials, W.H. Sutton, M.H. Brooks, and I.J. Chabinsky, eds.; Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol. 124 (Materials Research Society, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, 1988); p. 367.
Y.V. Bykov, A.G. Eremeev, M.Y. Glyavin, G.G. Denisov, G.I. Kalynova, E.A. Kopelovich, A.G. Luchinin, I.V. Plotnikov, M.D. Proyavin, M.M. Troitskiy, and V.V. Kholoptsev: Millimeter-wave gyrotron research system. I. Description of the facility. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 61, 752 (2019).
J.D. Jackson: Classical Electrodynamics (Wiley, New York, New York, 1962).
J. Narayan: A new mechanism for field-assisted processing and flash sintering of materials. Scr. Mater. 69, 107 (2013).
R. Chaim: Liquid film capillary mechanism for densification of ceramic powders during flash sintering. Materials 9, 280 (2016).
R. Chaim: On the kinetics of liquid-assisted densification during flash sintering of ceramic nanoparticles. Scr. Mater. 158, 88 (2019).
S.V. Egorov, Y.V. Bykov, A.G. Eremeev, I.V. Plotnikov, K.I. Rybakov, A.A. Sorokin, and V.V. Kholoptsev: Optical registration of shrinkage during ultra-rapid microwave sintering. In Proceedings of the International Conference on “Synthesis and Consolidation of Powder Materials” (Torus Press, Moscow, Russia, 2018); p. 277. doi: https://doi.org/10.30826/SCPM2018060 [in Russian].
R. Roy, D. Agrawal, J. Cheng, and S. Gedevanishvili: Full sintering of powdered-metal bodies in a microwave field. Nature 399, 668 (1999).
W.R. Tinga, W.A.G. Voss, and D.F. Blossey: Generalized approach to multiphase dielectric mixture theory. J. Appl. Phys. 44, 3897 (1973).
D.A.G. Bruggeman: Berechnung verschiedener physikalischer Konstanten von heterogenen Substanzen, I. Dielektriziätskonstanten und Leitfähigkeiten der Mischkörper aus isotropen Substanzen. Ann. Phys.–Berlin, Series 5, 24, 636 (1935) [in German].
K.I. Rybakov, V.E. Semenov, S.V. Egorov, A.G. Eremeev, I.V. Plotnikov, and Y.V. Bykov: Microwave heating of conductive powder materials. J. Appl. Phys. 99, 023506 (2006).
K.I. Rybakov and V.E. Semenov: Effective microwave dielectric properties of ensembles of spherical metal particles. IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 65, 1479 (2017).
I.I. Volkovskaya, V.E. Semenov, and K.I. Rybakov: Effective high-frequency permeability of compacted metal powders. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 60, 797 (2018).
H. Sueyoshi, T. Hashiguchi, N. Nakatsuru, and S. Kakiuchi: Effect of surface oxide film and atmosphere on microwave heating of compacted copper powder. Mater. Chem. Phys. 125, 723 (2011).
M.M. Mahmoud, G. Link, and M. Thumm: The role of the native oxide shell on the microwave sintering of copper metal powder compacts. J. Alloys Compd. 627, 231 (2015).
K.I. Rybakov and M.N. Buyanova: Microwave resonant sintering of powder metals. Scr. Mater. 149, 108 (2018).
C. Manière, G. Lee, T. Zahrah, and E.A. Olevsky: Microwave flash sintering of metal powders: From experimental evidence to multiphysics simulation. Acta Mater. 147, 24 (2018).
G. Mie: Beitrage zur optik trüber Medien, speziell kolloidaler Metallosungen. Ann. Phys. 330, 377 (1908) [in German].
H. Su and D.L. Johnson: Master sintering curve: A practical approach to sintering. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 79, 3211 (1996).
K.I. Rybakov and I.I. Volkovskaya: Electromagnetic field effects in the microwave sintering of electrically conductive powders. Ceram. Int. 45, 9567 (2019).
Y. Bykov, A. Eremeev, M. Glyavin, V. Kholoptsev, A. Luchinin, I. Plotnikov, G. Denisov, A. Bogdashev, G. Kalynova, V. Semenov, and N. Zharova: 24–84-GHz gyrotron systems for technological microwave applications. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 32, 67 (2004).
L. Esposito, A. Piancastelli, Y. Bykov, S. Egorov, and A. Eremeev: Microwave sintering of Yb:YAG transparent laser ceramics. Opt. Mater. 35, 761 (2013).
S.S. Balabanov, E.M. Gavrishchuk, A.M. Kut’in, and D.A. Permin: Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis of Y2O3 powders from Y(NO3)3x(CH3COO)3(1−x)·nH2O. Inorg. Mater. 47, 484 (2011).
I.M. Robertson and G.B. Schaffer: Some effects of particle size on the sintering of titanium and a master sintering curve model. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 40, 1968 (2009).
Acknowledgments
This research was supported in part by Russian Science Foundation, Grant No. 17-19-01530 (ultra-rapid microwave sintering of ceramic materials and powder metals), and Russian Foundation for Basic Research, Grant No. 18-29-11045 (the development of an additive manufacturing method based on ultra-rapid millimeter-wave sintering).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rybakov, K.I., Egorov, S.V., Eremeev, A.G. et al. Ultra-rapid microwave sintering employing thermal instability and resonant absorption. Journal of Materials Research 34, 2620–2634 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2019.232
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2019.232