Abstract
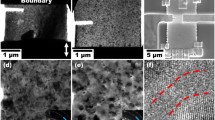
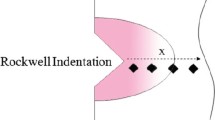
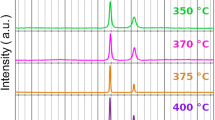
The article focuses on the fatigue performance after a moderate heat treatment of nanocrystalline (nc) nickel, which leads to the formation of a bimodal microstructure in the nc to ultrafine grained (ufg) regime. Electrodeposition was used to produce nc macro nickel samples with grain sizes of about 40 nm for mechanical testing. The thermal stability of the material as well as the influence on the mechanical properties and the fatigue crack propagation behavior was investigated. The results of tensile and fatigue tests are discussed in respect to the chosen production method and boundary conditions. In this context, the influence of the bath additives used during the plating process was investigated and rated as the major challenge for a further improvement of the thermal stability and mechanical properties of the material. Finally, a co-deposition of nickel and metal oxides with enhanced thermal stability is presented.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
U. Erb: Electrodeposited nanocrystals: Synthesis, properties and industrial applications. Nanostruct. Mater. 6 (5–8), 533 (1995).
F. Ebrahimi, G. Bourne, M. Kelly, and T. Matthews: Mechanical properties of nanocrystalline nickel produced by electrodeposition. Nanostruct. Mater. 11 (3), 343 (1999).
M.A. Meyers, A. Mishra, and D.J. Benson: Mechanical properties of nanocrystalline materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 51, 427 (2006).
Y.F. Shen, W.Y. Xue, Y.D. Wang, Z.Y. Liu, and L. Zuo: Mechanical properties of nanocrystalline nickel films deposited by pulse plating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 202 (21), 5140 (2008).
B. Yang, H. Vehoff, and R. Pippan: Overview of the grain size effects on the mechanical and deformation behaviour of electrodeposited nanocrystalline nickel-from nanoindentation to high pressure torsion. Mater. Sci. Forum 633–634 (1), 85 (2010).
E.N. Hahn and M.A. Meyers: Grain-size dependent mechanical behavior of nanocrystalline metals. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 646, 101 (2015).
W. Johnson, J. Doherty, B. Kear, and A. Giamei: Confirmation of sulfur embrittlement in nickel alloys. Scr. Metall. 8, 971–974 (1974).
C. Briant: Grain boundary segregation of sulfur in iron. Acta Metall. 33, 1241–1246 (1985).
Á. Cziráki, I. Gerőcs, E. Tóth-Kádár, and I. Bakonyi: TEM and XRD study of the microstructure of nanocrystalline Ni and Cu prepared by severe plastic deformation and electrodeposition. Nanostruct. Mater. 6 (5–8), 547 (1995).
T. Leitner, A. Hohenwarter, and R. Pippan: Revisiting fatigue crack growth in various grain size regimes of Ni. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 646, 294 (2015).
L. Oniciu and L. Mureşan: Some fundamental aspects of levelling and brightening in metal electrodeposition. J. Appl. Electrochem. 21 (7), 565 (1991).
T. Osaka: Effects of saccharin and thiourea on sulfur inclusion and coercivity of electroplated soft magnetic CoNiFe film. J. Electrochem. Soc. 146 (9), 3295 (1999).
U. Klement, U. Erb, A. El-Sherik, and K. Aust: Thermal stability of nanocrystalline Ni. Sci. Eng. A 203, 177–186 (1995).
V.L. Tellkamp, E.J. Lavernia, and A. Melmed: Mechanical behavior and microstructure of a thermally stable bulk nanostructured Al alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 32 (9), 2335 (2001).
H. Hosseini-Toudeshky and M. Jamalian: Simulation of micromechanical damage to obtain mechanical properties of bimodal Al using XFEM. Mech. Mater. 89, 229–240 (2015).
H.W. Höppel, M. Korn, R. Lapovok, and H. Mughrabi: Bimodal grain size distributions in UFG materials produced by SPD: Their evolution and effect on mechanical properties. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 240, 12147 (2010).
Y.G. Liu, X.D. Mi, and S.F. Tian: Effect of grain size on the fracture toughness of bimodal nanocrystalline materials. Adv. Mater. Res. 936, 400 (2014).
S. Kikuchi, Y. Hayami, T. Ishiguri, B. Guennec, A. Ueno, M. Ota, and K. Ameyama: Effect of bimodal grain size distribution on fatigue properties of Ti–6Al–4V alloy with harmonic structure under four-point bending. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 687, 269–275 (2017).
M. Ames, J. Markmann, R. Karos, A. Michels, and A. Tschöpe: Unraveling the nature of room temperature grain growth in nanocrystalline materials. Acta Mater. 56, 4255–4266 (2008).
D. Molodov and L. Shvindlerman: Impact of grain boundary character on grain boundary kinetics. Z. Metallkd. 94, 1117–1126 (2003).
R. Kirchheim: Reducing grain boundary, dislocation line and vacancy formation energies by solute segregation. I. Theoretical background. Acta Mater. 55 (15), 5129 (2007).
P. Choi, M. Da Silva, U. Klement, T. Al-Kassab, and R. Kirchheim: Thermal stability of electrodeposited nanocrystalline Co–1.1 at.% P. Acta Mater. 53 (16), 4473 (2005).
B. Färber, E. Cadel, A. Menand, G. Schmitz, and R. Kirchheim: Phosphorus segregation in nanocrystalline Ni–3.6 at.% P alloy investigated with the tomographic atom probe (TAP). Acta Mater. 48 (3), 789 (2000).
F. Liu and R. Kirchheim: Nano-scale grain growth inhibited by reducing grain boundary energy through solute segregation. J. Cryst. Growth 264 (1–3), 385 (2004).
A. Wimmer, M. Smolka, W. Heinz, T. Detzel, W. Robl, C. Motz, V. Eyert, E. Wimmer, F. Jahnel, R. Treichler, and G. Dehm: Temperature dependent transition of intragranular plastic to intergranular brittle failure in electrodeposited Cu micro-tensile samples. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 618, 398 (2014).
C.E. Krill, III, H. Ehrhardt, and R. Birringer: Thermodynamic stabilization of nanocrystallinity. Z. Metallkd. 96, 1134–1141 (2005).
A. Rollett, F. Humphreys, G. Rohrer, and M. Hatherly: Recrystallization and related annealing phenomena, 2nd Edition. (Elsevier, Oxford, United Kingdom, 2004).
C.C. Koch, R.O. Scattergood, M. Saber, and H. Kotan: High temperature stabilization of nanocrystalline grain size: Thermodynamic versus kinetic strategies. J. Mater. Res. 28, 1785–1791 (2013).
D. Morris and M. Morris: Microstructure and strength of nanocrystalline copper alloy prepared by mechanical alloying. Acta Metall. Mater. 39, 1763–1770 (1991).
A. Bachmaier, A. Hohenwarter, and R. Pippan: New procedure to generate stable nanocrystallites by severe plastic deformation. Scr. Mater. 61, 1016–1019 (2009).
A. Bachmaier and R. Pippan: Generation of metallic nanocomposites by severe plastic deformation. Int. Mater. Rev. 58 (1), 41 (2013).
J. Cahn: The impurity-drag effect in grain boundary motion. Acta Metall. 10, 789–798 (1962).
K. Lücke and H. Stüwe: On the theory of impurity controlled grain boundary motion. Acta Metall. 19, 1087–1099 (1971).
R. Choo, J. Toguri, A. El-Sherik, and U. Erb: Mass transfer and electrocrystallization analyses of nanocrystalline nickel production by pulse plating. J. Appl. Electrochem. 25, 384–403 (1995).
H. Natter and M. Schmelzer: Nanocrystalline nickel and nickel–copper alloys: Synthesis, characterization, and thermal stability. J. Mater. 13, 1186–1197 (1998).
H. Natter and R. Hempelmann: Nanocrystalline copper by pulsed electrodeposition: The effects of organic additives, bath temperature, and pH. J. Phys. Chem. 100 (50), 19525 (1996).
U. Klement, C. Oikonomou, and R. Chulist: Influence of additives on texture development of submicro-and nanocrystalline nickel. Mater. Sci. Forum 702, 928–931 (2012).
M. Stangl, J. Acker, S. Oswald, M. Uhlemann, T. Gemming, S. Baunack, and K. Wetzig: Incorporation of sulfur, chlorine, and carbon into electroplated Cu thin films. Microelectron. Eng. 84 (1), 54 (2007).
L. Oniciu and L. Mureşan: Some fundamental aspects of levelling and brightening in metal electrodeposition. J. Appl. Electrochem. 21, 565–574 (1991).
G. Hibbard, K. Aust, G. Palumbo, and U. Erb: Thermal stability of electrodeposited nanocrystalline cobalt. Scr. Mater. 44 (3) (2001).
T. Qian, I. Karaman, and M. Marx: Mechanical properties of nanocrystalline and ultrafine-grained nickel with bimodal microstructure. Adv. Eng. Mater. 16 (11), 1323 (2014).
G. Aronson and R. Ritchie: Optimization of the electrical potential technique for crack growth monitoring in compact test pieces using finite element analysis. J. Test. Eval. 7, 208–215 (1979).
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors would like to thank the DFG for their financial support of the project MA 3322/3-2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rathmann, D., Marx, M. & Motz, C. Crack propagation and mechanical properties of electrodeposited nickel with bimodal microstructures in the nanocrystalline and ultrafine grained regime. Journal of Materials Research 32, 4573–4582 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.353
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.353