Abstract
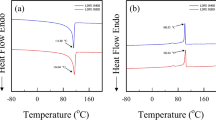
Asphalt bitumens are complex colloidal systems of high viscosity and complex behavior, which are mainly used for making asphalt concrete for road surfaces. Thermal and rheological characterizations are needed to understand their complex behavior, particularly at the processing stage. Prediction of properties at short and long observation times is usually performed through time-temperature superposition (TTS) models, which make use of some calculated shift factors. The influence of crystallization-like transformation processes on the validity of these shift factors is investigated here by temperature-modulated differential scanning calorimetry (TMDSC). Four asphalt emulsions are considered in this work, each one with a specific transformation behavior. The structure-properties relationships are explained on the basis of the transformation profiles and rheological data.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. Gonzalez, J. Pena, M. Munoz, A. Santamaria, A. Perez-Lepe, F. Martinez-Boza, and C. Gallegos: Rheological techniques as a tool to analyze polymer-bitumen interactions: Bitumen modified with polyethylene and polyethylene-based blends. Energy Fuels 16 (5), 1256 (2002).
O. Gonzalez, M. Munoz, A. Santamaria, M. Garcia-Morales, F. Navarro, and P. Partal: Rheology and stability of bitumen/EVA blends. Eur. Polym. J. 40 (10), 2365 (2004).
X. Lu and U. Isacsson: Rheological characterization of styrene-butadiene-styrene copolymer-modified bitumens. Constr. Build. Mater. 11 (1), 23 (1997).
H. Kim, S. Lee, and S.N. Amirkhanian: Effects of warm mix asphalt additives on performance properties of polymer-modified asphalt binders. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 37 (1), 17 (2010).
H. Behbahani, H. Ziari, H. Fazaeli, and J. Rahmani: Comparison of performance of asphalt mixtures containing polymer modifiers. J. Test. Eval. 37 (5), 431 (2009).
S. Kim, G.A. Sholar, T. Byron, and J. Kim: Performance of polymer-modified asphalt mixture with reclaimed asphalt pavement. Transp. Res. Rec. 2126, 109 (2009).
T. Yu, C. Li, and S. Wu: Performance of polymer-modified asphalt bridge expansion joints in low-temperature regions. J. Perform. Constr. Facil 23 (4), 227 (2009).
C. Fang, T. Li, Z. Zhang, and D. Jing: Modification of asphalt by packaging waste-polyethylene. Polymer Composites 29 (5), 500 (2008).
Y. Tasdemir and E. Agar: Investigation of the low-temperature performances of polymer and fiber modified asphalt mixtures RID A-6382-2009. Indian J. Eng. Mater. Sci. 14 (2), 151 (2007).
S. Tayfur, H. Ozen, and A. Aksoy: Investigation of rutting performance of asphalt mixtures containing polymer modifiers. Constr. Build. Mater. 21 (2), 328 (2007).
H.L. Von Quintus, J. Mallela, and M. Buncher: Quantification of effect of polymer-modified asphalt on flexible pavement performance. Transp. Res. Rec. 2001, 141 (2007).
K. Stuart, W. Mogawer, and J. Youtcheff: Performance of modified asphalt binders with identical high-temperature performance grades but varied polymer chemistries. Bituminous Binders 1875, 33 (2004).
G. Airey: Styrene butadiene styrene polymer modification of road bitumens. J. Mater. Sci. 39 (3), 951 (2004).
B. Sengoz and G. Isikyakar: Analysis of styrene-butadiene-styrene polymer-modified bitumen using fluorescent microscopy and conventional test methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 150 (2), 424 (2008).
A. Ait-Kadi, B. Brahimi, and M. Bousmina: Polymer blends for enhanced asphalt binders. Polym. Eng. Sci. 36 (12), 1724 (1996).
U. Isacsson and X. Lu: Characterization of bitumens modified with SEBS, EVA and EBA polymers. J. Mater. Sci. 34 (15), 3737 (1999).
J.W.H. Oliver: Changes in the chemical composition of Australian bitumens. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 10 (3), 569 (2009).
J.G. Speight: The Chemistry and Technology of Petroleum, 4th ed. (CRC Press/Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, 2007).
A. Kolbanov and A. Rudenski: Influence of solid paraffins on structural and rheological properties of bitumens. Colloid J. 30 (4), 390 (1968).
J. Planche, D. Martin, C. Rey, L. Champion, and J. Gerard: Evaluation of the Physical Hardening of Bitumens in the Cold: Another Method for Measuring their Paraffin Content (A A Balkema, BR Rotterdam, Netherlands, 1997).
D. Lesueur, J. Gerard, P. Claudy, J. Letoffe, J. Planche, and D. Martin: A structure-related model to describe asphalt linear viscoelasticity. J. Rheol. 40 (5), 813 (1996).
M. Reading, D. Elliott, and V. Hill: A new approach to the calorimetric investigation of physical and chemical-transitions. J. Therm. Anal. 40 (3), 949 (1993).
B. Wunderlich, Y. Jin, and A. Boller: Mathematical description of differential scanning calorimetry based on periodic temperature modulation. Thermochim. Acta 238, 277 (1994).
M. Garcia-Morales, P. Partal, F. Navarro, and C. Gallegos: Effect of waste polymer addition on the rheology of modified bitumen. Fuel 85 (7–8), 936 (2006).
P. Claudy, J. Letoffe, G.N. King, and J. Planche: Characterization of road bitumen by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Thermo optical analysis (TOA). Correlation between physical properties and DSC results. Correlation entre proprietes physiques et resultats ACD. Bulletin de Liaison des Laboratoires des Ponts et Chaussees (177), 45 (1992).
P. Claudy, J.M. Letoffe, G.N. King, and J.P. Plancke: Characterization asphalts cements by thermomicroscopy differential scanning calorimetry: Correlation classic physical properties. Fuel Sci. Technol. Int. 10 (4–6), 735 (1992).
D. Lesueur: The colloidal structure of bitumen: Consequences on the rheology and on the mechanisms of bitumen modification. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 145 (1–2), 42 (2009).
H. Leaderman: Elastic and Creep Properties of Filamentous Materials (Textile Foundation, Washington District of Columbia, 1943).
J.D. Ferry: Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers (Wiley, New York, NY, 1980).
K.G.N.C. Alwis and C.J. Burgoyne: Time-temperature superposition determines stress-rupture aramid fibers. Appl. Compos. Mater. 13 (4), 249 (2006).
R.G. Arridge: Mechanics of Polymers (Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1975).
V.S. Chevali, D.R. Dean, and G.M. Janowski: Flexural creep behavior of discontinuous thermoplastic composites: Nonlinear viscoelastic modeling and time–temperature–stress superposition. Composites Part A 40 (6–7), 870 (2009).
J.D. Menczel and R.B. Prime: Thermal Analysis of Polymers: Fundamentals and Applications (John Wiley, Hoboken, NJ, 2009).
V.M. Gurp and J. Palmen: Time-temperature superposition of polymer blends. Rheology Bulletin 67 (1), 5 (1998).
Acknowledgment
This work was partially funded by the Spanish Ministerio de Educacion y Ciencia MTM2008-00166 and MTM2011-22392.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
López-Paz, J., Gracia-Fernández, C., Gómez-Barreiro, S. et al. Study of bitumen crystallization by temperature-modulated differential scanning calorimetry and rheology. Journal of Materials Research 27, 1410–1416 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.73
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.73