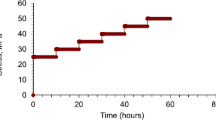
Abstract
Conventional creep testing takes a long time to obtain stress-rupture data for aramid fibres at the low stress levels likely to be used in practical applications. However, the rate of creep of aramid can be accelerated by a thermally activated process to obtain the failure of fibres within a few hours. It is possible to obtain creep curves at different temperature levels which can be shifted along the time axis to generate a single curve know as a master curve, from which stress-rupture data can be obtained. This technique is known as the time-temperature superposition principle and will be applied to Kevlar 49 yarns. Important questions relating to the techniques needed to obtain smooth master curves will be discussed, as will the validity the resulting curves and the corresponding stress-rupture lifetime.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guimaraes, G.B.: Parallel-lay aramid ropes for use in structural engineering, PhD thesis submitted to the University of London (1988)
Ferry, J.D.: Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers. Wiley (1970)
Markovitz, H.: Superposition in rheology. J. Polym. Sci., Polymer Symposium Series 50, 431–456, (1975)
Leaderman, H.: Elastic and Creep Properties of Filamentous Materials. Textile Foundation, Washington District of Columbia (1943)
Tobolsky, A.V., Andrews, R.D.: Systems manifesting superposed elastic and viscous behavior. J. Chem. Phys. 13, 3–27 (1945)
Brinson, H.F., Morris, D.H., Yeow, Y.T.: A new experimental method for the accelerated characterisation and prediction of the failure of polymer-based composites laminates, 6th International Conference for Experimental Stress Analysis, Munich, West Germany, Sept. (1978)
Griffith, W.I.: The accelerated characterisation of viscoelastic composite materials, PhD thesis submitted to the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University (1980)
Dutta, P.K., Hui, D.: Creep rupture of a GFRP composite at elevated temperatures. Composites and Structures 76, 153–161 (2000)
Marsimov, R.D., Plume, E.: Predicting the creep of unidirectional reinforced plastics with thermorheologically simple structural components. Mech. Compos. Mater. 18(6), 737–744 (1982)
Marsimov, R.D.: Prediction of the long-term resistance of polymer composites. Mech. Compos. Mater. 20(3), 376–388 (1984)
Jeon, H.Y., Kim, S.H., Yoo, H.K.: Assessment of long-term performances of polyester geogrids by accelerated creep test. Polym. Test. 21, 489–495 (2002)
Povolo, F.: Scaling relationships in a constitutive equation with one structure variable. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 4, 619–623 (1985)
Povolo, F., Fontelos, M.: Time-temperature superposition principle and scaling behaviour. J. Mater. Sci. 22, 1530–1534 (1987)
Povolo, F., Hermida, E.B.: Analysis of the master curve for the viscoelastic behaviour of polymers. Mech. Mater. 12, 35–46 (1991)
Hermida, E.B., Povolo, F.: Analytical–numerical procedure to determine if a set of experimental curves can be superimposed to form a master curve. Polym. J. 26(9), 981–992 (1994)
Brinson, L.C., Gates, T.S.: Effects of physical aging on long term creep of polymers and polymer matrix composites. Int. J. Solids Struct. 32(6/7), 827–846 (1995)
Wortmann, F.J., Schulz, K.V.: Investigations on the thermorheological simplicity of polypropylene fibres in the α-transition range. Polymer 36(8), 1611–1615 (1995)
Tamuzs, V., Maksimovs, R., Modniks, J.: Long-term creep of hybrid FRP bars. Burgoyne, C.J. (ed.) Fibre Reinforced Plastics for Reinforced Concrete Structures (FRPRCS-5), Cambridge, UK, pp. 527–534 (2001)
Arridge, R.G.C.: Mechanics of Polymers. Oxford University Press, London (1975)
Alwis, K.G.N.C.: Accelerated testing for long-term stress-rupture behaviour of aramid fibres. Thesis submitted to the University of Cambridge (2003)
Glaser, R.E., Moore, R.L., Chiao, T.T.: Life estimation of aramid/epoxy composites under sustained tension. Compos. Technol. Rev. 6(1) (1984)
Wu, H.F.: Lifetime statistics for single Kevlar 49 aramid filaments in creep-rupture at elevated temperatures. Thesis submitted to the Cornell University (1987)
Wagner, H.D., Phoenix, S.L.: A study of statistical variability in the strength of single aramid filaments. J. Compos. Mater. 18, 312–338 (1984)
Ericksen, R.H.: Creep of aromatic polyamide fibres. Polymer 26, 733–746 May (1985)
Alwis, K.G.N.C., Burgoyne, C.J.: Statistical lifetime prediction for aramid fibres. J. Compos. Constr. 9(2), 106–116, March/April (2005)
Alwis, K.G.N.C., Burgoyne, C.J.: Stepped isothermal testing of aramid fibres to determine stress-rupture lifetime. In preparation (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alwis, K.G.N.C., Burgoyne, C.J. Time-Temperature Superposition to Determine the Stress-Rupture of Aramid Fibres. Appl Compos Mater 13, 249–264 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-006-9017-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-006-9017-8