Abstract
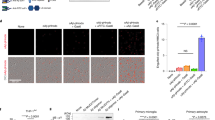
Inhibition of nuclear factor (NF)-κB has emerged as an important strategy for design of anti-inflammatory therapies. In neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s disease, inflammatory reactions mediated by glial cells are believed to promote disease progression. Here, we report that uptake of a double-stranded oligonucleotide NF-κB decoy in rat primary glial cells is clearly facilitated by noncovalent binding to a cell-penetrating peptide, transportan 10, via a complementary peptide nucleic acid (PNA) sequence. Fluorescently labeled oligonucleotide decoy was detected in the cells within 1 h only when cells were incubated with the decoy in the presence of cell-penetrating peptide. Cellular delivery of the decoy also inhibited effects induced by a neurotoxic fragment of the Alzheimer β amyloid peptide in the presence of the inflammatory cytokine interleukin (IL) 1β. Pretreatment of the cells with the complex formed by the decoy and the cell-penetrating peptide-PNA resulted in 80% and 50% inhibition of the NF-κB binding activity and IL-6 mRNA expression, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aisen P. S. (2002) The potential of anti-inflammatory drugs for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 1, 279–284.
Akama K. T., Albanese C., Pestell R. G., and Van Eldik L. J. (1998) Amyloid β-peptide stimulates nitric oxide production in astrocytes through an NFκB-dependent mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 95, 5795–5800.
Akiyama H., Barger S., Barnum S., et al. (2000) Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 21, 383–421.
Araujo D. M. and Cotman C. W. (1992) Beta-amyloid stimulates glial cells in vitro to produce growth factors that accumulate in senile plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 569, 141–145.
Bales K. R., Du Y., Dodel R. C., Yan G. M., Hamilton-Byrd E., and Paul S. M. (1998) The NF-κB/Rel family of proteins mediates Aβ-induced neurotoxicity and glial activation. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 57, 63–72.
Barger S. W., Horster D., Furukawa K., Goodman Y., Krieglstein J., and Mattson M. P. (1995) Tumor necrosis factors α and β protect neurons against amyloid β peptide toxicity: evidence for involvement of a κB-binding factor and attenuation of peroxide and Ca2+ accumulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 92, 9328–9332.
Beard C. M., Kokmen E., Sigler C., Smith G. E., Petterson T., and O’Brien P. C. (1996) Cause of death in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Epidemiol. 6, 195–200.
Breitner J. C., Welsh K. A., Helms M. J., et al. (1995) Delayed onset of Alzheimer’s disease with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory and histamine H2 blocking drugs. Neurobiol. Aging 16, 523–530.
Campbell I. L., Abraham C. R., Masliah E., et al. (1993) Neurologic disease induced in transgenic mice by cerebral overexpression of interleukin 6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 90, 10,061–10,065.
Combs C. K., Karlo J. C., Kao S. C., and Landreth G. E. (2001) β-Amyloid stimulation of microglia and monocytes results in TNFα-dependent expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and neuronal apoptosis. J. Neurosci. 21, 1179–1188.
D’Acquisto F., May M. J., and Ghosh S. (2002) Inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB): An emerging theme in anti-inflammatory therapies. Mol. Interv. 2, 22–35.
Del Bo R., Angeretti N., Lucca E., De Simoni M. G., and Forloni G. (1995) Reciprocal control of inflammatory cytokines, IL-1 and IL-6, and β-amyloid production in cultures. Neurosci. Lett. 188, 70–74.
Drin G., Cottin S., Blanc E., Rees A. R., and Temsamani J. (2003) Studies on the internalization mechanism of cationic cell-penetrating peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 31,192–31,201.
Eriksson G., Peterson A., Iverfeldt K., and Walum E. (1995) Sodium-dependent glutamate uptake as an activator of oxidative metabolism in primary astrocyte cultures from newborn rat. Glia 15, 152–156.
Fisher L., Soomets U., Cortes Toro V., et al. (2004) Cellular delivery of a double-stranded oligonucleotide NFκB decoy by hybridization to complementary PNA linked to a cell-penetrating peptide. Gene Ther. 11, 1264–1272.
Forloni G., Demicheli F., Giorgi S., Bendotti C., and Angeretti N. (1992) Expression of amyloid precursor protein mRNAs in endothelial, neuronal and glial cells: modulation by interleukin-1. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 16, 128–134.
Fujihara S. M., Cleaveland J-S., Grosmmaire L. S., et al. (2000) A D-amino acid peptide inhibitor of NF-κB nuclear localization is efficacious in models of inflammatory disease. J. Immunol. 165, 1004–1012.
Gadient R. A. and Otten U. H. (1997) Interleukin-6 (IL-6)—a molecule with both beneficial and destructive potentials. Prog. Neurobiol. 52, 379–390.
Goldgaber D., Harris H. W., Hla T., et al. (1989) Interleukin 1 regulates synthesis of amyloid β-protein precursor mRNA in human endothelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 86, 7606–7610.
Grilli M., Ribola M., Alberici A., Valerio A., Memo M., and Spano P. (1995) Identification and characterization of a κB/Rel binding site in the regulatory region of the amyloid precursor protein gene. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 26,774–26,777.
Guo Q., Robinson N., and Mattson M. P. (1998) Secreted β-amyloid precursor protein counteracts the proapoptotic action of mutant presenilin-1 by activation of NF-κB and stabilization of calcium homeostasis. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 12,341–12,351.
Holmlund L., Cortes Toro V., and Iverfeldt K. (2002) Additive effects of amyloid β fragment and interleukin-1β on interleukin-6 secretion in rat primary glial cultures. Int. J. Mol. Med. 10, 245–250.
Huell M., Strauss S., Volk B., Berger M., and Bauer J. (1995) Interleukin-6 is present in early stages of plaque formation and is restricted to the brains of Alzheimer’s disease patients. Acta Neuropathol. (Berl) 89, 544–551.
Hull M., Fiebich B. L., Lieb K., et al. (1996) Interleukin-6-associated inflammatory processes in Alzheimer’s disease: new therapeutic options. Neurobiol. Aging 17, 795–800.
Hungness E. S., Luo G. J., Pritts T. A., et al. (2002) Transcription factors C/EBP-β and -δ regulate IL-6 production in IL-1β-stimulated human enterocytes. J. Cell. Physiol. 192, 64–70.
in t’ Veld B. A., Ruitenberg A., Hofman A., et al. (2001) Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 345, 1515–1521.
Kaltschmidt B., Uherek M., Volk B., Baeuerle P. A., and Kaltschmidt C. (1997) Transcription factor NF-κB is activated in primary neurons by amyloid β peptides and in neurons surrounding early plaques from patients with Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 94, 2642–2647.
Khaled A. R., Butfiloski E. J., Sobel E. S., and Schiffenbauer J. (1998) Use of phosphorothioate-modified oligodeoxynucleotides to inhibit NF-κB expression and lymphocyte function. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 86, 170–179.
Libermann T. A. and Baltimore D. (1990) Activation of interleukin-6 gene expression through the NF-κB transcription factor. Mol. Cell Biol. 10, 2327–2334.
Lin Y. Z., Zao S. Y., Veach R. A., Togerson T. R., and Hawiger J. (1995) Inhibition of nuclear translocation of transcription factor NF-κB by a synthetic peptide containing a cell membrane-permeable motif and nuclear localization sequence. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 14,255–14,258.
Lindgren M. E., Hällbrink M. M., Elmquist A. M., and Langel Ü. (2004) Passage of cell-penetrating peptides across a human epithelial cell layer in vitro. Biochem. J. 377, 69–76.
May M. J., D’Acquisto F., Madge L. A., Glockner J., Pober J. S., and Ghosh S. (2000) Selective inhibition of NF-κB activation by a peptide that blocks the interaction of NEMO with the IκB kinase complex. Science 289, 1550–1554.
Meda L., Cassatella M. A., Szendrei G. I., et al. (1995). Activation of microglial cells by beta-amyloid protein and interferon-gamma. Nature 374, 647–750.
Miyazawa K., Mori A., Yamamoto K., and Okudaira H. (1998) Transcriptional roles of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-β, nuclear factor-κB, and C-promoter binding factor 1 in interleukin (IL)-1β-induced IL-6 synthesis by human rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 7620–7627.
Moerman A. M., Mao X., Lucas M. M., and Barger S. W. (1999) Characterization of a neuronal κB-binding factor distinct from NF-κB. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 67, 303–315.
Mrak R. E., Sheng J. G., and Griffin W. S. (1995) Glial cytokines in Alzheimer’s disease: review and pathogenic implications. Hum. Pathol. 26, 816–823.
Nekhotiaeva N., Elmquist A., Rajarao G. K., Hällbrink M., Langel Ü., and Good L. (2004) Cell entry and antimicrobial properties of eukaryotic cell-penetrating peptides. FASE B J. 18, 394–396.
O’Neill L. A. and Kaltschmidt C. (1997) NF-κB: a crucial transcription factor for glial and neuronal cell function. Trends Neurosci. 20, 252–258.
Padari K., Säälik P., Hansen M., et al. (2005) Cell transduction pathways of transportans. Bioconjugate Chem. 16, 1399–1410.
Perry V. H., Newman T. A., and Cunningham C. (2003) The impact of systemic infection on the progression of neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 4, 103–112.
Quintanilla R. A., Orellana D. I., Gonzalez-Billault C., and Maccioni R. B. (2004) Interleukin-6 induces Alzheimer-type phosphorylation of tau protein by deregulating the cdk5/p35 pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 295, 245–257.
Richard J. P., Melikov K., Vives E., et al. (2003) Cell-penetrating peptides. A reevaluation of the mechanism of cellular uptake. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 585–590.
Rogers J., Kirby L. C., Hempelman S. R., et al. (1993) Clinical trial of indomethacin in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 43, 1609–1611.
Saar K., Lindgren M., Hansen M., et al. (2005) Cell-penetrating peptides: A comparative membrane toxicity study. Anal. Biochem. 345, 55–65.
Schmedtje J. F., Jr., Ji Y. S., Liu W. L., DuBois R. N., and Runge M. S. (1997) Hypoxia induces cyclooxygenase-2 via the NF-κB p65 transcription factor in human vascular endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 601–608.
Sparacio S. M., Zhang Y., Vilcek J., and Benveniste E. N. (1992) Cytokine regulation of interleukin-6 gene expression in astrocytes involves activation of an NF-κB-like nuclear protein. J. Neuroimmunol. 39, 231–242.
Tomita N., Morishita R., Tomita S., et al. (1998) Transcription factor decoy for nuclear factor-κB inhibits tumor necrosis factor-α-induced expression of inter leukin-6 and intracellular adhesion molecule-1 in endothelial cells. J. Hypertens. 16, 993–1000.
Tomita N., Morishita R., Tomita S., et al. (2000) Transcription factor decoy for NFκB inhibits TNF-α-induced cytokine and adhesion molecule expression in vivo. Gene Ther. 7, 1326–1332.
Zorko M. and Langel Ü. (2005) Cell-penetrating peptides: mechanism and kinetics of cargo delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 57, 529–545.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fisher, L., Samuelsson, M., Jiang, Y. et al. Targeting cytokine expression in glial cells by cellular delivery of an NF-κB decoy. J Mol Neurosci 31, 209–219 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:31:03:209
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:31:03:209