Abstract
This paper reviews recent advances and current debates in modeling the solar cycle as a hydromagnetic dynamo process. Emphasis is placed on (relatively) simple dynamo models that are nonetheless detailed enough to be comparable to solar cycle observations. After a brief overview of the dynamo problem and of key observational constraints, we begin by reviewing the various magnetic field regeneration mechanisms that have been proposed in the solar context. We move on to a presentation and critical discussion of extant solar cycle models based on these mechanisms. We then turn to the origin and consequences of fluctuations in these models, including amplitude and parity modulation, chaotic behavior, intermittency, and predictability. The paper concludes with a discussion of our current state of ignorance regarding various key questions relating to the explanatory framework offered by dynamo models of the solar cycle.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
1.1 Scope of review
The cyclic regeneration of the Sun’s large-scale magnetic field is at the root of all phenomena collectively known as “solar activity”. A near-consensus now exists to the effect that this magnetic cycle is to be ascribed to the inductive action of fluid motions pervading the solar interior. However, at this writing nothing resembling consensus exists regarding the detailed nature and relative importance of various possible inductive flow contributions.
My assigned task, to review “dynamo models of the solar cycle”, is daunting. I will therefore interpret this task as narrowly as I can get away with. This review will not discuss in any detail solar magnetic field observations, the physics of magnetic flux tubes and ropes, the generation of small-scale magnetic field in the Sun’s near-surface layers, hydromagnetic oscillator models of the solar cycle, or magnetic field generation in stars other than the Sun. Most of these topics are all worthy of full-length reviews, and do have a lot to bear on “dynamo models of the solar cycle”, but a line needs to be drawn somewhere. With the exception of recent cycle prediction schemes based explicitly on dynamo models, I also chose to exclude from consideration the voluminous literature dealing with prediction of sunspot cycle amplitudes, including the related literature focusing exclusively on the mathematical modelling of the sunspot number time series, in manner largely or even sometimes entirely decoupled from the underlying physical mechanisms of magnetic field generation.
This review thus focuses on the cyclic regeneration of the large-scale solar magnetic field through the inductive action of fluid flows, as described by various approximations and simplifications of the partial differential equations of magnetohydrodynamics. Most current dynamo models of the solar cycle rely heavily on numerical solutions of these equations, and this computational emphasis is reflected throughout the following pages. Many of the mathematical and physical intricacies associated with the generation of magnetic fields in electrically conducting astrophysical fluids are well covered in a few recent reviews (see Hoyng, 2003; Ossendrijver, 2003), and so will not be addressed in detail in what follows. The focus is on models of the solar cycle, seeking primarily to describe the observed spatio-temporal variations of the Sun’s large-scale magnetic field.
1.2 What is a “model”?
The review’s very title demands an explanation of what is to be understood by “model”. A model is a theoretical construct used as thinking aid in the study of some physical system too complex to be understood by direct inferences from observed data. A model is usually designed with some specific scientific questions in mind, and asking different questions about a given physical system will, in all legitimacy, lead to distinct model designs. A well-designed model should be as complex as it needs to be to answer the questions having motivated its inception, but no more than that. Throwing everything into a model — usually in the name of “physical realism” — is likely to produce results as complicated as the data coming from the original physical system under study. Such model results are doubly damned, as they are usually as opaque as the original physical data, and, in addition, are not even real-world data!
Nearly all of the solar dynamo models discussed in this review rely on severe simplifications of the set of equations known to govern the dynamics of the Sun’s turbulent, magnetized fluid interior. Yet all of them are bona fide models, as defined here.
1.3 A brief historical survey
While regular observations of sunspots go back to the early seventeenth century, and discovery of the sunspot cycle to 1843, it is the landmark work of George Ellery Hale and collaborators that, in the opening decades of the twentieth century, demonstrated the magnetic nature of sunspots and of the solar activity cycle. In particular, Hale’s celebrated polarity laws established the existence of a well-organized toroidal magnetic flux system, residing somewhere in the solar interior, as the source of sunspots. In 1919, Larmor suggested the inductive action of fluid motions as one of a few possible explanations for the origin of this magnetic field, thus opening the path to contemporary solar cycle modelling. Larmor’s suggestion fitted nicely with Hale’s polarity laws, in that the inferred equatorial antisymmetry of the solar internal toroidal fields is precisely what one would expect from the shearing of a large-scale poloidal magnetic field by an axisymmetric and equatorially symmetric differential rotation pervading the solar interior. However, two decades later T.S. Cowling placed a major hurdle in Larmor’s path — so to speak — by demonstrating that even the most general purely axisymmetric flows could not, in themselves, sustain an axisymmetric magnetic field against Ohmic dissipation. This result became known as Cowling’s antidynamo theorem.
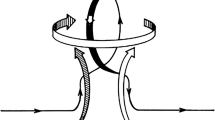
A way out of this quandary was only discovered in the mid-1950s, when E.N. Parker pointed out that the Coriolis force could impart a systematic cyclonic twist to rising turbulent fluid elements in the solar convection zone, and in doing so provide the break of axisymmetry needed to circumvent Cowling’s theorem (see Figure 1). This groundbreaking idea was put on firm quantitative footing by the subsequent development of mean-field electrodynamics, which rapidly became the theory of choice for solar dynamo modelling. By the late 1970s, concensus had almost emerged as to the fundamental nature of the solar dynamo, and the α-effect of mean-field electrodynamics was at the heart of it.
Serious trouble soon appeared on the horizon, however, and from no less than four distinct directions. First, it was realized that because of buoyancy effects, magnetic fields strong enough to produce sunspots could not be stored in the solar convection zone for sufficient lengths of time to ensure adequate amplification. Second, numerical simulations of turbulent thermallydriven convection in a thick rotating spherical shell produced magnetic field migration patterns that looked nothing like what is observed on the Sun. Third, and perhaps most decisive, the nascent field of helioseismology succeeded in providing the first determinations of the solar internal differential rotation, which turned out markedly different from those needed to produce solar-like dynamo solutions in the context of mean-field electrodynamics. Fourth, the ability of the α-effect and magnetic diffusivity to operate as assumed in mean-field electrodynamics was also called into question by theoretical calculations and numerical simulations.
It is fair to say that solar dynamo modelling has not yet recovered from this four-way punch, in that nothing remotely resembling concensus currently exists as to the mode of operation of the solar dynamo. As with all major scientific crises, this situation provided impetus not only to drastically redesign existing models based on mean-field electrodynamics, but also to explore new physical mechanisms for magnetic field generation, and resuscitate older potential mechanisms that had fallen by the wayside in the wake of the α-effect — perhaps most notably the so-called Babcock-Leighton mechanism, dating back to the early 1960s (see Figure 2). These post-helioseismic developments, beginning in the mid to late 1980s, are the primary focus of this review.
1.4 Sunspots and the butterfly diagram
Historically, next to cyclic polarity reversal the sunspot butterfly diagram has provided the most stringent observational constraints on solar dynamo models (see Figure 3). In addition to the obvious cyclic pattern, two features of the diagram are particularly noteworthy:
-
Sunspots are restricted to latitudinal bands some ≃ 30° wide, symmetric about the equator.
-
Sunspots emerge closer and closer to the equator in the course of a cycle, peaking in coverage at about ± 15° of latitude.
Sunspots appear when deep-seated toroidal flux ropes rise through the convective envelope and emerge at the photosphere. Assuming that they rise radially and are formed where the magnetic field is the strongest, the sunspot butterfly diagram can be interpreted as a spatio-temporal “map” of the Sun’s internal, large-scale toroidal magnetic field component. This interpretation is not unique, however, since the aforementioned assumptions may be questioned. In particular, we still lack even rudimentary understanding of the process through which the diffuse, large-scale solar magnetic field produces the concentrated toroidal flux ropes that will later, upon buoyant destabilisation, give rise to sunspots. This remains perhaps the most severe missing link between dynamo models and solar magnetic field observations. On the other hand, the stability and rise of toroidal flux ropes is now fairly well-understood (see, e.g., Fan, 2009, and references therein).
The sunspot “butterfly diagram”, showing the fractional coverage of sunspots as a function of solar latitude and time (courtesy of D. Hathaway, NASA/MSFC; see http://solarscience.msfc.nasa.gov/images/bfly.gif).
Magnetographic mapping of the Sun’s surface magnetic field (see Figure 4) have also revealed that the Sun’s poloidal magnetic component undergoes cyclic variations, changing polarities at times of sunspot maximum. Note in Figure 4 the poleward drift of the surface fields, away from sunspot latitudes. This pattern is believed to originate from the transport of magnetic flux released by the decay of sunspots at low latitudes (see Petrovay and Szakály, 1999, for an alternate explanation). The surface polar cap flux amounts to about 1022 Mx, while the total unsigned flux emerging in active regions in the course of a typical cycle adds up to a few 1025 Mx; this is usually taken to indicate that the solar internal magnetic field is dominated by its toroidal component.
Synoptic magnetogram of the radial component of the solar surface magnetic field. The low-latitude component is associated with sunspots. Note the polarity reversal of the high-latitude magnetic field, occurring approximately at time of sunspot maximum (courtesy of D. Hathaway, NASA/MSFC; see http://solarscience.msfc.nasa.gov/images/magbfly.jpg).
1.5 Organization of review
The remainder of this review is organized in five sections. In Section 2 the mathematical formulation of the solar dynamo problem is laid out in some detail, together with the various simplifications that are commonly used in modelling. Section 3 details various possible physical mechanisms of magnetic field generation. In Section 4, a selection of representative models relying on different such mechanisms are presented and critically discussed, with abundant references to the technical literature. Section 5 focuses on the origin of cycle amplitude fluctuations, again presenting some illustrative model results and reviewing recent literature on the topic. The concluding Section 6 offers a somewhat more personal discussion of current challenges and trends in solar dynamo modelling.
A great many review papers have been and continue to be written on dynamo models of the solar cycle, and the solar dynamo is discussed in most recent solar physics textbooks, notably Stix (2002), Foukal (2004), and Schrijver and Siscoe (2009). The series of review articles published in Proctor and Gilbert (1994) and Ferriz-Mas and Núñez (2003) are also essential reading for more in-depth reviews of some of the topics covered here. Among the most recent reviews, Petrovay (2000); Tobias (2002); Rüdiger and Arlt (2003); Usoskin and Mursula (2003); Ossendrijver (2003), and Brandenburg and Subramanian (2005) offer (in my opinion) particularly noteworthy alternate and/or complementary viewpoints to those expressed here.
2 Making a Solar Dynamo Model
2.1 Magnetized fluids and the MHD induction equation
In the interiors of the Sun and most stars, the collisional mean-free path of microscopic constituents is much shorter than competing plasma length scales, fluid motions are non-relativistic, and the plasma is electrically neutral and non-degenerate. Under these physical conditions, Ohm’s law holds, and so does Amp`ere’s law in its pre-Maxwellian form. Maxwell’s equations can then be combined into a single evolution equation for the magnetic field B, known as the magnetohydrodynamical (MHD) induction equation (see, e.g., Davidson, 2001):
where η = c2/4πσe is the magnetic diffusivity (σe being the electrical conductivity), in general only a function of depth for spherically symmetric solar/stellar structural models. Of course, the magnetic field is still subject to the divergence-free condition ∇ · B = 0, and an evolution equation for the flow field u must also be provided. This could be, e.g., the Navier.Stokes equations, augmented by a Lorentz force term:
where τ is the viscous stress tensor, and other symbols have their usual meaningFootnote 1. In the most general circumstances, Equations (1) and (2) must be complemented by suitable equations expressing conservation of mass and energy, as well as an equation of state. Appropriate initial and boundary conditions for all physical quantities involved then complete the specification of the problem. The resulting set of equations defines magnetohydrodynamics, quite literally the dynamics of magnetized fluids.
2.2 The dynamo problem
The first term on right hand side of Equation (1) represents the inductive action of the flow field, and it can act as a source term for B; the second term, on the other hand, describes the resistive dissipation of the current systems supporting the magnetic field, and is thus always a global sink for B. The relative importances of these two terms is measured by the magnetic Reynolds number Rm = μL/η, obtained by dimensional analysis of Equation (1). Here η, u, and L are “typical” numerical values for the magnetic diffusivity, flow speed, and length scale over which B varies significantly. The latter, in particular, is not easy to estimate a priori, as even laminar MHD flows have a nasty habit of generating their own magnetic length scales (usually ∝ Rm-1/2 at high Rm). Nonetheless, on length scales comparable to the sun itself, Rm is immense, and so is the usual viscous Reynolds number. This implies that energy dissipation will occur on length scales very much smaller than the solar radius.
The dynamo problem consists in finding/producing a (dynamically consistent) flow field u that has inductive properties capable of sustaining B against Ohmic dissipation. Ultimately, the amplification of B occurs by stretching of the pre-existing magnetic field. This is readily seen upon rewriting the inductive term in Equation (1) as
In itself, the first term on the right hand side of this expression can obviously lead to exponential amplification of the magnetic field, at a rate proportional to the local velocity gradient.
In the solar cycle context, the dynamo problem is reformulated towards identifying the circumstances under which the flow fields observed and/or inferred in the Sun can sustain the cyclic regeneration of the magnetic field associated with the observed solar cycle. This involves more than merely sustaining the field. A model of the solar dynamo should also reproduce
-
cyclic polarity reversals with a ∼ 10 yr half-period,
-
equatorward migration of the sunspot-generating deep toroidal field and its inferred strength,
-
poleward migration of the diffuse surface field,
-
observed phase lag between poloidal and toroidal components,
-
polar field strength,
-
observed antisymmetric parity,
-
predominantly negative (positive) magnetic helicity in the Northern (Southern) solar hemisphere.
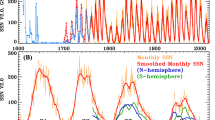
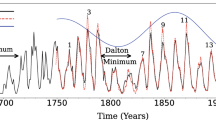
At the next level of “sophistication”, a solar dynamo model should also be able to exhibit amplitude fluctuations, and reproduce (at least qualitatively) the many empirical correlations found in the sunspot record. These include an anticorrelation between cycle duration and amplitude (Waldmeier Rule), alternation of higher-than-average and lower-than-average cycle amplitude (Gnevyshev-Ohl Rule), good phase locking, and occasional epochs of suppressed amplitude over many cycles (the so-called Grand Minima, of which the Maunder Minimum has become the archetype; more on this in Section 5 below). One should finally add to the list torsional oscillations in the convective envelope, with proper amplitude and phasing with respect to the magnetic cycle. This is a very tall order by any standard.
Because of the great disparity of time- and length scales involved, and the fact that the outer 30% in radius of the Sun are the seat of vigorous, thermally-driven turbulent convective fluid motions, the solar dynamo problem is very hard to tackle as a direct numerical simulation of the full set of MHD equations (but do see Section 4.9 below). Most solar dynamo modelling work has thus relied on simplification — usually drastic — of the MHD equations, as well as assumptions on the structure of the Sun’s magnetic field and internal flows.
2.3 Kinematic models
A first drastic simplification of the MHD system of equations consists in dropping Equation (2) altogether by specifying a priori the form of the flow field u. This kinematic regime remained until relatively recently the workhorse of solar dynamo modelling. Note that with u given, the MHD induction equation becomes truly linear in B. Moreover, helioseismology (Christensen-Dalsgaard, 2002) has now pinned down with good accuracy two important solar large-scale flow components, namely differential rotation throughout the interior, and meridional circulation in the outer half of the solar convection zone (for reviews, see Gizon, 2004; Howe, 2009). Given the low amplitude of observed torsional oscillations in the solar convective envelope, and the lack of significant cycle-related changes in the internal solar differential rotation inferred by helioseismology to this date, the kinematic approximation is perhaps not as bad a working assumption as one may have thought, at least for the differential rotation part of the mean flow u.
2.4 Axisymmetric formulation
The sunspot butterfly diagram, Hale’s polarity law, synoptic magnetograms, and the shape of the solar corona at and around solar activity minimum jointly suggest that, to a tolerably good first approximation, the large-scale solar magnetic field is axisymmetric about the Sun’s rotation axis, as well as antisymmetric about the equatorial plane. Under these circumstances it is convenient to express the large-scale field as the sum of a toroidal (i.e., longitudinal) component and a poloidal component (i.e., contained in meridional planes), the latter being expressed in terms of a toroidal vector potential. Working in spherical polar coordinates (r, θ, φ), one writes
Such a decomposition evidently satisfies the solenoidal constraint ∇ · B = 0, and substitution into the MHD induction equation produces two (coupled) evolution equations for A and B, the latter simply given by the φ-component of Equation (1), and the former, under the Coulomb gauge ∇ · A = 0, by
2.5 Boundary conditions and parity
The axisymmetric dynamo equations are to be solved in a meridional plane, i.e., Ri ≤ r ≤ R⊙ and 0 ≤ θ ≤ π, where the inner radial extent of the domain (Ri) need not necessarily extend all the way to r = 0. It is usually assumed that the deep radiative interior can be treated as a perfect conductor, so that Ri is chosen a bit deeper than the lowest extent of the region where dynamo action is taking place; the boundary condition at this depth is then simply A = 0, ∂(rB)/∂r = 0.
It is usually assumed that the Sun/star is surrounded by a vacuum, in which no electrical currents can flow, i.e., ∇ × B = 0; for an axisymmetric B expressed via Equation (4), this requires
It is therefore necessary to smoothly match solutions to Equations (1, 5) on solutions to Equations (6) at r/R⊙ = 1. Regularity of the solutions demands that A = 0 and B = 0 on the symmetry axis (θ = 0 and θ = π in a meridional plane). This completes the specification of the boundary conditions.
Formulated in this manner, the dynamo solution will spontaneously “pick” its own parity, i.e., its symmetry with respect to the equatorial plane. An alternative approach, popular because it can lead to significant savings in computing time, is to solve only in a meridional quadrant (0 ≤ θ ≤ π/2) and impose solution parity via the boundary condition at the equatorial plane (π/2):
3 Mechanisms of Magnetic Field Generation
The Sun’s poloidal magnetic component, as measured on photospheric magnetograms, flips polarity near sunspot cycle maximum, which (presumably) corresponds to the epoch of peak internal toroidal field T. The poloidal component P, in turn, peaks at time of sunspot minimum. The cyclic regeneration of the Sun’s full large-scale field can thus be thought of as a temporal sequence of the form
where the (+) and (-) refer to the signs of the poloidal and toroidal components, as established observationally. A full magnetic cycle then consists of two successive sunspot cycles. The dynamo problem can thus be broken into two sub-problems: generating a toroidal field from a pre-existing poloidal component, and a poloidal field from a pre-existing toroidal component. In the solar case, the former turns out to be easy, but the latter is not.
3.1 Poloidal to toroidal
Let us begin by expressing the (steady) large-scale flow field u as the sum of an axisymmetric azimuthal component (differential rotation), and an axisymmetric “poloidal” component up up (≡ ur(r, θ)êr + uθ(r, θ)êθ), i.e., a flow confined to meridional planes:
where \(\varpi = r\sin \theta and \Omega\) is the angular velocity (rad s-1). Substituting this expression into Equation (5) and into the φ-components of Equation (1) yields


Advection means bodily transport of B by the flow; globally, this neither creates nor destroys magnetic flux. Resistive decay, on the other hand, destroys magnetic flux and therefore acts as a sink of magnetic field. Diamagnetic transport can increase B locally, but again this is neither a source nor sink of magnetic flux. The compression/dilation term is a direct consequence of toroidal flux conservation in a flow moving across a density gradient. The shearing term in Equation (12), however, is a true source term, as it amounts to converting rotational kinetic energy into magnetic energy. This is the needed P → T production mechanism.
However, there is no comparable source term in Equation (11). No matter what the toroidal component does, A will inexorably decay. Going back to Equation (12), notice now that once A is gone, the shearing term vanishes, which means that B will in turn inexorably decay. This is the essence of Cowling’s theorem: An axisymmetric flow cannot sustain an axisymmetric magnetic field against resistive decayFootnote 2.
3.2 Toroidal to poloidal
In view of Cowling’s theorem, we have no choice but to look for some fundamentally non-axisymmetric process to provide an additional source term in Equation (11). It turns out that under solar interior conditions, there exist various mechanisms that can act as a source of poloidal field. In what follows we introduce and briefly describe the four classes of such mechanisms that appear most promising, but defer discussion of their implementation in dynamo models to Section 4, where illustrative solutions are also presented.
3.2.1 Turbulence and mean-field electrodynamics
The outer ∼ 30% of the Sun are in a state of thermally-driven turbulent convection. This turbulence is anisotropic because of the stratification imposed by gravity, and lacks reflectional symmetry due to the influence of the Coriolis force. Since we are primarily interested in the evolution of the largescale magnetic field (and perhaps also the large-scale flow) on time scales longer than the turbulent time scale, mean-field electrodynamics offers a tractable alternative to full-blown 3D turbulent MHD. The idea is to express the net flow and field as the sum of mean components, 〈u〉 and 〈B〉, and small-scale fluctuating components u′, B′. This is not a linearization procedure, in that we are not assuming that |u′|/|〈u〉| ≪ 1 or |B′|/|〈B〉| ≪ 1. In the context of the axisymmetric models to be described below, the averaging (“〈〉”) is most naturally interpreted as a longitudinal average, with the fluctuating flow and field components vanishing when so averaged, i.e., 〈u′〉 = 0 and 〈B′〉 = 0. The mean field 〈B〉 is then interpreted as the large-scale, axisymmetric magnetic field usually associated with the solar cycle. Upon this separation and averaging procedure, the MHD induction equation for the mean component becomes
which is identical to the original MHD induction Equation (1) except for the term 〈u′ × B′〉, which corresponds to a mean electromotive force ε induced by the fluctuating flow and field components. It appears here because, in general, the cross product u′ × B′ usually will not vanish upon averaging, even though u′ and B′ do so individually. Evidently, this procedure is meaningful if a separation of spatial and/or temporal scales exists between the (time-dependent) turbulent motions and associated small-scale magnetic fields on the one hand, and the (quasi-steady) large-scale axisymmetric flow and field on the other.
The reader versed in fluid dynamics will have recognized in the mean electromotive force the equivalent of Reynolds stresses appearing in mean-field versions of the Navier-Stokes equations, and will have anticipated that the next (crucial!) step is to express ε in terms of the mean field 〈B〉 in order to achieve closure. This is usually carried out by expressing ε as a truncated series expansion in 〈B〉 and its derivatives. Retaining the first two terms yields
where the colon indicates a tensorial inner product. The quantities α and β are in general pseudotensors, and specification of their components requires a turbulence model from which averages of velocity cross-correlations can be computed, which is no trivial task. We defer discussion of specific model formulations for these quantities to Section 4.2, but note the following:
-
Even if 〈B〉 is axisymmetric, the α-term in Equation (14) will effectively introduce source terms in both the A and B equations, so that Cowling’s theorem can be circumvented.
-
Parker’s idea of helical twisting of toroidal fieldlines by the Coriolis force corresponds to a specific functional form for α, and so finds formal quantitative expression in mean-field electrodynamics.
The production of a mean electromotive force proportional to the mean field is called the α-effect, and it can as a source of both A and B, and thus offers a viable T → P mechanism. Its existence was first demonstrated in the context of turbulent MHD, but it also arises in other contexts, as discussed immediately below. Although this is arguably a bit of a physical abuse, the term “α-effect” is used in what follows to denote any mechanism producing a mean poloidal field from a mean toroidal field, as is almost universally (and perhaps unfortunately) done in the contemporary solar dynamo literature.
Other forms of turbulent mean electromotive forces are possible when the large-scale magnetic field develops variations on scales comparable to that of large-scale flows, notably angular velocity shears (see Rädler et al., 2003; Pipin and Seehafer, 2009, and references therein). This can lead to the appearance of an additional contribution on the RHS of Equation (14), of the general form δ × (∇ × 〈B〉). Such a mean-field-aligned emf cannot contribute to the sustenance of 〈B〉, but operating concurently with other inductive mechanisms, can in principle contribute to dynamo action.
3.2.2 Hydrodynamical shear instabilities
The tachocline is the rotational shear layer uncovered by helioseismology immediately beneath the Sun’s convective envelope, providing smooth matching between the latitudinal differential rotation of the envelope, and the rigidly rotating radiative core (see, e.g., Spiegel and Zahn, 1992; Brown et al., 1989; Tomczyk et al., 1995; Charbonneau et al., 1999, and references therein). Stability analyses of the latitudinal shear within the tachocline carried out in the framework of shallow-water theory suggest that the latitudinal shear can become unstable when vertical fluid displacement is allowed (Dikpati and Gilman, 2001). These authors also find that vertical fluid displacements correlate with the horizontal vorticity pattern in a manner resulting in a net kinetic helicity that can, in principle, impart a systematic twist to an ambient mean toroidal field. This can thus serve as a source for the poloidal component, and, in conjunction with rotational shearing of the poloidal field, lead to cyclic dynamo action. This is a self-excited T → P mechanism, but it is not entirely clear at this juncture if (and how) it would operate in the strong-field regime (more on this in Section 4.5 below).
3.2.3 MHD instabilities
It has now been demonstrated, perhaps even beyond reasonable doubt, that the toroidal magnetic flux ropes that upon emergence in the photosphere give rise to sunspots can only be stored below the Sun’s convective envelope, more specifically in the thin, weakly subadiabatic overshoot layer conjectured to exist immediately beneath the core-envelope interface (see, e.g., Schüssler, 1996; Schüssler and Ferriz-Mas, 2003; Fan, 2009, and references therein). Only there are growth rates for the magnetic buoyancy instability sufficiently long to allow field amplification, while being sufficiently short for flux emergence to take place on time-scales commensurate with the solar cycle (Ferriz-Mas et al., 1994). These stability studies have also revealed the existence of regions of weak instability, in the sense that the growth rates are numbered in years. The developing instability is then strongly influenced by the Coriolis force, and develops in the form of growing helical waves travelling along the flux rope’s axis. This amounts to twisting a toroidal field in meridional planes, as with the Parker scenario, with the important difference that what is now being twisted is a flux rope rather than an individual fieldline. Nonetheless, an azimuthal electromotive force is produced. This represents a viable T → P mechanism, but one that can only act above a certain field strength threshold; in other words, dynamos relying on this mechanism are not self-excited, since they require strong fields to operate. On the other hand, they operate without difficulties in the strong field regime.
Another related class of poloidal field regeneration mechanism is associated with the buoyant breakup of the magnetized layer (Matthews et al., 1995). Once again it is the Coriolis force that ends up imparting a net twist to the rising, arching structures that are produced in the course of the instability’s development (see Thelen, 2000a, and references therein). This results in a mean electromotive force that peaks where the magnetic field strength varies most rapidly with height. This could provide yet another form of tachocline α-effect, again subjected to a lower operating threshold. MHD versions of the hydrodynamical shear instability discussed in Section 3.2.2 have also been studied (see, e.g., Arlt et al., 2007b; Cally et al., 2008; Dikpati et al., 2009, and references therein), but the fundamentally nonlinear nature of the flow-field interaction makes it difficult to construct physically credible poloidal source terms to be incoporated into dynamo models.
3.2.4 The Babcock-Leighton mechanism
The larger sunspot pairs (“bipolar magnetic regions”, hereafter BMR) often emerge with a systematic tilt with respect to the E-W direction, in that the leading sunspot (with respect to the direction of solar rotation) is located at a lower latitude than the trailing sunspot, the more so the higher the latitude of the emerging BMR. This pattern, known as “Joy’s law”, is caused by the action of the Coriolis force on the secondary azimuthal flow that develops within the buoyantly rising magnetic toroidal flux rope that, upon emergence, produces a BMR (see, e.g. Fan et al., 1993; D’Silva and Choudhuri, 1993; Caligari et al., 1995). In conjunction with the antisymmetry of the toroidal field giving rise to sunspots evidenced by Hale’s sunspot laws, this tilt is at the heart of the Babcock-Leighton mechanism for polar field reversal, as outlined in cartoon form in Figure 2.
Physically, what happens is that the leading spot of the BMR is located closer to the equator, and therefore experiences greater diffusive cancellation across the equatorial plane with the opposite polarity leading spots of the other hemisphere, than the trailing spots do. Upon decay, the latter’s magnetic flux is preferentially transported to the polar region by supergranular diffusion and the surface meridional flow. The net effect is to take a formerly toroidal magnetic field and convert a fraction of its associated flux into a net dipole moment, i.e., it represents a T → P mechanism. With the polar cap flux amounting to less than 0.1% of the unsigned magnetic flux emerging in active regions throughout a cycle, the efficiency of this so-called Babcock-Leighton mechanism needs not be very high. Here again the resulting dynamos are not self-excited, as the required tilt of the emerging BMR only materializes in a range of toroidal field strength going from a few 104 G to about 2 × 105 G.
4 A Selection of Representative Models
Each and every one of the T → P mechanisms described in Section 3.2 relies on fundamentally non-axisymmetric physical effects, yet these must be “forced” into axisymmetric dynamo equations for the mean magnetic field. There are a great many different ways of doing so, which explains the wide variety of dynamo models of the solar cycle to be found in the recent literature. The aim of this section is to provide representative examples of various classes of models, to highlight their similarities and differences, and illustrate their successes and failings. In all cases, the model equations are to be understood as describing the evolution of the mean field 〈B〉, namely the large-scale, axisymmetric component of the total solar magnetic field. Those wishing to code up their own versions of these (relatively) simple models should take note of the fact that Jouve et al. (2008) have set up a suite of benchmark calculations against which numerical dynamo solutions can be validated.
4.1 Model ingredients
All kinematic solar dynamo models have some basic “ingredients” in common, most importantly (i) a solar structural model, (ii) a differential rotation profile, and (iii) a magnetic diffusivity profile (possibly depth-dependent).
Helioseismology has pinned down with great accuracy the internal solar structure, including the internal differential rotation, and the exact location of the core-envelope interface. Unless noted otherwise, all illustrative models discussed in this section were computed using the following analytic formulae for the angular velocity Ω(r, θ) and magnetic diffusivity η(r):
with
and
With appropriately chosen parameter values, Equation (15) describes a solar-like differential rotation profile, namely a purely latitudinal differential rotation in the convective envelope, with equatorial acceleration and smoothly matching a core rotating rigidly at the angular speed of the surface mid-latitudesFootnote 3. This rotational transition takes place across a spherical shear layer of half-thickness w coinciding with the core-envelope interface at rc/R⊙ = 0.7 (see Figure 5, with parameter values listed in caption). As per Equation (17), a similar transition takes place with the net diffusivity, falling from some large, “turbulent” value ηT in the envelope to a much smaller diffusivity ηc in the convection-free radiative core, the diffusivity contrast being given by Δη = ηc/ηT. Given helioseismic constraints, these represent minimal yet reasonably realistic choices.
Isocontours of angular velocity generated by Equation (15), with parameter values w/R = 0.05, ΩC = 0.8752, a2 = 0.1264, a4 = 0.1591 (Panel A). The radial shear changes sign at colatitude θ = 55°. Panel B shows the corresponding angular velocity gradients, together with the total magnetic diffusivity profile defined by Equation (17) (dash-dotted line). The core-envelope interface is located at r/R⊙ = 0.7 (dotted lines).
It should be noted already that such a solar-like differential rotation profile is quite complex from the point of view of dynamo modelling, in that it is characterized by three partially overlapping shear regions: a strong positive radial shear in the equatorial regions of the tachocline, an even stronger negative radial shear in its the polar regions, and a significant latitudinal shear throughout the convective envelope and extending partway into the tachocline. As shown in panel B of Figure 5, for a tachocline of half-thickness w/R⊙ = 0.05, the mid-latitude latitudinal shear at ../... = 0.7 is comparable in magnitude to the equatorial radial shear; its potential contribution to dynamo action should not be casually dismissed.
4.2 αΩ mean-field models
4.2.1 Calculating the α-effect and turbulent diffusivity
Mean-field electrodynamics is a subject well worth its own full-length review, so the foregoing discussion will be limited to the bare essentials. Detailed discussion of the topic can be found in Krause and Rädler (1980), Moffatt (1978), and Rüdiger and Hollerbach (2004), and in the recent review articles by Ossendrijver (2003) and Hoyng (2003).
The task at hand is to calculate the components of the α and β tensor in terms of the statistical properties of the underlying turbulence. A particularly simple case is that of homogeneous, weakly anisotropic turbulence, which reduces the α and β tensor to simple scalars, so that the mean electromotive force becomes
This is the form commonly used in solar dynamo modelling, even though turbulence in the solar interior is most likely inhomogeneous and anisotropic. Moreover, hiding in the above expressions is the assumption that the small-scale magnetic Reynolds number vl/η is much smaller than unity, where v ∼ 103 cm s-1 and l ∼ 109 cm are characteristic velocities and length scales for the dominant turbulent eddies, as estimated, e.g., from mixing length theory. With η ∼ 104 cm2 s-1, one finds vl/η ∼ 108, so that on that basis alone Equation (18) should be dubious already. In the kinematic regime, α and β are independent of the magnetic field fluctuations, and end up simply proportional to the averaged kinetic helicity and square fluctuation amplitude:
where τc is the correlation time of the turbulent motions. Order-of-magnitude estimates of the scalar coefficients yield α ∼ Ωl and ηT ∼ vl, where Ω is the solar angular velocity. At the base of the solar convection zone, one then finds α ∼ 103 cm s-1 and ηT ∼ 1012 cm2 s-1, these being understood as very rough estimates. Because the kinetic helicity may well change sign along the longitudinal (averaging) direction, thus leading to cancellation, the resulting value of α may be much smaller than its r.m.s. deviation about the longitudinal mean. In contrast the quantity being averaged on the right hand side of Equation (20) is positive definite, so one would expect a more “stable” mean value (see Hoyng, 1993; Ossendrijver et al., 2001, for further discussion). At any rate, difficulties in computing α and ηT from first principle (whether as scalars or tensors) have led to these quantities often being treated as adjustable parameters of mean-field dynamo models, to be adjusted (within reasonable bounds) to yield the best possible fit to observed solar cycle characteristics, most importantly the cycle period. One finds in the literature numerical values in the approximate ranges 10 - 103 cm s-1 for α and 1010 - 1013 cm2 s-1 for ηT.
The cyclonic character of the α-effect also indicates that it is equatorially antisymmetric and positive in the Northern solar hemisphere, except perhaps at the base of the convective envelope, where the rapid variation of the turbulent velocity with depth can lead to a sign change. These expectations have been confirmed in a general sense by theory and numerical simulations (see, e.g., Rüdiger and Kitchatinov, 1993; Brandenburg et al., 1990; Ossendrijver et al., 2001; Käpylä et al., 2006a).
In cases where the turbulence is more strongly inhomogeneous, an additional effect comes into play: turbulent pumping. Mathematically it arises through an antisymmetric contribution to the α-tensor in Equation (14), whose three independent components can be recast as a velocity-like vector field γ that acts as an additional (and non-solenoidal) contribution to the mean flow:
The tensor αS now contains only the symmetric part of the original α tensor. Measurements of the α-tensor in MHD numerical simulations of turbulence in a box (see Ossendrijver et al., 2002; Käpylä et al., 2006a, and references therein) indicate that pumping is directed mostly downwards throughout the solar convection, as a result of stratification, and that a significant equatorward latitudinal pumping also arises once rotation becomes important, in the sense that the Coriolis number Co = 2Ωτc exceeds unity. Turbulent pumping speeds of a few m s-1 can be reached with Co in the range 4 – 10, according to the numerical simulations of Käpylä et al. (2006a).
4.2.2 α-quenching, diffusivity-quenching, and flux loss through buoyancy
Leaving the kinematic regime, it is expected that both α and ηT should depend on the strength of the magnetic field, since magnetic tension will resist deformation by the small-scale turbulent fluid motions. The groundbreaking numerical MHD simulations of Pouquet et al. (1976) suggested that Equation (19) should be replaced by something like
where \(a' = B'/\sqrt {4\pi \rho }\) is the Alfvén speed based on the small-scale magnetic component (see also Durney et al., 1993; Blackman and Brandenburg, 2002). This is rarely used in solar cycle modelling, since the whole point of the mean-field approach is to avoid dealing explicitly with the small-scale, fluctuating components. On the other hand, something is bound to happen when the growing dynamo-generated mean magnetic field reaches a magnitude such that its energy per unit volume is comparable to the kinetic energy of the underlying turbulent fluid motions. Denoting this equipartition field strength by Beq, one often introduces an ad hoc nonlinear dependency of α (and sometimes ηT as well) directly on the mean-field 〈B〉 by writing:
This expression “does the right thing”, in that α → 0 as 〈B〉 starts to exceed Beq. It remains an extreme oversimplification of the complex interaction between flow and field that characterizes MHD turbulence, but its wide usage in solar dynamo modeling makes it a nonlinearity of choice for the illustrative purpose of this section.
Diffusivity-quenching is an even more uncertain proposition than α-quenching, with various quenching models more complex than Equation (23) having been proposed (e.g., Rüdiger et al., 1994). Measurements of the components of the α and β tensors in the convective turbulence simulations of Brandenburg et al. (2008) do suggest a much stronger magnetic quenching of the α-effect than of the turbulent diffusivity, but many aspects of this problem remain open. One appealing aspect of diffusivity quenching is its potential ability to produce localized concentrations of strong magnetic fields, exceeding equipartition strength under some conditions (Gilman and Rempel, 2005). On the other hand, the stability analyses of Arlt et al. (2007b,a) suggests that there exist a lower limit to the magnetic diffusivity, below which equipartition-strength toroidal magnetic field beneath the core-envelope interface become unstable.
Another amplitude-limiting mechanism is the loss of magnetic flux through magnetic buoyancy. Magnetic fields concentrations are buoyantly unstable in the convective envelope, and so should rise to the surface on time scales much shorter than the cycle period (see, e.g., Parker, 1975; Schüssler, 1977; Moreno-Insertis, 1983, 1986). This is often incorporated on the right-hand-side of the dynamo equations by the introduction of an ad hoc loss term of the general form —ƒ(〈B〉) 〈B〉; the function ƒ measures the rate of flux loss, and is often chosen proportional to the magnetic pressure 〈B〉2, thus yielding a cubic damping nonlinearity in the mean-field.
4.2.3 The αΩ dynamo equations
Adding the mean-electromotive force given by Equation (18) to the MHD induction equation leads to the following form for the axisymmetric mean-field dynamo equations:


where, in general, ηT ≫ η. There are now source terms on both right hand sides, so that dynamo action becomes possible at least in principle. The relative importance of the α-effect and shearing terms in Equation (25) is measured by the ratio of the two dimensionless dynamo numbers
where, in the spirit of dimensional analysis, α0, η0, and (ΔΩ)0 are “typical” values for the α-effect, turbulent diffusivity, and angular velocity contrast. These quantities arise naturally in the non-dimensional formulation of the mean-field dynamo equations, when time is expressed in units of the magnetic diffusion time τ based on the envelope (turbulent) diffusivity:
In the solar case, it is usually estimated that Cα ≪ CΩ, so that the α-term is neglected in Equation (25); this results in the class of dynamo models known as αΩ dynamos, which will be the only ones discussed hereFootnote 4.
4.2.4 Eigenvalue problems and initial value problems
With the large-scale flows, turbulent diffusivity and α-effect considered given, Equations (24, 25) become truly linear in A and B. It becomes possible to seek eigensolutions in the form
Substitution of these expressions into Equations (24, 25) yields an eigenvalue problem for s and associated eigenfunction {a, b}. The real part σ ≡ Re s is then a growth rate, and the imaginary part ω ≡ Im s an oscillation frequency. One typically finds that σ < 0 until the product Cα × CΩ exceeds a certain critical value Dcrit beyond which σ > 0, corresponding to a growing solutions. Such solutions are said to be supercritical, while the solution with σ = 0 is critical.
Clearly exponential growth of the dynamo-generated magnetic field must cease at some point, once the field starts to backreact on the flow through the Lorentz force. This is the general idea embodied in α-quenching. If α-quenching — or some other nonlinearity — is included, then the dynamo equations are usually solved as an initial-value problem, with some arbitrary low-amplitude seed field used as initial condition. Equations (24, 25) are then integrated forward in time using some appropriate time-stepping scheme. A useful quantity to monitor in order to ascertain saturation is the magnetic energy within the computational domain:
4.2.5 Dynamo waves
One of the most remarkable property of the (linear) αΩ dynamo equations is that they support travelling wave solutions. This was first demonstrated in Cartesian geometry by Parker (1955), who proposed that a latitudinally-travelling “dynamo wave’ was at the origin of the observed equatorward drift of sunspot emergences in the course of the cycle. This finding was subsequently shown to hold in spherical geometry, as well as for non-linear models (Yoshimura, 1975; Stix, 1976). Dynamo wavesFootnote 5 travel in a direction s given by
a result now known as the “Parker-Yoshimura sign rule”. Recalling the rather complex form of the helioseismically inferred solar internal differential rotation (cf. Figure 5), even an α-effect of uniform sign in each hemisphere can produce complex migratory patterns, as will be apparent in the illustrative αΩ dynamo solutions to be discussed presently. Note already at this juncture that if the seat of the dynamo is to be identified with the low-latitude portion of the tachocline, and if the latter is thin enough for the (positive) radial shear therein to dominate over the latitudinal shear, then equatorward migration of dynamo waves will require a negative α-effect in the low latitudes of the Northern solar hemisphere.
4.2.6 Representative results
We first consider αΩ models without meridional circulation (up = 0 in Equations (24, 25)), with the α-term omitted in Equation (25), and using the diffusivity and angular velocity profiles of Figure 5. We will investigate the behavior of αΩ models with the α-effect concentrated just above the core-envelope interface (green line in Figure 6). We also consider two latitudinal dependencies, namely α ∝ cos θ, which is the “minimal” possible latitudinal dependency compatible with the required equatorial antisymmetry of the Coriolis force, and an α-effect concentrated towards the equatorFootnote 6 via an assumed latitudinal dependency α ∝ sin2 θ cos θ.
Figures 7 and 8 show a selection of such dynamo solutions, in the form of animations in meridional planes and time-latitude diagrams of the toroidal field extracted at the core-envelope interface, here rc/R⊙ = 0.7. If sunspot-producing toroidal flux ropes form in regions of peak toroidal field strength, and if those ropes rise radially to the surface, then such diagrams are directly comparable to the sunspot butterfly diagram of Figure 3. All models have CΩ = 25000, |Cα| = 10, ηT/ηc = 10, and ηT = 5 × 1011 cm2 s-1, which leads to τ ≃ 300 yr. To facilitate comparison between solutions, here antisymmetric parity was imposed via the boundary condition at the equator.
Stills from Meridional plane animations of various αΩ dynamo solutions using different latitudinal profiles and sign for the α-effect, as labeled. The polar axis coincides with the left quadrant boundary. The toroidal field is plotted as filled contours (constant increments, green to blue for negative B, yellow to red for positive B), on which poloidal fieldlines are superimposed (blue for clockwise-oriented fieldlines, orange for counter-clockwise orientation). The dashed line is the core-envelope interface at rc/R = 0.7. Time-latitude “butterfly” diagrams for these three solutions are plotted in Figure 8. (To watch the movie, please go to the online version of this review article at http://www.livingreviews.org/lrsp-2010-3.)
Northern hemisphere time-latitude (“butterfly”) diagrams for the three αΩ dynamo solutions of Figure 7, constructed at the depth rc/R⊙ = 0.7 corresponding to the core-envelope interface. Isocontours of toroidal field are normalized to their peak amplitudes, and plotted for increments ΔB/ max(B) = 0.2, with yellow-to-red (green-to-blue) contours corresponding to B > 0 (< 0). The assumed latitudinal dependency of the α-effect is given above each panel. Other model ingredients as in Figure 5. Note the co-existence of two distinct cycles in the solution shown in Panel B.
Examination of these animations reveals that the dynamo is concentrated in the vicinity of the core-envelope interface, where the adopted radial profile for the α-effect is maximal (cf. Figure 6). In conjunction with a fairly thin tachocline, the radial shear therein then dominates the induction of the toroidal magnetic component. With an eye on Figure 5, notice also how the dynamo waves propagates along isocontours of angular velocity, in agreement with the Parker-Yoshimura sign rule (cf. Section 4.2.5). In the butterfly diagram, this translates a systematic tilt of the isocontours of toroidal magnetic field. Note that even for an equatorially-concentrated α-effect (Panels B and C), a strong polar branch is nonetheless apparent in the butterfly diagrams, a direct consequence of the stronger radial shear present at high latitudes in the tachocline (see also corresponding animations). Models using an α-effect operating throughout the whole convective envelope, on the other hand, would feed primarily on the latitudinal shear therein, so that for positive Cα the dynamo mode would propagate radially upward in the envelope (see Lerche and Parker, 1972).
It is noteworthy that co-existing dynamo branches, as in Panel B of Figure 8, can have distinct dynamo periods, which in nonlinearly saturated solutions leads to long-term amplitude modulation. This is typically not expected in dynamo models where the only nonlinearity present is a simple algebraic quenching formula such as Equation (23). Note that this does not occur for the Cα < 0 solution, where both branches propagate away from each other, but share a common latitude of origin and so are phased-locked at the onset (cf. Panel C of Figure 8).
A common property of all oscillatory αΩ solutions discussed so far is that their period, for given values of the dynamo numbers Cα, CΩ, is inversely proportional to the numerical value adopted for the (turbulent) magnetic diffusivity ηT. The ratio of poloidal-to-toroidal field strength, in turn, is found to scale as some power (usually close to 1/2) of the ratio Cα/CΩ, at a fixed value of the product Cα × CΩ.
The models discussed above are based on rather minimalistics and partly ad hoc assumptions on the form of the α-effect. More elaborate models have been proposed, relying on calculations of the full α-tensor based on some underlying turbulence models (see, e.g., Kitchatinov and Rüdiger, 1993). While this approach usually displaces the ad hoc assumptions into the turbulence model, it has the definite merit of offering an internally consistent approach to the calculation of turbulent diffusivities and large-scale flows. Rüdiger and Brandenburg (1995) remain a good example of the current state-of-the-art in this area; see also Rüdiger and Arlt (2003), and references therein.
4.2.7 Critical assessment
From a practical point of view, the outstanding success of the mean-field αΩ model remains its robust explanation of the observed equatorward drift of toroidal field-tracing sunspots in the course of the cycle in terms of a dynamo-wave. On the theoretical front, the model is also buttressed by mean-field electrodynamics which, in principle, offers a physically sound theory from which to compute the (critical) α-effect and magnetic diffusivity. The models’ primary uncertainties turn out to lie at that level, in that the application of the theory to the Sun in a tractable manner requires additional assumptions that are most certainly not met under solar interior conditions. Those uncertainties are exponentiated when taking the theory into the nonlinear regime, to calculate the dependence of the α-effect and diffusivity on the magnetic field strength. This latter problem remains very much open at this writing.
4.3 Interface dynamos
4.3.1 Strong α-quenching and the saturation problem
The α-quenching expression (23) used in the preceding section amounts to saying that dynamo action saturates once the mean, dynamo-generated field reaches an energy density comparable to that of the driving turbulent fluid motions, i.e., \(B_{eq} \sim \sqrt {4\pi \rho } v\), where v is the turbulent velocity amplitude. This appears eminently sensible, since from that point on a toroidal fieldline would have sufficient tension to resist deformation by cyclonic turbulence, and so could no longer feed the α-effect. At the base of the solar convective envelope, one finds Beq ∼ 1 kG, for v ∼ 103 cm s-1, according to standard mixing length theory of convection. However, various calculations and numerical simulations have indicated that long before the mean field 〈B〉 reaches this strength, the helical turbulence reaches equipartition with the small-scale, turbulent component of the magnetic field (e.g., Cattaneo and Hughes, 1996, and references therein). Such calculations also indicate that the ratio between the small-scale and mean magnetic components should itself scale as Rm1/2, where Rm = vl/η is a magnetic Reynolds number based on the microscopic magnetic diffusivity. This then leads to the alternate quenching expression
known in the literature as strong α-quenching or catastrophic quenching. Since Rm ∼ 108 in the solar convection zone, this leads to quenching of the α-effect for very low amplitudes for the mean magnetic field, of order 10-1 G. Even though significant field amplification is likely in the formation of a toroidal flux rope from the dynamo-generated magnetic field, we are now a very long way from the 10 – 100 kG demanded by simulations of buoyantly rising flux ropes (see Fan, 2009).
A way out of this difficulty was proposed by Parker (1993), in the form of interface dynamos. The idea is beautifully simple: If the toroidal field quenches the α-effect, amplify and store the toroidal field away from where the α-effect is operating! Parker showed that in a situation where a radial shear and α-effect are segregated on either side of a discontinuity in magnetic diffusivity (taken to coincide with the core-envelope interface), the αΩ dynamo equations support solutions in the form of travelling surface waves localized on the discontinuity in diffusivity. The key aspect of Parker’s solution is that for supercritical dynamo waves, the ratio of peak toroidal field strength on either side of the discontinuity surface is found to scale with the diffusivity ratio as
where the subscript “1” refers to the low-η region below the core-envelope interface, and “2” to the high-η region above. If one assumes that the envelope diffusivity η2 is of turbulent origin then η2 ∼ lv, so that the toroidal field strength ratio then scales as ∼ (vl/η1)1/2 ≡ Rm1/2. This is precisely the factor needed to bypass strong α-quenching (Charbonneau and MacGregor, 1996). Somewhat more realistic variations on Parker’s basic model were later elaborated (MacGregor and Charbonneau, 1997 and Zhang et al., 2004), and, while differing in important details, nonetheless confirmed Parker’s overall picture.
Tobias (1996a) discusses in detail a related Cartesian model bounded in both horizontal and vertical direction, but with constant magnetic diffusivity η throughout the domain. Like Parker’s original interface configuration, his model includes an α-effect residing in the upper half of the domain, with a purely radial shear in the bottom half. The introduction of diffusivity quenching then reduces the diffusivity in the shear region, “naturally” turning the model into a bona fide interface dynamo, supporting once again oscillatory solutions in the form of dynamo waves travelling in the “latitudinal” x-direction. This basic model was later generalized by various authors (Tobias, 1997; Phillips et al., 2002) to include the nonlinear backreaction of the dynamo-generated magnetic field on the differential rotation; further discussion of such nonlinear models is deferred to Section 5.3.1.
4.3.2 Representative results
The next obvious step is to construct an interface dynamo in spherical geometry, using a solarlike differential rotation profile. This was undertaken by Charbonneau and MacGregor (1997). Unfortunately, the numerical technique used to handle the discontinuous variation in η at the core-envelope interface turned out to be physically erroneous for the vector potential A describing the poloidal fieldFootnote 7 (see Markiel and Thomas, 1999, for a discussion of this point), which led to spurious dynamo action in some parameter regimes. The matching problem is best avoided by using a continuous but rapidly varying diffusivity profile at the core-envelope interface, with the α-effect concentrated at the base of the envelope, and the radial shear immediately below, but without significant overlap between these two source regions (see Panel B of Figure 9). Such numerical models can be constructed as a variation on the αΩ models considered earlier.
A representative interface dynamo model in spherical geometry. This solution has CΩ = 2.5×105, Cα = +10, and a core-to-envelope diffusivity contrast of 10-2. Panel A shows a sunspot butterfly diagram, and Panel B a series of radial cuts of the toroidal field at latitude 15°. The (normalized) radial profiles of magnetic diffusivity, α-effect, and radial shear are also shown, again at latitude 15°. The core-envelope interface is again at r/R⊙ = 0.7 (dotted line), where the magnetic diffusivity varies near-discontinuously. Panels C and D show the variations of the core-to-envelope peak toroidal field strength and dynamo period with the diffusivity contrast, for a sequence of otherwise identical dynamo solutions.
In spherical geometry, and especially in conjunction with a solar-like differential rotation profile, making a working interface dynamo model is markedly trickier than if only a radial shear is operating, as in the Cartesian models discussed earlier (see Charbonneau and MacGregor, 1997; Markiel and Thomas, 1999; Zhang et al., 2003a). Panel A of Figure 9 shows a butterfly diagram for a numerical interface solution with CΩ = 2.5 × 105, Cα = +10, and a core-to-envelope diffusivity contrast Δη = 10-2. The poleward propagating equatorial branch is precisely what one would expect from the combination of positive radial shear and positive α-effect according to the Parker-Yoshimura sign ruleFootnote 8. Here the α-effect is (artificially) concentrated towards the equator, by imposing a latitudinal dependency α ∼ sin(4θ) for π/4 ≤ θ ≤ 3π/4, and zero otherwise.
The model does achieve the kind of toroidal field amplification one would like to see in interface dynamos. This can be seen in Panel B of Figure 9, which shows radial cuts of the toroidal field taken at latitude π/8, and spanning half a cycle. Notice how the toroidal field peaks below the core-envelope interface (vertical dotted line), well below the α-effect region and near the peak in radial shear. Panel C of Figure 9 shows how the ratio of peak toroidal field below and above rc varies with the imposed diffusivity contrast Δη. The dashed line is the dependency expected from Equation (32). For relatively low diffusivity contrast, -1.5 ≤ log(Δη) ≲ 0, both the toroidal field ratio and dynamo period increase as ∼ (Δη)-1/2. Below log(Δη) ∼ -1.5, the max(B)-ratio increases more slowly, and the cycle period falls, contrary to expectations for interface dynamos (see, e.g., MacGregor and Charbonneau, 1997). This is basically an electromagnetic skin-depth effect; the cycle period is such that the poloidal field cannot diffuse as deep as the peak in radial shear in the course of a half cycle. The dynamo then runs on a weaker shear, thus yielding a smaller field strength ratio and weaker overall cycle; on the energetics of interface dynamos (see Ossendrijver and Hoyng, 1997, also Steiner and Ferriz-Mas, 2005).
4.3.3 Critical assessment
So far the great success of interface dynamos remains their ability to evade α-quenching even in its “strong” formulation, and so produce equipartition or perhaps even super-equipartition mean toroidal magnetic fields immediately beneath the core-envelope interface. They represent the only variety of dynamo models formally based on mean-field electrodynamics that can achieve this without additional physical effects introduced into the model. All of the uncertainties regarding the calculations of the α-effect and magnetic diffusivity carry over from αΩ to interface models, with diffusivity quenching becoming a particularly sensitive issue in the latter class of models (see, e.g., Tobias, 1996a).
Interface dynamos suffer acutely from something that is sometimes termed “structural fragility”. Many gross aspects of the model’s dynamo behavior often end up depending sensitively on what one would normally hope to be minor details of the model’s formulation. For example, the interface solutions of Figure 9 are found to behave very differently if the α-effect region is displaced slightly upwards, or assumes other latitudinal dependencies. Moreover, as exemplified by the calculations of Mason et al. (2008), this sensitivity carries over to models in which the coupling between the two source regions is achieved by transport mechanisms other than diffusion. This sensitivity is exacerbated when a latitudinal shear is present in the differential rotation profile; compare, e.g., the behavior of the Cα > 0 solutions discussed here to those discussed in Markiel and Thomas (1999). Often in such cases, a mid-latitude αΩ dynamo mode, powered by the latitudinal shear within the tachocline and envelope, interferes with and/or overpowers the interface mode (see also Dikpati et al., 2005).
Because of this structural sensitivity, interface dynamo solutions also end up being annoyingly sensitive to choice of time-step size, spatial resolution, and other purely numerical details. From a modelling point of view, interface dynamos lack robustness.
4.4 Mean-field models including meridional circulation
Meridional circulation is unavoidable in turbulent, compressible rotating convective shells. It basically results from an imbalance between Reynolds stresses and buoyancy forces. The ∼ 15 m s-1 poleward flow observed at the surface (see, e.g., Hathaway, 1996; Ulrich and Boyden, 2005) has now been detected helioseismically, down to r/R⊙ ≃ 0.85 (Schou and Bogart, 1998; Braun and Fan, 1998), without significant departure from the poleward direction except locally and very close to the surface, in the vicinity of active region belts (see Gizon, 2004; Gizon and Rempel, 2008, and references therein), and in polar latitudes at some phases of the solar cycle (Haber et al., 2002). Long considered unimportant from the dynamo point of view, meridional circulation has gained popularity in recent years, initially in the Babcock-Leighton context but now also in other classes of models.
Accordingly, we now add a steady meridional circulation to our basic αΩ models of Section 4.2. The convenient parametric form developed by van Ballegooijen and Choudhuri (1988) is used here and in all later illustrative models including meridional circulation (Sections 4.5 and 4.8). This parameterization defines a steady quadrupolar circulation pattern, with a single flow cell per quadrant extending from the surface down to a depth rb. Circulation streamlines are shown in Figure 10, together with radial cuts of the latitudinal component at mid-latitudes (θ = π/4). The flow is poleward in the outer convection zone, with an equatorial return flow peaking slightly above the core-envelope interface, and rapidly vanishing below.
Streamlines of meridional circulation (Panel A), together with the total magnetic diffusivity profile defined by Equation (17) (dash-dotted line) and a mid-latitude radial cut of uθ (bottom panel). The dotted line is the core-envelope interface. This is the analytic flow of van Ballegooijen and Choudhuri (1988), with parameter values m = 0.5, p = 0.25, q = 0, and rb = 0.675.
The inclusion of meridional circulation in the non-dimensionalized αΩ dynamo equations leads to the appearance of a new dimensionless quantity, again a magnetic Reynolds number, but now based on an appropriate measure of the circulation speed u0:
Using the value u0 = 1500 cm s-1 from observations of the observed poleward surface meridional flow leads to Rm ≃ 200, again with ηT = 5 × 1011 cm2 s-1. In the solar cycle context, using higher values of Rm thus implies proportionally lower turbulent diffusivities.
4.4.1 Representative results
Meridional circulation can bodily transport the dynamo-generated magnetic field (terms labeled “advective transport” in Equations (11, 12)), and therefore, for a (presumably) solar-like equatorward return flow that is vigorous enough — in the sense of Rm being large enough — overpower the Parker-Yoshimura propagation rule embodied in Equation (30). This was nicely demonstrated by Choudhuri et al. (1995), in the context of a mean-field αΩ model with a positive α-effect concentrated near the surface, and a latitude-independent, purely radial shear at the core-envelope interface. The behavioral turnover from dynamo wave-like solutions to circulation-dominated magnetic field transport sets in when the circulation speed becomes comparable to the propagation speed of the dynamo wave. In the circulation-dominated regime, the cycle period loses sensitivity to the assumed turbulent diffusivity value, and becomes determined primarily by the circulation’s turnover time. Models achieving equatorward propagation of the deep toroidal magnetic component in this manner are now often called flux-transport dynamos.
With a solar-like differential rotation profile, however, once again the situation is far more complex. Starting from the most basic αΩ dynamo solution with α ∼ cos θ (Figure 8A), new solutions are now recomputed, this time including meridional circulation. An animation of a typical solution is shown in Figure 11, and a sequence of time-latitude diagrams for four increasing values of the circulation flow speed, as measured by Rm, are plotted in Figure 12.
mpg-Movie ((2347.42480469 KB) Still from a movie showing Meridional plane animations for an αΩ dynamo solutions including meridional circulation. With Rm = 103, this solution is operating in the advection-dominated regime as a flux-transport dynamo. The corresponding time-latitude “butterfly” diagram is plotted in Figure 12C below. Color-coding of the toroidal magnetic field and poloidal fieldlines as in Figure 7. (For video see appendix)
Time-latitude “butterfly” diagrams for the α-quenched αΩ solutions depicted earlier in Panel A of Figure 8, except that meridional circulation is now included, with (A) Rm = 50, (B) Rm = 100, (C) Rm = 1000, and (D) Rm = 2000 For the turbulent diffusivity value adopted here, ηT = 5 × 1011 cm2 s-1, Rm = 200 would corresponds to a solar-like circulation speed.
At Rm = 50, little difference is seen with the circulation-free solutions (cf. Figure 8A), except for an increase in the cycle frequency, due to the Doppler shift experienced by the equatorwardly propagating dynamo wave (see Roberts and Stix, 1972). At Rm = 100 (part B), the cycle frequency has further increased and the poloidal component produced in the high-latitude region of the tachocline is now advected to the equatorial regions on a timescale becoming comparable to the cycle period, so that a cyclic activity, albeit with a longer period, becomes apparent at low latitudes. At Rm = 103 (panel C and animation in Figure 11) the dynamo mode now peaks at mid-latitude, a consequence of the inductive action of the latitudinal shear, favored by the significant stretching experienced by the poloidal fieldlines as they get advected equatorward. At Rm = 2000 the original high latitude dynamo mode has all but vanished, and the mid-latitude mode is dominant. The cycle period is now set primarily by the turnover time of the meridional flow; this is the telltale signature of flux-transport dynamos.
All this may look straightforward, but it must be emphasized that not all dynamo models with solar-like differential rotation behave in this (relatively) simple manner. For example, the Cα = -10 solution with α ∼ sin2 θ cos θ (Figure 8C) transits to a steady mode as Rm increases above ∼ 102. Moreover, the sequence of α ∼ cos θ shown in Figure 12 actually presents a narrow window around Rm ∼ 200 where the dynamo is decaying, due to a form of destructive interference between the high-latitude αΩ mode and the mid-latitude advection-dominated dynamo mode that dominates at higher values of Rm. Qualitatively similar results were obtained by Küker et al. (2001) using different prescriptions for the α-effect and solar-like differential rotation (see in particular their Figure 11; see also Rüdiger and Elstner, 2002; Bonanno et al., 2003). When field transport by turbulent pumping are included (see Käpylä et al., 2006b), αΩ models including meridional circulation can provide time-latitude “butterfly” diagrams that are reasonably solar-like.
Even if the meridional flow is too slow — or the turbulent magnetic diffusivity too high — to force the dynamo model in the advection-dominated regime, being much faster at the surface the poleward flow can dominate the spatio-temporal evolution of the radial surface magnetic field, as shown in Figure 13, for the same sequence of αΩ solutions with α ∼ cos θ as in Figure 12, at Rm = 0, 50, 100, and 500 (panels A – D). For low circulation speeds (Rm ≲ 50), the equatorward drift of the surface radial field is simply a diffused imprint of the equatorward drift of the deep-seated toroidal field (cf. Figure 8A and 12A). At higher circulation speeds, however, the surface magnetic field is swept instead towards the pole (see Figure 13C), becoming strongly concentrated and amplified there for Rm exceeding a few hundreds (Figures 11 and 13D).
Time-latitude diagrams of the surface radial magnetic field, for increasing values of the circulation speed, as measured by the Reynolds number Rm. This is for the same reference αΩ with α ∼ cos θ as in Figures 8A and 12. Note the marked increased of the peak surface field strength as Rm exceeds ∼ 100.
4.4.2 Critical assessment
From the modelling point-of-view, in the kinematic regime at least the inclusion of meridional circulation yields a much better fit to observed surface magnetic field evolution, as well as a robust setting of the cycle period. Whether it can provide an equally robust equatorward propagation of the deep toroidal field is less clear. The results presented here in the context of mean-field αΩ models suggest a rather complex overall picture, and in interface dynamos the cartesian solutions obtained by Petrovay and Kerekes (2004) even suggest that dynamo action can be severely hindered. Yet, in other classes of models discussed below (Sections 4.5 and 4.8), circulation does have this desired effect (see also Seehafer and Pipin, 2009, for an intriguing mean-field model calculation not relying on the α-effect).
On the other hand, dynamo models including meridional circulation tend to produce surface polar field strength largely in excess of observed values, unless magnetic diffusion is significantly enhanced in the surface layers, and/or field submergence takes place very efficiently. This is a direct consequence of magnetic flux conservation in the converging poleward flow. This situation carries over to the other types of models to be discussed in Sections 4.5 and 4.8, unless additional modelling assumptions are introduced (e.g., enhanced surface magnetic diffusivity, see Dikpati et al., 2004), or if a counterrotating meridional flow cell is introduced in the high latitude regions (Dikpati et al., 2004; Jiang et al., 2009), a feature that has actually been detected in surface Doppler measurements as well as helioseismically during cycle 22 (see Haber et al., 2002; Ulrich and Boyden, 2005).
A more fundamental and potential serious difficulty harks back to the kinematic approximation, whereby the form and speed of up is specified a priori. Meridional circulation is a relatively weak flow in the bottom half of the solar convective envelope (see Miesch, 2005), and the stochastic fluctuations of the Reynolds stresses powering it are expected to lead to strong spatiotemporal variations, and expectation verified by both analytical models (Rempel, 2005) and numerical simulations (Miesch, 2005). The ability of thus meridional flow to merrily advect equipartition-strength magnetic fields should not be taken for granted (but do see Rempel, 2006a,b).
Before leaving the realm of mean-field dynamo models it is worth noting that many of the conceptual difficulties associated with calculations of the α-effect and turbulent diffusivity are not unique to the mean-field approach, and in fact carry over to all models discussed in the following sections. In particular, to operate properly all of the upcoming solar dynamo models require the presence of a strongly enhanced magnetic diffusivity, presumably of turbulent origin, at least in the convective envelope. In this respect, the rather low value of the turbulent magnetic diffusivity needed to achieve high enough Rm in flux transport dynamos is also somewhat problematic, since the corresponding turbulent diffusivity ends up some two orders of magnitude below the (uncertain) mean-field estimates. However, the model calculations of Muñoz-Jaramillo et al. (2010a) indicate that magnetic diffusivity quenching may offer a viable solution to this latter quandary.
4.5 Models based on shear instabilities
We now turn to a recently proposed class of flux transport dynamo models relying on the latitudinal shear instability of the angular velocity profiles in the upper radiative portion of the solar tachocline (Dikpati and Gilman, 2001; Dikpati et al., 2004). These authors work with what are effectively the mean field αΩ dynamo equations including meridional circulation. They design their “tachocline α-effect” in the form of a latitudinal parameterization of the longitudinally-averaged kinetic helicity associated with the planforms they obtain from a linear hydrodynamical stability analysis of the latitudinal differential rotation in the part of the tachocline coinciding with the overshoot region. The analysis is carried out in the framework of shallow-water theory (see Dikpati and Gilman, 2001). In analogy with mean-field theory, the resulting α-effect is assumed to be proportional to kinetic helicity but of opposite sign (see Equation (19)), and ends up predominantly positive at mid-latitudes in the Northern solar hemisphere. In their dynamo model, Dikpati and Gilman (2001) use a solar-like differential rotation, depth-dependent magnetic diffusivity and meridional circulation pattern much similar to those shown in Figures 5, 6, and 10 herein. The usual ad hoc α-quenching formula (cf. Equation (23)) is introduced as the sole amplitude-limiting nonlinearity.
4.5.1 Representative solutions
Many representative solutions for this class of dynamo models can be examined in Dikpati and Gilman (2001) and Dikpati et al. (2004), where their properties are discussed at some length. Figure 14 shows time-latitude diagrams of the toroidal field at the core-envelope interface, and surface radial field. This is a solar-like solution with a mid-latitude surface meridional (poleward) flow speed of 17 m s-1, envelope diffusivity ηT = 5 ¢ 1011 cm2 s-1, and a core-to-envelope magnetic diffusivity contrast Δη = 10-3. Note the equatorward migration of the deep toroidal field, set here by the meridional flow in the deep envelope, and the poleward migration and intensification of the surface poloidal field, again a direct consequence of advection by meridional circulation, as in the mean-field dynamo models discussed in Section 4.4, when operating in the advection-dominated, high Rm regime. The three-lobe structure of each spatio-temporal cycle in the butterfly diagram reflects the presence of three peaks in the latitudinal profile of kinetic helicity for this model.
Time-latitude “butterfly” diagrams of the toroidal field at the core-envelope interface (top), and surface radial field (bottom) for a representative dynamo solution computed using the model of Dikpati and Gilman (2001). Note how the deep toroidal field peaks at very low latitudes, in good agreement with the sunspot butterfly diagram. For this solution the equatorial deep toroidal field and polar surface radial field lag each other by ∼ π, but other parameter settings can bring this lag closer to the observed π/2 (diagrams kindly provided by M. Dikpati).
4.5.2 Critical assessment
While these models are only a recent addition to the current “zoo” of solar dynamo models, they have been found to compare favorably to a number of observed solar cycle features. The model can be adjusted to yield equatorward propagating dominant activity belts, solar-like cycle periods, and correct phasing between the surface polar field and the tachocline toroidal field. These features can be traced primarily to the advective action of the meridional flow. They also yield the correct solution parity, and are self-excited. Like conventional αΩ models relying on meridional circulation to set the propagation direction of dynamo waves (see Section 4.4.2), the meridional flow must remain unaffected by the dynamo-generated magnetic field at least up to equipartition strength, a potentially serious difficulty also shared by the Babcock-Leighton models to be discussed in Section 4.8 below.
The primary weakness of these models, in their present form, is their reliance on a linear stability analysis that altogether ignores the destabilizing effect of magnetic fields. Gilman and Fox (1997) have demonstrated that the presence of even a weak toroidal field in the tachocline can very efficiently destabilize a latitudinal shear profile that is otherwise hydrodynamically stable (see also Zhang et al., 2003b). Relying on a purely hydrodynamical stability analysis is then hard to reconcile with a dynamo process producing strong toroidal field bands of alternating polarities migrating towards the equator in the course of the cycle, especially since latitudinally concentrated toroidal fields have been found to be unstable over a very wide range of toroidal field strengths (see Dikpati and Gilman, 1999). Achieving dynamo saturation through a simple amplitude-limiting quenching formula such as Equation (23) is then also hard to justify. Progress has been made in studying non-linear development of both the hydrodynamical and MHD versions of the shear instability (see, e.g., Cally, 2001; Cally et al., 2003), so that the needed improvements on the dynamo front are hopefully forthcoming.
4.6 Models based on buoyant instabilities of sheared magnetic layers
Dynamo models relying on the buoyant instability of magnetized layers have been presented in Thelen (2000b), the layer being identified with the tachocline. Here also the resulting azimuthal electromotive force is parameterized as a mean-field-like α-effect, introduced into the standard αΩ dynamo equations. The model is nonlinear, in that it includes the magnetic backreaction on the large-scale, purely radial velocity shear within the layer. The analysis of Thelen (2000a) indicates that the α-effect is negative in the upper part of the shear layer. Cyclic solutions are found in substantial regions of parameter space, and, not surprisingly, the solutions exhibit migratory wave patterns compatible with the Parker-Yoshimura sign rule.
Representative solutions for this class of dynamo models can be examined in Thelen (2000b). These models are not yet at the stage where they can be meaningfully compared with the solar cycle. They do have a number of attractive features, including their ability to operate in the strong field regime.
4.7 Models based on flux tube instabilities
4.7.1 From instability to α-effect
To date, stability studies of toroidal flux ropes stored in the overshoot layer have been carried out in the framework of the thin-flux tube approximation (Spruit, 1981). It is possible to construct “stability diagrams” taking the form of growth rate contours in a parameter space comprised of flux tube strength, latitudinal location, depth in the overshoot layer, etc. One such diagram, taken from Ferriz-Mas et al. (1994), is reproduced in Figure 15. The key is now to identify regions in such stability diagrams where weak instability arises (growth rates ≳ 1 yr). In the case shown in Figure 15, these regions are restricted to flux tube strengths in the approximate range 60 – 150 kG. The correlation between the flow and field perturbations is such as to yield a mean azimuthal electromotive force equivalent to a positive α-effect in the N-hemisphere (Ferriz-Mas et al., 1994; Brandenburg and Schmitt, 1998).
Stability diagram for toroidal magnetic flux tubes located in the overshoot layer immediately beneath the core-envelope interface. The plot shows contours of growth rates in the latitude-field strength plane. The gray scale encodes the azimuthal wavenumber of the mode with largest growth rate, and regions left in white are stable. Dynamo action is associated with the regions with growth rates ∼ 1 yr, here labeled I and II (diagram kindly provided by A. Ferriz-Mas).
4.7.2 Representative solutions
Dynamo models relying on the non-axisymmetric buoyant instability of toroidal magnetic fields were first proposed by Schmitt (1987), and further developed by Ferriz-Mas et al. (1994); Schmitt et al. (1996), and Ossendrijver (2000a) for the case of toroidal flux tubes. These dynamo models are all mean-field-like, in that the mean azimuthal electromotive force arising from instability of the flux tubes is parametrized as an α-effect, and the dynamo equations solved are then the same as those of the conventional αΩ mean-field model (see Section 4.2.3), including various forms of algebraic α-quenching as the sole amplitude-limiting nonlinearity. As with mean-field models, the dynamo period presumably depends sensitively on the assumed value of (turbulent) magnetic diffusivity, and equatorward propagation of the dynamo wave requires a negative α-effect at low latitudes.
4.7.3 Critical assessment
Although it has not yet been comprehensively studied, this dynamo mechanism has a number of very attractive properties. It operates without difficulty in the strong field regime (in fact it requires strong fields to operate). It also naturally yields dynamo action concentrated at low latitudes, so that a solar-like butterfly diagram can be readily produced from a negative α-effect even with a solar-like differential rotation profile, at least judging from the solutions presented in Schmitt et al. (1996) and Ossendrijver (2000a,b).
Difficulties include the need of a relatively finely tuned magnetic diffusivity to achieve a solar-like dynamo period, and a finely tuned level of subadiabaticity in the overshoot layer for the instability to kick on and off at the appropriate toroidal field strengths (compare Figures 1 and 2 in Ferriz-Mas et al., 1994). The non-linear saturation of the instability is probably less of an issue here than with the α-effect based on purely hydrodynamical shear instability (see Section 4.5 above), since, as the instability grows, the flux ropes leave the site of dynamo action by entering the convection zone and buoyantly rising to the surface.
The effects of meridional circulation in this class of dynamo models has yet to be investigated; this should be particularly interesting, since both analytic calculations and numerical simulations suggest a positive α-effect in the Northern hemisphere, which should then produce poleward propagation of the dynamo wave at low latitude. Meridional circulation could then perhaps produce equatorward propagation of the dynamo magnetic field even with a positive α-effect, as it does in true mean-field models (cf. Section 4.4).
4.8 Babcock-Leighton models
Solar cycle models based on what is now called the Babcock-Leighton mechanism were first proposed by Babcock (1961) and further elaborated by Leighton (1964, 1969), yet they were all but eclipsed by the rise of mean-field electrodynamics in the mid- to late 1960s. Their revival was motivated not only by the mounting difficulties with mean-field models alluded to earlier, but also by the fact that synoptic magnetographic monitoring over solar cycles 21 and 22 has offered strong evidence that the surface polar field reversals are indeed triggered by the decay of active regions (see Wang et al., 1989; Wang and Sheeley Jr, 1991, and references therein). The crucial question is whether this is a mere side-effect of dynamo action taking place independently somewhere in the solar interior, or a dominant contribution to the dynamo process itself.
The mode of operation of a generic solar cycle model based on the Babcock-Leighton mechanism is illustrated in cartoon form in Figure 16. Let Pn represent the amplitude of the high-latitude, surface (“A”) poloidal magnetic field in the late phases of cycle n, i.e., after the polar field has reversed. The poloidal field Pn is advected downward by meridional circulation (A → B), where it then starts to be sheared by the differential rotation while being also advected equatorward (B → C). This leads to the growth of a new low-latitude (C) toroidal flux system Tn+1, which becomes buoyantly unstable (C→D) and starts producing sunspots (D) which subsequently decay and release the poloidal flux Pn+1 associated with the new cycle n + 1. Poleward advection and accumulation of this new flux at high latitudes (D→A) then obliterates the old poloidal flux Pn, and the above sequence of steps begins anew.
Operation of a solar cycle model based on the Babcock-Leighton mechanism. The diagram is drawn in a meridional quadrant of the Sun, with streamlines of meridional circulation plotted in blue. Poloidal field having accumulated in the surface polar regions (“A”) at cycle n must first be advected down to the core-envelope interface (dotted line) before production of the toroidal field for cycle n + 1 can take place (B→C). Buoyant rise of flux rope to the surface (C→D) is a process taking place on a much shorter timescale.
Meridional circulation clearly plays a key role in this “conveyor belt” model of the solar cycle, by providing the needed link between the two spatially segregated source regions. Not surprisingly, topologically more complex multi-cells circulation patterns can lead to markedly different dynamo behavior (see, e.g., Bonanno et al., 2006; Jouve and Brun, 2007), and can also have a profound impact on the evolution of the surface magnetic field (Dikpati et al., 2004; Jiang et al., 2009).
4.8.1 Formulation of a poloidal source term
As with all other dynamo models discussed thus far, the troublesome ingredient in dynamo models relying on the Babcock-Leighton mechanism is the specification of an appropriate poloidal source term, to be incorporated into the mean-field axisymmetric dynamo equations. In essence, all implementations discussed here are inspired by the results of numerical simulations of the buoyant rise of thin flux tubes, which, in principle allow to calculate the emergence latitudes and tilts of BMRs, which is at the very heart of the Babcock-Leighton mechanism.
The first post-helioseismic dynamo model based on the Babcock-Leighton mechanism is due to Wang et al. (1991); these authors developed a coupled two-layer model (2 × 1D), where a poloidal source term is introduced in the upper (surface) layer, and made linearly proportional to the toroidal field strength at the corresponding latitude in the bottom layer. A similar non-local approach was later used by Dikpati and Charbonneau (1999), Charbonneau et al. (2005) and Guerrero and de Gouveia Dal Pino (2008) in their 2D axisymmetric model implementation, using a solar-like differential rotation and meridional flow profiles similar to Figures 5 and 10 herein. The otherwise much similar implementation of Nandy and Choudhuri (2001, 2002) and Chatterjee et al. (2004), on the other hand, uses a mean-field-like local α-effect, concentrated in the upper layers of the convective envelope and operating in conjunction with a “buoyancy algorithm” whereby toroidal fields located at the core-envelope interface are locally removed and deposited in the surface layers when their strength exceed some preset threshold. The implementation developed by Durney (1995) is probably closest to the essence of the Babcock-Leighton mechanism (see also Durney et al., 1993; Durney, 1996, 1997); whenever the deep-seated toroidal field exceeds some preset threshold, an axisymmetric “double ring” of vector potential is deposited in the surface layer, and left to spread latitudinally under the influence of magnetic diffusion. As shown by Muñoz-Jaramillo et al. (2010b), this formulation, used in conjunction with the axisymmetric models discussed in what follows, also leads to a good reproduction of the observed synoptic evolution of surface magnetic flux.
In all cases the poloidal source term is concentrated in the outer convective envelope, and, in the language of mean-field electrodynamics, amounts to a positive α-effect, in that a positive dipole moment is being produced from a positive deep-seated mean toroidal field. The Dikpati and Charbonneau (1999) and Nandy and Choudhuri (2001) source terms both have an α-quenching-like upper operating threshold on the toroidal field strength. This is motivated by simulations of rising thin flux tubes, indicating that tubes with strengths in excess of about 100 kG emerge without the E-W tilt required for the Babcock-Leighton mechanism to operate. The Durney (1995), Nandy and Choudhuri (2001), and Charbonneau et al. (2005) implementations also have a lower operating threshold, as suggested by thin flux tubes simulations.
4.8.2 Representative results
Figure 17 is a meridional plane animation of a representative Babcock-Leighton dynamo solution computed following the model implementation of Charbonneau et al. (2005). The equatorward advection of the deep toroidal field by meridional circulation is here clearly apparent. Note also how the surface poloidal field first builds up at low latitudes, and is subsequently advected poleward and concentrated near the pole.
mpg-Movie (6019.31738281 KB) Still from a movie showing Meridional plane animation of a representative Babcock-Leighton dynamo solution from Charbonneau et al. (2005). Color coding of the toroidal field and poloidal fieldlines as in Figure 7. This solution uses the same differential rotation, magnetic diffusivity, and meridional circulation profile as for the advection-dominated αΩ solution of Section 4.4, but now with the non-local surface source term, as formulated in Charbonneau et al. (2005), and parameter values Cα = 5, CΩ = 5 × 104, Δη = 0.003, Rm = 840. Note again the strong amplification of the surface polar fields, the latitudinal stretching of poloidal fieldlines by the meridional flow at the core-envelope interface. (For video see appendix)
Figure 18 shows N-hemisphere time-latitude diagrams for the toroidal magnetic field at the core-envelope interface (Panel A), and the surface radial field (Panel B), for a Babcock-Leighton dynamo solution now computed following the closely similar model implementation of Dikpati and Charbonneau (1999). Note how the polar radial field changes from negative (blue) to positive (red) at just about the time of peak positive toroidal field at the core-envelope interface; this is the phase relationship inferred from synoptic magnetograms (see, e.g., Figure 4 herein) as well as observations of polar faculae (see Sheeley Jr, 1991).
Time-latitude diagrams of the toroidal field at the core-envelope interface (Panel A), and radial component of the surface magnetic field (Panel B) in a Babcock-Leighton model of the solar cycle. This solution is computed for solar-like differential rotation and meridional circulation, the latter here closing at the core-envelope interface. The core-to-envelope contrast in magnetic diffusivity is Δη = 1/300, the envelope diffusivity ηT = 2.5 × 1011 cm2 s-1, and the (poleward) mid-latitude surface meridional flow speed is u0 = 16 m s-1.
Although it exhibits the desired equatorward propagation, the toroidal field butterfly diagram in Panel A of Figure 18 peaks at much higher latitude (∼ 45°) than the sunspot butterfly diagram (∼ 15° – 20°, cf. Figure 3). This occurs because this is a solution with high magnetic diffusivity contrast, where meridional circulation closes at the core-envelope interface, so that the latitudinal component of differential rotation dominates the production of the toroidal field, a situation that persists in models using more realistic differential profiles taken from helioseismic inversions (see Muñoz-Jaramillo et al., 2009). This difficulty can be alleviated by letting the meridional circulation penetrate below the core-envelope interface. Solutions with such flows are presented, e.g., in Dikpati and Charbonneau (1999) and Nandy and Choudhuri (2001, 2002). These latter authors have argued that this is in fact essential for a solar-like butterfly diagram to materialize, but this conclusion appears to be model-dependent at least to some degree (Guerrero and Muñoz, 2004; Guerrero and de Gouveia Dal Pino, 2007; Muñoz-Jaramillo et al., 2009). From the hydrodynamical standpoint, the boundary layer analysis of Gilman and Miesch (2004) (see also Rüdiger et al., 2005) indicates no significant penetration below the base of the convective envelope, although this conclusion has not gone unchallenged (see Garaud and Brummell, 2008), leaving the whole issue somewhat muddled at this juncture. The present-day observed solar abundances of Lithium and Beryllium restrict the penetration depth to r/R ≃ 0.62 (Charbonneau, 2007b), which is unfortunately too deep to pose very useful constraints on dynamo models, so that the final word will likely come from helioseismology, hopefully in the not too distant future.
A noteworthy property of this class of model is the dependency of the cycle period on model parameters; over a wide portion of parameter space, the meridional flow speed is found to be the primary determinant of the cycle period P. For example, in the Dikpati and Charbonneau (1999) model, this quantity is found to scale as
This behavior arises because, in these models, the two source regions are spatially segregated, and the time required for circulation to carry the poloidal field generated at the surface down to the tachocline is what effectively sets the cycle period. The corresponding time delay introduced in the dynamo process has rich dynamical consequences, to be discussed in Section 5.4 below. The weak dependency of P on ηT and on the magnitude ..0 of the poloidal source term is very much unlike the behavior typically found in mean-field models, where both these parameters usually play a dominant role in setting the cycle period. The analysis of Hathaway et al. (2003) supports the idea that the solar cycle period is indeed set by the meridional flow speed (but do see Schmitt and Schüssler, 2004, for an opposing viewpoint). As demonstrated by Jouve et al. (2010), interesting constraints can also be obtained from the observed dependence of stellar cycle periods on rotation rates.
An interesting variation on the above model follows from the inclusion of turbulent pumping. With the expected downward pumping throughout the bulk of the convective envelope, and with a significant equatorward latitudinal component at low latitudes, the Babcock-Leighton mechanism can lead to dynamo action even if the meridional flow is constrained to the upper portion of the convective envelope. Downward turbulent pumping then links the two sources regions, and latitudinal pumping provides the needed equatorward concentration of the deep-seated toroidal component. An example taken from Guerrero and de Gouveia Dal Pino (2008) is shown in Figure 19. In this specific solution the circulation penetrates only down to r/R = 0.8, and the radial and latitudinal peak pumping speed are γr0 = 0.3 m s-1 and γθ0 = 0.9 m s-1, respectively.
Time-latitude diagrams of the toroidal field at the core-envelope interface (Panel A), and radial component of the surface magnetic field (Panel B) in a Babcock-Leighton model of the solar cycle with a meridional flow restricted to the upper half of the convective envelope, and including (parametrized) radial and latitudinal turbulent pumping. This is a solution from Guerrero and de Gouveia Dal Pino (2008) (see their Section 3.3 and Figure 5), but the overall modelling framework is almost identical to that described earlier, and used to generate Figure 18. The core-to-envelope contrast in magnetic diffusivity is Δη = 1/100, the envelope diffusivity ηT = 1011 cm2 s-1, and the (poleward) mid-latitude surface meridional flow speed is u0 = 13 m s-1 (figure produced from numerical data kindly provided by G. Guerrero).
With downward turbulent pumping now the primary mechanism linking the surface and tachocline, the dynamo period loses sensitivity to the meridional flow speeds, and becomes set primary by the radial pumping speed. Indeed the dynamo solutions presented Guerrero and de Gouveia Dal Pino (2008) are found to obey a scaling law of the form
over a fairly wide range of parameter values. The radial pumping speed γr0 emerges here as the primary determinant of the cycle period. Finally, one can note in Figure 19 that the surface magnetic field no longer shows the strong concentration in the polar region that usually characterizes Babcock-Leighton dynamo solutions operating in the advection-dominate regime. This can be traced primarily to the efficient downward turbulent pumping that subducts the poloidal field as it is carried poleward by the meridional flow.
4.8.3 Critical assessment
As with most models including meridional circulation published to date, Babcock-Leighton dynamo models usually produce excessively strong polar surface magnetic fields. While this difficulty can be fixed by increasing the magnetic diffusivity in the outermost layers, in the context of the Babcock-Leighton models this then leads to a much weaker poloidal field being transported down to the tachocline, which can be problematic from the dynamo point-of-view. On this see Dikpati et al. (2004) for illustrative calculations, and Mason et al. (2002) on the closely related issue of competition between surface and deep-seated α-effect. The model calculations of Guerrero and de Gouveia Dal Pino (2008) suggest that downward turbulent pumping may be a better option to reduce the strength of the polar field without impeding dynamo action.
Because of the strong amplification of the surface poloidal field in the poleward-converging meridional flow, Babcock-Leighton models tend to produce a significant — and often dominant — polar branch in the toroidal field butterfly diagram. Many of the models explored to date tend to produce symmetric-parity solutions when computed pole-to-pole over a full meridional plane (see, e.g., Dikpati and Gilman, 2001), but it is not clear how serious a problem this is, as relatively minor changes to the model input ingredients may flip the dominant parity (see Chatterjee et al., 2004; Charbonneau, 2007a, for specific examples). Nonetheless, in the advection-dominated regime there is definitely a tendency for the quadrupolar symmetry of the meridional flow to imprint itself on the dynamo solutions. A related difficulty, in models operating in the advection-dominated regime, is the tendency for the dynamo to operate independently in each solar hemisphere, so that cross-hemispheric synchrony is lost (Charbonneau, 2005, 2007a; Chatterjee and Choudhuri, 2006).
Because the Babcock-Leighton mechanism is characterized by a lower operating threshold, the resulting dynamo models are not self-excited. On the other hand, the Babcock-Leighton mechanism is expected to operate even for toroidal fields exceeding equipartition, the main uncertainties remaining the level of amplification taking place when sunspot-forming toroidal flux ropes form from the dynamo-generated mean magnetic field. The nonlinear behavior of this class of models, at the level of magnetic backreaction on the differential rotation and meridional circulation, remains largely unexplored.
4.9 Numerical simulations of solar dynamo action
Ultimately, the solar dynamo problem should be tackled as a (numerical) solution of the complete set of MHD partial differential equations in a rotating, stratified spherical domain undergoing thermally-driven turbulent convection in its outer 30% in radius. The first full-fledged attempts to do so go back some some thirty years, to the simulations of Gilman and Miller (1981); Gilman (1983); Glatzmaier (1985a,b). These epoch-making simulations did produce cyclic dynamo action and latitudinal migratory patterns suggestive of the dynamo waves of mean-field theory. However, the associated differential rotation profile turned out non-solar, as did the magnetic field’s spatio-temporal evolution. In retrospect this is perhaps not surprising, as limitations in computing resources forced these simulations to be carried out in a parameter regime far removed from solar interior conditions. Later simulations taking advantages of massively parallel computing architectures did managed to produce tolerably solar-like mean internal differential rotation (see, e.g., Miesch and Toomre, 2009, and references therein), as well as copious small-scale magnetic field, but failed to generate a spatially well-organized large-scale magnetic component (see Brun et al., 2004). Towards this end the inclusion of a stably stratified fluid layer below the convecting layers is now believed to be advantageous (although not strictly necessary, see Brown et al., 2010) as it allows the development of a tachocline-like shear layer where magnetic field produced within the convection zone can accumulate in response to turbulent pumping from above, and be further amplified by the rotational shear (see Browning et al., 2006, also Tobias et al., 2001, 2008, and references therein, for related behavior in local cartesian simulations).
Some of these simulations are now beginning to yield regular polarity reversals of the large-scale magnetic components. Figures 20 and 21 present some sample results taken from Ghizaru et al. (2010), see also Brown et al. (2009) and Käpylä et al. (2010). Figure 20 is an animation in Mollweide latitude-longitude projection of the toroidal magnetic component 0.02R⊙ below the nominal interface between the convecting layers and underlying stable layers in one of these simulations. This toroidal component reaches some 2.5 kG here, and shows a very clear global antisymmetry about the equator, despite strong spatiotemporal fluctuations produced by convective undershoot. The cyclic variation of this large-scale field is quite apparent on the animation, with polarity reversals approximately synchronous across hemispheres.
mpg-Movie (31113.9941406 KB) Still from a movie showing Latitude-Longitude Mollweide projection of the toroidal magnetic component at depth r/R = 0.695 in the 3D MHD simulation of Ghizaru et al. (2010). This large-scale axisymmetric component shows a well-defined overall antisymmetry about the equatorial plane, and undergoes polarity reversals approximately every 30 yr. The animation spans a little over three half-cycles, including three polarity reversals. Time is given in solar days, with 1 s.d. = 30 d. (For video see appendix)
Figure 21A shows, for the same simulation as in Figure 20, a time-latitude diagram of the zonally-averaged toroidal component, now constructed at a depth corresponding to the core-envelope interface in the model. This is again assumed to be the simulation’s equivalent to the sunspot butterfly diagram. This simulation was run for 255 yr, in the course of which eight polarity reversals have taken place, with a mean (half-)period of about 30 yr. Note the tendency for equatorward migration of the toroidal flux structures, and the good long-term synchrony between the Northern and Southern hemispheres, persisting despite significant fluctuations in the amplitude and duration of cycles in each hemiphere. Figure 21B shows the corresponding time-evolution of the zonaly-averaged radial surface magnetic component, again in a time-latitude diagram. The surface field is characterized by a well-defined dipole moment aligned with the rotational axis, with transport of surface fields taking place from lower latitudes and (presumably) contributing to the reversal of the dipole moment. Compare these time-latitude diagrams to the sunspot butterfly diagram of Figure 3 and synoptic magnetogram of Figure 4, and reflect upon the similarities and differences.
(A) Time-latitude diagram of the zonally-averaged toroidal magnetic component the coreenvelope interface (r/R = 0.718) and (B) corresponding time-latitude diagram of the surface radial field, in the 3D MHD simulations presented in Ghizaru et al. (2010). Note the regular polarity reversals, the weak but clear tendency towards equatorial migration of the deep toroidal magnetic component, and the good coupling between the two hemispheres despite marked fluctuations in successive cycles. The color scale codes the magnetic field strength, in Tesla.
Although much remains to be investigated regarding the mode of dynamo action in these simulations, some encouraging links to mean-field theory (Section 3.2.1) do emerge. The fact that a positive toroidal component breeds here a positive dipole moment is what one would expect from a turbulent α-effect (more precisely, the αφφ tensor component) positive in the Northern hemisphere. A posteriori calculation of the mean electromotive force \(\mathcal{E} = \left\langle {u' \times B'} \right\rangle\) does reveal a clear hemispheric pattern, with εφ having the same sign in both hemisphere, but changing sign from one cycle to the next, again consistent with the idea that the turbulent ..-effect is the primary source of the large-scale poloidal component. Likewise, having a well-defined axisymmetric dipolar component being sheared by an axisymmetric differential rotation is consistent with the buildup of a large-scale toroidal component antisymmetric about the equatorial plane.
On the other hand, calculation of the r and θ-components of the mean electromotive force indicates that the latter contributes to the production of the toroidal field at a level comparable to shearing of the poloidal component by differential rotation, suggestive of what, in mean-field electrodynamics parlance, is known as an α2Ω dynamo. Calculation of the α-tensor components also reveals that the latter do not undergo significant variations between maximal and minimal phases of the cycle, suggesting that α-quenching is not the primary amplitude-limiting mechanism in this specific simulation run. Although it would premature to claim that these simulations vindicate the predictions of mean-field theory, to the level at which they have been analyzed thus far, they do not appear to present outstanding departures from the mean-field Weltanschau.
5 Amplitude Fluctuations, Multiperiodicity, and Grand Minima
Since the basic physical mechanism(s) underlying the operation of the solar cycle are not yet agreed upon, attempting to understand the origin of the observed fluctuations of the solar cycle may appear to be a futile undertaking. Nonetheless, work along these lines continues at full steam in part because of the high stakes involved; varying levels of solar activity may contribute significantly to climate change (see Haigh, 2007, and references therein). Moreover, the frequencies of all eruptive phenomena relevant to space weather are strongly modulated by the amplitude of the solar cycle. Finally, certain aspects of the observed fluctuations may actually hold important clues as to the physical nature of the dynamo process.
5.1 The observational evidence: An overview
Hathaway (2010) offers a comprehensive review of the observational phenomenology of the solar cycle, as viewed through the sunspot number and other activity indicators; what follows is restricted to feature having most direct bearing on dynamo modeling. Panel A of Figure 22 shows a time series of the so-called Zürich sunspot numbers, starting in the mid-eighteenth century and extending to the present. The 11-year sunspot cycle is the most obvious feature of this time series, although the period of the underlying magnetic cycle is in fact twice that (sunspot counts being insensitive to magnetic polarity). Cycle-to-cycle variations in sunspot counts are usually taken to indicate a corresponding variation in the amplitude of the Sun’s dynamo-generated internal magnetic field. As reasonable as this may sound, it remains a working assumption; at this writing, the process via which the dynamo-generated mean magnetic field produces sunspot-forming concentrated flux ropes is not understood. One should certainly not take for granted that a difference by a factor of two in sunspot count indicates a corresponding variation by a factor of two in the strength of the internal magnetic field.
Fluctuations of the solar cycle, as measured by the sunspot number. Panel A is a time series of the Zürich monthly sunspot number (with a 13-month running mean in red). Cycles are numbered after the convention introduced in the mid-nineteenth century by Rudolf Wolf. Note how cycles vary significantly in both amplitude and duration. Panel B is a portion of the 10Be time series spanning the Maunder Minimum (data courtesy of J. Beer). Panel C shows a time series of the yearly group sunspot number of Hoyt and Schatten (1998) (see also Hathaway et al., 2002) over the same time interval, together with the yearly Zürich sunspot number (purple) and auroral counts (green). Panels D and E illustrate the pronounced anticorrelation between cycle amplitude and rise time (Waldmeier Rule), and alternation of higher-thanaverage and lower-that-average cycle amplitudes (Gnevyshev-Ohl Rule, sometimes also referred to as the “odd-even effect”).
At any rate, the notion of a nicely regular 11/22-year cycle does not hold long upon even cursory scrutiny, as the amplitude of successive cycles is clearly not constant, and their overall shape often differs significantly from one cycle to another (cf. cycles 14 and 15 in Panel A of Figure 22). Closer examination of Figure 22 also reveals that even the cycle’s duration is not uniform, spanning in fact a range going from 9 yr (cycle 2) to nearly 14 yr (cycles 4 and 23). These amplitude and duration variations are not a sunspot-specific artefact; similar variations are in fact observed in other activity proxies with extended records, most notably the 10.7 cm radio flux (Tapping, 1987), polar faculae counts (Sheeley Jr, 1991), and the cosmogenic radioisotopes 14C and 10Be (Beer et al., 1991; Beer, 2000).
Equally striking is the pronounced dearth of sunspots in the interval 1645 – 1715 (see Panel C of Figure 22); this is not due to lack of observational data (see Ribes and Nesme-Ribes, 1993; Hoyt and Schatten, 1996), but represents instead a phase of strongly suppressed activity now known as the Maunder Minimum (Eddy, 1976, 1983, and references therein). Evidence from cosmogenic radioisotopes indicates that similar periods of suppressed activity have taken place in ca. 1282 – 1342 (Wolf Minimum) and ca. 1416 – 1534 (Spörer Minimum), as well as a period of enhanced activity in ca. 1100 – 1250 (the Medieval Maximum), and have recurred irregularly over the more distant past (Usoskin, 2008).
The various incarnations of the sunspot number time series (monthly SSN, 13-month smoothed SSN, yearly SSN, etc.) are arguably the most intensely studied time series in astrophysics, as measured by the number of published research paper pages per data points. Various correlations and statistical trends have been sought in these datasets. Panels D and E of Figure 22 present two such classical trends. The “Waldmeier Rule”, illustrated in Panel D of Figure 22, refers to a statistically significant anticorrelation between cycle amplitude and rise time (linear correlation coefficient r = -0.68). A similar anticorrelation exists between cycle amplitude and duration, but is statistically more dubious (r = -0.37). The “Gnevyshev-Ohl” rule, illustrated in Panel E of Figure 22, refers to a marked tendency for odd (even) numbered cycles to have amplitudes above (below) their running mean (blue line in Panel E of Figure 22), a pattern that seems to have held true without interruption between cycles 9 and 21 (see also Mursula et al., 2001). For more on these empirical sunspot “Rules”, see Hathaway (2010).
A number of long-timescale modulations have also been extracted from these data, most notably the so-called Gleissberg cycle (period = 88 yr), but the length of the sunspot number record is insufficient to firmly establish the reality of these periodicities. One must bring into the picture additional solar cycle proxies, primarily cosmogenic radioisotopes, but difficulties in establishing absolute amplitudes of production rates introduce additional uncertainties into what is already a complex endeavour (for more on these matters, see Beer, 2000; Usoskin and Mursula, 2003). Likewise, the search for chaotic modulation in the sunspot number time series has produced a massive literature (see, e.g., Feynman and Gabriel, 1990; Mundt et al., 1991; Carbonell et al., 1994; Rozelot, 1995, and references therein), but without really yielding firm, statistically convincing conclusions, again due to the insufficient lengths of the datasets.
The aim in this section is to examine in some detail the types of fluctuations that can be produced in the various dynamo models discussed in the preceding sectionFootnote 9. After going briefly over the potential consequences of fossil fields (Section 5.2), dynamical nonlinearities are first considered (Section 5.3), followed by time-delay effects (Section 5.4). We then turn to stochastic forcing (Section 5.5), which leads naturally to the issue of intermittency (Section 5.6).
5.2 Fossil fields and the 22-yr cycle
The presence of a large-scale, quasi-steady magnetic field of fossil origin in the solar interior has long been recognized as a possible explanation of the Gnevyshev-Ohl rule (Panel E of Figure 22). The basic idea is quite simple: The slowly-decaying, deep fossil field being effectively steady on solar cycle timescales, its superposition with the 11-yr polarity reversal of the overlying dynamogenerated field will lead to a 22-yr modulation, whereby the cycle is stronger when the fossil and dynamo field have the same polarity, and weaker when these polarities are opposite (see, e.g., Boyer and Levy, 1984; Boruta, 1996). The magnitude of the effect is directly related to the strength of the fossil field, versus that of the dynamo-generated magnetic field. All of this, however, presumes that flows and dynamical effects within the tachocline still allow “coupling” between the deep fossil field below, and the cyclic dynamo-generated field above. However, models of the solar tachocline taking into account its interaction with an underlying fossil field (see, e.g., Kitchatinov and Rüdiger, 2006) suggest that it is unlikely for this coupling to take place in the simple manner implicitly assumed in dynamo models, that typically incorporate the effect of fossil fields via the lower boundary condition (see also Dikpati et al., 2005).
One strong prediction is associated with this explanation of the Gnevyshev-Ohl rule: While the pattern may become occasionally lost due to large amplitude fluctuations of other origin, whenever it is present even-numbered cycles should always be of lower amplitudes and odd-numbered cycles of higher amplitude (under Wolf’s cycle numbering convention). Evidently, this prediction can be tested observationally, provided one can establish a measure of sunspot cycle amplitude that is truly characteristic of the strength of the underlying dynamo magnetic field. Taken at face value, the analysis of Mursula et al. (2001), based on cycle-integrated group sunspot numbers, indicates that the odd/even pattern has reversed between the time periods 1700 – 1800 and 1850 – 1990 (see their Figure 1). This would then rule out the fossil field hypothesis unless, as argued by some authors (see Usoskin et al., 2009a, and references therein), a sunspot cycle has been “lost” around 1790, at the onset of the so-called Dalton minimum.
5.3 Dynamical nonlinearity
5.3.1 Backreaction on large-scale flows
The dynamo-generated magnetic field will, in general, produce a Lorentz force that will tend to oppose the driving fluid motions. This is a basic physical effect that should be included in any dynamo model. It is not at all trivial to do so, however, since in a turbulent environment both the fluctuating and mean components of the magnetic field can affect both the large-scale flow components, as well as the small-scale turbulent flow providing the Reynolds stresses powering the large-scale flows. One can thus distinguish a number of (related) amplitude-limiting mechanisms:
-
Lorentz force associated with the mean magnetic field directly affecting large-scale flow (sometimes called the “Malkus-Proctor effect”, after the groudbreaking numerical investigations of Malkus and Proctor, 1975).
-
Large-scale magnetic field indirectly affecting large-scale flow via effects on small-scale turbulence and associated Reynolds stresses (sometimes called “Λ-quenching”, see, e.g., Kitchatinov and Rüdiger, 1993).
-
Maxwell stresses associated with small-scale magnetic field directly affecting flows at all scales.
The α-quenching formulae introduced in Section 4.2.1 is a particularly simple — some would say simplistic — way to model the backreaction of the magnetic field on the turbulent fluid motions producing the α-effectFootnote 10. In the context of solar cycle models, one could also expect the Lorentz force to reduce the amplitude of differential rotation until the effective dynamo number falls back to its critical value, at which point the dynamo again saturatesFootnote 11. The third class of quenching mechanism listed above has not yet been investigated in detail, but numerical simulations of MHD turbulence indicate that the effects of the small-scale turbulent magnetic field on the α-effect can be profound (see Pouquet et al., 1976; Durney et al., 1993; Brandenburg, 2009; Cattaneo and Hughes, 2009).
Introducing magnetic backreaction on differential rotation is a tricky business, because one must then also, in principle, provide a model for the Reynolds stresses powering the large-scale flows in the solar convective envelope (see, e.g., Kitchatinov and Rüdiger, 1993), as well as a procedure for computing magnetic backreaction on these. This rapidly leads into the unyielding realm of MHD turbulence, although algebraic “Λ-quenching” formulae akin to α-quenching have been proposed based on specific turbulence models (see, e.g., Kitchatinov et al., 1994). Alternately, one can add an ad hoc source term to the right hand side of Equation (2), designed in such a way that in the absence of the magnetic field, the desired solar-like large-scale flow is obtained. As a variation on this theme, one can simply divide the large-scale flow into two components, the first (U) corresponding to some prescribed, steady profile, and the second (U′) to a time-dependent flow field driven by the Lorentz force (see, e.g., Tobias, 1997; Moss and Brooke, 2000; Thelen, 2000b):
with the (non-dimensional) governing equation for U′ including only the Lorentz force and a viscous dissipation term on its right hand side. If u amounts only to differential rotation, then B′ must obey a (nondimensional) differential equation of the form
where time has been scaled according to the magnetic diffusion time \(\tau = R_ \odot ^2 /\eta _T\) as before. Two dimensionless parameters appear in Equation (37). The first (Λ) is a numerical parameter measuring the influence of the Lorentz force, and which can be set to unity without loss of generality (cf. Tobias, 1997; Phillips et al., 2002). The second, Pm = v/η, is the magnetic Prandtl number. It measures the relative importance of viscous and Ohmic dissipation. When Pm ≪ 1, large velocity amplitudes in U′ can be produced by the dynamo-generated mean magnetic field. This effectively introduces an additional, long timescale in the model, associated with the evolution of the magnetically-driven flow; the smaller Pm, the longer that timescale (cf. Figures 4 and 10 in Brooke et al., 1998).
The majority of studies published thus far and using this approach have only considered the nonlinear magnetic backreaction on differential rotation. This has been shown to lead to a variety of behaviors, including amplitude and parity modulation, periodic or aperiodic, as well as intermittency (more on the latter in Section 5.6).
Figure 23 shows two butterfly diagrams produced by the nonlinear mean-field interface model of Tobias 1997 (see also Beer et al., 1998; Bushby, 2006). The model is defined on a Cartesian slab with a reference differential rotation varying only with depth, and includes backreaction on the differential rotation according to the procedure described above. The model exhibits strong, quasi-periodic modulation of the basic cycle, leading to epochs of strongly reduced amplitude, with the modulation period controlled by the magnetic Prandtl number. Note how the dynamo can emerge from such epochs with strong hemispheric asymmetries (top panel), or with a different parity (bottom panel).
Amplitude and parity modulation in a 1D slab dynamo model including magnetic backreaction on the differential rotation. These are the usual time-latitude diagrams for the toroidal magnetic field, now covering both solar hemispheres, and exemplify the two basic types of modulation arising in nonlinear dynamo models with backreaction on the differential rotation (see text; figure kindly provided by S.M. Tobias).
It is not clear, at this writing, to what degree these behaviors are truly generic, as opposed to model-dependent. The analysis of Knobloch et al. (1998) suggests that generic behaviors do exist. On the other hand, a number of counterexamples have been published, showing that even in a qualitative sense, the nonlinear behavior can be strongly dependent on what one would have hoped to be minor modelling details (see, e.g., Moss and Brooke, 2000; Phillips et al., 2002).
The differential rotation can also be suppressed indirectly by magnetic backreaction on the small-scale turbulent flows that produce the Reynolds stresses driving the large-scale mean flow. Inclusion of this so-called “Λ-quenching” in mean-field dynamo models, alone or in conjunction with other amplitude-limiting nonlinearities, has also been shown to lead to a variety of periodic and aperiodic amplitude modulations, provided the magnetic Prandtl number is small (see Küker et al., 1999; Pipin, 1999; Rempel, 2006b). This type of models stand or fall with the turbulence model used to compute the various mean-field coefficients, and it is not yet clear which aspects of the results are truly generic to Λ-quenching. Gizon and Rempel (2008) do show that information is present in subsurface measurements of the time-varying component of large-scale flows, which can be used to constrain the Λ-effect and its cycle-related variations.
To date, dynamical backreaction on large-scale flows has only been studied in detail in the context of dynamo models based on mean-field electrodynamics. Equivalent studies must be carried out in the other classes of solar cycle models discussed in Section 4. In particular, it is essential to model the effect of the Lorentz force on meridional circulation in models based on the Babcock- Leighton mechanism and/or hydrodynamical instabilities in the tachocline, since in these models the circulation is the primary determinant of the cycle period and enforces equatorward propagation in the butterfly diagram.
5.3.2 Dynamical α-quenching
A number of authors have attempted to bypass the shortcomings of α-quenching by introducing into dynamo models an additional, physically-inspired partial differential equation for the α-coefficient itself (e.g., Kleeorin et al., 1995; Blackman and Brandenburg, 2002, and references therein). The basic physical idea is that magnetic helicity must be conserved in the high-Rm regime, so that production of helicity in the mean field implies a corresponding production of helicity of opposite sign at the scales of the fluctuating components of the flow and field, which ends up acting in such a way as to reduce the α-effect. Most investigations published to date have made used of severely truncated models, and/or models in one spatial dimensions (see, e.g., Weiss et al., 1984; Schmalz and Stix, 1991; Jennings and Weiss, 1991; Roald and Thomas, 1997; Covas et al., 1997; Blackman and Brandenburg, 2002), so that the model results can only be compared to solar data in some general qualitative sense. Rich dynamical behavior definitely arises in such models, including multiperiodicity, amplitude modulation, and chaos, and some of these behaviors do carry over to into a two-dimensional spherical axisymmetric mean-field dynamo model (see Covas et al., 1998).
5.4 Time-delay dynamics
The introduction of ad hoc time-delays in dynamo models is long known to lead to pronounced cycle amplitude fluctuations (see, e.g., Yoshimura, 1978). Models including nonlinear backreaction on differential rotation can also exhibit what essentially amounts to time-delay dynamics in the low Prandtl number regime, with the large-scale flow perturbations lagging behind the Lorentz force because of inertial effects. Finally, time-delay effects can arise in dynamo models where the source regions for the poloidal and toroidal magnetic components are spatially segregated. This is a type of time delay we now turn to, in the context of dynamo models based on the Babcock-Leighton mechanism.
5.4.1 Time-delays in Babcock-Leighton models
It was already noted that in solar cycle models based on the Babcock-Leighton mechanism of poloidal field generation, meridional circulation effectively sets — and even regulates — the cycle period (cf. Section 4.8.2; see also Dikpati and Charbonneau, 1999; Charbonneau and Dikpati, 2000; Muñoz-Jaramillo et al., 2009). In doing so, it also introduces a long time delay in the dynamo mechanism, “long” in the sense of being comparable to the cycle period. This delay originates with the time required for circulation to advect the surface poloidal field down to the core-envelope interface, where the toroidal component is produced (A→C in Figure 16). In contrast, the production of poloidal field from the deep-seated toroidal field (C→D), is a “fast” process, growth rates and buoyant rise times for sunspot-forming toroidal flux ropes being of the order of a few months (see Moreno-Insertis, 1986; Fan et al., 1993; Caligari et al., 1995, and references therein). The first, long time delay turns out to have important dynamical consequences.
5.4.2 Reduction to an iterative map
The long time delay inherent in B-L models of the solar cycle allows a formulation of cycle-tocycle amplitude variations in terms of a simple one-dimensional iterative map (Durney, 2000; Charbonneau, 2001). Working in the kinematic regime, neglecting resistive dissipation, and in view of the conveyor belt argument of Section 4.8, the toroidal field strength Tn+1 at cycle n + 1 is assumed to be linearly proportional to the poloidal field strength Pn of cycle n, i.e.,
Now, because flux eruption is a fast process, the strength of the poloidal field at cycle n + 1 is (nonlinearly) proportional to the toroidal field strength of the current cycle:
Here the “Babcock-Leighton” function ƒ(Tn+1) measures the efficiency of surface poloidal field production from the deep-seated toroidal field. Substitution of Equation (38) into Equation (39) leads immediately to a one-dimensional iterative map,
where the pn’s are normalized amplitudes, and the normalization constants as well as the constant a in Equation (38) have been absorbed into the definition of the map’s parameter a, here operationally equivalent to a dynamo number (see Charbonneau, 2001). We consider here the following nonlinear function,
with p1 = 0.6, w1 = 0.2, p2 = 1.0, and w2 = 0.8. This catches an essential feature of the B-L mechanism, namely the fact that it can only operate in a finite range of toroidal field strength.
A bifurcation diagram for the resulting iterative map is presented in Panel A of Figure 24. For a given value of the map parameter α, the diagram gives the locus of the amplitude iterate pn for successive n values. The “critical dynamo number” above which dynamo action becomes possible, is here α = 0.851 (pn = 0 for smaller α values). For 0.851 ≤ α ≤ 1.283, the iterate is stable at some finite value of pn, which increases gradually with α. This corresponds to a constant amplitude cycle. As α reaches 1.283, period doubling occurs, with the iterate pn alternating between high and low values (e.g., pn = 0.93 and pn = 1.41 at α = 1.4). Further period doubling occurs at α = 1.488, then at α = 1.531, then again at α = 1.541, and ever faster until a point is reached beyond which the amplitude iterate seems to vary without any obvious pattern (although within a bounded range); this is in fact a chaotic regime.
As in any other dynamo model where the source regions for the poloidal and toroidal magnetic field components are spatially segregated, the type of time delay considered here is unavoidable. The B-L model is just a particularly clear-cut example of such a situation. One is then led to anticipate that the map’s rich dynamical behavior should find its counterpart in the original, arguably more realistic spatially-extended, diffusive axisymmetric model that inspired the map formulation. Remarkably, this is indeed the case.
Panel B of Figure 24 shows a bifurcation diagram, conceptually equivalent to that shown in Panel A, but now constructed from a sequence of numerical solutions of the Babcock-Leighton model of Charbonneau et al. (2005), for increasing values of the dynamo number. Time series of magnetic energy were calculated from the numerical solutions, and successive peaks found and plotted for each individual solution. The sequence of period doubling, eventually leading to a chaotic regime, is strikingly similar to the bifurcation diagram constructed from the corresponding iterative map, down to the narrow multiperiodic windows interspersed in the chaotic domain. This demonstrates that time delay effects are a robust feature, and represent a very powerful source of cycle amplitude fluctuation in Babcock-Leighton models, even in the kinematic regime (for further discussion see Charbonneau, 2001; Charbonneau et al., 2005; Wilmot-Smith et al., 2006).
Two bifurcation diagrams for a kinematic Babcock-Leighton model, where amplitude fluctuations are produced by time-delay feedback. The top diagram is computed using the one-dimensional iterative map given by Equations (40, 41), while the bottom diagram is reconstructed from numerical solutions in spherical geometry, of the type discussed in Section 4.8. The shaded area in Panel A maps the attraction basin for the cyclic solutions, with initial conditions located outside of this basin converging to the trivial solution pn = 0.
5.5 Stochastic forcing
Another means of producing amplitude fluctuations in dynamo models is to introduce stochastic forcing in the governing equations. Sources of stochastic “noise” certainly abound in the solar interior; large-scale flows in the convective envelope, such as differential rotation and meridional circulation, are observed to fluctuate, an unavoidable consequence of dynamical forcing by the surrounding, vigorous turbulent flow. Ample observational evidence now exists that a substantial portion of the Sun’s surface magnetic flux is continuously being reprocessed on a timescale commensurate with convective motions (see Schrijver et al., 1997; Hagenaar et al., 2003). The culprit is most likely the generation of small-scale magnetic fields by these turbulent fluid motions (see, e.g., Cattaneo, 1999; Cattaneo et al., 2003, and references therein). This amounts to a form of zero-mean “noise” superimposed on the slowly-evolving mean magnetic field. In addition, the azimuthal averaging implicit in all models of the solar cycle considered above will yield dynamo coefficients showing significant deviations about their mean values, as a consequence of the spatiotemporally discrete nature of the physical events (e.g., cyclonic updrafts, sunspot emergences, flux rope destabilizations, etc.) whose collective effects add up to produce a mean azimuthal electromotive force.
The (relative) geometrical and dynamical simplicity of the various types of dynamo models considered earlir severely restricts the manner in which such stochastic effects can be modeled. Perhaps the most straightforward is to let the dynamo number fluctuate randomly in time about some preset mean value. By most statistical estimates, the expected magnitude of these fluctuations is quite large, i.e., many times the mean value (Hoyng, 1988, 1993), a conclusion also supported by numerical simulations (see, e.g., Otmianowska-Mazur et al., 1997; Ossendrijver et al., 2001). One typically also introduces a coherence time during which the dynamo number retains a fixed value. At the end of this time interval, this value is randomly readjusted. Depending on the dynamo model at hand, the coherence time can be physically related to the lifetime of convective eddies (α-effect-based mean-field models), to the decay time of sunspots (Babcock-Leighton models), or to the growth rate of instabilities (hydrodynamical shear or buoyant MHD instability-based models).
Figure 25 shows some representative results for an αΩ dynamo solutions including meridional circulation and operating in the advection-dominated regime, similar to that of Figure 11, with imposed stochastic fluctuation at the ± 100% level in Cα, and coherence time amounting to 5% of the cycle period in the deterministic parent solution. The red curve is the total magnetic energy in the solution domain, used here as a measure of cycle amplitude and proxy for the sunspot number. The green curve is the absolute value of the N-hemisphere surface polar field strength. Perhaps the most striking feature of these curves is the fact that even with a coherence time much smaller than the cycle period, zero-mean stochastic forcing can induce patterns of amplitude modulation with characteristic timescales spanning many cycles (e.g., at 0.01 ≤ t/τ ≤ 0.11 and 0.49 ≤ t/τ ≤ 0.62 in Figure 25A). This can be traced to the buildup of strong magnetic fields in the low-diffusivity layers underlying the convective envelope.
Effect of stochastic fluctuations in the Cα dynamo number on an advection-dominated αΩ mean-field dynamo solution including meridional circulation (see Figure 11), here with Rm = 2500, CΩ = 5 × 105, Cα = 0.5, and Δη = 0.1. The fluctuation amplitude is ΔCα/Cα = 1, and the correlation time of the imposed fluctuations amounts to about 5% of the mean half-cycle period. Panel A shows a portion of the time series of total magnetic energy (red), used here as a proxy for cycle amplitude, and of the surface polar field strength (green), both scaled to their peak value over the full simulation run. Panel B shows a correlation plot of cycle amplitude and duration, both now normalized to their respective means over the simulation interval. Panel C snows a correlation plot of cycle amplitude versus the preceding peak value of the surface polar field.
Stochastic forcing of the dynamo number can also produce a significant spread in cycle period, although in the model run used to produce Figure 25 the very weak positive correlation between cycle amplitude and rise time is anti-solar (the Waldmeier rule has r = -0.68, based on smoothed monthly SSN, cf. Figure 22D), and the positive correlation between rise time and cycle duration (r = +0.27, not shown) is comparable to solar (r = +0.4). It must be kept in mind that these inferences are all predicated on the use of total magnetic energy as a SSN proxy; different choices can lead to varying degrees of correlation.
The effect of noise has been investigated in most detail in the context of classical mean-field models (see Choudhuri, 1992; Hoyng, 1993; Ossendrijver and Hoyng, 1996; Ossendrijver et al., 1996; Mininni and Gómez, 2002, 2004; Moss et al., 2008). A particularly interesting consequence of random variations of the dynamo number, in mean-field models at or very close to criticality, is the coupling of the cycle’s duration and amplitude (Hoyng, 1993; Ossendrijver and Hoyng, 1996; Ossendrijver et al., 1996), leading to a pronounced anticorrelation between these two quantities that is reminiscent of the Waldmeier Rule (cf. Panel D of Figure 22), and hard to produce by purely nonlinear effects (cf. Ossendrijver and Hoyng, 1996). However, this behavior does not carry over to the supercritical regime, so it is not clear whether this can indeed be accepted as a robust explanation of the observed amplitude-duration anticorrelation. In the supercritical regime, α-quenched mean-field models are less sensitive to noise (Choudhuri, 1992), unless of course they happen to operate close to a bifurcation point, in which case large amplitude and/or parity fluctuations can be produced (see, e.g., Moss et al., 1992).
In the context of Babcock-Leighton models, introducing stochastic forcing of the dynamo numbers leads to amplitude fluctuation patterns qualitatively similar to those plotted in Figure 25: long timescale amplitude modulation, spread in cycle period, (non-solar) positive correlations between cycle amplitude and rise time, and (solar-like) positive correlation between duration and rise time, with the interesting addition that in some model formulations cycle-to-cycle amplitude variation patterns reminiscent of the Gnevyshev-Ohl Rule are also produced (see Charbonneau et al., 2007). Charbonneau and Dikpati (2000) have presented a series of dynamo simulations including stochastic fluctuations in the dynamo number as well as in the meridional circulation. Working in the supercritical regime with a form of algebraic α-quenching as the sole amplitude-limiting nonlinearity, they succeed in producing a solar-like weak anticorrelation between cycle amplitude and duration for fluctuations in the dynamo numbers in excess of 200% of its mean value, with coherence time of one month. However, these encouraging results did not prove very robust across the model’s parameter space.
A different approach is followed by Passos and Lopes (2008) and Lopes and Passos (2009), who used a low-order dynamo model resulting from truncation of the 2D axisymmetric mean-field dynamo equations, with flux loss due to magnetic buoyancy as the amplitude-limiting nonlinearity. Fitting equilibrium solutions to their low-order model to the smoothed SSN time series, one magnetic cycle at a time (Figure 26A), they can plausibly interpret variations in their fitting parameters as being due to systematic, persistent variations of the meridional flow speed on decadal timescales (Figure 26B). They then input these variations in the kinematic axisymmetric Babcock-Leighton model of Chatterjee et al. (2004), conceptually similar to that described in Section 4.8 but replacing the nonlinearity on the poloidal source term by a threshold function for magnetic flux loss through magnetic buoyancy. The resulting SSN-proxy time series reconstructed in this manner shows some remarkable similarities to the true SSN time series, including an epoch of strongly reduced cycle amplitude in the opening decades of the nineteenth century, and secular rise of cycle amplitudes from the mid-nineteenth to the mid-twentieth century (Figure 26C). This suggests that relatively small but persistent changes in the meridional flow, at the ∼ 5 – 30% level, could account for much of the variation in amplitude and duration observed in the solar cycle, and possibly even Grand Minima of activity (see Passos and Lopes, 2009), the topic to which we now turn.
Effect of persistent variations in meridional circulation on the amplitude of the solar cycle, as modeled by Lopes and Passos (2009). Panel A shows the signed square root of the sunspot number (gray), here used as a proxy of the solar internal magnetic field. A smoothed version of this time series (black) is fitted, one magnetic cycle at a time (green), with the equilibrium solution of the truncated dynamo model of Passos and Lopes (2008); assuming that variations in the fitting parameters are due to variations in the meridional flow speed (vp), the coarse time series of vp of panel B (in green) is obtained, scaled to the magnetic cycle 1 value and with error bars from the fitting procedure. Input of this piecewise-constant meridional flow variation (scaled down by a factor of two, in red in panel B) in the 2D Babcock-Leighton dynamo model of Chatterjee et al. (2004) yields the pseudo-SSN time series plotted in Panel C (figure produced from numerical data kindly provided by D. Passos).
5.6 Intermittency
5.6.1 The Maunder Minimum and intermittency
The term “intermittency” was originally coined to characterize signals measured in turbulent fluids, but has now come to refer more generally to systems undergoing apparently random, rapid switching from quiescent to bursting behaviors, as measured by the magnitude of some suitable system variable (see, e.g., Platt et al., 1993). Intermittency thus requires at least two distinct dynamical states available to the system, and a means of transiting from one to the other.
In the context of solar cycle model, intermittency refers to the existence of quiescent epochs of strongly suppressed activity randomly interspersed within periods of “normal” cyclic activity. Observationally, the Maunder Minimum is usually taken as the exemplar for such quiescent epochs. It should be noted, however, that dearth of sunspots does not necessarily mean a halted cycle; as noted earlier, flux ropes of strengths inferior to ∼ 10 kG will not survive their rise through the convective envelope, and the process of flux rope formation from the dynamo-generated mean magnetic field may itself be subjected to a threshold in field strength. The same basic magnetic cycle may well have continued unabated all the way through the Maunder Minimum, but at an amplitude just below one of these thresholds. This idea finds support in the 10Be radioisotope record, which shows a clear and uninterrupted cyclic signal through the Maunder Minimum (see Panels B and C of Figure 22; also Beer et al., 1998). Strictly speaking, thresholding a variable controlled by a single dynamical state subject to amplitude modulation is not intermittency, although the resulting time series for the variable may well look quite intermittent.
Much effort has already been invested in categorizing intermittency-like behavior observed in solar cycle models in terms of the various types of intermittency known to characterize dynamical systems (see Ossendrijver and Covas, 2003, and references therein). In what follows, we attempt to pin down the physical origin of intermittent behavior in the various types of solar cycle models discussed earlier.
5.6.2 Intermittency from stochastic noise
Intermittency has been shown to occur through stochastic fluctuations of the dynamo number in linear mean-field dynamo models operating at criticality (see, e.g., Hoyng, 1993). Such models also exhibit a solar-like anticorrelation between cycle amplitude and phase. However there is no strong reason to believe that the solar dynamo is running just at criticality, so that it is not clear how good an explanation this is of Maunder-type Grand Minima.
Mininni and Gómez (2004) have presented a stochastically-forced 1D (in latitude) αΩ meanfield model, including algebraic α-quenching as the amplitude-limiting nonlinearity, that exhibits a form of intermittency arising from the interaction of dynamo modes of opposite parity. The solution aperiodically produces episodes of markedly reduced cycle amplitude, and often showing strong hemispheric asymmetry. This superficially resembles the behavior associated with the nonlinear amplitude modulation discussed in Section 5.3.1 (compare the top panel in Figure 23 herein to Figure 7 in Mininni and Gómez, 2004). However, here it is the stochastic forcing that occasionally excites the higher-order modes that perturb the normal operation of the otherwise dominant dynamo mode. Moss et al. (2008) and Usoskin et al. (2009a) present more elaborate versions of such models, that do reproduce many salient features of observed grand activity minima.
5.6.3 Intermittency from nonlinearities
Another way to trigger intermittency in a dynamo model, deterministically this time, is to let nonlinear dynamical effects, for example a reduction of the differential rotation amplitude, push the effective dynamo number below its critical value; dynamo action then ceases during the subsequent time interval needed to reestablish differential rotation following the diffusive decay of the magnetic field; in the low Pm regime, this time interval can amount to many cycle periods, but Pm must not be too small, otherwise Grand Minima become too rare (see, e.g., Küker et al., 1999). Values Pm ∼ 10-2 seem to work best. Such intermittency is most readily produced when the dynamo is operating close to criticality. For representative models, see Tobias (1996b, 1997); Brooke et al. (1998); Küker et al. (1999); Brooke et al. (2002).
Intermittency of this type has some attractive properties as a Maunder Minimum scenario. First, the strong hemispheric asymmetry in sunspots distributions in the final decades of the Maunder Minimum (Ribes and Nesme-Ribes, 1993) can occur naturally via parity modulation (see Figure 23 herein). Second, because the same cycle is operating at all times, cyclic activity in indicators other than sunspots (such as radioisotopes, see Beer et al., 1998) is easier to explain; the dynamo is still operating and the solar magnetic field is still undergoing polarity reversal, but simply fails to reach the amplitude threshold above which the sunspot-forming flux ropes can be generated from the mean magnetic field, or survive their buoyant rise through the envelope.
There are also important difficulties with this explanatory scheme. Grand Minima tend to have similar durations and recur in periodic or quasi-periodic fashion, while the sunspot and radioisotope records, taken at face value, suggest a pattern far more irregular (Usoskin, 2008). Moreover, the dynamo solutions in the small Pm regime are characterized by large, non-solar angular velocity fluctuations. In such models, solar-like, low-amplitude torsional oscillations do occur, but for Pm ∼ 1. Unfortunately, in this regime the solutions then lack the separation of timescales needed for Maunder-like Grand Minima episodes. One is stuck here with two conflicting requirements, neither of which easily evaded (but do see Bushby, 2006).
Intermittency has also been observed in strongly supercritical model including α-quenching as the sole amplitude-limiting nonlinearity. Such solutions can enter Grand Minima-like epochs of reduced activity when the dynamo-generated magnetic field completely quenches the α-effect. The dynamo cycle restarts when the magnetic field resistively decays back to the level where the α-effect becomes operational once again. The physical origin of the “long” timescale governing the length of the “typical” time interval between successive Grand Minima episodes is unclear, and the physical underpinning of intermittency harder to identify. For representative models exhibiting intermittency of this type, see Tworkowski et al. (1998).
5.6.4 Intermittency from threshold effects
Intermittency can also arise naturally in dynamo models characterized by a lower operating threshold on the magnetic field. These include models where the regeneration of the poloidal field takes place via the MHD instability of toroidal flux tubes (Sections 4.7 and 3.2.3). In such models, the transition from quiescent to active phases requires an external mechanism to push the field strength back above threshold. This can be stochastic noise (see, e.g., Schmitt et al., 1996), or a secondary dynamo process normally overpowered by the “primary” dynamo during active phases (see Ossendrijver, 2000a). Figure 27 shows one representative solution of the latter variety, where intermittency is driven by a weak α-effect-based kinematic dynamo operating in the convective envelope, in conjunction with magnetic flux injection into the underlying region of primary dynamo action by randomly positioned downflows (see Ossendrijver, 2000a, for further details). The top panel shows a sample trace of the toroidal field, and the bottom panel a butterfly diagram constructed near the core-envelope interface in the model.
Intermittency in a dynamo model based on flux tube instabilities (cf. Sections 3.2.3 and 4.7). The top panel shows a trace of the toroidal field, and the bottom panel is a butterfly diagram covering a shorter time span including a quiescent phase at 9.6 ≲ t ≲ 10.2, and a “failed minimum” at t ≃ 11 (figure produced from numerical data kindly provided by M. Ossendrijver).
The model does produce irregularly-spaced quiescent phases, as well as an occasional “failed minimum” (e.g., at t ≃ 11), in qualitative agreement with the solar record. Note here how the onset of a Grand Minimum is preceded by a gradual decrease in the cycle’s amplitude, while recovery to normal, cyclic behavior is quite abrupt. The fluctuating behavior of this promising class of dynamo models clearly requires further investigation.
5.6.5 Intermittency from time delays
Dynamo models exhibiting amplitude modulation through time-delay effects are also liable to show intermittency in the presence of stochastic noise. This was demonstrated in Charbonneau (2001) in the context of Babcock-Leighton models, using the iterative map formalism described in Section 5.4.2. The intermittency mechanism hinges on the fact that the map’s attractor has a finite basin of attraction (indicated by gray shading in Panel A of Figure 24). Stochastic noise acting simultaneously with the map’s dynamics can then knock the solution out of this basin of attraction, which then leads to a collapse onto the trivial solution pn = 0, even if the map parameter remains supercritical. Stochastic noise eventually knocks the solution back into the attractor’s basin, which signals the onset of a new active phase (see Charbonneau, 2001, for details).
A corresponding behavior was subsequently found in a spatially-extended model similar to that described in Section 4.8 (see Charbonneau et al., 2004). Figure 28 shows one such representative solution, in the same format as Figure 27. This is a dynamo solution which, in the absence of noise, operates in the singly-periodic regime. Stochastic noise is added to the vector potential Aêφ in the outermost layers, and the dynamo number is also allowed to fluctuate randomly about a pre-set mean value. The resulting solution exhibits both amplitude fluctuations and intermittency.
Intermittency in a dynamo model based on the Babcock-Leighton mechanism (cf. Sections 3.2.4 and 4.8). The top panel shows a trace of the toroidal field sampled at (r, θ) = (0.7, π/3). The bottom panel is a time-latitude diagram for the toroidal field at the core-envelope interface (numerical data from Charbonneau et al., 2004).
With its strong polar branch often characteristic of dynamo models with meridional circulation, Figure 28 is not a particularly good fit to the solar butterfly diagram, yet its fluctuating behavior is solar-like in a number of ways, including epochs of alternating higher-than-average and lower-than-average cycle amplitudes (the Gnevyshev-Ohl rule, cf. Panel E of Figure 22), and residual pseudocyclic variations during quiescent phases, as suggested by 10Be data, cf. Panel B of Figure 22. This later property is due at least in part to meridional circulation, which continues to advect the (decaying) magnetic field after the dynamo has fallen below threshold (see Charbonneau et al., 2004, for further discussion). Note also in Figure 28 how the onset of Grand Minima is quite sudden, while recovery to normal activity is more gradual, which is the opposite behavior to the Grand Minima in Figure 27.
5.7 Solar cycle predictions based on dynamo models
The idea that measurements of the solar surface magnetic field in the descending phase of a cycle can be used to forecast the amplitude (and/or timing) of the next cycle goes back many decades, but it is Schatten et al. (1978) who explicitly justified this procedure on the basis of dynamo models, which led to a wide variety of dynamo-inspired precursor schemes (see Hathaway et al., 1999, for a review).
This dynamo logic has recently been pushed further, by using dynamo models to actually advance in time measurements of the solar surface magnetic field in order to produce a cycle forecast. This approach is justified if the surface magnetic field is indeed a significant source of the poloidal field to be sheared into a toroidal component in the upcoming cycle, so that using this approach to forecasting already amounts to a strong assumption on the mode of solar dynamo action. In the stochastically-forced flux-transport αΩ dynamo solution of Figure 25, a strong correlation materializes between the peak polar field at cycle minimum, and amplitude of the subsequent cycle (see panel C). This occurs because in this model the surface polar field is advected down by the meridional flow to the dynamo source region at the base of the convection, and ends up feeding back into the dynamo loop. In other types of dynamo models where this feedback of the surface field does not occur, no such correlation materializes. For more on these matters see Charbonneau and Barlet (2010).
It is particularly instructive to compare and contrast the forecast schemes (and cycle 24 predictions) of Dikpati et al. 2006 (see also Dikpati and Gilman, 2006) and Choudhuri et al. 2007 (see also Jiang et al., 2007). Both groups use a dynamo model of the Babcock-Leighton variety (Section 4.8), in conjunction with input of solar magnetic field observations in a manner often (and incorrectly) described as “data assimilation”. The model parameters are adjusted to reproduce the known amplitudes of previous sunspot cycles, and the model is then integrated forward in time beyond this calibration interval to provide a forecast.
Table 1 details the various modelling components associated with each forecasting scheme. Both are remarkably similar, differing at the level of what one would usually consider modelling details, and do about as well at reproducing amplitude of past cycles over their respective calibration intervals. Yet, they end up producing cycle 24 amplitude forecasts that stand at opposite ends of the very wide range of cycle 24 forecasts produced by other techniques. A cycle 24 with SSN = 80 would place it amongst the weakest of the past century (cycles 14 and 16), while SSN = 180 would rank it on par with the two highest cycle amplitude on record (cycles 4 and 19; see Figure 22).
Much criticism has been leveled at these dynamo model-based cycle forecasting schemes, and sometimes unfairly so. To dismiss the whole idea on the grounds that the solar dynamo is a chaotic system is likely too extreme a stance, especially since (1) even chaotic systems can be amenable to prediction over a finite temporal window, and (2) input of data (even if not via true data assimilation) can in principle lead to some correction of the system’s trajectory in phase space. More relevant (in my opinion) has been the explicit demonstration that (1) very small changes in some unobservable and poorly constrained input parameters to the dynamo model used for the forecast can introduce significant errors already for next-cycle amplitude forecasts (see Bushby and Tobias, 2007, also Yeates et al., 2008); (2) the exact manner in which surface data drives the model can have a huge impact on the forecasting skill (Cameron and Schüssler, 2007). Consequently, the discrepant forecasts of Table 1 indicate mostly that current dynamo model-based predictive schemes still lack robustness. True data assimilation has been carried out using highly simplified dynamo models (Kitiashvili and Kosovichev, 2008), and clearly this must be carried over to more realistic dynamo models.
Finally, one must also keep in mind that other plausible explanations exist for the relatively good precursor potential of the solar surface magnetic field. In particular, Cameron and Schüssler (2008) have argued that the well-known spatiotemporal overlap of cycles in the butterfly diagram (see Figure 3), taken in conjunction with the empirical anticorrelation between cycle amplitude and rise time embodied in the Waldmeier Rule (Figure 22D; also Hathaway, 2010, Section 4.6), could in itself explain the precursor performance of the polar field strength at solar activity minimum. Given the unusually extended minimum phase between cycles 23 and 24, it will be very interesting to revisit all these model results once cycle 24 reaches its peak amplitude.
6 Open Questions and Current Trends
I close this review with the following discussion of a few open questions that, in my opinion, bear particularly heavily on our understanding (or lack thereof) of the solar cycle.
6.1 What is the primary poloidal field regeneration mechanism?
Given the amount of effort having gone into building detailed dynamo models of the solar cycle, it is quite sobering to reflect upon the fact that the physical mechanism responsible for the regeneration of the poloidal component of the solar magnetic field has not yet been identified with confidence. As discussed at some length in Section 4, current models relying on distinct mechanisms all have their strengths and weaknesses, in terms of physical underpinning as well as comparison with observations.
Something akin to the α-effect of mean-field electrodynamics has been measured in a number of local and global numerical simulations including rotation and stratification, so this certainly remains a favored magnetic field generation mechanism. Modelling of the evolution of the Sun’s surface magnetic flux has abundantly confirmed that the Babcock-Leighton mechanism is operating on the Sun, in the sense that magnetic flux liberated by the decay of tilted bipolar active regions does accumulate in the polar regions, where it triggers polarity reversal of the poloidal component (see Wang and Sheeley Jr, 1991; Schrijver et al., 2002; Wang et al., 2002; Baumann et al., 2004, and references therein). The key question is whether this is an active component of the dynamo cycle, or a mere side-effect of active region decay. Likewise, the buoyant instability of magnetic flux tubes (Section 4.7) is, in some sense, unavoidable; here again the question is whether or not the associated azimuthal mean electromotive force contributes significantly to dynamo action in the Sun.
6.2 What limits the amplitude of the solar magnetic field?
The amplitude of the dynamo-generated magnetic field is almost certainly restricted by the backreaction of Lorentz forces on the driving fluid motions. However, as outlined in Section 5.3.1, this backreaction can occur in many ways.
Helioseismology has revealed only small variations of the differential rotation profile in the course of the solar cycle. The observed variations amount primarily to an extension in depth of the pattern of low-amplitude torsional oscillations long known from surface Doppler measurements (but see also Basu and Antia, 2001; Toomre et al., 2003; Howe, 2009). Taken at face value, these results suggest that quenching of differential rotation is not the primary amplitude-limiting mechanism, unless the dynamo is operating very close to criticality. Once again the hope is that in the not-too-distant future, helioseismology will have mapped accurately enough cycle-induced variations of differential rotation in the convective envelope and tachocline, to settle this issue.
Algebraic quenching of the α-effect (or α-effect-like source terms) is the mechanism most often incorporated in dynamo models. However, this state of affairs usually has much more to do with computational convenience than commitment to a specific physical quenching mechanism. There is little doubt that the α-effect will be affected once the mean magnetic field reaches equipartition; the critical question is whether it becomes quenched long before that, for example by the small-scale component of the magnetic field. The issue hinges on helicity conservation and flux through boundaries, and subtleties of flow-field interaction in MHD turbulence. For recent entry points into this very active area of current research, see Cattaneo and Hughes (1996), Blackman and Field (2000), Brandenburg and Dobler (2001), and Brandenburg (2009).
Flux loss through magnetic buoyancy is the primary reason why most contemporary dynamo models of the solar cycle rely on the rotational shear in the tachocline to achieve toroidal field amplification. If the dynamo were to reside entirely in the convective envelope, then this would be an important, perhaps even dominant, amplitude limiting mechanism (see Schmitt and Schüssler, 1989; Moss et al., 1990). If, on the other hand, toroidal field amplification takes place primarily at or beneath the core-envelope interface, then it is less clear whether or not this mechanism plays a dominant role. In fact, it may even be that rising flux ropes amplify the deep-seated magnetic field, as nicely demonstrated by the numerical calculations of Rempel and Schüssler (2001). Magnetic flux loss through buoyancy can also have a large impact on the cycle period (see, e.g. Kitchatinov et al., 2000), and the model calculations of Lopes and Passos (2009) indicate that combined with fluctuations in the meridional flow speed, very solar-like cycle amplitude variations can be produced. The impact of this amplitude limiting mechanism clearly requires further investigation.
6.3 Flux tubes versus diffuse fields
The foregoing discussion has implicitly assumed that the dynamo process produces a mean, large-scale magnetic field that then concentrates itself into the flux ropes that subsequently give rise to sunspots. High-resolution observations of the photospheric magnetic field show that even outside of sunspots, the field is concentrated in flux tubes (see, e.g., Parker, 1982, and references therein), presumably as a consequence of convective collapse of magnetic flux concentrations too weak to block convection and form sunspots. In this picture, which is basically the framework of all dynamo models discussed above, the mean magnetic field is the dominant player in the cycle.
An alternate viewpoint is to assume that the solar magnetic field is a fibril state from beginning to end, throughout the convection zone and tachocline, and that whatever large-scale field there may be in the photosphere is a mere by-product of the decay of sunspots and other flux tube-like small-scale magnetic structures. The challenge is then to devise a dynamo process that operates entirely on flux tubes, rather than on a diffuse mean field. Some exploratory calculations have been made (e.g., DeLuca et al., 1993; Schatten, 2009), but this intriguing question has received far less attention than it deserves.
6.4 How constraining is the sunspot butterfly diagram?
The shape of the sunspot butterfly diagram (see Figure 3) continues to play a dominant constraining role in many dynamo models of the solar cycle. Yet caution is in order on this front. Calculations of the stability of toroidal flux ropes stored in the overshoot region immediately beneath the core-envelope interface indicate that instability is much harder to produce at high latitudes, primarily because of the stabilizing effect of the magnetic tension force; thus strong fields at high latitudes may well be there, but not produce sunspots. Likewise, the process of flux rope formation from the dynamo-generated mean magnetic field is currently not understood. Are flux ropes forming preferentially in regions of most intense magnetic fields, in regions of strongest magnetic helicity, or in regions of strongest hydrodynamical shear? Is a stronger diffuse toroidal field forming more strongly magnetized flux ropes, or a larger number of flux ropes always of the same strength?
These are all crucial questions from the point of view of comparing results from dynamo models to sunspot data. Until they have been answered, uncertainty remains as to the degree to which the sunspot butterfly diagram can be compared in all details to time-latitude diagrams of the toroidal field, as produced by this or that dynamo model.
6.5 Is meridional circulation crucial?
The main question regarding meridional circulation is not whether it is there or not, but rather what role it plays in the solar cycle. The answer hinges on the value of the turbulent diffusivity ηT, which is notoriously difficult to estimate with confidence. It is probably essential in mean-field and mean-field-like dynamo models characterized by positive α-effects in the Northern hemisphere, in order to ensure equatorward transport of the sunspot-forming, deep-seated toroidal magnetic field (see Sections 4.4, 4.5, and 4.7), unless the latitudinal turbulent pumping speeds turn out significantly larger than currently estimated (Käpylä et al., 2006a). It also appears to be a major determinant in the evolution of the surface magnetic field in the course of the solar cycle. Something like it is certainly needed in dynamo models based on the Babcock-Leighton mechanism, to carry the poloidal field generated at the surface down to the tachocline, where production of the toroidal field is taking place (see Section 4.8).
The primary unknown at this writing is the degree to which meridional circulation is affected by the Lorentz force associated with the dynamo-generated magnetic field. Recent calculations (Rempel, 2006a,b) suggest that the backreaction is limited to regions of strongest toroidal fields, so that the “conveyor belt” is still operating in the bulk of the convective envelope, but this issue requires further study. Another important related issue is the advective role of turbulent pumping, which may well compete and/or complement the advective effect of the meridional flow.
6.6 Is the mean solar magnetic field really axisymmetric?
While the large-scale solar magnetic field is axisymmetric about the Sun’s rotation axis to a good first approximation, various lines of observational evidence point to a persistent, low-level non-axisymmetric component; such evidence includes the so-called active longitudes (see Henney and Harvey, 2002, and references therein), rotationally-based periodicity in cycle-related eruptive phenomena (Bai, 1987), and the shape of the white-light corona in the descending phase of the cycle.
Various mean-field-based dynamo models are known to support non-axisymmetric modes over a substantial portion of their parameter space (see, e.g., Moss et al., 1991; Moss, 1999; Bigazzi and Ruzmaikin, 2004, and references therein). At high Rm, strong differential rotation (in the sense that CΩ ≪ Cα) is known to favor axisymmetric modes, because it efficiently destroys any non-axisymmetric component on a timescale much faster than diffusive (∝ Rm1/3 at high Rm, instead of ∝ Rm). Although it is not entirely clear that the Sun’s differential rotation is strong enough to place it in this regime (see, e.g., Rüdiger and Elstner, 1994), some 3D models do show this symmetrizing effect of differential rotation (see, e.g., Zhang et al., 2003a). Likewise, the recent numerical 3D MHD simulations of solar-like cycles by Ghizaru et al. (2010) do produce a large-scale magnetic field with a dominant axisymmetric component. These types of simulations will probably offer the best handle on this question.
6.7 What causes Maunder-type Grand Minima?
The origin of Grand Minima in solar activity also remains a question subjected to intense scrutiny. Broadly speaking, Grand Minima can occur either through amplitude modulation of a basic underlying dynamo cycle, or through intermittency. In this latter case, the transition from one state to another can take place via the system’s internal dynamics, or through the influence of external stochastic noise, or both. Not surprisingly, a large number of plausible Grand Minima models can now be found in the extant literature (cf. Section 5.6).
Historical researches have shown that the Sun climbed out of the Maunder Minimum gradually, and showing strongly asymmetric activity, with nearly all sunspots observed between 1670 and 1715 located in the Southern solar hemisphere (see Ribes and Nesme-Ribes, 1993). Some historical reconstructions of the butterfly diagram in the pre-photographic era also suggest the presence of what could be interpreted as a quadrupolar component (Arlt, 2009). These are the kind of pattern that can be readily produced by nonlinear parity modulation (cf. Figure 23 herein; see also Beer et al., 1998; Sokoloff and Nesme-Ribes, 1994; Usoskin et al., 2009b). Then again, in the context of an intermittency-based model, it is quite conceivable that one hemisphere can pull out of a quiescent epoch before the other, thus yielding sunspot distributions compatible with the aforecited observations in the late Maunder Minimum. Such scenarios, relying on cross-hemispheric coupling, have hardly begun to be explored (Charbonneau, 2005, 2007a; Chatterjee and Choudhuri, 2006).
Another possible avenue for distinguishing between these various scenarios is the persistence of the primary cycle’s phase through Grand Minima. Generally speaking, models relying on amplitude modulation can be expected to exhibit good phase persistence across such minima, because the same basic cycle is operating at all times (cf. Figure 23). Intermittency, on the other hand, should not necessarily lead to phase persistence, since the active and quiescent phases are governed by distinct dynamics. One can but hope that careful analysis of cosmogenic radioisotope data may soon indicate the degree to which the solar cycle’s phase persisted through the Maunder, Spörer, and Wolf Grand Minima, in order to narrow down the range of possibilities.
6.8 Where do we go from here?
Recent years have witnessed a number of significant advances in solar cycle modelling. Local magnetohydrodynamical simulations of thermally-driven convection have now allowed measurements of the α-tensor, and of its variation with depth and latitude in the solar interior, and with rotation rate; and global magnetohydrodynamical simulation of solar convection are now producing large-scale magnetic fields, in some cases even undergoing polarity reversals on decadal timescales. Such simulations are ideally suited for investigating a number of important issues, such as the mechanism(s) responsible for regulating the amplitude of the solar cycle, the magnetically-driven temporal variations of the large-scale flows important for the solar cycle, and the possible impact of a cycling large-scale magnetic field on convective energy transport, to mention but a few.
Despites continuing advances in computing power, global MHD simulations remain extremely demanding, and proper capture of important solar cycle elements — most notably the formation, emergence and surface decay sunspots and active regions— are certainly not forthcoming. Nonetheless, comparison between cyclic solutions arising in full numerical simulations and those characterizing simpler mean-field-like models should also allow to test the validity limit of the kinematic approximation and of the simple algebraic amplitude-limiting nonlinearities still so prevalent in the latter class of solar cycle models. It appears likely that in the foreseeable future, the simpler, mean-field and mean-field-like solar cycle models reviewed here will remain the workhorses of research on long timescale phenomena such as grand activity minima and maxima, on the evolution of surface magnetic flux, on dynamo-model-based solar cycle prediction, and on the modelling and interpretation of stellar activity cycles.
Notes
1 Equation (2) is written here in a frame of reference rotating with angular velocity Ω, so that a Coriolis force term appears explicitly, while the centrifugal force has been subsumed into the gravitational term.
2 Note, however, that an axisymmetric flow can sustain a non-axisymmetric magnetic field against resistive decay.
3 Helioseismology has also revealed the existence of a significant radial shear in the outermost layers of the solar convective envelope. Even if the storage problem could be somehow bypassed, it does not appear possible to construct a viable solar dynamo model relying exclusively on this angular velocity gradient (see, e.g., Dikpati et al., 2002; Brandenburg, 2005, for illustrative calculations).
4 Models retaining both α-terms are dubbed α2Ω dynamos, and may be relevant to the solar case even in the Cα ≪ CΩ regime, if the latter operates in a very thin layer, e.g. the tachocline (see, e.g., DeLuca and Gilman, 1988; Gilman et al., 1989; Choudhuri, 1990); this is because the α-effect gets curled in Equation (25) for the mean toroidal field. Models relying only on the α-terms are said to be α2 dynamos. Such models are relevant to dynamo action in planetary cores and convective stars with vanishing differential rotation (if such a thing exists).
5 These are not “waves” in usual sense of the word, although they are described by modal solutions of the form exp(ik · x - ωt).
6 Although some turbulence model predict such higher-order latitudinal dependencies, the functional forms adopted here are largely ad hoc, and are made for strictly illustrative purposes.
7 Mea culpa on this one...
8 For this particular choice of α, η, and Ω profiles, solutions with negative Cα are non-oscillatory in most of the [Cα,CΩ,Δη] parameter space. This is in agreement with the results of Markiel and Thomas (1999).
9 We largely exclude from the foregoing discussion mathematical toy-models that aim exclusively at reproducing the shape of the sunspot number time series. For recent entry points in this literature, see, e.g., Mininni et al. (2002).
10 Dynamo saturation can also occur by magnetically-mediated changes in the “topological” properties of a turbulent flow, without significant decrease in the turbulent flow amplitudes; see Cattaneo et al. (1996) for a nice, simple example.
References
Arlt, R., 2009, “The Butterfly Diagram in the Eighteenth Century”, Solar Phys., 255, 143–153. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0812.2233] (Cited on page 72.)
Arlt, R., Sule, A. and Filter, R., 2007a, “Stability of the solar tachocline with magnetic fields”, Astron. Nachr., 328, 1142. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 22.)
Arlt, R., Sule, A. and Rüdiger, G., 2007b, “Stability of toroidal magnetic fields in the solar tachocline”, Astron. Astrophys., 461, 295–301. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 18 and 22.)
Babcock, H.W., 1961, “The Topology of the Sun’s Magnetic Field and the 22-Year Cycle”, Astrophys. J., 133, 572–589. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 9 and 41.)
Bai, T., 1987, “Distribution of flares on the sun: superactive regions and active zones of 1980-1985”, Astrophys. J., 314, 795–807. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 72.)
Basu, S. and Antia, H.M., 2001, “A study of possible temporal and latitudinal variations in the properties of the solar tachocline”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 324, 498–508. [DOI], [ADS], [astro-ph/0101314] (Cited on page 70.)
Baumann, I., Schmitt, D., Schüssler, M. and Solanki, S., 2004, “Evolution of the large-scale magnetic field on the solar surface: a parameter study”, Astron. Astrophys., 426, 1075–1091. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 70.)
Beer, J., 2000, “Long-term indirect indices of solar variability”, Space Sci. Rev., 94, 53.66. [ADS] (Cited on pages 51 and 53.)
Beer, J., Raisbeck, G.M. and Yiou, F., 1991, “Time variation of 10Be and solar activity”, in The Sun in Time, (Eds.) Sonett, C.P., Giampapa, M.S., Matthews, M.S., pp. 343–359, University of Arizona Press, Tucson (Cited on page 51.)
Beer, J., Tobias, S.M. and Weiss, N.O., 1998, “An Active Sun Throughout the Maunder Minimum”, Solar Phys., 181, 237–249. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 55, 64, and 72.)
Bigazzi, A. and Ruzmaikin, A., 2004, “The sun’s preferred longitudes and the coupling of magnetic dynamo modes”, Astrophys. J., 604, 944–959. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 72.)
Blackman, E.G. and Brandenburg, A., 2002, “Dynamical nonlinearity in large-scale dynamo with shear”, Astrophys. J., 579, 359–373. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 22 and 57.)
Blackman, E.G. and Field, G.B., 2000, “Constraints on the magnitude of α in dynamo theory”, Astrophys. J., 534, 984–988. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 70.)
Bonanno, A., Elstner, D., Rüdiger, G. and Belvedere, G., 2003, “Parity properties of an advectiondominated solar α2Ω-dynamo”, Astron. Astrophys., 390, 673–680. [ADS] (Cited on page 34.)
Bonanno, A., Elstner, D. and Belvedere, G., 2006, “Advection-dominated solar dynamo model with two-cell meridional flow and a positive α-effect in the tachocline”, Astron. Nachr., 327, 680. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 41.)
Boruta, N., 1996, “Solar dynamo surface waves in the presence of a primordial magnetic field: a 30 Gauss upper limit in the solar core”, Astrophys. J., 458, 832–849. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 53.)
Boyer, D.W. and Levy, E.H., 1984, “Oscillating dynamo magnetic field in the presence of an external nondynamo field: the influence of a solar primordial field”, Astrophys. J., 277, 848–861. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 53.)
Brandenburg, A., 2005, “The Case for a Distributed Solar Dynamo Shaped by Near-Surface Shear”, Astrophys. J., 625, 539–547. [DOI], [ADS], [astro-ph/0502275] (Cited on page 19.)
Brandenburg, A., 2009, “Advances in Theory and Simulations of Large-Scale Dynamos”, Space Sci. Rev., 144, 87–104. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0901.0329] (Cited on pages 54 and 70.)
Brandenburg, A. and Dobler, W., 2001, “Large scale dynamos with helicity loss through boundaries”, Astron. Astrophys., 369, 329–338. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 70.)
Brandenburg, A. and Schmitt, D., 1998, “Simulations of an alpha-effect due to magnetic buoyancy”, Astron. Astrophys., 338, L55–L58. [ADS] (Cited on page 40.)
Brandenburg, A. and Subramanian, K., 2005, “Astrophysical magnetic fields and nonlinear dynamo theory”, Phys. Rep., 417, 1–209. [DOI], [ADS], [astro-ph/0405052] (Cited on page 11.)
Brandenburg, A., Tuominen, I., Nordlund, Å., Pulkkinen, P. and Stein, R.F., 1990, “3-D simulations of turbulent cyclonic magneto-convection”, Astron. Astrophys., 232, 277–291. [ADS] (Cited on page 21.)
Brandenburg, A., Rädler, K.-H., Rheinhardt, M. and Subramanian, K., 2008, “Magnetic Quenching of α and Diffusivity Tensors in Helical Turbulence”, Astrophys. J. Lett., 687, L49–L52. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0805.1287] (Cited on page 22.)
Braun, D.C. and Fan, Y., 1998, “Helioseismic measurements of the subsurface meridional flow”, Astrophys. J. Lett., 508, L105–L108. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 31.)
Brooke, J.M., Pelt, J., Tavakol, R. and Tworkowski, A., 1998, “Grand minima and equatorial symmetry breaking in axisymmetric dynamo models”, Astron. Astrophys., 332, 339–352. [ADS] (Cited on pages 55 and 64.)
Brooke, J.M., Moss, D. and Phillips, A., 2002, “Deep minima in stellar dynamos”, Astron. Astrophys., 395, 1013–1022. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 64.)
Brown, B.P., Browning, M.K., Miesch, M.S., Brun, A.S. and Toomre, J., 2009, “Wreathes of Magnetism in Rapidly Rotating Suns”, arXiv, e-print. [ADS], [arXiv:0906.2407] (Cited on page 48.)
Brown, B.P., Browning, M.K., Brun, A.S., Miesch, M.S. and Toomre, J., 2010, “Persistent Magnetic Wreaths in a Rapidly Rotating Sun”, Astrophys. J., 711, 424–438. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 48.)
Brown, T.M., Christensen-Dalsgaard, J., Dziembowski, W.A., Goode, P., Gough, D.O. and Morrow, C.A., 1989, “Inferring the Sun’s internal angular velocity from observed p-mode frequency splittings”, Astrophys. J., 343, 526–546. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 17.)
Browning, M.K., Miesch, M.S., Brun, A.S. and Toomre, J., 2006, “Dynamo Action in the Solar Convection Zone and Tachocline: Pumping and Organization of Toroidal Fields”, Astrophys. J. Lett., 648, L157–L160. [DOI], [ADS], [astro-ph/0609153] (Cited on page 48.)
Brun, A.S., Miesch, M.S. and Toomre, J., 2004, “Global-scale turbulent convection and magnetic dynamo action in the solar envelope”, Astrophys. J., 614, 1073–1098. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 48.)
Bushby, P.J., 2006, “Zonal flows and grand minima in a solar dynamo model”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 371, 772–780. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 55 and 65.)
Bushby, P.J. and Tobias, S.M., 2007, “On Predicting the Solar Cycle Using Mean-Field Models”, Astrophys. J., 661, 1289–1296. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0704.2345] (Cited on page 69.)
Caligari, P., Moreno-Insertis, F. and Schüssler, M., 1995, “Emerging flux tubes in the solar convection zone. I. Asymmetry, tilt, and emergence latitudes”, Astrophys. J., 441, 886–902. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 18 and 57.)
Cally, P.S., 2001, “Nonlinear Evolution of 2D Tachocline Instability”, Solar Phys., 199, 231–249. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 38.)
Cally, P.S., Dikpati, M. and Gilman, P.A., 2003, “Clamshell and Tipping Instabilities in a Twodimensional Magnetohydrodynamic Tachocline”, Astrophys. J., 582, 1190–1205. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 38.)
Cally, P.S., Dikpati, M. and Gilman, P.A., 2008, “Three-dimensional magneto-shear instabilities in the solar tachocline. II. Axisymmetric case”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 391, 891–900. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 18.)
Cameron, R. and Schüssler, M., 2007, “Solar Cycle Prediction Using Precursors and Flux Transport Models”, Astrophys. J., 659, 801–811. [DOI], [ADS], [astro-ph/0612693] (Cited on page 69.)
Cameron, R. and Schüssler, M., 2008, “A Robust Correlation between Growth Rate and Amplitude of Solar Cycles: Consequences for Prediction Methods”, Astrophys. J., 685, 1291–1296. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 69.)
Carbonell, M., Oliver, R. and Ballester, J.L., 1994, “A search for chaotic behaviour in solar activity”, Astron. Astrophys., 290, 983–994. [ADS] (Cited on page 53.)
Cattaneo, F., 1999, “On the origin of magnetic fields in the quiet photosphere”, Astrophys. J. Lett., 515, L39–L42. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 60.)
Cattaneo, F. and Hughes, D.W., 1996, “Nonlinear saturation of the turbulent α-effect”, Phys. Rev. E, 54, R4532–R4535. [ADS] (Cited on pages 28 and 70.)
Cattaneo, F. and Hughes, D.W., 2009, “Problems with kinematic mean field electrodynamics at high magnetic Reynolds numbers”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 395, L48–L51. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0805.2138] (Cited on page 54.)
Cattaneo, F., Hughes, D.W. and Kim, E.-J., 1996, “Suppression of Chaos in a Simplified Nonlinear Dynamo Model”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 76, 2057–2060. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 54.)
Cattaneo, F., Emonet, T. and Weiss, N.O., 2003, “On the interaction between convection and magnetic fields”, Astrophys. J., 588, 1183–1198. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 60.)
Charbonneau, P., 2001, “Multiperiodicity, Chaos, and Intermittency in a Reduced Model of the Solar Cycle”, Solar Phys., 199, 385–404. [ADS] (Cited on pages 57, 58, and 65.)
Charbonneau, P., 2005, “A Maunder Minimum Scenario Based on Cross-Hemispheric Coupling and Intermittency”, Solar Phys., 229, 345–358. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 47 and 73.)
Charbonneau, P., 2007a, “Cross-hemispheric coupling in a Babcock-Leighton model of the solar cycle”, Adv. Space Res., 40, 899–906. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 47 and 73.)
Charbonneau, P., 2007b, “Babcock-Leighton models of the solar cycle: Questions and issues”, Adv. Space Res., 39, 1661–1669. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 45.)
Charbonneau, P. and Barlet, G., 2010, “The dynamo basis of solar cycle precursor schemes”, J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys., 2010, in press. [DOI] (Cited on page 68.)
Charbonneau, P. and Dikpati, M., 2000, “Stochastic Fluctuations in a Babcock-Leighton Model of the Solar Cycle”, Astrophys. J., 543, 1027–1043. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 57 and 62.)
Charbonneau, P. and MacGregor, K.B., 1996, “On the generation of equipartition-strength magnetic fields by turbulent hydromagnetic dynamos”, Astrophys. J. Lett., 473, L59–L62. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 29.)
Charbonneau, P. and MacGregor, K.B., 1997, “Solar Interface Dynamos. II. Linear, Kinematic Models in Spherical Geometry”, Astrophys. J., 486, 502–520. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 29.)
Charbonneau, P., Christensen-Dalsgaard, J., Henning, R., Larsen, R.M., Schou, J., Thompson, M.J. and Tomczyk, S., 1999, “Helioseismic Constraints on the Structure of the Solar Tachocline”, Astrophys. J., 527, 445–460. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 17.)
Charbonneau, P., Blais-Laurier, G. and St-Jean, C., 2004, “Intermittency and Phase Persistence in a Babcock-Leighton Model of the Solar Cycle”, Astrophys. J. Lett., 616, L183–L186. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 65, 67, and 68.)
Charbonneau, P., St-Jean, C. and Zacharias, P., 2005, “Fluctuations in Babcock-Leighton models of the solar cycle. I. period doubling and transition to chaos”, Astrophys. J., 619, 613–622. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 42, 43, and 58.)
Charbonneau, P., Beaubien, G. and St-Jean, C., 2007, “Fluctuations in Babcock-Leighton Dynamos. II. Revisiting the Gnevyshev-Ohl Rule”, Astrophys. J., 658, 657–662. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 62.)
Chatterjee, P. and Choudhuri, A.R., 2006, “On Magnetic Coupling Between the Two Hemispheres in Solar Dynamo Models”, Solar Phys., 239, 29–39. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 47 and 73.)
Chatterjee, P., Nandy, D. and Choudhuri, A.R., 2004, “Full-sphere simulations of a circulation dominated solar dynamo: exploring the parity issue”, Astron. Astrophys., 427, 1019–1030. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 42, 47, 62, and 63.)
Choudhuri, A.R., 1990, “On the possibility of αΩ-type dynamo in a thin layer inside the sun”, Astrophys. J., 355, 733–744. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 23.)
Choudhuri, A.R., 1992, “Stochastic fluctuations of the solar dynamo”, Astron. Astrophys., 253, 277–285. [ADS] (Cited on pages 60 and 62.)
Choudhuri, A.R., Schüssler, M. and Dikpati, M., 1995, “The solar dynamo with meridional circulation”, Astron. Astrophys., 303, L29–L32. [ADS] (Cited on page 32.)
Choudhuri, A.R., Chatterjee, P. and Jiang, J., 2007, “Predicting Solar Cycle 24 With a Solar Dynamo Model”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 98, 131103. [DOI], [ADS], [astro-ph/0701527] (Cited on pages 68 and 69.)
Christensen-Dalsgaard, J., 2002, “Helioseismology”, Rev. Mod. Phys., 74, 1073–1129. [ADS] (Cited on page 13.)
Covas, E., Tavakol, R., Tworkowski, A. and Brandenburg, A., 1997, “Robustness of truncated αΩ dynamos with a dynamic alpha”, Solar Phys., 172, 3–13. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 57.)
Covas, E., Tavakol, R., Tworkowski, A. and Brandenburg, A., 1998, “Axisymmetric mean field dynamos with dynamic and algebraic α-quenching”, Astron. Astrophys., 329, 350–360. [ADS] (Cited on page 57.)
Davidson, P.A., 2001, An Introduction to Magnetohydrodynamics, Cambridge Texts in Applied Mathematics, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge; New York. [Google Books] (Cited on page 12.)
DeLuca, E.E. and Gilman, P.A., 1988, “Dynamo theory for the interface between the convection zone and the radiative interior of a star”, Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn., 43, 119–148. [DOI] (Cited on pages 23 and 54.)
DeLuca, E.E., Fisher, G.H. and Patten, B.M., 1993, “The dynamics of magnetic flux rings”, Astrophys. J., 411, 383–393. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 71.)
Dikpati, M. and Charbonneau, P., 1999, “A Babcock-Leighton Flux Transport Dynamo with Solar-like Differential Rotation”, Astrophys. J., 518, 508–520. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 42, 43, 45, and 57.)
Dikpati, M. and Gilman, P.A., 1999, “Joint instability of latitudinal differential rotation and concentrated toroidal fields below the solar convection zone”, Astrophys. J., 512, 417–441. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 38.)
Dikpati, M. and Gilman, P.A., 2001, “Flux-Transport Dynamos with..-Effect from Global Instability of Tachocline Differential Rotation: A Solution for Magnetic Parity Selection in the Sun”, Astrophys. J., 559, 428–442. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 17, 37, 39, and 47.)
Dikpati, M. and Gilman, P.A., 2006, “Simulating and Predicting Solar Cycles Using a Flux- Transport Dynamo”, Astrophys. J., 649, 498–514. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 68.)
Dikpati, M., Corbard, T., Thompson, M.J. and Gilman, P.A., 2002, “Flux Transport Solar Dynamos with Near-Surface Radial Shear”, Astrophys. J. Lett., 575, L41–L45. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 19.)
Dikpati, M., De Toma, G., Gilman, P.A., Arge, C.N. and White, O.R., 2004, “Diagnostic of polar field reversal in solar cycle 23 using a flux transport dynamo model”, Astrophys. J., 601, 1136–1151. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 37, 41, and 47.)
Dikpati, M., Gilman, P.A. and MacGregor, K.B., 2005, “Constraints on the Applicability of an Interface Dynamo to the Sun”, Astrophys. J., 631, 647–652. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 31 and 53.)
Dikpati, M., de Toma, G. and Gilman, P.A., 2006, “Predicting the strength of solar cycle 24 using a flux-transport dynamo-based tool”, Geophys. Res. Lett., 33, L05102. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 68 and 69.)
Dikpati, M., Gilman, P.A., Cally, P.S. and Miesch, M.S., 2009, “Axisymmetric MHD Instabilities in Solar/Stellar Tachoclines”, Astrophys. J., 692, 1421–I, [ADS] (Cited on page 18.)
D’Silva, S. and Choudhuri, A.R., 1993, “A theoretical model for tilts of bipolar magnetic regions”, Astron. Astrophys., 272, 621–633. [ADS] (Cited on page 18.)
Durney, B.R., 1995, “On a Babcock-Leighton dynamo model with a deep-seated generating layer for the toroidal magnetic field”, Solar Phys., 160, 213–235. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 42 and 43.)
Durney, B.R., 1996, “On a Babcock-Leighton dynamo model with a deep-seated generating layer for the toroidal magnetic field, II”, Solar Phys., 166, 231–260. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 42.)
Durney, B.R., 1997, “On a Babcock-Leighton solar dynamo model with a deep-seated generating layer for the toroidal magnetic field. IV”, Astrophys. J., 486, 1065–1077. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 42.)
Durney, B.R., 2000, “On the differences between odd and even solar cycles”, Solar Phys., 196, 421–426. [ADS] (Cited on page 57.)
Durney, B.R., De Young, D.S. and Roxburgh, I.W., 1993, “On the generation of the large-scale and turbulent magnetic field in solar-type stars”, Solar Phys., 145, 207–225. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 22, 42, and 54.)
Eddy, J.A., 1976, “The Maunder Minimum”, Science, 192, 1189–1202. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 51.)
Eddy, J.A., 1983, “The Maunder Minimum: A reappraisal”, Solar Phys., 89, 195–207. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 51.)
Fan, Y., 2009, “Magnetic Fields in the Solar Convection Zone”, Living Rev. Solar Phys., 6, lrsp–2009–4. [ADS]. URL (accessed 9 April 2010): http://www.livingreviews.org/lrsp-2009-4(Cited on pages 10, 17, and 28.)
Fan, Y., Fisher, G.H. and Deluca, E.E., 1993, “The origin of morphological asymmetries in bipolar active regions”, Astrophys. J., 405, 390–401. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 18 and 57.)
Ferriz-Mas, A. and Núñez, M. (Eds.), 2003, Advances in Nonlinear Dynamos, vol. 9 of The Fluid Mechanics of Astrophysics and Geophysics, Taylor & Francis, London, New York (Cited on page 11.)
Ferriz-Mas, A., Schmitt, D. and Schüssler, M., 1994, “A dynamo effect due to instability of magnetic flux tubes”, Astron. Astrophys., 289, 949–956. [ADS] (Cited on pages 17, 40, and 41.)
Feynman, J. and Gabriel, S.B., 1990, “Period and phase of the 88-year solar cycle and the Maunder minimum: Evidence for a chaotic Sun”, Solar Phys., 127, 393–403. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 53.)
Foukal, P.V., 2004, Solar Astrophysics, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2nd edn. (Cited on page 11.) Garaud, P. and Brummell, N.H., 2008, “On the Penetration of Meridional Circulation below the Solar Convection Zone”, Astrophys. J., 674, 498–510. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0708.0258] (Cited on page 45.)
Ghizaru, M., Charbonneau, P. and Smolarkiewicz, P.K., 2010, “Magnetic cycles in global largeeddy simulations of solar convection”, Astrophys. J. Lett., 715, L133–L137. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 48, 49, and 72.)
Gilman, P.A., 1983, “Dynamically consistent nonlinear dynamos driven by convection on a rotating spherical shell. II. Dynamos with cycles and strong feedback”, Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser., 53, 243–268. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 47 and 54.)
Gilman, P.A. and Fox, P.A., 1997, “Joint instability of latitudinal differential rotation and toroidal magnetic fields below the solar convection zone”, Astrophys. J., 484, 439–454. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 38.)
Gilman, P.A. and Miesch, M.S., 2004, “Limits to penetration of meridional circulation below the solar convection zone”, Astrophys. J., 611, 568–574. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 45.)
Gilman, P.A. and Miller, J., 1981, “Dynamically consistent nonlinear dynamos driven by convection in a rotating spherical shell”, Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser., 46, 211–238. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 47.)
Gilman, P.A. and Rempel, M., 2005, “Concentration of Toroidal Magnetic Field in the Solar Tachocline by η-Quenching”, Astrophys. J., 630, 615–622. [DOI], [ADS], [astro-ph/0504003] (Cited on page 22.)
Gilman, P.A., Morrow, C.A. and Deluca, E.E., 1989, “Angular momentum transport and dynamo action in the sun. Implications of recent oscillation measurements”, Astrophys. J., 46, 528–537. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 23.)
Gizon, L., 2004, “Helioseismology of Time-Varying Flows Through The Solar Cycle”, Solar Phys., 224, 217–228. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 13 and 31.)
Gizon, L. and Rempel, M., 2008, “Observation and Modeling of the Solar-Cycle Variation of the Meridional Flow”, Solar Phys., 251, 241–250. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0803.0950] (Cited on pages 31 and 55.)
Glatzmaier, G.A., 1985a, “Numerical simulations of stellar convective dynamos. II. Field propagation in the convection zone”, Astrophys. J., 291, 300–307. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 47.)
Glatzmaier, G.A., 1985b, “Numerical simulations of stellar convective dynamos. III. At the base of the convection zone”, Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn., 31, 137–150. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 47.)
Guerrero, G. and de Gouveia Dal Pino, E.M., 2007, “How does the shape and thickness of the tachocline affect the distribution of the toroidal magnetic fields in the solar dynamo?”, Astron. Astrophys., 464, 341–349. [DOI], [ADS], [astro-ph/0610703] (Cited on page 45.)
Guerrero, G. and de Gouveia Dal Pino, E.M., 2008, “Turbulent magnetic pumping in a Babcock- Leighton solar dynamo model”, Astron. Astrophys., 485, 267–273. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0803.3466] (Cited on pages 42, 45, 46, and 47.)
Guerrero, G.A. and Muñoz, J.D., 2004, “Kinematic solar dynamo models with a deep meridional flow”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 350, 317–322. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 45.)
Haber, D.A., Hindman, B.W., Toomre, J., Bogart, R.S., Larsen, R.M. and Hill, F., 2002, “Evolving Submerged Meridional Circulation Cells within the Upper Convection Zone Revealed by Ring- Diagram Analysis”, Astrophys. J., 570, 855–864. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 31 and 37.)
Hagenaar, H.J., Schrijver, C.J. and Title, A.M., 2003, “The Properties of Small Magnetic Regions on the Solar Surface and the Implications for the Solar Dynamo(s)”, Astrophys. J., 584, 1107–1119. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 60.)
Haigh, J.D., 2007, “The Sun and the Earth’s Climate”, Living Rev. Solar Phys., 4, lrsp–2007–2.[ADS]. URL (accessed 9 April 2010): http://www.livingreviews.org/lrsp-2007-2(Cited on page 51.)
Hathaway, D.H., 1996, “Doppler measurements of the sun’s meridional flow”, Astrophys. J., 460, 1027–1033. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 31.)
Hathaway, D.H., 2010, “The Solar Cycle”, Living Rev. Solar Phys., 7, lrsp–2010–1. [ADS]. URL (accessed 9 April 2010): http://www.livingreviews.org/lrsp-2010-1 (Cited on pages 51, 53, and 69.)
Hathaway, D.H., Wilson, R.M. and Reichmann, E.J., 1999, “A Synthesis of Solar Cycle Prediction Techniques”, J. Geophys. Res., 104, 22,375–22,388. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 68.)
Hathaway, D.H., Wilson, R.M. and Reichmann, E.J., 2002, “Group sunspot numbers: sunspot cycle characteristics”, Solar Phys., 211, 357–370. [ADS] (Cited on page 52.)
Hathaway, D.H., Nandy, D., Wilson, R.M. and Reichmann, E.J., 2003, “Evidence that a deep meridional flow sets the sunspot cycle period”, Astrophys. J., 589, 665–670. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 45.)
Henney, C.J. and Harvey, J.W., 2002, “Phase coherence analysis of solar magnetic activity”, Solar Phys., 207, 199–218. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 72.)
Howe, R., 2009, “Solar Interior Rotation and its Variation”, Living Rev. Solar Phys., 6, lrsp–2009–1. [ADS], [arXiv:0902.2406]. URL (accessed 9 April 2010): http://www.livingreviews.org/lrsp-2009-1 (Cited on pages 13 and 70.)
Hoyng, P., 1988, “Turbulent transport of magnetic fields. III. Stochastic excitation of global magnetic modes”, Astrophys. J., 332, 857–871. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 60.)
Hoyng, P., 1993, “Helicity fluctuations in mean field theory: an explanation for the variability of the solar cycle?”, Astron. Astrophys., 272, 321–339. [ADS] (Cited on pages 21, 60, and 64.)
Hoyng, P., 2003, “The field, the mean and the meaning”, in Advances in Nonlinear Dynamos, (Eds.) Ferriz-Mas, A., Núñez, M., vol. 9 of The Fluid Mechanics of Astrophysics and Geophysics, pp. 1–36, Taylor & Francis, London, New York. [Google Books] (Cited on pages 7 and 21.)
Hoyt, D.V. and Schatten, K., 1998, “Group Sunspot Numbers: A New Solar Activity Reconstruction”, Solar Phys., 179, 189–219. [ADS] (Cited on page 52.)
Hoyt, D.V. and Schatten, K.H., 1996, “How Well Was the Sun Observed during the Maunder Minimum?”, Solar Phys., 165, 181–192. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 51.)
Jennings, R.L. and Weiss, N.O., 1991, “Symmetry breaking in stellar dynamos”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 252, 249–260. [ADS] (Cited on page 57.)
Jiang, J., Chatterjee, P. and Choudhuri, A.R., 2007, “Solar activity forecast with a dynamo model”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 381, 1527–1542. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0707.2258] (Cited on page 68.)
Jiang, J., Cameron, R., Schmitt, D. and Schüssler, M., 2009, “Countercell Meridional Flow and Latitudinal Distribution of the Solar Polar Magnetic Field”, Astrophys. J., 693, L96–L99. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 37 and 41.)
Jouve, L. and Brun, A.S., 2007, “On the role of meridional flows in flux transport dynamo models”, Astron. Astrophys., 474, 239–250. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0712.3200] (Cited on page 41.)
Jouve, L., Brun, A.S., Arlt, R., Brandenburg, A., Dikpati, M., Bonanno, A., Käpylä, P.J., Moss, D., Rempel, M., Gilman, P., Korpi, M.J. and Kosovichev, A.G., 2008, “A solar mean field dynamo benchmark”, Astron. Astrophys., 483, 949–960. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 19.)
Jouve, L., Brown, B.P. and Brun, A.S., 2010, “Exploring the Pcyc vs. Prot relation with flux transport dynamo models of solar-like stars”, Astron. Astrophys., 509, A32. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0911.1947] (Cited on page 45.)
Käpylä, P.J., Korpi, M.J., Ossendrijver, M. and Stix, M., 2006a, “Magnetoconvection and dynamo coefficients. III. α-effect and magnetic pumping in the rapid rotation regime”, Astron. Astrophys., 455, 401–412. [DOI], [ADS], [astro-ph/0602111] (Cited on pages 21, 22, and 72.)
Käpylä, P.J., Korpi, M.J. and Tuominen, I., 2006b, “Solar dynamo models with α-effect and turbulent pumping from local 3D convection calculations”, Astron. Nachr., 327, 884. [DOI], [ADS], [astro-ph/0606089] (Cited on page 34.)
Käpylä, P.J., Korpi, M.J., Brandenburg, A., Mitra, D. and Tavakol, R., 2010, “Convective dynamos in spherical wedge geometry”, Astron. Nachr., 331, 73. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 48.)
Kitchatinov, L.L. and Rüdiger, G., 1993, “Λ-effect and differential rotation in stellar convection zones”, Astron. Astrophys., 276, 96–102. [ADS] (Cited on pages 28 and 54.)
Kitchatinov, L.L. and Rüdiger, G., 2006, “Magnetic field confinement by meridional flow and the solar tachocline”, Astron. Astrophys., 453, 329–333. [DOI], [ADS], [astro-ph/0603417] (Cited on page 53.)
Kitchatinov, L.L., Rüdiger, G. and Küker, M., 1994, “Λ-quenching as the nonlinearity in stellar-turbulence dynamos”, Astron. Astrophys., 292, 125–132. [ADS] (Cited on page 54.)
Kitchatinov, L.L., Mazur, M.V. and Jardine, M., 2000, “Magnetic field escape from a stellar convection zone and the dynamo-cycle period”, Astron. Astrophys., 359, 531–538. [ADS] (Cited on page 71.)
Kitiashvili, I. and Kosovichev, A.G., 2008, “Application of Data Assimilation Method for Predicting Solar Cycles”, Astrophys. J., 688, L49–L52. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0807.3284] (Cited on page 69.)
Kleeorin, N., Rogachevskii, I. and Ruzmaikin, A., 1995, “Magnitude of the dynamo-generated magnetic field in solar-type convective zones”, Astron. Astrophys., 297, 159–167. [ADS] (Cited on page 57.)
Knobloch, E., Tobias, S.M. and Weiss, N.O., 1998, “Modulation and symmetry changes in stellar dynamos”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 297, 1123–1138. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 55.)
Krause, F. and Rädler, K.-H., 1980, Mean-Field Magnetohydrodynamics and Dynamo Theory, Pergamon Press, Oxford; New York (Cited on page 21.)
Küker, M., Arlt, R. and Rüdiger, R., 1999, “The Maunder minimum as due to magnetic Λ-quenching”, Astron. Astrophys., 343, 977–982. [ADS] (Cited on pages 55 and 64.)
Küker, M., Rüdiger, G. and Schulz, M., 2001, “Circulation-dominated solar shell dynamo models with positive alpha effect”, Astron. Astrophys., 374, 301–308. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 34.)
Leighton, R.B., 1964, “Transport of magnetic fields on the sun”, Astrophys. J., 140, 1547–1562. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 41.)
Leighton, R.B., 1969, “A magneto-kinematic model of the solar cycle”, Astrophys. J., 156, 1–26. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 41.)
Lerche, I. and Parker, E.N., 1972, “The Generation of Magnetic Fields in Astrophysical Bodies. IX. A Solar Dynamo Based on Horizontal Shear”, Astrophys. J., 176, 213. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 25.)
Lopes, I. and Passos, D., 2009, “Solar Variability Induced in a Dynamo Code by Realistic Meridional Circulation Variations”, Solar Phys., 257, 1–12. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 62, 63, and 71.)
MacGregor, K.B. and Charbonneau, P., 1997, “Solar interface dynamos. I. Linear, kinematic models in cartesian geometry”, Astrophys. J., 486, 484–501. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 29 and 31.)
Malkus, W.V.R. and Proctor, M.R.E., 1975, “The macrodynamics of α-effect dynamos in rotating fluids”, J. Fluid Mech., 67, 417–443 (Cited on page 54.)
Markiel, J.A and Thomas, J.H., 1999, “Solar interface dynamo models with a realistic rotation profile”, Astrophys. J., 523, 827–837. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 29 and 31.)
Mason, J., Hughes, D.W. and Tobias, S.M., 2002, “The competition in the solar dynamo between surface and deep-seated α-effect”, Astrophys. J. Lett., 580, L89–L92. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 47.)
Mason, J., Hughes, D.W. and Tobias, S.M., 2008, “The effects of flux transport on interface dynamos”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 391, 467–480. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0812.0199] (Cited on page 31.)
Matthews, P.C., Hughes, D.W. and Proctor, M.R.E., 1995, “Magnetic Buoyancy, Vorticity, and Three-dimensional Flux-Tube Formation”, Astrophys. J., 448, 938–941. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 18.)
Miesch, M.S., 2005, “Large-Scale Dynamics of the Convection Zone and Tachocline”, Living Rev. Solar Phys., 2, lrsp–2005–1. URL (accessed 1 May 2005): http://www.livingreviews.org/lrsp-2005-1 (Cited on page 37.)
Miesch, M.S. and Toomre, J., 2009, “Turbulence, Magnetism, and Shear in Stellar Interiors”, Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech., 41, 317–345. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 48.)
Mininni, P.D. and Gómez, D.O., 2002, “Study of Stochastic Fluctuations in a Shell Dynamo”, Astrophys. J., 573, 454–463. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 60.)
Mininni, P.D. and Gómez, D.O., 2004, “A new technique for comparing solar dynamo models and observations”, Astron. Astrophys., 426, 1065–1073. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 60 and 64.)
Mininni, P.D., Gómez, D.O. and Mindlin, G.B., 2002, “Instantaneous phase and amplitude correlation in the solar cycle”, Solar Phys., 208, 167–179. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 53.)
Moffatt, H.K., 1978, Magnetic Field Generation in Electrically Conducting Fluids, Cambridge Monographs on Mechanics and Applied Mathematics, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge; New York (Cited on page 21.)
Moreno-Insertis, F., 1983, “Rise time of horizontal magnetic flux tubes in the convection zone of the Sun”, Astron. Astrophys., 122, 241–250. [ADS] (Cited on page 22.)
Moreno-Insertis, F., 1986, “Nonlinear time-evolution of kink-unstable magnetic flux tubes in the convective zone of the sun”, Astrophys. J., 166, 291–305. [ADS] (Cited on pages 22 and 57.)
Moss, D., 1999, “Non-axisymmetric solar magnetic fields”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 306, 300–306. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 72.)
Moss, D. and Brooke, J.M., 2000, “Towards a model of the solar dynamo”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 315, 521–533. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 54 and 55.)
Moss, D., Tuominen, I. and Brandenburg, A., 1990, “Buoyancy-limited thin-shell dynamos”, Astron. Astrophys., 240, 142–149. [ADS] (Cited on page 71.)
Moss, D., Brandenburg, A. and Tuominen, I., 1991, “Properties of mean field dynamos with nonaxisymmetric α-effect”, Astron. Astrophys., 347, 576–579. [ADS] (Cited on page 72.)
Moss, D., Brandenburg, A., Tavakol, R. and Tuominen, I., 1992, “Stochastic effects in mean-field dynamos”, Astron. Astrophys., 265, 843–849. [ADS] (Cited on page 62.)
Moss, D., Sokoloff, D., Usoskin, I. and Tutubalin, V., 2008, “Solar Grand Minima and Random Fluctuations in Dynamo Parameters”, Solar Phys., 250, 221–234. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0806.3331] (Cited on pages 60 and 64.)
Mundt, M.D., Maguire II, W.B. and Chase, R.R.P., 1991, “Chaos in the Sunspot Cycle: Analysis and Prediction”, J. Geophys. Res., 96, 1705–1716. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 53.)
Muñoz-Jaramillo, A., Nandy, D. and Martens, P.C.H., 2009, “Helioseismic Data Inclusion in Solar Dynamo Models”, Astrophys. J., 698, 461–478. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0811.3441] (Cited on pages 45 and 57.)
Muñoz-Jaramillo, A., Nandy, D. and Martens, P.C.H., 2010a, “Magnetic Quenching of Turbulent Diffusivity: Reconciling Mixing-length Theory Estimates with Kinematic Dynamo Models of the Solar Cycle”, arXiv, e-print. [ADS], [arXiv:1007.1262] (Cited on page 37.)
Muñoz-Jaramillo, A., Nandy, D., Martens, P.C.H. and Yeates, A.R., 2010b, “A Double-Ring Algorithm for Modeling Solar Active Regions: Unifying Kinematic Dynamo Models and Surface Flux-Transport Simulations”, arXiv, e-print. [ADS], [arXiv:1006.4346] (Cited on page 42.)
Mursula, K., Usoskin, I.G. and Kovaltsov, G.A., 2001, “Persistent 22-year cycle in sunspot activity: Evidence for a relic solar magnetic field”, Solar Phys., 198, 51–56. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 53.)
Nandy, D. and Choudhuri, A.R., 2001, “Toward a mean-field formulation of the Babcock-Leighton type solar dynamo. I. α-coefficient versus Durney’s double-ring approach”, Astrophys. J., 551, 576–585. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 42, 43, and 45.)
Nandy, D. and Choudhuri, A.R., 2002, “Explaining the latitudinal distribution of sunspots with deep meridional flow”, Science, 296, 1671–1673. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 42 and 45.)
Ossendrijver, A.J.H., Hoyng, P. and Schmitt, D., 1996, “Stochastic excitation and memory of the solar dynamo”, Astron. Astrophys., 313, 938–948. [ADS] (Cited on page 60.)
Ossendrijver, M., 2003, “The solar dynamo”, Astron. Astrophys. Rev., 11, 287–367. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 7, 11, and 21.)
Ossendrijver, M.A.J.H., 2000a, “Grand minima in a buoyancy-driven solar dynamo”, Astron. Astrophys., 359, 364–372. [ADS] (Cited on pages 40, 41, and 65.)
Ossendrijver, M.A.J.H., 2000b, “The dynamo effect of magnetic flux tubes”, Astron. Astrophys., 359, 1205–1210. [ADS] (Cited on page 41.)
Ossendrijver, M.A.J.H. and Covas, E., 2003, “Crisis-induced intermittency due to attractor-widening in a buoyancy-driven solar dynamo”, Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos, 13, 2327–2333. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 64.)
Ossendrijver, M.A.J.H. and Hoyng, P., 1996, “Stochastic and nonlinear fluctuations in a mean field dynamo”, Astron. Astrophys., 313, 959–970. [ADS] (Cited on page 60.)
Ossendrijver, M.A.J.H. and Hoyng, P., 1997, “Mean magnetic field and energy balance of Parker’s surface-wave dynamo”, Astron. Astrophys., 324, 329–343. [ADS] (Cited on page 31.)
Ossendrijver, M.A.J.H., Stix, M. and Brandenburg, A., 2001, “Magnetoconvection and dynamo coefficients: dependence of the α-effect on rotation and magnetic fields”, Astron. Astrophys., 376, 713–726. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 21 and 60.)
Ossendrijver, M.A.J.H., Stix, M., Brandenburg, A. and Rüdiger, G., 2002, “Magnetoconvection and dynamo coefficients. II. Field-direction dependent pumping of magnetic field”, Astron. Astrophys., 394, 735–745. [ADS] (Cited on page 22.)
Otmianowska-Mazur, K., Rüdiger, G., Elstner, D. and Arlt, R., 1997, “The turbulent EMF as a time series and the ‘equality’ of dynamo cycles”, Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn., 86, 229–247. [DOI] (Cited on page 60.)
Parker, E.N., 1955, “Hydromagnetic Dynamo Models”, Astrophys. J., 122, 293–314. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 8 and 24.)
Parker, E.N., 1975, “The Generation of Magnetic Fields in Astrophysical Bodies. X. Magnetic Buoyancy and the Solar Dynamo”, Astrophys. J., 198, 205–209. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 22.)
Parker, E.N., 1982, “The dynamics of fibril magnetic fields. I. Effect of flux tubes on convection”, Astrophys. J., 256, 292–301. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 71.)
Parker, E.N., 1993, “A solar dynamo surface wave at the interface between convection and nonuniform rotation”, Astrophys. J., 408, 707–719. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 28.)
Passos, D. and Lopes, I., 2008, “A Low-Order Solar Dynamo Model: Inferred Meridional Circulation Variations Since 1750”, Astrophys. J., 686, 1420–1425. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 62 and 63.)
Passos, D. and Lopes, I.P., 2009, “Grand Minima Under the Light of a Low Order Dynamo Model”, arXiv, e-print. [ADS], [arXiv:0908.0496] (Cited on page 62.)
Petrovay, K., 2000, “What makes the Sun tick?”, in The Solar Cycle and Terrestrial Climate, Proceedings of the 1st Solar and Space Weather Euroconference: 25-29 September 2000, Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, Santa Cruz de Tenerife, Tenerife, Spain, (Eds.) Vázquez, M., Schmieder, B., vol. SP-463 of ESA Conference Proceedings, pp. 3–14, European Space Agency, Nordwijk (Cited on page 11.)
Petrovay, K. and Kerekes, A., 2004, “The effect of a meridional flow on Parker’s interface dynamo”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 351, L59–L62. [DOI], [ADS], [astro-ph/0404607] (Cited on page 34.)
Petrovay, K. and Szakály, G., 1999, “Transport effects in the evolution of the global solar magnetic field”, Solar Phys., 185, 1–13. [ADS] (Cited on page 10.)
Phillips, J.A., Brooke, J.M. and Moss, D., 2002, “The importance of physical structure in solar dynamo models”, Astron. Astrophys., 392, 713–727. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 29 and 55.)
Pipin, V.V., 1999, “The Gleissberg cycle by a nonlinear αΛ dynamo”, Astron. Astrophys., 346, 295–302. [ADS] (Cited on page 55.)
Pipin, V.V. and Seehafer, N., 2009, “Stellar dynamos with Ω × J effect”, Astron. Astrophys., 493, 819–828. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0811.4225] (Cited on page 17.)
Platt, N., Spiegel, E.A. and Tresser, C., 1993, “On-off intermittency: A mechanism for bursting”, Phys. Rev. Lett., 70, 279–282. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 62.)
Pouquet, A., Frish, U. and Leorat, J., 1976, “Strong MHD helical turbulence and the nonlinear dynamo effect”, J. Fluid Mech., 77, 321–354. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 22 and 54.)
Proctor, M.R.E. and Gilbert, A.D. (Eds.), 1994, Lectures on Solar and Planetary Dynamos, Publications of the Newton Institute, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge; New York (Cited on page 11.)
Rädler, K.-H., Kleeorin, N. and Rogachevskii, I., 2003, “The Mean Electromotive Force for MHD Turbulence: The Case of a Weak Mean Magnetic Field and Slow Rotation”, Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn., 97, 249–274. [DOI], [ADS], [astro-ph/0209287] (Cited on page 17.)
Rempel, M., 2005, “Influence of Random Fluctuations in the Λ-Effect on Meridional Flow and Differential Rotation”, Astrophys. J., 631, 1286–1292. [DOI], [ADS], [astro-ph/0610132] (Cited on page 37.)
Rempel, M., 2006a, “Transport of Toroidal Magnetic Field by the Meridional Flow at the Base of the Solar Convection Zone”, Astrophys. J., 637, 1135–1142. [DOI], [ADS], [astro-ph/0610133] (Cited on pages 37 and 72.)
Rempel, M., 2006b, “Flux-Transport Dynamos with Lorentz Force Feedback on Differential Rotation and Meridional Flow: Saturation Mechanism and Torsional Oscillations”, Astrophys. J., 647, 662–675. [DOI], [ADS], [astro-ph/0604446] (Cited on pages 37, 55, and 72.)
Rempel, M. and Schüssler, M., 2001, “Intensification of magnetic fields by conversion of potential energy”, Astrophys. J. Lett., 552, L171–L174. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 71.)
Ribes, J.C. and Nesme-Ribes, E., 1993, “The solar sunspot cycle in the Maunder minimum AD1645 to AD1715”, Astron. Astrophys., 276, 549–563. [ADS] (Cited on pages 51, 64, and 72.)
Roald, C.B. and Thomas, J.H., 1997, “Simple solar dynamo models with variable α and ω effects”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 288, 551–564. [ADS] (Cited on page 57.)
Roberts, P.H. and Stix, M., 1972, “α-Effect Dynamos, by the Bullard-Gellman Formalism”, Astron. Astrophys., 18, 453. [ADS] (Cited on page 32.)
Rozelot, J.P., 1995, “On the chaotic behaviour of the solar activity”, Astron. Astrophys., 297, L45–L48. [ADS] (Cited on page 53.)
Rüdiger, G. and Arlt, R., 2003, “Physics of the solar cycle”, in Advances in Nonlinear Dynamos, (Eds.) Ferriz-Mas, A., N’uñez, M., vol. 9 of The Fluid Mechanics of Astrophysics and Geophysics, pp. 147–195, Taylor & Francis, London, New York. [Google Books] (Cited on pages 11 and 28.)
Rüdiger, G. and Brandenburg, A., 1995, “A solar dynamo in the overshoot layer: cycle period and butterfly diagram”, Astron. Astrophys., 296, 557–566. [ADS] (Cited on page 28.)
Rüdiger, G. and Elstner, D., 1994, “Non-axisymmetry vs. axisymmetry in dynamo-excited stellar magnetic fields”, Astron. Astrophys., 281, 46–50. [ADS] (Cited on page 72.)
Rüdiger, G. and Elstner, D., 2002, “Is the Butterfly diagram due to meridional motions?”, Astron. Nachr., 323, 432–435. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 34.)
Rüdiger, G. and Hollerbach, R., 2004, The Magnetic Universe: Geophysical and Astrophysical Dynamo Theory, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. [ADS], [Google Books] (Cited on page 21.)
Rüdiger, G. and Kitchatinov, L.L., 1993, “Alpha-effect and alpha-quenching”, Astron. Astrophys., .269, 581–588. [ADS] (Cited on page 21.)
Rüdiger, G., Kitchatinov, L.L., Küker, M. and Schultz, M., 1994, “Dynamo models with magnetic diffusivity-quenching”, Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn., 78, 247–259. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 22.)
Rüdiger, G., Kitchatinov, L.L. and Arlt, R., 2005, “The penetration of meridional flow into the tachocline and its meaning for the solar dynamo”, Astron. Astrophys., 444, L53–L56. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 45.)
Schatten, K.H., 2009, “Modeling a Shallow Solar Dynamo”, Solar Phys., 255, 3–38. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 71.)
Schatten, K.H., Scherrer, P.H., Svalgaard, L. and Wilcox, J.M., 1978, “Using dynamo theory to predict the sunspot number during solar cycle 21”, Geophys. Res. Lett., 5, 411–414. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 68.)
Schmalz, S. and Stix, M., 1991, “An αΩ dynamo with order and chaos”, Astron. Astrophys., 245, 654–661. [ADS] (Cited on page 57.)
Schmitt, D., 1987, “An αω-dynamo with an α-effect due to magnetostrophic waves”, Astron. Astrophys., 174, 281–287. [ADS] (Cited on page 40.)
Schmitt, D. and Schüssler, M., 1989, “Non-linear dynamos I. One-dimensional model of a thin layer dynamo”, Astron. Astrophys., 223, 343–351. [ADS] (Cited on page 71.)
Schmitt, D. and Schüssler, M., 2004, “Does the butterfly diagram indicate a solar flux-transport dynamo”, Astron. Astrophys., 421, 349–351. [ADS] (Cited on page 45.)
Schmitt, D., Schüssler, M. and Ferriz-Mas, A., 1996, “Intermittent solar activity by an on-off dynamo”, Astron. Astrophys., 311, L1–L4. [ADS] (Cited on pages 40, 41, and 65.)
Schou, J. and Bogart, R.S., 1998, “Flows and Horizontal Displacements from Ring Diagrams”, Astrophys. J. Lett., 504, L131–L134. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 31.)
Schrijver, C.J. and Siscoe, G.L. (Eds.), 2009, Heliophysics: Plasma Physics of the Local Cosmos, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (Cited on page 11.)
Schrijver, C.J., Title, A.M., van Ballegooijen, A.A., Hagenaar, H.J. and Shine, R.A., 1997, “Sustaining the Quiet Photospheric Network: The Balance of Flux Emergence, Fragmentation, Merging, and Cancellation”, Astrophys. J., 487, 424–436. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 60.)
Schrijver, C.J., DeRosa, M.L. and Title, A.M., 2002, “What Is Missing from Our Understanding of Long-Term Solar and Heliospheric Activity?”, Astrophys. J., 577, 1006–1012. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 70.)
Schüssler, M., 1977, “On Buoyant Magnetic Flux Tubes in the Solar Convection Zone”, Astron. Astrophys., 56, 439–442. [ADS] (Cited on page 22.)
Schüssler, M., 1996, “Magnetic flux tubes and the solar dynamo”, in Solar and Astrophysical Magnetohydrodynamic Flows, Proceedings of the NATO Advanced Study Institute, held in Heraklion, Crete, Greece, June 1995, (Ed.) Tsinganos, K.C., vol. 481 of NATO ASI Series C, pp. 17–37, Kluwer, Dordrecht; Boston (Cited on page 17.)
Schüssler, M. and Ferriz-Mas, A., 2003, “Magnetic flux tubes and the dynamo problem”, in Advances in Nonlinear Dynamos, (Eds.) Ferriz-Mas, A., Núñez, M., vol. 9 of The Fluid Mechanics of Astrophysics and Geophysics, pp. 123–146, Taylor & Francis, London, New York. [Google Books] (Cited on page 17.)
Seehafer, N. and Pipin, V.V., 2009, “An advective solar-type dynamo without the α effect”, Astron. Astrophys., 508, 9–16. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0910.2614] (Cited on page 34.)
Sheeley Jr, N.R., 1991, “Polar faculae: 1906-1990”, Astrophys. J., 374, 386–389. [ADS] (Cited on pages 43 and 51.)
Sokoloff, D. and Nesme-Ribes, E., 1994, “The Maunder minimum: A mixed-parity dynamo mode?”, Astron. Astrophys., 288, 293–298. [ADS] (Cited on page 72.)
Spiegel, E.A. and Zahn, J.-P., 1992, “The solar tachocline”, Astron. Astrophys., 265, 106–114. [ADS] (Cited on page 17.)
Spruit, H.C., 1981, “Equations for Thin Flux Tubes in Ideal MHD”, Astron. Astrophys., 102, 129–133. [ADS] (Cited on page 40.)
Steiner, O. and Ferriz-Mas, A., 2005, “Connecting solar radiance variability to the solar dynamo with the virial theorem”, Astron. Nachr., 326, 190–193. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 31.)
Stix, M., 1976, “Differential Rotation and the Solar Dynamo”, Astron. Astrophys., 47, 243–254. [ADS] (Cited on page 24.)
Stix, M., 2002, The Sun: An introduction, Astronomy and Astrophysics Library, Springer, Berlin, New York, 2nd edn. (Cited on page 11.)
Tapping, K., 1987, “Recent solar radio astronomy at centimeter wavelengths: the temporal variability of the 10.7 cm flux”, J. Geophys. Res., .92, 829–838. [DOI] (Cited on page 51.)
Thelen, J.-C., 2000a, “A mean electromotive force induced by magnetic buoyancy instabilities”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 315, 155–164. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 18 and 38.)
Thelen, J.-C., 2000b, “Nonlinear αω-dynamos driven by magnetic buoyancy”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 315, 165–183. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 38 and 54.)
Tobias, S.M., 1996a, “Diffusivity quenching as a mechanism for Parker’s surface dynamo”, Astrophys. J., 467, 870–880. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 29 and 31.)
Tobias, S.M., 1996b, “Grand minimia in nonlinear dynamos”, Astron. Astrophys., 307, L21–L24. [ADS] (Cited on page 64.)
Tobias, S.M., 1997, “The solar cycle: parity interactions and amplitude modulation”, Astron. Astrophys., 322, 1007–1017. [ADS] (Cited on pages 29, 54, 55, and 64.)
Tobias, S.M., 2002, “Modulation of solar and stellar dynamos”, Astron. Nachr., 323, 417–423. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 11.)
Tobias, S.M., Brummell, N.H., Clune, T.L. and Toomre, J., 2001, “Transport and storage of magnetic fields by overshooting turbulent convective convection”, Astrophys. J., 549, 1183–1203. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 48.)
Tobias, S.M., Cattaneo, F. and Brummell, N.H., 2008, “Convective Dynamos with Penetration, Rotation, and Shear”, Astrophys. J., 685, 596–605. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 48.)
Tomczyk, S., Schou, J. and Thompson, M.J., 1995, “Measurement of the Rotation Rate in the Deep Solar Interior”, Astrophys. J. Lett., 448, L57–L60. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 17.)
Toomre, J., Christensen-Dalsgaard, J., Hill, F., Howe, R., Komm, R.W., Schou, J. and Thompson, M.J., 2003, “Transient oscillations near the solar tachocline”, in Local and Global Helioseismology: The Present and Future, Proceedings of SOHO 12/GONG+ 2002, 27 October - 1 November 2002, Big Bear Lake, California, U.S.A.,.(Ed.) Sawaya-Lacoste, H., vol. SP-517 of ESA Conference Proceedings, pp. 409–412, ESA, Noordwijk. [ADS] (Cited on page 70.)
Tworkowski, A., Tavakol, R., Brandenburg, A., Brooke, J.M., Moss, D. and Tuominen, I., 1998, “Intermittent behaviour in axisymmetric mean-field dynamo models in spherical shells”, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 296, 287–295. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 65.)
Ulrich, R.K. and Boyden, J.E., 2005, “The Solar Surface Toroidal Magnetic Field”, Astrophys. J. Lett., 620, L123–L127. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 31 and 37.)
Usoskin, I.G., 2008, “A History of Solar Activity over Millennia”, Living Rev. Solar Phys., 5, lrsp–2008–3. [ADS], [arXiv:0810.3972]. URL (accessed 9 April 2010): http://www.livingreviews.org/lrsp-2008-3 (Cited on pages 51 and 64.)
Usoskin, I.G. and Mursula, K., 2003, “Long-term solar cycle evolution: Review of recent developments”, Solar Phys., 218, 319–343. [DOI] (Cited on pages 11 and 53.)
Usoskin, I.G., Mursula, K., Arlt, R. and Kovaltsov, G.A., 2009a, “A Solar Cycle Lost in 1793-1800: Early Sunspot Observations Resolve the Old Mystery”, Astrophys. J. Lett., 700, L154–L157. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0907.0063] (Cited on pages 54 and 64.)
Usoskin, I.G., Sokoloff, D. and Moss, D., 2009b, “Grand Minima of Solar Activity and the Mean- Field Dynamo”, Solar Phys., 254, 345–355. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 72.)
van Ballegooijen, A.A. and Choudhuri, A.R., 1988, “The possible role of meridional circulation in suppressing magnetic buoyancy”, Astrophys. J., 333, 965–977. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 32 and 33.)
Wang, Y.-M. and Sheeley Jr, N.R., 1991, “Magnetic flux transport and the Sun’s dipole moment: New twists to the Babcock-Leighton model”, Astrophys. J., 375, 761–770. [ADS] (Cited on pages 41 and 70.)
Wang, Y.-M., Nash, A.G. and Sheeley Jr, N.R., 1989, “Magnetic flux transport on the sun”, Science, 245, 712–718. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 41.)
Wang, Y.-M., Sheeley Jr, N.R. and Nash, A.G., 1991, “A new cycle model including meridional circulation”, Astrophys. J., 383, 431–442. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 42.)
Wang, Y.-M., Lean, J. and Sheeley Jr, N.R., 2002, “Role of Meridional Flow in the Secular Evolution of the Sun’s Polar Fields and Open Flux”, Astrophys. J. Lett., 577, L53–L57. [ADS] (Cited on page 70.)
Weiss, N.O., Cattaneo, F. and Jones, C.A., 1984, “Periodic and aperiodic dynamo waves”, Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn., 30, 305–341. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 57.)
Wilmot-Smith, A.L., Nandy, D., Hornig, G. and Martens, P.C.H., 2006, “A Time Delay Model for Solar and Stellar Dynamos”, Astrophys. J., 652, 696–708. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 58.)
Yeates, A.R., Nandy, D. and Mackay, D.H., 2008, “Exploring the Physical Basis of Solar Cycle Predictions: Flux Transport Dynamics and Persistence of Memory in Advection- versus Diffusiondominated Solar Convection Zones”, Astrophys. J., 673, 544–556. [DOI], [ADS], [arXiv:0709.1046] (Cited on page 69.)
Yoshimura, H., 1975, “Solar-cycle dynamo wave propagation”, Astrophys. J., 201, 740–748. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 24.)
Yoshimura, H., 1978, “Nonlinear astrophysical dynamos: Multiple-period dynamo wave oscillations and long-term modulations of the 22 year solar cycle”, Astrophys. J., 226, 706–719. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 57.)
Zhang, K., Chan, K.H., Zou, J., Liao, X. and Schubert, G., 2003a, “A three-dimensional spherical nonlinear interface dynamo”, Astrophys. J., 596, 663–679. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on pages 29 and 72.)
Zhang, K., Liao, X. and Schubert, G., 2003b, “Nonaxisymmetric Instability of a Toroidal Magnetic Field in a Rotating Sphere”, Astrophys. J., 585, 1124–1137. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 38.)
Zhang, K., Liao, X. and Schubert, G., 2004, “A sandwich interface dynamo: linear dynamo waves in the sun”, Astrophys. J., 602, 468–480. [DOI], [ADS] (Cited on page 29.)
Acknowledgement
I wish to thank Jürg Beer, John Brooke, Mausumi Dikpati, Antonio Ferriz-Mas, Mihai Ghizaru, Gustavo Guerrero, David Hathaway, Mathieu Ossendrijver, Dário Passos, and Steve Tobias for providing data and/or graphical material for inclusion in this review; its original 2005 version also benefited from the constructive criticism of Peter Gilman and Michael Stix. At this point, usually all that would normally be left for me to do is to assure readers and colleagues that any error, omission or misrepresentation of their work is not intentional, and to offer general advanced apologies to all slighted. Here however, the organic format of Living Reviews allows actual amendments and additions. Please send your comments/suggestions/criticisms to the above e-mail address. And for this I offer advanced thanks to all future correspondents.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
41116_2015_9142_MOESM1_ESM.mpg
mpg-Movie ((2347.42480469 KB) Still from a movie showing Meridional plane animations for an αΩ dynamo solutions including meridional circulation. With Rm = 103, this solution is operating in the advection-dominated regime as a flux-transport dynamo. The corresponding time-latitude “butterfly” diagram is plotted in Figure 12C below. Color-coding of the toroidal magnetic field and poloidal fieldlines as in Figure 7.
41116_2015_9142_MOESM5_ESM.mpg
mpg-Movie (6019.31738281 KB) Still from a movie showing Meridional plane animation of a representative Babcock-Leighton dynamo solution from Charbonneau et al. (2005). Color coding of the toroidal field and poloidal fieldlines as in Figure 7. This solution uses the same differential rotation, magnetic diffusivity, and meridional circulation profile as for the advection-dominated αΩ solution of Section 4.4, but now with the non-local surface source term, as formulated in Charbonneau et al. (2005), and parameter values Cα = 5, CΩ = 5 × 104, Δη = 0.003, Rm = 840. Note again the strong amplification of the surface polar fields, the latitudinal stretching of poloidal fieldlines by the meridional flow at the core-envelope interface.
41116_2015_9142_MOESM6_ESM.gif
mpg-Movie (31113.9941406 KB) Still from a movie showing Latitude-Longitude Mollweide projection of the toroidal magnetic component at depth r/R = 0.695 in the 3D MHD simulation of Ghizaru et al. (2010). This large-scale axisymmetric component shows a well-defined overall antisymmetry about the equatorial plane, and undergoes polarity reversals approximately every 30 yr. The animation spans a little over three half-cycles, including three polarity reversals. Time is given in solar days, with 1 s.d. = 30 d.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits use, duplication, adaptation, distribution, and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Charbonneau, P. Dynamo Models of the Solar Cycle. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 7, 3 (2010). https://doi.org/10.12942/lrsp-2010-3
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12942/lrsp-2010-3
Keywords
Article history
Latest
Dynamo models of the solar cycle- Published:
- 17 June 2020
- Received:
- 16 December 2019
- Accepted:
- 12 May 2020
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41116-020-00025-6
- Dynamo Models of the Solar Cycle
- Published:
- 04 September 2010
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12942/lrsp-2010-3
Original
Dynamo Models of the Solar Cycle- Published:
- 13 June 2005
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12942/lrsp-2005-2