Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study is to evaluate the results of high tibial osteotomy (HTO) in patients with bone marrow edema (BME) and assess the effect of factors on the subsequent results.
Methods
A total of 138 patients who underwent medial open-wedge HTO using locking plate were included in this study. BME was observed in 108 patients using preoperative magnetic resonance imaging. Clinical results were evaluated before HTO and postoperatively at 12 months. Moreover, we evaluated the factors affecting the clinical results.
Results
The clinical scores were all significantly improved regardless of the presence of BME. There were no differences in improvement of clinical scores between patients with BME and without BME. Patients with BME showed higher postoperative Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index (WOMAC) stiffness scores than patients without BME. Furthermore, patients with BME on both the femur and tibia showed lower Knee Society function scores than patients with BME on either the femur or the tibia. Patients with large BME lesions exhibited a lower Hospital for Special Surgery score and WOMAC pain scores, postoperatively. In patients with BME, patients with undercorrection showed significantly lower improvement in WOMAC pain scores compared with patients with acceptable correction.
Conclusions
The clinical improvement after HTO in patients with varus and medial osteoarthritis was not different regardless of the presence or absence of BME. However, accurate alignment should be considered essential for achieving better clinical outcomes in patients with preoperative BME.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
High tibial osteotomy (HTO) is an effective treatment option for medial osteoarthritis (OA) with varus deformity, especially in young (< 65 years old), active patients [1,2,3,4,5]. This surgical procedure can reduce abnormal loads in the medial compartment by correcting the mechanical axis to the lateral compartment [4, 6,7,8]. Furthermore, this operation can shift load bearing from the medial compartment to lateral compartments that are less affected, a method that has been shown to facilitate cartilage regeneration [9]. These good clinical results have been reported by several studies following HTO [10, 11].
Bone marrow edema (BME) is a nonspecific finding characterized by an ill-defined marrow area of T1-weighted images with low signal intensity and hyperintensity on short tau inversion recovery images and on T2-weighted, fat-suppressed magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) [12, 13]. This condition can be diagnosed in patients with trauma, stress fracture, osteonecrosis, and reactive OA [12, 14]. Especially, BME of the knee joint can be observed in patients even with mild OA and with varus deformities due to the effect of overloading on the subchondral bone.
In patients with varus deformities and medial knee OA, HTO can be an effective treatment modality. Therefore, good clinical results can be obtained in patients with BME, and medial OA could also be treated using HTO. Moreover, the extent of BME or postoperative alignment can affect the postoperative clinical results. The aim of this study is to evaluate how BME could affect the clinical results of patients who underwent HTO. Moreover, this study evaluated the correlation between the postoperative results and the factors including the location, extent, or volume of preoperative BME and postoperative alignment.
Patients and methods
In this study, 138 patients (31 men and 107 women) who underwent medial open-wedge HTO owing to varus deformity and medial OA were selected between October 2010 and December 2019 with a mean age of 58.6 (35–70) years. Among our subjects, BME was observed in 108 patients using preoperative MRI. All patients underwent open-wedge HTO with locking plates. TomoFix locking plates (Synthes GmbH, Solothurn, Switzerland) were used in 62 patients and OhtoFix locking plates (Ohtomedical Co., Ltd., Goyang, Korea) were used in 76 patients. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) age ≤ 70 years, (2) body mass index (BMI) ≤ 30 kg/m2, (3) only medial-side pain, (4) sports activity except running and jumping, (5) varus angle < 15°, and (6) < 10° of knee extension loss and > 90° of knee flexion. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) flexion contracture > 25°, (2) bicompartmental disease, (3) elderly patients with difficulty mobilizing, and (4) BMI > 30 kg/m2. There were no differences in demographics, including age, sex, and preoperative varus deformity between patients with or without BME (Table 1).
This study was approved by the institutional review board (IRB) of our institution (IRB no. 2021-06-023).
Surgical technique
The patients underwent full-length anteroposterior lower limb weight-bearing radiography preoperatively. The target point was determined to be the mechanical axis of the limb located at the 62.5% point from the medial border along the longest medial-to-lateral width of the tibial plateau.
A single surgeon performed all surgeries. A proximal biplanar osteotomy was performed behind the tibial tuberosity after the pes anserinus was completely separated, and the superficial medial collateral ligament was elevated from the periosteum. Thereafter, the posteromedial tibial osteotomy site was opened, and locking plate fixation was performed. Allogeneic bone chips (ReadiGRAFT Cancellous Chips, LifeNet Health, Virginia Beach, Virginia) mixed with autologous bone marrow were harvested from the ipsilateral anterior superior iliac spine and were grafted into the osteotomy gap. The osteotomy site was covered with the superficial medial collateral ligament, and the pes anserinus was resutured to the periosteal membrane.
All patients performed range of motion activities from the second day with maintenance of a night splint. A partial weight bearing was permitted from 2 weeks postoperatively, whereas full weight bearing with a brace was allowed after 4 weeks.
Assessment
Clinical results, including the Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) score, Knee Society knee score (KS), and function score (FS), and The Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index (WOMAC), were evaluated before HTO and postoperatively at 12 months. Moreover, we evaluated the factors affecting the clinical results, including the existence, position, extent, and volume of BME and postoperative correction degree.
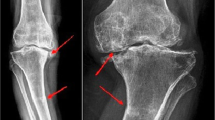
Patients underwent preoperative MRI to evaluate BME, and all planes (coronal, sagittal, and axial) and T1 and T2-weighted sequences were reviewed in a picture archiving and communication system. BME on MRI was characterized by an ill-defined marrow area of T1-weighted images with low signal intensity and hyperintensity on short tau inversion recovery images and on T2-weighted, fat-suppressed MRI. Furthermore, the existence, position, extent, and volume of BME were evaluated using MRI. BME was all in the weight-bearing area. The position of BME was divided into groups of (a) only femur, (b) only tibia, and (c) both femur and tibia. The extent of BME was evaluated in accordance with the report of Welsch et al. [15]. The maximum BME diameter scores were determined as follows: 1 = small (< 1 cm), 2 = medium (< 2 cm), 3 = large (< 4 cm), and 4 = very large (> 4 cm). The scores of each tibia and femur were summarized and divided into two groups. The large group was defined as the summarized scores being 5 or more, and the small group being 4 or less. The volume of BME was calculated using the formula for prolate ellipsoid: length × width × depth × π/6(Fig. 1) [16]. The median value of the volume was 2.98 cm3, and groups were classified according to this value.
A preoperative coronal and sagittal MR image of a 52-year-old woman shows subchondral BME in the medial femoral condyle. The greatest lateral (L = length) and cranial (W = width) extents were measured on coronal images and the greatest sagittal extent (D = depth) was measured on sagittal images. The volumes were calculated using the formula for a prolate ellipsoid: length × width × depth × π/6
The alignment of the patients was evaluated using full-length lower limb radiographs. The percentages of crossing points of the weight-bearing line and tibial plateau with respect to the medial border were measured. As mentioned above, the target point was defined the 62.5% point from the medial border along the longest medial-to-lateral width of the tibial plateau. The postoperative correction degree was divided into three types. Acceptable correction was determined to be within 5% of the target point (57.5–67.5%), undercorrection was determined to be under 5% of the target point (57.5%), and overcorrection was determined to be over 5% of the target point (67.5%) [17].
Statistical analysis
The paired t-test was used to compare preoperative and postoperative values. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) test and independent t-test were used for evaluation of the factors, including the existence, position, extent, and volume of BME. ANOVA test was used for evaluating the differences of clinical results based on postoperative correction acceptability. Moreover, Scheffé’s post hoc analysis was performed to confirm the difference among groups.
Statistical significance was assumed at a p value < 0.05. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS Statistics version 21.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY).
Results
Alignment was corrected from 14.1 ± 12.4% (−20.5% to 46.1%) preoperatively to 58.3 ± 6.7% (45.9–73.9%) postoperatively after medial open-wedge HTO in a total of 138 patients. All clinical scores were significantly improved in both groups, 103 patients with BME and 30 patients without BME (Table 2). The mean improvement of all scores was not different between two groups (Table 3). There were not postoperative complications including the fracture, nonunion, or infection.
Patients with BME on both femur and tibia showed lower FS than patients with BME on either femur or tibia (p = 0.045) (Table 4). Pertaining to the BME extent, patients with large BME lesions exhibited lower HSS and WOMAC pain scores, postoperatively (p = 0.030 and p = 0.039, respectively) (Table 5). With respect to the BME volume, there were no significant differences in clinical scores between patients with high and low volume (Table 6).
According to postoperative alignment, the postoperative clinical scores were not different in both patients with and without BME (Table 7). However, in patients with BME, the change of WOMAC pain score was correlated to the degree of correction (p = 0.016). Especially, in patients with BME, patients with undercorrection showed significantly lower improvement compared with patients with acceptable corrections (p = 0.019) (Table 8).
Discussion
In the present study, the clinical improvement after HTO was not different regardless of the presence or absence of BME. The extent and location of BME could also affect the postoperative clinical results. Furthermore, patients with postoperative undercorrection showed less improvement in the WOMAC pain score compared with patients with acceptable corrections. Therefore, accurate alignment should be considered essential for achieving better clinical outcomes in patients with preoperative BME.
BME could be diagnosed in patients with trauma, stress fracture, osteonecrosis, and reactive change of OA [12, 14]. Especially BME on the medial compartment of the knee joint can be observed mostly in patients with varus deformities due to the effect of overloading on the subchondral bone. Felson et al. [18] reported that BME lesions were present in half of patients with pain, and pain was improved as the BME lesions disappeared. Furthermore, the risk of progression of knee OA could be increased by BME lesions [19]. However, in this study, the preoperative clinical scores were not different regardless of the presence or absence of BME. Moreover, the improvement of all clinical scores after HTO also was not different. Therefore, it was considered that BME was not significantly associated with preoperative clinical scores such as pain and postoperative clinical improvement after HTO.
Several results have reported the effect of BME lesions on the results after HTO. For instance, Kröner et al. [16] have reported BME reduction and clinical improvement. After HTO, postoperative valgus knee showed reduced edema, whereas neutral or varus knee showed either increased or unchanged BME in 40% of the patients and unsatisfactory clinical results. In this study, patients with undercorrection demonstrated a higher WOMAC pain score postoperatively compared with patients with acceptable corrections. HTO aims to correct mild valgus alignment postoperatively [6, 8, 20,21,22]. Postoperative varus correction may lead to recurrence of lower deformity, whereas overcorrection may cause lateral compartment knee OA [7, 23]. Therefore, accurate correction could be one of the most critical factors that affects postoperative results in patients with BME. Kim et al. [24] reported that the severity of BME is associated with the subsequent clinical outcomes. Especially, 1-year postoperative results are associated with the extent or intensity of BME, and clinical improvements were shown at 2 years postoperatively regardless of the severity of BME. In this study, the maximal diameter of BME could affect the postoperative clinical results, whereas the volume of BME was not associated with the postoperative clinical results. Yang et al. [25] reported on the midterm results after HTO in patients with tibial BME. The authors did not find any correlation between preoperative BME severity and postoperative clinical outcomes, and HTO could be considered an effective treatment option regardless of the degree of preoperative tibial BME. In this study, the position of BME, especially in patients with BME on both femur and tibia, was related to a lower Knee Society function score as opposed to patients with BME on either femur or tibia. Consequently, the position of BME could be associated with postoperative clinical outcomes.
In the present study, patients with BME did not exhibit poor postoperative clinical scores compared with patients without BME. More specifically, the clinical scores of patients without BME were not affected by the postoperative correction degrees. However, undercorrected BME patients showed lower WOMAC pain score improvements compared with well-corrected patients. Therefore, it can be suggested that accurate correction is an essential factor for achieving better clinical outcomes of HTO.
The limitations of this study include its small number of patients, retrospective design, and postoperative evaluation using clinical scores without using MRI to perform BME measurements. And, the status of cartilage, meniscus, or grade of OA were not considered. These variables could affect the postoperative clinical outcomes. Moreover, the mean postoperative mechanical axis was 58.3 ± 6.7%, which is lower than the target point (62.5%), and the high rate of patients with undercorrection after HTO could be the limitation of this study. A further long-term follow-up and prospective study with a large sample and evaluation of BME change should be performed.
Conclusions
The clinical improvement after HTO in patients with varus and medial OA was not different regardless of the presence or absence of BME. However, accurate alignment should be considered essential for achieving better clinical outcomes in patients with preoperative BME.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- HTO:
-
High tibial osteotomy
- BME:
-
Bone marrow edema
- WOMAC:
-
Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index
- OA:
-
Osteoarthritis
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- IRB:
-
Institutional review board
- HSS:
-
Hospital for Special Surgery
- KS:
-
Knee score
- FS:
-
Function score
References
Amendola A, Bonasia DE (2010) Results of high tibial osteotomy: review of the literature. Int Orthop 34:155–160
Sprenger TR, Doerzbacher JF (2003) Tibial osteotomy for the treatment of varus gonarthrosis. Survival and failure analysis to twenty-two years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 85:469–474
Park SH, Jung KH, Chang SW, Jang SM, Park KB (2020) Trends in knee surgery research in the official journal of the Korean knee society during the period 1999–2018: a bibliometric review. Knee Surg Relat Res 32:28
Na YG, Lee BK, Choi JU, Lee BH, Sim JA (2021) Change of joint-line convergence angle should be considered for accurate alignment correction in high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Relat Res 33:4
Kang BY, Lee DK, Kim HS, Wang JH (2022) How to achieve an optimal alignment in medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy? Knee Surg Relat Res 34:3
Fujisawa Y, Masuhara K, Shiomi S (1979) The effect of high tibial osteotomy on osteoarthritis of the knee. An arthroscopic study of 54 knee joints. Orthop Clin North Am. 10:585–608
Hernigou P, Medevielle D, Debeyre J, Goutallier D (1987) Proximal tibial osteotomy for osteoarthritis with varus deformity. A ten to thirteen-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 69:332–354
Matsushita T, Watanabe S, Araki D, Nagai K, Hoshino Y, Kanzaki N, Matsumoto T, Niikura T, Kuroda R (2021) Differences in preoperative planning for high-tibial osteotomy between the standing and supine positions. Knee Surg Relat Res 33:8
Jung WH, Takeuchi R, Chun CW, Lee JS, Ha JH, Kim JH, Jeong JH (2014) Second-look arthroscopic assessment of cartilage regeneration after medial opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Arthroscopy 30:72–79
Niinimäki T, Eskelinen A, Mann B, Junnila M, Ohtonen P, Leppilahti J (2012) Survivorship of high tibial osteotomy in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: Finnish registry-based study of 3195 knees. J Bone Jt Surg. 94:1517–1521
Schallberger A, Jacobi M, Wahl P, Maestretti G, Jakob RP (2011) High tibial valgus osteotomy in unicompartmental medial osteoarthritis of the knee: a retrospective follow-up study over 13–21 years. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19:122–127
Yu JS, Cook PA (1996) Magnetic resonance imaging (mri) of the knee: a pattern approach for evaluating bone marrow edema. Crit Rev Diagn Imaging 37:261–303
Zanetti M, Bruder E, Romero J, Hodler J (2000) Bone marrow edema pattern in osteoarthritic knees: correlation between MR imaging and histologic findings. Radiology 215:835–840
Hayes CW, Conway WF, Daniel WW (1993) Mr imaging of bone marrow edema pattern: transient osteoporosis, transient bone marrow edema syndrome, or osteonecrosis. Radiographics 13:1001–1011 (discussion 12)
Welsch GH, Zak L, Mamisch TC, Resinger C, Marlovits S, Trattnig S (2009) Three-dimensional magnetic resonance observation of cartilage repair tissue (mocart) score assessed with an isotropic three-dimensional true fast imaging with steady-state precession sequence at 3.0 tesla. Invest Radiol. 44:603–612
Kroner AH, Berger CE, Kluger R, Oberhauser G, Bock P, Engel A (2007) Influence of high tibial osteotomy on bone marrow edema in the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res 454:155–162
Kim HJ, Park J, Shin JY, Park IH, Park KH, Kyung HS (2018) More accurate correction can be obtained using a three-dimensional printed model in open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 26:3452–3458
Felson DT, Chaisson CE, Hill CL, Totterman SM, Gale ME, Skinner KM, Kazis L, Gale DR (2001) The association of bone marrow lesions with pain in knee osteoarthritis. Ann Intern Med 134:541–549
Felson DT, McLaughlin S, Goggins J, LaValley MP, Gale ME, Totterman S, Li W, Hill C, Gale D (2003) Bone marrow edema and its relation to progression of knee osteoarthritis. Ann Intern Med 139:330–336
Moore J, Mychaltchouk L, Lavoie F (2017) Applicability of a modified angular correction measurement method for open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 25:846–852
Elson DW, Petheram TG, Dawson MJ (2015) High reliability in digital planning of medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy, using miniaci’s method. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23:2041–2048
Jones LD, Brown CP, Jackson W, Monk AP, Price AJ (2017) Assessing accuracy requirements in high tibial osteotomy: a theoretical, computer-based model using ap radiographs. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 25:2952–2956
Ivarsson I, Myrnerts R, Gillquist J (1990) High tibial osteotomy for medial osteoarthritis of the knee. A 5 to 7 and 11 year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 72:238–244
Kim MS, Koh IJ, Sohn S, Sung HS, In Y (2019) Degree of preoperative subchondral bone marrow lesion is associated with postoperative outcome after medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy. Am J Sports Med 47:2454–2463
Yang HY, Kang SJ, Kwak WK, Song EK, Seon JK (2020) The influence of preoperative tibial bone marrow edema on outcomes after medial opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy. J Bone Joint Surg Am 102:2068–2076
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Pioneer Research Center Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (Project No. 2022M3C1A3091627).
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.-J.K. designed the study, collected data and wrote the manuscript. J.-Y.S. analyzed the data. H.-J.L. wrote the manuscript. D.-H.K. collected data and wrote the manuscript. Y.J. wrote the manuscript. J.-W.K. wrote the manuscript. C.-W.O. wrote the manuscript. H.-S.K. designed the study, performed the surgery, and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the institutional review board (IRB) of Kyungpook National University Hospital (IRB no. KNUH 2021-06-023).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, HJ., Shin, JY., Lee, HJ. et al. Does preoperative bone marrow edema affect clinical outcomes after medial open-wedge high tibial osteotomy?. Knee Surg & Relat Res 36, 9 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43019-023-00200-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43019-023-00200-7