Abstract
Purpose
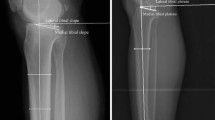
Pre-operative planning is essential in high tibial osteotomy (HTO). Miniaci’s method employs Mikulicz’s weight-bearing line and is advantageous because the point of mechanical loading is related to the known degenerative condition of the knee. Miniaci’s geometrical method has been modified for an opening wedge and described for use with a digital picture archiving and communications system viewer. Reliability for this method was hypothesised to be equivalent to published reliability for landmark-based commercial software and independent of observer experience.
Methods
Twenty-four patients awaiting HTO had standardised long-leg radiographs. Mikulicz’s weight-bearing line was projected through the lateral compartment of the knee at Fujisawa’s point. The correction angle was generated at the hinge point subtending the current and proposed ankle centres. The opening wedge was plotted to measure an opening distance. Observations were recorded twice by three observers. Agreement was reported as intraclass correlation coefficients with 95 % confidence intervals.
Results
Intra-rater agreement was excellent for the correction angle (0.965–0.985) and opening distance (0.928–0.980). If no set hinge point was used, then the inter-rater reliability was 0.986 for the correction angle and 0.984 for the opening distance. There was no discernible pattern demonstrating improved reliability from the experienced observer.
Conclusions
Reliability is comparable to commercially based landmark software and independent of observer experience. This makes such geometrical pre-operative planning accessible to surgeons who perform HTO with insufficient frequency to justify the investment in commercial software.
Level of evidence
Diagnostic study, Level II.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akamatsu Y, Mitsugi N, Mochida Y, Taki N, Kobayashi H, Takeuchi R, Saito T (2012) Navigated opening wedge high tibial osteotomy improves intraoperative correction angle compared with conventional method. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20:586–593
Akizuki S, Shibakawa A, Takizawa T, Yamazaki I, Horiuchi H (2008) The long-term outcome of high tibial osteotomy: a 10–20-year follow-up. J Bone Jt Surg Br 90:592–596
Boesecke R, Bruckner T, Ende G (2000) Landmark based correlation of medical images. Phys Med Biol 35:121–126
Brown GA, Amendola A (2000) Radiographic evaluation and preoperative planning for high tibial osteotomies. Oper Tech Sports Med 8:2–14
Coventry MB (1985) Upper tibial osteotomy for osteoarthritis. J Bone Jt Surg Am 67:1136–1140
Demange MK, Camanho GL, Pécora JR, Gobbi RG, Tirico LEP, da Mota E, Albuquerque RF (2011) Simultaneous anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction and computer-assisted open-wedge high tibial osteotomy: a report of eight cases. Knee 18:387–391
Engel GM, Lippert FG (1981) Valgus tibial osteotomy: avoiding the pitfalls. Clin Orthop Rel Res 160:137–143
Flecher X, Parratte S, Aubaniac J-M, Argenson J-NA (2006) A 12–28-year followup study of closing wedge high tibial osteotomy. Clin Orthop Rel Res 452:91–96
Fujisawa Y, Masuhara K, Shiomi S (1979) The effect of high tibial osteotomy on osteoarthritis of the knee. An arthroscopic study of 54 knee joints. Orthop Clin North Am 10:585–608
Han SB, Lee DH, Shetty GM, Chae DJ, Song JG, Nha KW (2013) A “safe zone” in medial open-wedge high tibia osteotomy to prevent lateral cortex fracture. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21:90–95
Hankemeier S, Gosling T, Richter M, Hufner T, Hochhausen C, Krettek C (2006) Computer-assisted analysis of lower limb geometry: higher intraobserver reliability compared to conventional method. Comput Aided Surg 11:81–86
Harris WR, Kostuik JP (1970) High tibial osteotomy for osteo-arthritis of the knee. J Bone Jt Surg Am 52:330–336
Hernigou P, Medevielle D, Debeyre J, Goutallier D (1987) Proximal tibial osteotomy for osteoarthritis with varus deformity: a 10–13-year follow-up study. J Bone Jt Surg Am 69:332–354
Insall J, Shoji H, Mayer V (1974) High tibial osteotomy: a 5-year evaluation. J Bone Jt Surg Am 56:1397–1405
Iorio R, Pagnottelli M, Vadalà A, Giannetti S, Di Sette P, Papandrea P, Conteduca F, Ferretti A (2013) Open-wedge high tibial osteotomy: comparison between manual and computer-assisted techniques. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21:113–119
Ivarsson I, Myrnerts R, Gillquist J (1990) High tibial osteotomy for medial osteoarthritis of the knee: A 5–7 and 11 year follow-up. J Bone Jt Surg Br 72:238–244
Jackson JP, Waugh W (1961) Tibial osteotomy for osteoarthritis of the knee. J Bone Jt Surg Br 43-B:746–751
Kettelkamp DB, Chao EY (1972) A method for quantitative analysis of medial and lateral compression forces at the knee during standing. Clin Orthop Relat Res 83:202–213
Koshino T, Morii T, Wada J, Saito H, Ozawa N, Noyori K (1989) High tibial osteotomy with fixation by a blade plate for medial compartment osteoarthritis of the knee. Orthop Clin North Am 20:227–243
Koshino T, Yoshida T, Ara Y, Saito I, Saito T (2004) Fifteen to twenty-eight years’ follow-up results of high tibial valgus osteotomy for osteoarthritic knee. Knee 11:439–444
Lee YS, Kim MG, Byun HW, Kim SB, Kim JG (2013) Reliability of the imaging software in the preoperative planning of the open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. doi:10.1007/s00167-013-2700-z
Macewen W (1879) Antiseptic osteotomy in genu valgum and anterior tibial curves: with a few remarks on the pathology of knock-knee. Br Med J 2:607–609
McGraw KO, Wong SP (1996) Forming inferences about some intraclass correlation coefficients. Psychol Method 1:30–46
Miniaci A, Ballmer FT, Ballmer PM, Jakob RP (1989) Proximal tibial osteotomy: a new fixation device. Clin Orthop Relat Res 246:250–259
Myrnerts R (1980) Failure of the correction of varus deformity obtained by high tibial osteotomy. Acta Orthop Scand 51:569–573
Pape D, Lobenhoffer P, Galla M (2009) Detailed planning algorithm for high tibial osteotomy. In: Lobenhoffer P, Heerwaarden RJ, Staubli AE, Jakob RP (eds) Osteotomies around the knee, 1st edn. Thieme, New York, p 43
Riddle DL, Jiranek WA, Hull JR (2013) Validity and reliability of radiographic knee osteoarthritis measures by arthroplasty surgeons. Orthopedics 36:e25–e32
Schmidutz F, Steinbrück A, Wanke-Jellinek L, Pietschmann M, Jansson V, Fottner A (2012) The accuracy of digital templating: a comparison of short-stem total hip arthroplasty and conventional total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop 36:1767–1772
Schröter S, Ihle C, Mueller J, Lobenhoffer P, Stöckle U, van Heerwaarden R (2013) Digital planning of high tibial osteotomy: interrater reliability by using two different software. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21:189–196
Shrout PE, Fleiss JL (1979) Intraclass correlations: uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol Bull 86:420–428
Sled EA, Sheehy LM, Felson DT, Costigan PA, Lam M, Cooke TDV (2011) Reliability of lower limb alignment measures using an established landmark-based method with a customized computer software program. Rheumatol Int 31:71–77
Smith JO, Wilson AJ, Thomas NP (2013) Osteotomy around the knee: evolution, principles and results. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21:3–22
Specogna AV, Birmingham TB, DaSilva JJ, Milner JS, Kerr J, Hunt MA, Jones IC, Jenkyn TR, Fowler PJ, Giffin JR (2004) Reliability of lower limb frontal plane alignment measurements using plain radiographs and digitized images. J Knee Surg 17:203–210
Sprenger TR, Doerzbacher JF (2003) Tibial osteotomy for the treatment of varus gonarthritis: survival and failure analysis to 22 years. J Bone Jt Surg Am 85-A:469–474
Wiig O, Terjesen T, Svenningsen S (2002) Inter-observer reliability of radiographic classifications and measurements in the assessment of Perthes’ disease. Acta Orthop Scand 73:523–530
Conflict of interest
No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elson, D.W., Petheram, T.G. & Dawson, M.J. High reliability in digital planning of medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy, using Miniaci’s method. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23, 2041–2048 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-014-2920-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-014-2920-x