Abstract
Background
The safe disposal of green waste is necessary for a clean environment, with the safe disposal of waste contaminated with aflatoxins being of particular importance. This work presents a novel route for utilizing contaminated grains in the production of clay bricks. In this work, the contaminated peanut (P) with aflatoxins (AFs) is divided into two categories: PA is the contaminated peanut kernel (without the outer shell), and PB is contaminated whole peanut grain (with the outer shell). Both of ground PA and PB were used to replace the clay in fired building bricks. The raw materials were characterized using X-ray fluorescence (XRF), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and thermo-gravimetric analyses (TGA). The effectiveness of this approach was evaluated by measuring the effect of the replacement percentage and firing temperature on the properties of the produced building bricks.
Results
The optimization of the process parameters was performed using central composite design as a tool in the response surface methodology. The ANOVA analysis of the predicted quadratic model elucidated significant models’ terms and adequate precision that emphasizes the applicability of the model to navigate the design space. The results revealed that the optimum conditions are 6% clay replacement and 725 °C firing temperature, resulting in a compressive strength of 109.85 kg cm−2 for clay bricks with PA and 126.33 kg cm−2 for clay bricks with PB.
Conclusions
The objective of clay replacement by the contaminated peanut is not to improve the clay brick properties but to perform safe disposal of the accumulated contaminated peanut without deviating from the standards. The design of experiment using response surface method enables studying the effect of several factors on the clay brick properties simultaneously. Subsequently, this approach elucidates a sustainable route for accumulated contaminated green peanut waste disposal as the other alternatives have realized risks.

Similar content being viewed by others
Highlights
-
A new, green, and novel disposal of Aflatoxins in peanut was presented in the current study as additive in bricks production.
-
The produced green bricks will withstand handling with negligible losses.
-
This study paves the way for a more sustainable environment with zero-waste production.
Background
Aflatoxins (AFs) are mycotoxins produced by toxigenic molds, such as Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus, the most toxic types of which are B1, B2, G1, and G2. AFs are highly genotoxic carcinogenic compounds, classified as a Group I carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) (Saha and Wu 2019). AFs-producing fungi are predominantly found in hot and humid climate zones and their presence in food can be due to both preharvest and postharvest fungal contamination. The level and degree of contamination depend on the temperature, moisture content, soil type, and storage conditions (Schrenk et al. 2020). AF contamination is very common in many foods, including peanuts, nuts, spices, oilseeds, and products of these foodstuffs (Mohammed et al. 2018; Al Ayoubi et al. 2021; Kortei et al. 2021). Various health risk assessment studies have been published recently regarding AFs worldwide; these were prompted due to health concerns and alerts for potential health effects on humans (Wang et al. 2018; Sebaei et al. 2020). Significantly, more rigid guidelines have been set up by the European Commission (EC) with a maximum permissible limit (MPL) of 4 μg kg−1 for AFs in peanuts, dried organic products, and cereals for direct human consumption or use as food ingredients (EC, 2010). All shipments exceeding the MPL are rejected, and many of them represent a health risk when returning to exporting countries, especially developing countries.
Because of the extreme stability of AFs under different harsh conditions, including high heat and extreme pH (measurement of pH below about 2.5, and above about 10.5), it is very hard to eliminate AFs completely from food and fodder. Various techniques to minimize the risk of exposure to AFs have been reported. These approaches can be classified as a preharvest counteraction to the creation of AFs and postharvest AF reduction or detoxification. The use of good manufacturing practices, i.e., the utilization of fertilizers, pest control, antifungal crop varieties, harvesting at the opportune time, and keeping up low dampness and temperature during marketing, can reduce fungal growth and the production of AFs in grains. These methodologies are generally unsuccessful in the elimination of AFs from food and fodder (Guo et al. 2021). This emphasizes the need for postharvest elimination of AF contamination. Traditional postharvest reduction techniques to detoxify AFs include physical and chemical treatments, such as irradiation, extrusion cooking, ozone treatment, reaction with organic acids, and ammoniation. Meanwhile, biocontrol by microorganisms has acquired prominence because of its friendliness to both the environment and humans (Peng et al. 2018).
Several attempts at waste utilization and recycling have been conducted in numerous countries worldwide to achieve reduced ecological impact or increased economic savings (Gupta et al. 2020). Some interesting research has combined different waste products into clay bricks as a substitute, additive, or support; this research has frequently shown that the concept is of positive value both economically and environmentally. The use of organic waste additives has also been recommended by several authors because of the exothermic character of their oxidation, which represents a key factor in decreasing the fuel required for firing.
Such works have used many waste products, including waste tea (Demir, 2006), cigarette butts (Abdul-Kadir and Mohajerani 2008; 2011), dried mango leaves (Folaranmi, 2009), pineapple leaves and oil palm fruit bunch (Chan 2011), sugarcane bagasse ash (Faria et al. 2012), plastic waste (Mobili et al. 2018), travertine sludge (Shishegaran et al. 2021), wastewater treatment plant sludge (Limami et al. 2021), industrial waste (Balasubramaniam et al. 2021), waste products from concrete (Mahmoodi et al. 2021), industrial acetylene biomass ash (Eliche-Quesada et al. 2021), potato peel powder and sour orange leaf (Ghorbani et al. 2021), coal dust (Vasić et al. 2021), date palm waste (Khoudja et al. 2021), and peanut shell ash (Diedhiou et al. 2019).
The utilization of whole contaminated grains in the production of fired clay bricks has not been reported previously. In this work, the evaluation of this novel approach has been undertaken by investigating the properties of the fired bricks and the effect of the replacement percentage and the firing temperature on the product characteristics. The optimization of these parameters was performed using central composite design (CCD) as a tool for use in the response surface methodology (RSM) to minimize the number of experiments (El-Mekkawi et al. 2020).
The present work investigates the possibility of utilizing peanuts contaminated with AFs in the manufacture of clay building bricks. Such a method would constitute a step toward an integrated sustainable solution for diminishing the harmful effect of contaminated grains, providing an ecofriendly product, and preserving clay as a natural resource. In this study, peanuts contaminated with AFs are divided into two groups. The first group (PA) is the contaminated peanut kernel (without the outer shell), and the second (PB) is the contaminated whole peanut grain (with the outer shell). Ground PA and PB are added to the clay in certain proportions and fired at scheduled temperatures to examine their effect on the clay brick characteristics.
Methods
Raw materials
Peanuts
Ten kilograms of contaminated peanut samples without their shell (peanut kernel) and with their shell was used in this experiment. The peanut stock was collected from local retail sources. The peanuts were analyzed for AFs in the Central Laboratory of Pesticides and Heavy Metals in Food, which showed high contamination levels with an AF concentration exceeding 100 µg/kg. The two samples were crushed and blended for homogenization using a high-speed blender; the samples after preparation had a particle size smaller than 2 mm. They were then tested for the main chemical composition and ash content using the standard test method AOAC 923.03 (2016), for moisture content following the test procedure AOAC 925.09 (2016), and for fat content according to the standard AOAC 2003.05 (2016). A chemical analysis of the two peanut wastes was undertaken using an X-ray fluorescence (XRF) diffractometer (Philips PW 1730).
Clay brick basic mix
The clay material used in the manufacture of the clay bricks was obtained from Arab Abu-Saed, Helwan, Cairo, Egypt. The clay material used was subjected to the following analyses: The chemical composition was assessed using an XRF diffractometer (Philips PW1730), the mineralogical composition was obtained using a computerized X-ray diffractometer (Bruker D8), and a thermal analysis was conducted using a combined DTA and TGA apparatus (Netzsch STA 409 C/CD) at a heating rate of 10 °C min−1 in nitrogen. The clay material was screened according to ASTM D 422 (2007) to estimate its particle size distribution using a standard set of sieves in agreement with ASTM E 11 (2021). The screen apertures varied from 4.75 mm (4 mesh) to 45 µm (325 mesh). Finally, the free silica content was determined via the standard method of Kumari and Mohan (2021), and the powder density was determined using the liquid pycnometer method (ASTM D 854/2014 2021; ISO 1183-1/2019).
Design of experiments
The simultaneous optimization of the degree of clay replacement (whether using sample PA or PB) and the firing temperature is necessary to investigate any possible interaction between these two parameters and to optimize the compressive strength of the fired brick sample. With this aim, 13 duplicated experiments were performed on the basis of a range of replacement percentages (6%–35%) and a range of firing temperatures (725–875°C) using central composite design (CCD) in the response surface methodology (RSM) by the Design Expert 6.0.8 software during a trial period. The specified ranges, as shown in Table 1, were selected on the basis of preliminary experiments. The parameters used in this study are given in Table 1. Each parameter was analyzed statistically at five levels; these levels were coded as −α, −1, 0, +1, +α, respectively. The total number of experiments undertaken was 13, with four factorial points (22), four axial points (2 × 2), and five replicate points in accordance with the CCD.
The mathematical relationship between the parameters and the response can be approximated using the following second-order polynomial model (El-Mekkawi et al. 2020):
where Y is the predicted response; a0 is the intercept regression constant; a1, a2,…, a12 are regression coefficients; and X1 and X2 are the independent variables investigated. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed to judge the significance and goodness of fitting using the developed model.
Preparation of the brick samples
The set of 13 triplicated cubic samples were molded with dimensions of 50 × 50 × 50 mm3 by dry pressing using a laboratory hydraulic press under uniaxial pressure of 40 kg cm−2 with 15% water as a binder. The samples were dried in three phases using a laboratory dryer. The first phase was at 50 °C for 24 h, followed by drying at 80 °C for 3 h, and finally drying at 110 °C for 3 h. The linear shrinkage and green compressive strength of the unfired brick samples were determined according to the ASTM standards (ASTM C 326/2018 2021; ASTM C 67/2020 2021). The samples were fired at the five temperatures stated in Table 1, using a Prothem electrical furnace model PLF 14,015 with a heating rate of 10 °C/min and a total firing time of 2 h.
Determination of the properties of the fired bricks
The physical and mechanical properties of the fired clay brick samples were tested according to the ASTM standards. The firing shrinkage was measured according to ASTM C 326 (2021), whereas the cold and boiling water absorption as well as the saturation coefficient were calculated following ASTM C 67 (2021). The bulk density and apparent porosity were determined according to ASTM C 20 (2015). Finally, the compressive strength was determined following ASTM C 67 (2021).
Results
Raw materials characterization
Peanuts
Table 2 addresses the compositions of moisture, ash, and oil in the two contaminated peanut samples, PA and PB. The bricks using the additive PA showed a lower ash and a higher oil content than did the bricks using the additive PB.
The chemical composition of the two samples, as determined by the XRF analysis, is presented in Table 3. Generally, the higher silica content in PB is due to the peanut shell composition, which is present in sample PB but not in PA, and the elevated loss on ignition of both PA and PB is due to the high content of organic compounds in both samples.
Clay brick basic mix
The chemical composition of the clay material used was obtained via XRF analysis and is given in Table 4. This table shows that the main components present are SiO2, Al2O3, and Fe oxides, which account for approximately 86% of the composition. Minor oxides also present include alkaline earth oxides (CaO and MgO) and alkali oxides (Na2O and K2O). The SO3 appearing in the analysis is related to the presence of small quantities of gypsum (CaSO4.2H2O), anhydrite (CaSO4), or MgCO3.
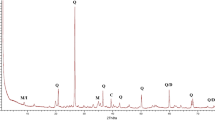
The X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis of the clay material indicates that the clay raw material is mainly composed of kaolinite (Al2O3.2SiO2.2H2O), quartz (SiO2), montmorillonite (Nax(Al,Mg)2Si4O10(OH)2.zH2O), and hematite (Fe2O3), as shown in Fig. 1. Other probable compounds, including calcium carbonate, magnesium carbonate, sulfates, and chlorides, were not detected because of their low percentages. These results are incongruent with those obtained via XRF analysis (Rahaman, 2003; Földvári, 2011).
The DTA trace of the clay material used in this work is shown in Fig. 2. It shows three principle endothermic peaks besides the first peak at approximately 100 °C, which is associated with the elimination of moisture: The first peak at about 270 °C is hypothesized to correspond to the decomposition of gypsum to anhydrite and magnesium carbonate to magnesium oxide (Rahaman, 2003; Földvári, 2011), the second peak starting at approximately 400 °C and ending at approximately 600 °C corresponds to the dehydroxylation of kaolinite, and finally the minor peak at approximately 870 °C corresponds to the calcination of calcium carbonate. All these peaks are accompanied by weight losses, which can be observed in the TGA–DTG traces shown in Fig. 3.
The calculated weight loss excluding that due to physical moisture loss was approximately 4.4%, implying the presence of a large quantity of free silica. If all the available alumina was assumed to be present in kaolinite, then the combined silica would represent approximately 17.3% of the total silica present, and the available kaolinite would make up 37.1%. This leaves approximately 41.4% as free quartz. Because the mass of the dry clay sample used in the TGA was 15.08 mg, then the calculated amount of free silica was 6.24 mg and the mass of kaolinite was 5.59 mg. The loss in weight for dehydroxylation was found to be 0.53 mg, representing a loss of approximately 9.5%, a typical figure for weight loss of kaolin minerals. The fact that the actual LOI is approximately 7% is hypothesized to be due to kaolinite being assumed to have the model structure, which neglects the possibility of impurities, such as iron oxides.
The particle size distribution of the clay material used is shown in Fig. 4. It reveals a median particle size, D50, of 0.31 mm. The bimodal nature of the curve is due to the presence of free silica, which is harder to grind than kaolin. The first peak is found at a particle size of approximately 0.16 mm, and the second peak, corresponding to quartz, can be observed corresponding to a particle size of 1 mm.
Following Mc Cabe et al. (2005), the mean particle size of a powder having the same specific surface area of the material can be calculated according to:
where n represents the number of sieves, xi represents the mass fraction of solid retained between sieve i − 1 and i, and Davi represents the average screen opening between sieve i − 1 and i. Using this method, the mean particle size was found to be 0.183 mm.
Finally, the free silica content of the clay material used in this study was found to be 41%. This implies that it was not necessary to add any sand to the clay in the brick mix. The powder density was found to be 2.58 g cm−3.
Characterization of green bodies
Linear drying shrinkage
The results shown in Fig. 5 indicate a significant increase in the linear drying shrinkage percentage for both the clay-PA and clay-PB compared with the control clay specimen without the addition of waste products. This increase is a consequence of the presence of oil, which facilitates the motion of the constituent particles during shrinkage. The stability against shrinking is enhanced by increasing the ash content and inhibited by increasing the oil content in the bricks. The general trend of decreasing shrinkage on increased replacement is due to the non-plastic nature of peanuts, the effect of which is greater than the effect of the oil.
Green compressive strength
Green compressive strength does not have a standard limitation; however, it indicates the capacity of the specimen to be formed and handled without failure. Figure 6 shows a linear decrease in the green compressive strength as the replacement percentage of the two mixtures increases. The non-plastic nature of both waste products will induce a lack of cohesion between the constituent particles and hence decrease the green strength. This severe increase is due to the significant oil content, 47.6% ± 1.14% of PA and 34.0% ± 0.81% of PB. The minimum strength observed in both cases exceeds 20 kg cm−2. This figure is high enough to suggest that the green bricks will withstand handling with negligible losses.
Discussion
The compressive strength was determined experimentally to determine the fired bodies characterization. The clay-PA and clay-PB fired bricks at the chosen values of the parameters X1 and X2, as illustrated in Table 5. The experiments were analyzed using the Design-Expert software. Two predicted models were obtained that exhibit significant curvature for both the clay-PA (model I) and clay-PB (model II) fired bricks through the design points. This finding has required supplementary axial points to be added to fit the models.
Regression model for clay-PA fired bricks (model I)
A logarithmic quadratic model was suggested by the software, as shown in Table 6. The regression coefficient R2 and the adjusted R2 are close to 1; the predicted R2 is in reasonable agreement with the adjusted R2. Both the linear and quadratic models are valid when the probability F-value (p) is less than 0.05. However, the error function is significant for all the models except for the quadratic model. All the terms of the quadratic model are significant according to the ANOVA undertaken, which is summarized in Table 7. The model terms are two linear factors (\(X_{1} ,X_{2}\)), a quadratic factor \(X_{1}^{2}\), and the product (\(X_{1} . X_{2}\)). The coefficient of variance (CV) is 2.32, which suggests the relationships between the model terms could be predicted within the selected range.
The regression equation of the actual variables is
where \(Y = \ln \sigma\), \(\sigma\) is the compressive strength and all other variables have been previously defined.
The notable curvature of the model output displayed in Fig. 7a demonstrates the necessity to perform runs 5–8 using the axial points to fit the model. There is no interaction between the parameters of the model in the design space for replacement levels lower than 35%, as shown in Fig. 7b. Plotting the residuals against the normal percent probability (Fig. 7c) illustrates a normal distribution through a linear relationship. The response actual values and the response predicted values are congruent, as shown in Fig. 7d.
Optimization of model I parameters
The main objective of this model is to estimate the maximum compressive strength. This target is achieved at a 6% clay replacement and a 725 °C firing temperature. The predicted compressive strength under these conditions was found to be 117.57 kg cm−2, whereas the experimental value is 109.85 kg cm−2, meeting ASTM C 62 (2021), which requires a minimum compressive strength of 89.74 kg cm−2. This value is located within the 95% confidence interval (CI) and 95% prediction interval (PI), as illustrated in Table 8.
Other vitrification properties, such as loss on ignition (LOI), total linear shrinkage (TLS), cold water absorption (CWA), boiling water absorption (BWA), saturation coefficient (SC), and bulk density (BD), were determined to investigate the behavior of fired bricks with PA replacement. The regression equations that describe the relationship between the parameters and their responses are as follows:
It is noteworthy that, as illustrated in Fig. 8, according to the model, the LOI is a quadratic model that depends predominantly on the replacement percentage. However, the lowest LOI was required to maintain high compressive strength and no black core formation. This is because the black core was present for replacements > 10%. The minimum LOI was achieved at 6% clay replacement and 725 °C.
The TLS showed a linear dependence on both parameters, as can be noted from the regression equations, although the level of clay replacement showed a stronger effect. The contour of the TLS model shows that the minimum response is located at the minimum values of both parameters. Using 6% clay replacement and firing at 725 °C resulted in a high BD and a suitable SC of 0.89.
Regression model for clay-PB fired bricks (model II)
As explained in model I, a quadratic model with a natural log was suggested by the software for model II (see Table 9). The model terms of the quadratic model are significant, as shown in Table 10. The relationships between the model terms could be predicted within the selected range since the C.V. is 2.39.
The regression equation of the actual variables was found to be:
A notable curvature of the model output is presented in Fig. 9a. There is no interaction between the parameters of the model in the design space for replacements lower than 35%, as shown in Fig. 9b. The normal residual graph is linear, as illustrated in Fig. 9c, and the response actual values and the response predicted values are congruent and form a linear relationship, as shown in Fig. 9d.
Optimization of model II parameters
The principal objective of this model is to obtain the maximum compressive strength. This target is achieved at a 6% clay replacement and a 725 °C firing temperature. The predicted compressive strength under these conditions is 128.895 kg cm−2, whereas the experimental value is 126.33 kg cm−2, thus exceeding ASTM C 62 (2021), which states that the minimum compressive strength is 89.74 kg cm−2. This value is located within the 95% CI and 95% PI, as illustrated in Table 11. The other investigated characteristics were LOI, TLS, CWA, BWA, SC, and BD. The regression equations of the model describe the relationship between the parameters and their responses is:
As illustrated in Fig. 10, the model of LOI is a quadratic model that depends predominantly on the replacement percentage. The minimum LOI is achieved with a 6% clay replacement and 725 °C firing temperature. The TLS has a linear relationship between it and the investigated parameters. As can be seen in the regression equations, the clay replacement percentage has a dominant effect on TLS. The contour of TLS shows the minimum response is obtained for the minimum parameter values investigated.
The modeling of the remaining characteristics of clay-PB fired bricks shows considerable differences to clay-PA fired bricks. These variations are related to the material of the peanut shell. The modeling of the CWA is a quadratic model for only one parameter, and the firing temperature is not significant. The BWA has a linear relationship with the replacement percentage. The minimum values of both CWA and BWA were obtained with the minimum value of clay replacement. The BD also has a linear relationship with the clay replacement percentage, and the temperature is not a significant parameter. The lowest tested values of the parameters under investigation result in a high BD and a sufficient SC of 0.89. Thus, the condition suggested by this investigation is that of a 6% clay replacement and a 725 °C firing temperature.
Conclusions
Contaminated green waste represents a danger to human and animal health. It is the main cause of cancer and liver fibrosis, so the safe disposal of such waste is necessary unless propagation of the contamination of peanut crops can be prevented. This work showed that both the kernel and whole-grain peanut could be used as a clay replacement in the preparation of fired bricks to conserve natural resources and safely dispose of waste. The oil content of the peanut was found to decrease the required firing temperatures. Moreover, the fibrous material of the grain contributes to increasing the compressive strength of the green bricks. The RSM facilitates the optimization of the parameters affecting the quality of the product and creates models used to predict the characteristics of the product. Using a 6% clay replacement and a 725 °C firing temperature yields bricks of sufficient compressive strength (109.85 kg cm−2 for clay bricks with PA and 126.33 kg cm−2 for clay bricks with PB). This study paves the way for a more sustainable environment with zero-waste production.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- AFs:
-
Aflatoxins
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of Variance-Statistics
- B1, B2, G1, G2:
-
Mycotoxins types
- BD:
-
Bulk density
- BWA:
-
Boiling water absorption
- CCD:
-
Central Composite Design
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- CV:
-
Coefficient of variance
- CWA:
-
Cold water absorption
- DTA:
-
Differential thermal analysis
- EC:
-
European Commission
- FTIR:
-
Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy
- IARC:
-
International Agency for Research on Cancer
- LOI:
-
Loss on ignition
- MPL:
-
Maximum permissible limit
- P:
-
Contaminated peanut
- PA:
-
Contaminated peanut kernel (without the outer shell)
- PB:
-
Contaminated whole peanut grain (with the outer shell)
- RSM:
-
Response surface method
- TGA:
-
Thermo-gravimetric analyses
- TLS:
-
Total linear shrinkage
- SC:
-
Saturation coefficient
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
- XRF:
-
X-ray fluorescence
References
Abdul-Kadir A, Mohajerani A (2008) Possible utilization of cigarette butts in lightweight fired clay bricks. World Acad Sci Eng Technol Int J Environ Earth Sci Eng 2(9):32–36
Abdul-Kadir A, Mohajerani A (2011) Recycling cigarette butts in lightweight fired clay bricks. Proc Inst Civ Eng Constr Mater (UK) 164(5):219–229
Al Ayoubi M, Solfrizzo M, Gambacorta L, Watson I, El-Darra N (2021) Risk of exposure to aflatoxin B1, ochratoxin A, and fumonisin B1 from spices used routinely in Lebanese cooking. Food Chem Toxicol 147:111895
AOAC, Official method 923.03 (2016) Ash of flour, 20th ed
AOAC, Official method 925.09 (2016) Solids (total) and moisture in flour, 20th ed
AOAC, Official method 2003.05 (2016) Crude fat in feeds, cereal grains, and forages, 20th ed
ASTM C 20/2000 (Reapproved 2015) (2021) Standard test methods for apparent porosity, water absorption, apparent specific gravity, and bulk density of burned refractory brick and shapes by boiling water. ASTM annual book, U.S.A., 15(1)
ASTM C 67/2020 (2021) Standard test methods for sampling and testing brick and structural clay tile. ASTM annual book, U.S.A., 4(5)
ASTM C 62/2017 (2021) Standard specification for building brick (Solid masonry units made from clay or shale). ASTM annual book, U.S.A., 4(5)
ASTM C 326/2009 (Reapproved 2018) (2021) Standard test method for drying and firing shrinkages of ceramic whiteware clays. ASTM annual book, U.S.A. 15(2)
ASTM D 422/1963 (Reapproved 2007) (2015) Method for particle-size analysis of soils. ASTM annual book, U.S.A., 4(8)
ASTM D 854/2014 (2021) Standard test methods for specific gravity of soil solids by water pycnometer. ASTM annual book, U.S.A., 4(8)
ASTM E 11/2020 (2021) Specifications for wire-cloth sieves for testing purposes. ASTM annual book, U.S.A., 14(2)
Balasubramaniam T, Karthik PS, Sureshkumar S, Bharath M, Arun M (2021) Effectiveness of industrial waste materials used as ingredients in fly ash brick manufacturing. Mater Today Proc 45(9):7850–7858
Chan CM (2011) Effect of natural fibres inclusion in clay bricks: physico-mechanical properties. Int J Civ Environ Eng 3(1):51–57
Demir I (2006) An investigation on the production of construction brick with processed waste tea. Build Environ 41:1274–1278
Diedhiou A, Ndiaye LG, Bensakhria A, Sock O (2019) Thermochemical conversion of cashew nut shells, palm nut shells and peanut shells char with CO2 and/or steam to aliment a clay brick firing unit. Renew Energy 142:581–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.04.129
EC (2010) Commission Regulation (EU) No 165/2010 of 26 February 2010 amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 Setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs as regards aflatoxins. Off J Eur Union L50/8–L50/12
Eliche-Quesada D, Felipe-Sesé MA, Fuentes-Sánchez MJ (2021) Biomass bottom ash waste and by-products of the acetylene industry as raw materials for unfired bricks. J Build Eng 38:102191
El-Mekkawi SA, El-Ibiari NN, El-Ardy OA, Abdelmonem NM, Elahwany AH, Abadir MF, Ismail IM (2020) Optimization of cultivation conditions for Microcystis aeruginosa for biodiesel production using response surface methodology. Bull Natl Res Cent 44:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-019-0265-9
Faria KCP, Gurgel RF, Holanda JNF (2012) Recycling of sugarcane bagasse ash waste in the production of clay bricks. J Environ Manag 101:7–12
Folaranmi J (2009) Effect of additives on the thermal conductivity of clay. Leonardo J Sci 14:74–77
Földvári M (2011) Handbook of thermogravimetric system of minerals and its use in geological practice, 1st ed. The Geological Institute of Hungary, pp 108–109. ISBN: 978-963-671-288-4
Ghorbani M, Dahrazma B, Saghravani SF, Yousofizinsaz G (2021) A comparative study on physicochemical properties of environmentally friendly lightweight bricks having potato peel powder and sour orange leaf. Constr Build Mater 276:121937
Guo Y, Zhao L, Ma Q, Ji C (2021) Novel strategies for degradation of aflatoxins in food and feed: a review. Food Res Int 140:109878
Gupta V, Chai HK, Lu Y, Chaudhary S (2020) A state-of-the-art review to enhance the industrial scale waste utilization in sustainable unfired bricks. Constr Build Mater 254:119220
ISO 1183–1/2019. Plastics-Methods for determining the density of non-cellular plastics-Part (1): immersion method, liquid pycnometer method and titration method. International Organization for Standardization (ISO), Geneva, pp 1–12
Khoudja D, Taallah B, Izemmouren O, Aggoun S, Herihiri O, Guettala A (2021) Mechanical and thermophysical properties of raw earth bricks incorporating date palm waste. Constr Build Mater 270:121824
Kortei NK, Annan T, Akonor PT, Richard SA, Annan HA, Wiafe-Kwagyan M, Akpaloo GP (2021) Aflatoxins in randomly selected groundnuts (Arachis hypogaea) and its products from some local markets across Ghana: Human risk assessment and monitoring. Toxicol Rep 8:186–195
Kumari N, Mohan C (2021) Chapter (2): Basics of clay minerals and their characteristic properties. In: Clay and clay minerals. Intech-Open, London, pp 1–29. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.97672
Limami H, Manssouri I, Cherkaoui K, Khaldoun A (2021) Recycled wastewater treatment plant sludge as a construction material additive to ecological lightweight earth bricks. Clean Eng Technol 2:100050
Mahmoodi O, Siad H, Lachemi M, Sahmaran M (2021) Synthesis and optimization of binary systems of brick and concrete wastes geopolymers at ambient environment. Constr Build Mater 276:122217
Mc Cabe WL, Smith JC, Harriott P (2005) Unit operations of chemical engineering. Chemical engineering series, 7th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Mobili A, Giosuè C, Tittarelli F (2018) Valorisation of GRP dust waste in fired clay bricks. Adv Civ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5256741
Mohammed S, Munissi JJ, Nyandoro SS (2018) Aflatoxins in sunflower seeds and unrefined sunflower oils from Singida. Tanzania Food Addit Contam B 11(3):161–166
Peng Z, Chen L, Zhu Y, Huang Y, Hu X, Wu Q, Yang W (2018) Current major degradation methods for aflatoxins: a review. Trends Food Sci Technol 80:155–166
Rahaman MN (2003) Ceramic processes and sintering, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York
Saha TN, Wu F (2019) Risk assessment of aflatoxin related liver cancer in Bangladesh. Food Addit Contam A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess 36(2):320–326
Schrenk D, Bignami M, Bodin L, Chipman JK, del Mazo J, Wallace H (2020) Risk assessment of aflatoxins in food. EFSA J 18(3):e06040
Sebaei AS, Refai HM, El-badry HT, Armeya SM (2020) First risk assessment report of aflatoxins in Egyptian tahini. J Food Compos Anal 92:103550
Shishegaran A, Saeedi M, Mirvalad S, Korayem AH (2021) The mechanical strength of the artificial stones, containing the travertine wastes and sand. J Mater Res Technol 11:1688–1709
Vasić MV, Goel G, Vasić M, Radojević Z (2021) Recycling of waste coal dust for the energy-efficient fabrication of bricks: a laboratory to industrial-scale study. Environ Technol Innov 21:101350
Wang X, Lien KW, Ling MP (2018) Probabilistic health risk assessment for dietary exposure to aflatoxin in peanut and peanut products in Taiwan. Food Control 91:372–380
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their appreciation to the staff of the central laboratory in National Research Centre (NRC) for performing the analysis of raw material.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SAE-M performed the design of the experiments through response surface method, performed the computations, verified the analytical methods, and wrote the manuscript. ASS conceived of the presented idea and developed the theory, and performed the analysis of peanut feedstock. SKA conceived of the presented idea and developed the theory, performed the clay bricks experimental work, and wrote the manuscript. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
El-Mekkawi, S.A., Sebaei, A.S. & Amin, S.K. Green waste recycling of peanuts highly contaminated with aflatoxins in clay brick manufacturing. Bull Natl Res Cent 46, 91 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-022-00780-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-022-00780-6