Abstract
Purpose
Yeasts are gaining attention as potential emerging tools for enhancing the dietary benefits of food attributes and for preventing food spoilage because of their anti-microbial properties.
Methods
In this study, both Torulaspora delbrueckii (T. delbrueckii) as a prospective probiotic and bananas as a prebiotic were used to investigate their potential roles in modulating the lipid content and bacterial number in the feces of examined rats.
Results
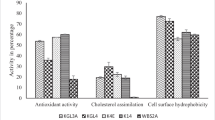
Milk has been used to isolate a yeast stain that has been identified using conventional and molecular tools as T. delbrueckii. The isolated yeast showed promising results upon testing for acid and bile tolerance. T. delbrueckii also had the capacity to thrive on simulating stomach and intestinal fluids. According to an animal feeding experiment, rats fed T. delbrueckii developed and acquired mass in a regular manner. Consuming T. delbrueckii also dramatically lowers LDL, cholesterol, and triglyceride levels while dramatically raising HDL levels. Consuming both T. delbrueckii and bananas along with regular animals’ diet considerably reduced the amount of coliforms and Staphylococcus sp. in the rats’ excrement.
Conclusions
These findings suggested a potential function for T. delbrueckii in treating hypocholesteremia and controlling the bacterial flora of the intestine, which can then be used widely after more confirmation of the outcomes.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data is available in the manuscript.
Abbreviations
- T. delbrueckii:
-
Torulaspora delbrueckii
- TC:
-
Total cholesterol
- TG:
-
Triacylglycerol
- LDL-C:
-
Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- HDL-C:
-
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- HFD:
-
High fat diet
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- VRBA:
-
Violet red bile agar medium
References
Hill C, Guarner F, Reid G, Gibson GR, Merenstein DJ, Pot B, Morelli L, Canani RB, Flint HJ, Salminen S, et al. The international scientific association for probiotics and prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;11:506–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2014.66.
Xavier-Santos D, Bedani R, Lima ED, Saad SMI. Impact of probiotics and prebiotics targeting metabolic syndrome. J Funct Foods. 2020;64:e103666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2019.103666.
Thursby E, Juge N. Introduction to the human gut microbiota. Biochem J. 2017;474:1823–36. https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20160510.
Suez J, Zmora N, Segal E, Elinav E. The pros, cons, and many unknowns of probiotics. Nat Med. 2019;25:716–29. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-019-0439-x.
Durmaz S, Kurtoğlu T, Barbarus E, Çetin NK, Yılmaz M, Rahman ÖF, Abacıgil F. Probiotic Saccharomyces boulardii alleviates lung injury by reduction of oxidative stress and cytokine response induced by supraceliac aortic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2021;36(4):515–21. https://doi.org/10.21470/1678-9741-2020-0153.
Amorim JC, Piccoli RH, Duarte WF. Probiotic potential of yeasts isolated from pineapple and their use in the elaboration of potentially functional fermented beverages. Food Res Int. 2018;107:518–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2018.02.054.
Menezes AGT, Ramos CL, Cenzi G, Melo DS, Dias DR, Schwan RF. Probiotic potential, antioxidant activity, and phytase production of indigenous yeasts isolated from indigenous fermented foods. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2020;12(1):280–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-019-9518-z.
Shakira G, Qubtia M, Ahmed I, Hasan F, Anjum MI, Imran M. Effect of indigenously isolated Saccharomyces cerevisiae probiotics on milk production, nutrient digestibility, blood chemistry and fecal microbiota in lactating dairy cows. The J Anim Plant Sci. 2018;28(2):201.
Kalathinathan P, Kodiveri MG. Characterization of a potential probiotic strain Paracoccus marcusii KGP and its application in whey bioremediation. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2021;66(5):819–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-021-00886-w.
Dai FJ, Hsu WH, Huang JJ, Wu SC. Effect of pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan L.) on high-fat diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in hamsters. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013;53:384–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2012.12.029.
Bellosta S, Paoletti R, Corsini A. Safety of statins: focus on clinical pharmacokinetics and drug interactions. Circulation. 2004;109:50–7. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000131519.15067.1f.
Puttarat N, Kasorn A, Vitheejongjaroen P, Chantarangkul C, Tangwattanachuleeporn M, Taweechotipatr M. Beneficial effects of indigenous probiotics in high-cholesterol diet-induced hypercholesterolemic rats. Nutrients. 2023;15(12):2710. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15122710.
Ramírez M, Velázquez R. The yeast Torulaspora delbrueckii: an interesting but difficult-to-use tool for winemaking. Fermentation. 2018;4(4):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation4040094.
Zhang BQ, Luan Y, Duan CQ, Yan GL. Use of Torulaspora delbrueckii co-fermentation with two Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains with different aromatic characteristic to improve the diversity of red wine aroma profile. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:606. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00606.
Davani-Davari D, Negahdaripour M, Karimzadeh I, Seifan M, Mohkam M, Masoumi SJ, Berenjian A, Ghasemi Y. Prebiotics: definition, types, sources, mechanisms, and clinical applications. Foods. 2019;8(3):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8030092.
Collins S, Reid G. Distant site effects of ingested prebiotics. Nutrients. 2016;8:523. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8090523.
Younis K, Ahmad S, Jahan K. Health benefits and application of prebiotics in foods. J Food Process Technol. 2015;6(4):1–7.
Abatenh E, Gizaw B, Tsegay Z, Tefera G, Aynalem E. Health benefits of probiotics. J Bacteriol Infec Dis. 2018;2(1):8–27.
Posteraro B, Efremov L, Leoncini E, Amore R, Posteraro P, Ricciardi W, Sanguinetti M. Are the conventional commercial yeast identification methods still helpful in the era of new clinical microbiology diagnostics? A meta-analysis of their accuracy. J Clin Microbiol. 2015;53(8):2439–50. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.00802-15.
Díaz PE, Aranda C, Martínez O, Godoy R, Gonzales A, Valenzuela E. Characterization of yeast in hapludands soil with biotechnological potential. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr. 2017;17:4. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162017000400009.
Qvirist LA, De Filippo C, Strati F, Stefanini I, Sordo M, Andlid T, Felis GE, Mattarelli P, Cavalieri D. Isolation, identification and characterization of yeasts from fermented goat milk of the Yaghnob Valley in Tajikistan. Front Microbiol. 2016;7:1690. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01690.
Karimi L, Mirhendi H, Khodadadi H, Mohammadi R. Molecular identification of uncommon clinical yeast species in Iran. Curr Med Mycol. 2015;1(2):1–6. https://doi.org/10.18869/acadpub.cmm.1.2.1.
Bessadok B, Jaouadi B, Brück T, Santulli A, Messina CM, Sadok S. Molecular identification and biochemical characterization of novel marine yeast strains with potential application in industrial biotechnology. Fermentation. 2022;8(10):538. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8100538.
Moradi R, Nosrati R, Zare H, Tahmasebi T, Saderi H, Owlia P. Screening and characterization of in-vitro probiotic criteria of Saccharomyces and Kluyveromyces strains. Iran J Microbiol. 2018;10(2):123–31.
Boranbayeva T, Karahan AG, Tulemissova Z, Myktybayeva R, Özkaya S. Properties of a new probiotic candidate and lactobacterin-TK2 against diarrhea in calves. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2020;12(3):918–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-020-09649-4.
Al-Seraih A, Flahaut C, Krier F, Cudennec B, Drider D. Characterization of Candida famata isolated from poultry feces for possible probiotic applications. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2015;7(4):233–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-015-9201-y.
Fernández-Pacheco P, Pintado C, Briones PA, Arévalo-Villena M. Potential probiotic strains of Saccharomyces and non-Saccharomyces: functional and biotechnological characteristics. J Fungi (Basel). 2021;7(3):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7030177.
Zhang X, Wu C, Wu H, Sheng L, Su Y, Zhang X, Luan H, Sun G, Sun X, Tian Y, Ji Y, Guo P, Xu X. Anti-hyperlipidemic effects and potential mechanisms of action of the caffeoylquinic acid-rich Pandanus tectorius fruit extract in hamsters fed a high fat-diet. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e61922. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0061922.
Yang R, Wang C, Ye H, Gao F, Cheng J, Zhang T, Guo M. Effects of feeding hyperlipidemia rats with symbiotic oat-based frozen yogurt on serum triglycerides and cholesterol. Food Sci Nutr. 2019;7(3):1096–103. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.949.
Wan X, Li T, Liu D, Chen Y, Liu Y, Liu B, Zhang H, Zhao C. Effect of marine microalga Chlorella pyrenoidosa ethanol extract on lipid metabolism and gut microbiota composition in high-fat diet-fed rats. Mar Drugs. 2018;16(12):498. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16120498.
Ahmad U, Ahmad RS, Arshad MS, Mushtaq Z, Hussain SM, Hameed A. Antihyperlipidemic efficacy of aqueous extract of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni in albino rats. Lipids Health Dis. 2018;17(1):175. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-018-0810-9.
Parwin A, Najmi AK, Ismail MV, Kaundal M, Akhtar M. Protective effects of alendronate in Triton X-100-induced hyperlipidemia in rats. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2019;30(6):557–64. https://doi.org/10.5152/tjg.2019.18076.
Tanaka S, Madokoro S, Inaoka PT, Yamazaki T. Blood lipid profile changes in type 2 diabetic rats after tail suspension and reloading. Lipids Health Dis. 2021;20(1):84. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-021-01511-y.
Ebrahimi MN, Khaksari M, Sepehri G, Karam GA, Raji-Amirhasani A, Azizian H. The effects of alone and combination tamoxifen, raloxifene and estrogen on lipid profile and atherogenic index of ovariectomized type 2 diabetic rats. Life Sci. 2020;263:118573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118573.
Feng X, Maze M, Koch LG, Britton SL, Hellman J. Exaggerated acute lung injury and impaired antibacterial defenses during Staphylococcus aureus infection in rats with the metabolic syndrome. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0126906. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0126906.
Chettaoui R, Mayot G, De Almeida L, Di Martino P. Cranberry (Vaccinium macrocarpon) dietary supplementation and fecal microbiota of Wister rats. AIMS Microbiol. 2021;7(2):257–70. https://doi.org/10.3934/microbiol.2021016.
Arévalo-Villena M, Fernandez-Pacheco P, Castillo N, Bevilacqua A, Briones Pérez A. Probiotic capability in yeasts: set-up of a screening method. LWT. 2018;89:657–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2017.11.047.
Ochangco HS, Gamero A, Smith IM, Christensen JE, Jespersen L, Arneborg N (2016) In vitro investigation of Debaryomyces hansenii strains for potential probiotic properties. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol 32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-016-2109-1.
Oliveira T, Ramalhosa E, Nunes L, Pereira JA, Colla E, Pereira EL. Probiotic potential of indigenous yeasts isolated during the fermentation of table olives from Northeast of Portugal. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol. 2017;44:167–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2017.06.003.
Roberfroid MB. Prebiotics and probiotics: are they functional foods? Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;71:1682S-1687S. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/71.6.1682S.
Senkarcinova B, Graça Dias IA, Nespor J, Branyik T. Probiotic alcohol-free beer made with Saccharomyces cerevisiae var. boulardii. LWT. 2019;100:362–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2018.10.082.
Fernandes T, Silva-Sousa F, Pereira F, Rito T, Soares P, Franco-Duarte R, Sousa MJ. Biotechnological importance of Torulaspora delbrueckii: from the obscurity to the spotlight. J Fungi (Basel). 2021;7(9):712. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7090712.
Silva-Sousa F, Fernandes T, Pereira F, Rodrigues D, Rito T, Camarasa C, Franco-Duarte R, Sousa MJ. Torulaspora delbrueckii phenotypic and metabolic profiling towards its biotechnological exploitation. J Fungi (Basel). 2022;8(6):569. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8060569.
Ho VTT, Zhao J, Fleet G. Yeasts are essential for cocoa bean fermentation. Int J Food Microbiol. 2014;174:72–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2013.12.014.
Alkalbani NS, Osaili TM, Al-Nabulsi AA, Obaid RS, Olaimat AN, Liu SQ, Ayyash M. In vitro characterization and identification of potential probiotic yeasts isolated from fermented dairy and non-dairy food products. J Fungi (Basel). 2022;8(5):544. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8050544.
Diguță CF, Mihai C, Toma RC, Cîmpeanu C, Matei F. In vitro assessment of yeasts strains with probiotic attributes for aquaculture use. Foods. 2023;12(1):124. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12010124.
Cressey R, Kumsaiyai W, Mangklabruks A. Daily consumption of banana marginally improves blood glucose and lipid profile in hypercholesterolemic subjects and increases serum adiponectin in type 2 diabetic patients. Indian J Exp Biol. 2014;52(12):1173–81.
Konda PY, Poondla V, Jaiswal KK, Dasari S, Uyyala R, Surtineni VP, Egi JY, Masilamani AJA, Bestha L, Konanki S, Muthulingam M, Lingamgunta LK, Aloor BP, Tirumalaraju S, Sade A, Ratnam Kamsala V, Nagaraja S, Ramakrishnan R, Natesan V. Pathophysiology of high fat diet induced obesity: impact of probiotic banana juice on obesity associated complications and hepatosteatosis. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):16894. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-73670-4.
Rosado CP, Rosa VHC, Martins BC, Soares AC, Almo A, Monteiro EB, Mulder ADRP, Moura-Nunes N, Daleprane JB. Green banana flour supplementation improves obesity-associated systemic inflammation and regulates gut microbiota profile in mice fed high-fat diets. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2021;46(12):1469–75. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2021-0288.
Kuo SM, Merhige PM, Hagey LR. The effect of dietary prebiotics and probiotics on body weight, large intestine indices, and fecal bile acid profile in wild type and IL10-/- mice. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e60270. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0060270.
Morales-Ferré C, Azagra-Boronat I, Massot-Cladera M, Tims S, Knipping K, Garssen J, Knol J, Franch À, Castell M, Pérez-Cano FJ, Rodríguez-Lagunas MJ. Preventive effect of a postbiotic and prebiotic mixture in a rat model of early life rotavirus induced-diarrhea. Nutrients. 2022;14(6):1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061163.
Shao T, Yu Q, Zhu T, Liu A, Gao X, Long X, Liu Z. Inulin from Jerusalem artichoke tubers alleviates hyperglycaemia in high-fat-diet-induced diabetes mice through the intestinal microflora improvement. Br J Nutr. 2020;123(3):308–18. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114519002332.
Shehata MG, El Sohaimy SA, El-Sahn MA, Youssef MM. Screening of isolated potential probiotic lactic acid bacteria for cholesterol lowering property and bile salt hydrolase activity. Ann Agric Sci. 2016;61:65–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aoas.2016.03.001.
Choi SB, Lew LC, Yeo SK, Nair Parvathy S, Liong MT. Probiotics and the BSH-related cholesterol lowering mechanism: a Jekyll and Hyde scenario. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2015;35:392–401. https://doi.org/10.3109/07388551.2014.889077.
Jarocki P, Podlesny M, Glibowski P, Targonski Z. A new insight into the physiological role of bile salt hydrolase among intestinal bacteria from the genus Bifidobacterium. PLoS One. 2014;9:e114379. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0114379.
Lye HS, Rahmat-Ali GR, Liong MT. Mechanisms of cholesterol removal by lactobacilli under conditions that mimic the human gastrointestinal tract. Int Dairy J. 2010;20:169–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2009.10.003.
Molska M, Reguła J, Rudzińska M, Świeca M. Fatty acids profile, atherogenic and thrombogenic health lipid indices of lyophilized buckwheat sprouts modified with the addition of Saccharomyces cerevisiae var. boulardii. Acta Sci Pol Technol Aliment. 2020;19(4):483–90. https://doi.org/10.17306/J.AFS.0866.
Cangiano LR, Yohe TT, Steele MA, Renaud DL. Strategic use of microbial-based probiotics and prebiotics in dairy calf rearing. Appl Anim Sci. 2020;36(5):630–51. https://doi.org/10.15232/aas.2020-02049.
Evdokimova SA, Nokhaeva VS, Karetkin BA, Guseva EV, Khabibulina NV, Kornienko MA, Grosheva VD, Menshutina NV, Shakir IV, Panfilov VIA. Study on the Synbiotic Composition of Bifidobacterium bifidum and Fructans from Arctium lappa Roots and Helianthus tuberosus tubers against Staphylococcus aureus. Microorganisms. 2021;9(5):930. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9050930.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
E.A.H. and M.Y. contributed to conceptualization and investigation; E.H. and R.H.A contributed to conceptualization; E.A.H. and M.Y. contributed to supervision, methodology, and validation; E.E.H., E.H., and R.H.A. contributed to methodology; E.A.H., M.Y., R.H.A., and E.H. contributed to formal analysis and roles/writing—original draft; E.A.H., M.Y., and E.H. contributed to roles/writing—original draft; E.H. contributed to resources and writing—review and editing; E.A.H., M.Y., and E.H. contributed to project administration, validation, and resources; E.A.H., M.Y., and E.H. contributed to project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Animal experiments have the ethical approval numbers (RCMB00022072020). All animal experiments comply with ARRIVE guidelines in accordance with the National Institute of Health guide for the care and use of laboratory animals (NIH Publication No. 8023, revised 1987).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Helmy, E.A., Abdel-Fadeel, R.H., Yosri, M. et al. Does Torulaspora delbrueckii has some probiotic capabilities? In vitro and in vivo assessment. Nutrire 49, 15 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41110-024-00258-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s41110-024-00258-7