Abstract
Background
The use of microbial biomasses, such as fungal biomass, to catalyze the transesterification of triglycerides (TG) for biodiesel production provides a sustainable, economical alternative while still having the main advantages of expensive immobilized enzymes.
Results
Biomasses of Aspergillus flavus and Rhizopus stolonifera were used to catalyze the transesterification of TG in waste frying oil (WFO). Isopropanol as an acyl-acceptor reduced the catalytic capability of the biomasses, while methanol was the most potent acyl-acceptor with a final fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) concentration of 85.5 and 89.7%, w/w, for R. stolonifer and A. flavus, respectively. Different mixtures of the fungal biomasses were tested, and higher proportions of A. flavus biomass improved the mixture's catalytic capability. C. sorokiniana cultivated in synthetic wastewater was used as feedstock to cultivate A. flavus. The biomass produced had the same catalytic capability as the biomass produced in the control culture medium. Response surface methodology (RSM) was adopted using central composite design (CCD) to optimize the A. flavus biomass catalytic transesterification reaction, where temperature, methanol concentration, and biomass concentration were selected for optimization. The significance of the model was verified, and the suggested optimum reaction conditions were 25.5 °C, 250 RPM agitation with 14%, w/w, biomass, 3 mol/L methanol, and a reaction duration of 24 h. The suggested optimum conditions were tested to validate the model and a final FAME concentration of 95.53%. w/w was detected.
Conclusion
Biomasses cocktails might be a legitimate possibility to provide a cheaper technical solution for industrial applications than immobilized enzymes. The use of fungal biomass cultivated on the microalgae recovered from wastewater treatment for the catalysis of transesterification reaction provides an additional piece of the puzzle of biorefinery. Optimizing the transesterification reaction led to a valid prediction model with a final FAME concentration of 95.53%, w/w.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Low volatility, high viscosity, and polyunsaturated criteria are the primary disadvantages of using crude vegetable oils as diesel. Several methods were employed to overcome these problems, including blending with hydrocarbons [1], pyrolysis [2], micro-emulsions preparation[3], and transesterification [4]. The industrial production of biodiesel relies mainly on the transesterification of vegetable oils [5]. Triglycerides react with alcohol to produce fatty acid alkyl ester (FAAE) in a catalytic reaction, as shown in Fig. 1.
Catalyst improves the transesterification reaction rate and increases the yield of the FAAE. The catalysts used in biodiesel production are classified as homogeneous, heterogeneous, and biocatalysts. Employing a homogenous catalyst (acid or base) was not applicable on a large scale due to the poor quality of the produced biodiesel, which requires multiple washing and purification steps to meet the quality, hence increasing the cost, in addition to the risk of saponification of the oil [6]. On the other hand, heterogeneous catalysis demands high energy and pressure inputs and a free fatty acid (FFA) free feedstock [7].
Biocatalysts provide an eco-friendly option that usually catalyze the transesterification reaction under mild operation conditions and facilitate product separation without any byproduct formation. Employing enzymes for the catalysis transesterification reactions face critical problems, such as the cost and stability of enzymes. The use of microbial biomasses to catalyze transesterification, such as fungal biomasses, has been gaining research interest [8, 9] because it provides a potential cost-competitive option while still having the main advantages of immobilized enzymes that include reusability, mild reaction conditions, the capability of catalyzing glycerides and free fatty acids (FFA), no risk of saponification, producing high degree glycerol as a side reaction, short reaction time, and being an environmentally friendly option [10].
Microalgae biorefineries could efficiently fulfill a considerable part of the increasing fuel demand and reduce greenhouse gases, directly interacting with global warming and climate change. However, developing a biorefinery resembles the mosaic assembly that requires gathering numerous sustainable approaches and techniques and connecting them to build an overview of the whole process. In this regard, a biorefinery approach was assessed, in this study, by examining the ability of fungal biomass produced by cultivation in a culture medium of microalgae feedstock collected from wastewater treatment was examined, and the transesterification reaction conditions were optimized to maximize the transesterification capability of the fungal biomass. In addition, the capability of biomass cocktails from different fungal species to catalyze the transesterification reaction was evaluated.
Results
One factor at a time (OFAT) investigations
Aspergillus flavus and Rhizopus stolonifer were cultivated in a control medium under submerged conditions, and the produced biomass was harvested by filtration. Dried biomass was used as a catalyst for the transesterification reactions carried out in this section.
Different short-chain alcohols were tested as acyl-acceptors for the transesterification of TG in WFO. Stepwise addition of alcohol was employed where alcohols were added in 3 doses separated within 24 h. Results (Fig. 2) showed that under the investigated reaction conditions, isopropanol as an acyl-acceptor inhibited the transesterification of TG, where R. stolonifer biomass was used as the catalyst, while a relatively low FAAE concentration was achieved where A. flavus biomass was employed. FAAE maximum concentration was detected in reactions where methanol was used as the acyl-acceptor, and it showed a significant difference between A. flavus and R. stolonifer biomasses, 89.09 and 85.50, respectively. Hence methanol was selected for further investigations.
TLC separation pattern (Fig. 3) of the transesterification reaction products revealed a difference in the accumulated intermediates during the reaction and over the reaction time between reactions catalyzed by A. flavus and R. stolonifer biomasses. In the reaction catalyzed by R. stolonifer biomass, the accumulation of the fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) was accompanied by the accumulation of free fatty acids (FFA), diglycerides (DG), and monoglycerides (MG). On the other hand, in the reaction catalyzed by A. flavus biomass, the accumulation of FFA, DG, and MG was minimal. These observations could only be understood in light of the reaction mechanism. Still, because biomass is used, only the dominant reaction mechanism could be discussed without excluding the presence of other mechanisms.
Different biomass mixtures (Table 1) were tested as catalysts for the transesterification of TG in WFO, FAME concentration by the end of the reaction time was 84.43–90.07%, w/w. Mixtures A and B were just pure biomasses as reference values, revealing that A. flavus biomass catalytic capability was significantly superior to R. stolonifera biomass. None of the tested mixtures showed a transesterification capability higher than mixture B which was the pure A. flavus biomass.
Biorefinery approach
Chlorella sorokiniana was cultivated in synthetic wastewater and produced microalgae biomass was used as a feedstock for the cultivation of A. flavus. The final concentration of C. sorokiniana biomass was 3.5 gL−1 after eight days of 500 mL cultures incubation in 1L Erlenmeyer flasks, daylight, and room temperature. Algal biomass was harvested by centrifugation, and the harvested biomass was used as feedstock. The growth of A. flavus and its biomass transesterification capability was tested at different concentrations of C. sorokiniana feedstock. Results (Table 2) show that A. flavus could grow in culture media containing only C. sorokiniana biomass and olive oil. Although the final A. flavus concentration was low compared to the control, the yield in terms of conversion is higher in the C. sorokiniana biomass-containing medium. On the other hand, no significant difference was observed in the lipase activity or the transesterification capability of the produced A. flavus biomass, which indicates that the produced biomass was efficient as a catalyst for tested reactions.
Reaction optimization:
Response surface methodology (RSM), using a central composite design (CCD), was adopted to determine the optimum levels of the selected factors (temperature, methanol concentration, and biomass concentration), where FAME concentration was defined as the response. The design matrix and the corresponding results of CCD experiments to assess the effects of the three investigated factors are shown in Table 3. The prediction formula was simplified to a second-order polynomial equation. The response, FAME (Y), can be expressed in terms of the following regression equation:
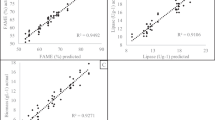
The model was verified via the results of the analysis of variance, ANOVA (Table 4). The model was significant, with p-values below 0.0001. The model's lack of fit was insignificant, with p-values higher than 0.05. Plotting the actual values obtained from the experiments against the predicted values deducted by the model (Fig. 4) supports the findings of the adequacy of the models, where R2 values were 0.95.
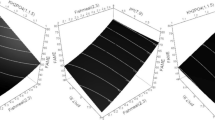
Surface plots (Fig. 5) were constructed to determine the optimum conditions, where the response was plotted on the Z axis against the two of the investigated factors were plotted on the X and Y axes. In contrast, the third factor was set to the given value.
A significant linear correlation between the response and X1, X2, and X3, where temperature and methanol concentration had negative estimates, while the amount of biomass used had a positive effect. The interaction influences of the investigated factors were significant, where X1X2 and X2X3 had negative estimates, while X1X3 had a positive estimate. The model was set to maximize the FAME concentration, and the suggested optimum conditions were X1 = 25.5 °C, X2 = 3 mol/L, and X3 = 0.7 g. A FAME concentration of 97.5 ± 8.91%, w/w, was predicted under the suggested conditions. A validation experiment was conducted where the actual FAME concentration produced was 95.53 ± 1.59%, w/w.
Discussion
In the transesterification reaction, the inhibitory effect of methanol as an acyl-acceptor on the catalytic enzyme has been reported [11]. Several strategies have been tested to overcome the inhibitory effect of alcohols, such as using solvents along with the methanol that increases the reaction rate [12] and replacing methanol with methyl or ethyl acetate [13]. Stepwise addition [14] and replacing methanol with longer-chain alcohols (Mateos et al., 202) were adopted during this study.
Fungal biomasses of A. flavus and R. stolonifer could not catalyze the production of FAAE, where alcohols were added in a single dose from time zero. Isopropanol was tested as an example of secondary alcohol acyl-acceptors. Isopropanol inhibited the transesterification of TG, where R. stolonifer biomass was used as the catalyst, while a relatively low FAAE concentration was achieved where A. flavus biomass was employed, indicating the inhibitory effect of secondary alcohol isopropanol, which might result from the competitive inhibition effect of secondary alcohol [16].
On the other hand, a clear trend was observed when A. flavus biomass was used. The longer the alcohol chain, the less the FAAE produced; this trend was also observed when some lipases, such as Novozym SP435 in an n-hexane medium and lipase SP-35 in a solvent-free medium were tested to produce FAAE [17, 18]. FAAE maximum concentration was detected in reactions where methanol was used. Hence methanol was selected for further investigations. The strains used in this study were isolated and mutated in previous studies [19, 20], where the screening and selection of potent catalytic biomasses relied on using methanol as an acyl-acceptor which might create a positive bias towards methanol. However, methanol is still a vital cheap option readily available and recoverable.
A dominant Ping pong Bi Bi reaction mechanism is thought to be employed in the lipase-catalyzed transesterification reaction. TG or DG binds to the active site of the catalytic protein(s) embedded in the biomass, which catalyzes the separation of DG or MG and the formation of an intermediate protein-acyl complex intermediate. The protein-acyl complex intermediate bind to methanol, where the formation of FAME is catalyzed, and FAME and catalytic protein(s) are released. The Ping pong Bi Bi reaction mechanism has been reported for TG transesterification in a solvent-free medium using immobilized lipases and lipases of fungal origin [21, 22]. The accumulation of FFA, DG, and MG in reactions catalyzed by R. stolonifera might result from the slower reaction rate and/or competitive alcohol inhibition [23], which might not influence the A. flavus biomass catalytic activity. The difference between the catalytic behavior of the biomasses suggests that combining both biomasses in the same reaction vessel might bring further understanding. Thus, biomass mixtures were prepared, as shown in Table 4, and each mix was tested as a catalyst for TG transesterification.
Lipase cocktails or mixtures have been reported as an efficient technique to facilitate hydrolysis and transesterification [24, 25]. Different biomass mixtures were tested as catalysts for the transesterification of TG in WFO. The catalytic capability of mixtures that contain R. stolonifer biomass was significantly improved compared to pure R. stolonifer biomass, i.e., the more the proportion of A. flavus biomass, the higher the FAME concentration. Hence, A. flavus biomass was selected for further trials. However, no antagonistic effect between the biomasses was observed, and the potential of mixing two fungal biomasses or even more is an option. In other words, biomasses cocktails might be a legitimate possibility as the enzyme's cocktails, which might provide a cheaper technical solution for industrial applications, but still require further investigation.
Using microalgae for wastewater treatment provides a sustainable alternative to traditional wastewater treatment processes. Microalgae biorefineries allow inexpensive and energy-saving wastewater treatment and the recovery of add-value compounds [26]. Chlorella sorokiniana is a well-studied candidate for wastewater treatment [27,28,29]. The co-cultivation of fungi and microalgae has been studied lately for several purposes, including harvesting microalgae by flocculation [30, 31]. The pretreatment of algal feedstock has tentatively explored the ability of fungi to utilize algae as the sole source of nutrients [32,33,34].
The ability of A. flavus to grow efficiently on C. sorokiniana feedstock and the capability of the produced biomass to catalyze the transesterification reaction might provide an additional piece of the puzzle of biorefinery. The use of fungal biomass cultivated on the microalgae recovered from wastewater treatment for the catalysis of transesterification reaction, but this puzzle piece needs evaluation at a larger scale.
Reaction temperature, acyl-acceptor concentration, catalyst concentration, and reaction time have been reported to be the most crucial factors influencing transesterification reactions [35, 36]. One of the main drawbacks of biocatalytic production of FAME using a stepwise methanol addition strategy is the reaction time. In previous experiments, the reaction was carried out for 72 h, where tested acyl-acceptors were added on 24 h basis. Adding the final acyl-acceptor concentration at the beginning of the reaction inhibited the tested biomass's catalytic capability. Thus, the reaction time was fixed to 24 h, and methanol addition was carried out in four doses on a six hour basis for the following experiments. Temperature, Methanol concentration, and catalyst concentration were optimized using CCD. The adequacy of the model was verified, and the prediction formula was simplified. The high temperature and methanol concentration levels negatively influenced the catalyst capability, especially when combined with a low biomass concentration level, where the FAME concentration was dropped in runs 27 – 28 to 2.9%. The negative impact of temperature methanol interaction could be understood in light of the methanol's toxic influence on the catalytic proteins, which was reported to increase with higher temperatures [37, 38]. The optimum conditions validation experiment showed that the produced FAME concentration was in the predicted range considering the standard errors suggested by the model.
Conclusion
Fungal biomasses of A. flavus and R. stolonifer showed considerable capability for catalysis of the transesterification of triglycerides in WFO. Single-dose addition of short-chain alcohols had a toxic effect on the fungal biomass catalytic capability. Thus stepwise addition of acyl-acceptor provided a proper alternative strategy with minimal toxicity. Isopropanol as branched alcohol reduced the transesterification capability of fungal biomass, while methanol was the most potent acyl-acceptor. The catalytic capability of A. flavus biomass was superior to R. stolonifer, and different accumulation rates of transesterification reaction intermediates accompanied the difference in activity. Biomass mixtures efficiently catalyze the transesterification reaction. However, the more the ratio of A. flavus biomass, the more efficient the catalytic capability suggesting that there is no antagonism when different biomasses are mixed. The biorefinery approach was valid as a remarkable biomass yield was produced when A. flavus was cultivated on the biomass of C. sorokiniana cultivated in synthetic wastewater. The produced biomass catalyzed the transesterification reaction with the same efficiency as A. flavus biomass produced on synthetic culture media. Statistical optimization of the transesterification reaction using A. flavus biomass as a catalyst improved the FAME produced to a final concentration of 95.53 ± 1.59%, w/w.
Methods
Microbial strains
In previous studies, several fungal isolates belonging to Aspergilli and Mucoralean fungi were screened for their biomasses' capability of catalyzing the methanolysis of WFO. Potent isolates were identified as Aspergillus flavus NDA04a (MK811208) and Rhizopus stolonifer 1aNRC11 (MN689079). Selected isolates were chemically mutated, and A. flavus NDA04a mutant D and R. stolonifer 1aNRC11 mutant G were used in this study [19, 20]. The mutant was preserved on potato dextrose agar (PDA) slants supplemented with olive oil, 1%. The inoculum was prepared by subculturing the mutant on PDA plates incubated at 28 °C for three days. Agar disks (5 mm diameter) were used as inoculum.
Aspergillus flavus NDA04a was cultivated in a control culture medium containing 5% glucose, 7% urea, 0.9% KH2PO4, 0.09% MgSO4.7H2O, and 3% olive oil, w/v, with an initial pH of 5. Sterile 50 mL cultures were inoculated with three disks (0.5 cm) and incubated in an orbital shaker at 28 °C and 200 RPM for four days.
Chlorella sorokiniana was kindly provided by the culture collection of Algae, City University of applied science, Bremen, Germany. Pre-cultures were cultivated axenically in Wuxal medium (a commercially available liquid plant fertilizer consisting of 8% N, 8% P2O5, 6% K2O, 0.01% B, 0.004% Cu, 0.02% Fe, 0.012% Mn and 0.004% Zn (Wilhelm Haug GmbH & Co.KG Germany)).
Biorefinery approach
Production of Chlorella sorokiniana biomass
Synthetic wastewater was prepared according to the composition listed in Table 5 [39], 500 mL cultures were inoculated with 50 mL pre-cultures of Chlorella sorokiniana incubated at room temperature on an orbital shaker, and no additional light source was applied. Culture viability was observed using optical density at 680 nm. Once the optical density showed stable values, the culture pH was adjusted, then distributed to 50 mL cultures, supplemented with olive oil 3%, w/v, and autoclaved.
Production of fungal biomass
A. flavus NDA04a was cultivated on C. sorokiniana feedstock, where microalgal biomass was suspended in tap water at different concentrations and 3%, w/v, olive oil. Autoclaved cultures were inoculated with three disks (0.5 cm) and incubated in an orbital shaker at 28 °C and 200 RPM for four days.
Rhizopus stolonifer 1aNRC11 was cultivated in a control culture medium containing 5% glucose, 2.26% Fishmeal, 3% KH2PO4, 0.09% MgSO4.7H2O, and 3% olive oil, w/v, with an initial pH of 7.4. Sterile 50 mL cultures were inoculated with three disks (0.5 cm) and incubated in an orbital shaker at 25 °C and 200 RPM for three days.
Biomasses were collected by filtration using Whatman filter paper no. 1. Harvested biomass was washed thoroughly three times with tapwater, followed by lyophilization using a freeze dryer (Martin Christ, alpha LSC basic; Germany).
Transesterification reaction
Fractured lyophilized fungal biomass, 0.5 g, was used as the biocatalyst for an emulsion of 5 g WFO and 0.75 mL of 1 M phosphate buffer pH 7.5 in a 50 mL Erlenmeyer flask. The reaction was carried out at 35 °C and 250 rpm for 72 h. Alcohol doses were added at 0, 24, and 48 h to a final concentration of 3 M. Methanol, Ethanol, Isopropanol, and Butanol were tested.
Lipase assay
Lyophilized biomass (0.5 g) was inoculated to an emulsion of 5.5 g WFO and 30 mL of 1 M Tris buffer, pH 7.5. The reaction was carried out in an orbital shaker at 35 °C and 200 rpm for two h. The reaction mixture was centrifuged for 10 min at 5000 rpm. A gram of supernatant, two drops of phenolphthalein color indicator, and 25 mL diethyl ether and ethanol (1:1) solvent mixture were titrated against freshly prepared 0.1 N NaOH in 100 mL Erlenmeyer flask. Lipase activity (as the amount of enzyme required to produce 1 μmol free fatty acid per min) was determined in unit per gram cell weight (U/g) [40].
Response surface methodology (RSM)
Reaction temperature, Methanol concentration, and biomass concentration were optimized using a central composite design (CCD). The investigated levels of each factor are presented in Table 6, and the response was the final FAME concentration. Reactions were carried out using different biomass weights to catalyze the transesterification of triglycerides in an emulsion of 5 g WFO and 0.75 mL of 1 M phosphate buffer pH 7.5 in a 50 mL Erlenmeyer flask. The reactions were carried out at different temperatures and 250 rpm for 24 h. Methanol doses were added to a final given methanol concentration at 0, 6, 12, and 18 h.
FAAE analysis
The reaction mixture was transferred to a 15 mL centrifuge tube and spun at 10,000 rpm for 5 min. Fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) was detected in the supernatant by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) with silica gel 60 F254 (E. Merck, Mumbai, India) using a solvent system of hexane /diethyl ether /acetic acid. Spots were stained in an iodine chamber and were investigated by Just TLC software (Sweday, Lund, Sweden).
Agilent Technologies 6890N gas chromatography (GC) provided a flame ionization detector, and a capillary column (HP-5 5% phenyl methyl siloxane, 30 m by 320 μm by 0.25 mm) was used to quantify the FAMEs content in the supernatant. Peaks determination was carried out by comparing the retention time of FAMEs of the sample (100 mg) and a known concentration of FAME standard mixture C8 – C24 (Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Co. St. Louis, MO, USA), each dissolved in 1 mL hexane. One μL sample was injected into the GC, where the oven was adjusted at 210 ℃, isothermally for 15 min, and helium was used as the carrier gas.
Statistical analysis
The data obtained in triplicates were subjected to statistical analysis using IBM SPSS Statistics (Version 16. IBM, Chicago, USA), where one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by mean comparison using the LSD test, was carried out. Response surface methodology was designed and analyzed using JMP statistical software (Version 8. SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC), where duplicates of each design run were conducted.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study and not included in this published article are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Mishra VK, Goswami R. A review of production, properties and advantages of biodiesel. Biofuels. 2018;9:273–89. https://doi.org/10.1080/17597269.2017.1336350.
Goyal HB, Seal D, Saxena RC. Bio-fuels from thermochemical conversion of renewable resources: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2008;12:504–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2006.07.014.
Nagy HAE, El-Aziz Mohamed MA. Preparation of stable diesel waste cooking oil microemulsion fuel using ionic liquid based benzimidazole derivatives: fuel properties, particle size characteristics, and statistical investigation. Fuel. 2023;337:127217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.127217.
Kalita P, Basumatary B, Saikia P, Das B, Basumatary S. Biodiesel as renewable biofuel produced via enzyme-based catalyzed transesterification. Energy Nexus. 2022;6:100087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nexus.2022.100087.
Nayab R, Imran M, Ramzan M, Tariq M, Taj MB, Akhtar MN, et al. Sustainable biodiesel production via catalytic and non-catalytic transesterification of feedstock materials—a review. Fuel. 2022;328:125254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.125254.
Semwal S, Arora AK, Badoni RP, Tuli DK. Biodiesel production using heterogeneous catalysts. Bioresour Technol. 2011;102:2151–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.10.080.
Aransiola EF, Ojumu TV, Oyekola OO, Madzimbamuto TF, Ikhu-Omoregbe DIO. A review of current technology for biodiesel production: state of the art. Biomass Bioenergy. 2014;61:276–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2013.11.014.
Szczęsna-Antczak M, Struszczyk-Świta K, Rzyska M, Szeląg J, Stańczyk Ł, Antczak T. Oil accumulation and in situ trans/esterification by lipolytic fungal biomass. Bioresour Technol. 2018;265:110–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.05.094.
Sharma A, Melo JS, Prakash R, Tejo PN. Biomass suspension catalysed the generation of various alkyl esters from acid oil and virgin cottonseed oil. Biocatal Biotransform. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1080/10242422.2022.2107427.
Bandikari R, Qian J, Baskaran R, Liu Z, Wu G. Bio-affinity mediated immobilization of lipase onto magnetic cellulose nanospheres for high yield biodiesel in one time addition of methanol. Bioresour Technol. 2018;249:354–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.156.
Bajaj A, Lohan P, Jha PN, Mehrotra R. Biodiesel production through lipase catalyzed transesterification: an overview. J Mol Catal B Enzym. 2010;62:9–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2009.09.018.
Navarro López E, Robles Medina A, González Moreno PA, Esteban Cerdán L, Martín Valverde L, Molina GE. Biodiesel production from Nannochloropsis gaditana lipids through transesterification catalyzed by Rhizopus oryzae lipase. Bioresour Technol. 2016;203:236–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.12.036.
Razack SA, Duraiarasan S. Response surface methodology assisted biodiesel production from waste cooking oil using encapsulated mixed enzyme. Waste Manag. 2016;47:98–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.07.036.
Gotlib E, Cherezova E, Nguyen Thi Lan A, Prabhakaran V, Wang G, et al. Enzymatic transesterification of rubber seed oil using immobilized Pseudomonas cepacia lipase. J Phys Conf Ser. 2022;2266:012013. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2266/1/012013.
Mateos PS, Navas MB, Morcelle SR, Ruscitti C, Matkovic SR, Briand LE. Insights in the biocatalyzed hydrolysis, esterification and transesterification of waste cooking oil with a vegetable lipase. Catal Today. 2021;372:211–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2020.09.027.
Mandari V, Devarai SK. Biodiesel production using homogeneous, heterogeneous, and enzyme catalysts via transesterification and esterification reactions: a critical review. BioEnergy Res. 2021;15:935–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-021-10333-w.
Rodrigues RC, Volpato G, Wada K, Ayub MAZ. Enzymatic synthesis of biodiesel from transesterification reactions of vegetable oils and short chain alcohols. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 2008;85:925–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-008-1284-0.
Akoh CC, Chang SW, Lee GC, Shaw JF. Enzymatic approach to biodiesel production. J Agric Food Chem. 2007;55:8995–9005. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf071724y.
Elhussiny NI, Khattab AENA, El-Refai HA, Mohamed SS, Shetaia YM, Amin HA. Assessment of waste frying oil transesterification capacities of local isolated Aspergilli species and mutants. Mycoscience. 2020;61:136–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.myc.2020.01.003.
Elhussiny NI, Khattab AENA, El-Refai HA, Mohamed SS, Shetaia YM, Amin HA. Biotransesterification capabilities of Mucorales whole-cell lipase isolates and mutants. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. 2020;28:101722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101722.
Facin BR, Melchiors MS, Valériovalério A, Oliveira JV, Débora De Oliveira D. Driving immobilized lipases as biocatalysts: 10 years state of the art and future prospects. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2019;58:5358–78. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.9b00448.
Nematian T, Barati M. Nanobiocatalytic processes for producing biodiesel from algae. In: Rai M, Ingle AP, editors. Sustainable bioenergy: advances and impacts. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2019. p. 299–326.
Gog A, Roman M, Toşa M, Paizs C, Irimie FD. Biodiesel production using enzymatic transesterification—current state and perspectives. Renew Energy. 2012;39:10–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2011.08.007.
Rocha TG, Pedro PH, de Souza MCM, Monteiro RRC, dos Santos JCS. Lipase cocktail for optimized biodiesel production of free fatty acids from residual chicken oil. Catal Lette. 2021;151:1155–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-020-03367-w.
Amoah J, Ho SH, Hama S, Yoshida A, Nakanishi A, Hasunuma T, et al. Lipase cocktail for efficient conversion of oils containing phospholipids to biodiesel. Bioresour Technol. 2016;211:224–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.03.062.
Mehariya S, Goswami RK, Verma P, Lavecchia R, Zuorro A. Integrated approach for wastewater treatment and biofuel production in microalgae biorefineries. Energies. 2021;14:2282. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14082282.
Rani S, Ojha CSP. Chlorella sorokiniana for integrated wastewater treatment, biomass accumulation and value-added product estimation under varying photoperiod regimes: a comparative study. J Water Process Eng. 2021;39:101889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101889.
Asadi P, Rad HA, Qaderi F. Comparison of Chlorella vulgaris and Chlorella sorokiniana pa.91 in post treatment of dairy wastewater treatment plant effluents. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2019;26:29473–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06051-8.
Chen CY, Kuo EW, Nagarajan D, Ho SH, Di DC, Lee DJ, et al. Cultivating Chlorella sorokiniana AK-1 with swine wastewater for simultaneous wastewater treatment and algal biomass production. Bioresour Technol. 2020;302:122814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.122814.
Chu R, Li S, Zhu L, Yin Z, Hu D, Liu C, et al. A review on co-cultivation of microalgae with filamentous fungi efficient harvesting, wastewater treatment and biofuel production. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2021;139:110689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2020.110689.
Nazari MT, Freitag JF, Cavanhi VAF, Colla LM. Microalgae harvesting by fungal-assisted bioflocculation. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol. 2020;19:369–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-020-09528-y.
Liu J, Qiu W, Wang Y. Fungal pretreatment of raw digested piggery wastewater enhancing the survival of algae as biofuel feedstock. Bioresour Bioprocess. 2017;4:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-016-0136-2.
Lange L, Bak UG, Hansen SCB, Gregersen O, Harmsen P, Karlsson EN, Meyer A, Mikkelsen MD, Van Den Broek L, Hreggviðsson GÓ. Opportunities for seaweed biorefinery. In: Torres MD, Kraan S, Dominguez H, editors. Sustainable seaweed technologies: cultivation, biorefinery, and applications. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2020. p. 3–31.
Sulfahri MS, Husain DR, Langford A, Tassakka ACMAR. Fungal pretreatment as a sustainable and low cost option for bioethanol production from marine algae. J Clean Prod. 2020;265:121763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121763.
Mohamed M, Nur R, Rajali A, Radzi SM, Amalina N, Amin M. Optimization of the biodiesel production via transesterification reaction of palm oil using response surface methodology (RSM): a review. Malays J Sci Health Tech. 2022;8:58–67. https://doi.org/10.33102/mjosht.v8i2.292.
Thakkar K, Kachhwaha SS, Kodgire P. Multi-response optimization of transesterification reaction for biodiesel production from castor oil assisted by hydrodynamic cavitation. Fuel. 2022;308:121907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.121907.
Wang J, Li K, He Y, Wang Y, Han X, Yan Y. Enhanced performance of lipase immobilized onto Co2+-chelated magnetic nanoparticles and its application in biodiesel production. Fuel. 2019;255:115794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.115794.
Abdulmalek SA, Li K, Wang J, Ghide MK, Yan Y. Enhanced performance of Rhizopus oryzae lipase immobilized onto a hybrid-nanocomposite matrix and its application for biodiesel production under the assistance of ultrasonic technique. Fuel Process Tech. 2022;232:107274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2022.107274.
Schmidt JJ, Gagnon GA, Jamieson RC. Microalgae growth and phosphorus uptake in wastewater under simulated cold region conditions. Ecol Eng. 2016;95:588–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.06.114.
Jensen RG. Detection and determination of lipase (acylglycerol hydrolase) activity from various sources. Lipids. 1983;18:650–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02534677/metrics.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GK, HA, and NE conceived and designed the research. NE conducted experiments, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript. GK, HA, HE, SS, YS, AM revision of the text. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This article contains no studies with human participants or animals performed by authors.
Consent for publication
The authors consent to publish the original article (Bio-catalysis of triglycerides transesterification using fungal biomass: Reaction optimization and a biorefinery approach) in Fungal biology and biotechnology.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Elhussiny, N.I., Mohamed, A.M.A., El-Refai, H.A. et al. Biocatalysis of triglycerides transesterification using fungal biomass: a biorefinery approach. Fungal Biol Biotechnol 10, 12 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40694-023-00160-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40694-023-00160-3