Abstract
The lunar surface and interior are highly reducing, resulting in the virtually absence of ferric ion. However, recent studies suggest the presence of ferric iron in lunar samples, and in most cases they were found in amorphous silicates (e.g., glass beads) measured by TEM–EELS. In this work, we conducted a systematic TEM–EELS analysis on the iron valence states of Chang’e-5 impact glass beads. The Fe3+/ΣFe ratio of each silicate glass sample was determined from integral intensity of Fe L3 and L2 edge. The measurements show a positive correlation between the dwell time and Fe3+/ΣFe ratio, which reveals that ferric iron can be significantly produced by electron beam bombardment under routine analytical condition. The calculated Fe3+/ΣFe with short dwell times (≤ 20 ms) in our Chang’e-5 impact glass beads show no detectable inherent ferric iron, suggesting that the ferric iron is not ubiquitous as previously reported. It is obvious that a careful control of experiment conditions is critical to determine the inherent redox state of other beam-sensitive terrestrial and extraterrestrial samples.
Graphical Abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Conditions on the Moon are highly reducing with oxygen fugacity at or below the iron-wüstite buffer (Lucey et al. 2006; Wieczorek et al. 2006). Iron is generally considered to be exist as ferrous iron (Fe2+), except a small fraction of iron exist as the metallic state (Fe0) in mare basalts (Wieczorek et al. 2006) and lunar soils associated with space weathering processes (Gu et al. 2022; Pieters et al. 2000). However, recent studies reported the presence of ferric iron in lunar samples (Cymes et al. 2023; Li et al. 2020). A portion of ferric iron in the form of magnetite was reported in lunar breccia 60016 (Joy et al. 2015), Apollo 17 soil 71501 (Burgess and Stroud 2018a), and Chang'e-5 (CE-5) soil (Guo et al. 2022). More frequently, the occurrences of ferric iron were found in amorphous silicates such as glass beads and agglutinate glasses (Burgess and Stroud 2018a; Li et al. 2022; McCanta et al. 2017; Mo et al. 2022; Thompson et al. 2016; Xian et al. 2023). Several formation mechanisms of Fe3+ were proposed, including oxidation caused by magmatic degassing of H or OH (McCanta et al. 2017), diffusion effects (Burgess and Stroud 2018a; Thompson et al. 2016), oxidation due to Earth’s upper atmosphere (Li et al. 2020), or disproportionation reaction (Li et al. 2022; Xian et al. 2023). However, other studies argued that the presence of Fe3+ could be due to terrestrial contamination (Griscom 1974; Taylor and Burton 1976). The occurrence of ferric iron remains elusive and requires more detailed analysis.
Different techniques have been used to measure the iron valence states. Traditional methods such as wet chemical analysis and Mössbauer spectroscopy are performed on bulk material. Electron microprobe analysis (EPMA) and synchrotron-based X-ray absorption near-edge structure spectroscopy (XANES) present the opportunity to measure Fe3+/ΣFe at microscales (Fialin et al. 2004; McCanta et al. 2017; Wang and Li 2022). However, the best spatial resolution to date is based on electron energy Loss spectroscopy (EELS) in the transmission electron microscope (TEM) (Cavé et al. 2006; Aken and Liebscher 2002). This technique enables imaging and spectroscopic analysis at nanometer or even atomic resolution (Gloter et al. 2017; Aken and Liebscher 2002), and has made important progress in determining the oxidation state of individual nanoparticles (Burgess and Stroud 2018b, 2021) and revealing mineral evolution processes (Bindi et al. 2020; Sinmyo et al. 2011). However, previous studies have demonstrated that the high brightness and focused beam can cause significant damage to some terrestrial materials (e.g. H-bearing minerals), including changing the structure of the material and the valence state of elements (Burgess et al. 2016; Freeman et al. 2019; Garvie 2010; Pan et al. 2010). These issues raise concerns about the reliability of iron valence measurements of amorphous silicates in lunar soil samples. However, potential beam damage effect of these samples during the EELS analysis has rarely been discussed.
The Chang'e-5 (CE-5) mission has brought back new youngest (~ 2.0 Ga) mare basalt samples (Hu et al. 2021; Li et al. 2021; Tian et al. 2021). All the CE-5 glass beads reported so far are of impact origin, recording the impact history of the Moon (Long et al. 2022; Yang et al. 2022). In order to better constrain the redox conditions of glass beads formation, we conducted a systematic EELS analysis on the two typical CE-5 impact glasses.
Sample and methods
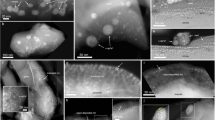
The CE-5 landing site is located in the mid-latitude region Northern Oceanus Procellarum of the Moon (43.06_N and 51.92_W). The lunar soil grains used here were allocated from the surface soil samples (labelled as CE5C0400YJFM00407/405, weighing 1 g and CE5C0100YJFM00103, weighing 1 g). Hundreds of glass spherules were picked out and embedded in one-inch epoxy mounts, and then were made into polished sections before analyses. In this work, based on the backscattered electron (BSE) images, we selected two typical silicate glasses (Fig. 1): one appears to be clean and homogeneous (#090), while the other is heterogeneous with bubbles and numerous small iron nanoparticles (#084).
Microscopic characteristics of CE-5 glass beads. a BSE image of sample #090, which has a homogeneous contrast. b HAADF image of foil 1 extracted from #090. c BSE image of sample #084, which contains vesicles and numerous metal particles. d HAADF image of foil 2 extracted from #084. Abundant nanoparticles are visible
SEM: The samples were observed using a Thermo Fisher Apreo scanning electron microscope (SEM) equipped with an energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS, Oxford X-Max 80) at the Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IGGCAS). The operating voltage was ~ 15 kV. Sample #090 was analysed with a CAMECA SXFive electron probe microanalyzer for composition prior to focused ion beam cutting.
FIB and TEM: Ultra-thin foils (< 100 nm in thickness) were prepared from each glass bead using the focused ion beam (FIB) equipped with an Omniprobe 200 micromanipulator at the IGGCAS. Ion milling was carried out with an accelerating voltage of 5–30 kV and various beam currents (50 pA to 2 nA). The FIB foils were characterized with a JEM-ARM200F spherical aberration scanning transmission electron microscopy. High angle annular dark field image (HAADF) was performed to record the microstructural changes of TEM foils; meanwhile, a dual electron energy loss spectrometer of Gatan Enfinium ER 977 was used to analyse the iron valences of samples. The STEM-EELS was operated at 200 kV and ~ 40 pA, with a 28 mrad convergence angle/0.1 to 0.2 nm probe size. The EELS were collected by line-scan integration to obtain high-quality spectrum and reduce possible variation in thickness and compositions. A series of dwell times from 0.01 s up to 30 s (0.01–10 s for #090 and 0.02–10 s for #084) were used to evaluate the beam damage effects. Energy resolution, measured from the zero-loss peak, is about 0.6 ~ 0.7 eV. EDS mapping from region where the beam dwelled for 30 s was acquired using the Super-X EDS detector in a Thermofisher Talos 200X TEM.
Quantification of Fe3+/ΣFe in glasses based on EELS data was done following the modified integral peak intensity ratio method (Aken and Liebscher 2002), as shown in Additional file 1: Figure S1 in Supporting Information. The background in the EELS was first removed using an inverse power law fitting in the Gatan Digital Micrograph software. Then a double arctan function was applied to subtract the continuum background. The integral intensity I(L3) and I(L2) is from two windows 2 eV wide centred around on the maximum of the L3Fe3+ peak (~ 709.7 eV) and at the L2 edge for Fe2+ (~ 720.7 eV). The intensity ratio I(L3)/I(L2) was converted to Fe3+/ΣFe using the universal calibration and compared with a number of reference materials, including Fe–Ni metal, olivine (Fa ~ 70) and hematite (Fig. 2). The spot size and beam current used in the EELS measurement of the reference materials are consistent with those in this study. The measurement accuracy of reference materials is mainly composed of the errors caused by quantitative method and sample damage induced by FIB preparation processes. In this study, the reference materials includes Fe–Ni metal, olivine (Fa ~ 70) and hematite, which have measured Fe3+/ΣFe values are 11%, 9%, and 97%, respectively, with deviations from the standard values of ~ 10%. Therefore, the measurement accuracy was roughly estimated as ~ 10%.
Fe L-edge EELS of reference materials, including hematite, olivine and Fe–Ni metal. The calculated Fe3+/ΣFe values are 97% for hematite, 9% for olivine, and 11% for Fe–Ni metal using the method described by figure S1. Except for the peak position features, peak tail features can be used to distinguish Fe0 from Fe2+ and Fe3+; that is, Fe0 has a tail feature with higher intensity than Fe2+ and Fe3+
Results and discussion
Based on the backscattered electron images, there are two main types of CE-5 impact glass beads: (1) clast fragment-bearing glass with definitive petrographic characteristics such as the presence of FeNi metal and vesicles; (2) clean glass, inferred to have been fully molten during their formation (Yang et al. 2022). In this study, one sample of each type (#090 and #084) were selected for iron oxidation states analysis. Glass #090 appears to be chemically homogeneous with no inclusion was observed (Fig. 1). Its composition (CaO/Al2O3 = 0.91; MgO/Al2O3 = 0.53) (Table 1) is similar to that of other reported CE-5 glass spherules (average composition: CaO/Al2O3 = 0.96; MgO/Al2O3 = 0.58) (Yang et al. 2022). Glass #084 contains bubbles and numerous metallic iron and iron sulfide nanoparticles (Fig. 1 and Additional file 1: Figure S2). The FeO content in the amorphous region of sample #084 (FeO ~ 17.2%) was slightly lower than that of sample #090 (FeO ~ 20%) based on TEM-EDS results (Table 1).
Evaluation of the electron beam damage during EELS measurement
As shown in Fig. 3b, EELS of sample #090 with shorter dwell time (< 50 ms) shows that the Fe L3-edge peak consists of a main peak at 708 eV and a very small shoulder around 710 eV. This feature is nearly identical to the observations of Fe2+ in reference sample olivine (Fig. 2). As the dwell time increases, the peak intensity around 710 eV increases rapidly and the peak of 708 eV is almost invisible at 10 s. Fe L2-edge peak at around 720 eV shifts slightly towards the high energy loss. These changes indicate that the iron valence converts from Fe2+ to Fe3+ with increasing dwell time, by comparing with reference minerals (Fig. 2). During the whole measurement, no Fe0 nanoparticle was observed in the HAADF image, consistent with no significant change in the Fe L2-edge peak tail intensity (Fig. 3b). In addition, EELS measurements on silicate glass lead to the creation of dark “spots” that are clearly visible in the HAADF image, except for 0.01 and 0.02 s (Fig. 3a). The damaged spot can be up to 5 nm when dwell time is 10 s, much larger than the diameter of electron beam. To verify the reliability of this change, we repeated the EELS measurements in other regions, and the results (Additional file 1: Figure S3) were consistent with those described above, indicating the change of iron valence state is induced by the electron beam damage rather than due to heterogeneity of the sample composition. This inference was further demonstrated by other comparative experiment conducted on the same location with 0.02 and 0.1 s, respectively (Additional file 1: Figure S4).
The Fe L-edge EELS analysis of sample #090. a HAADF image after EELS measurements show beam damage except for 0.01 and 0.02 s. b EELS with different dwell times show that the peak intensity around 710 eV increases rapidly with increasing dwell time and the peak of 708 eV is almost invisible at 10 s. Fe2+ and Fe3+ lines represent L3 peak positions of Fe2+ and Fe3+ reference materials, respectively. c Variations of Fe3+/ΣFe ratio versus the dwell time. The calculated Fe3+/ΣFe value is -3.8% at 10 ms. The negative value is mainly due to the quantitative method errors
Sample #084 shows the similar changes as sample #090 during the Fe L-edge EELS measurements (Fig. 3). As the dwell time was increased, the intensity ratio of L3Fe3+ to L3Fe2+ peak increased significantly (Fig. 4b). This change indicates that the beam damage also occurs in the glass region of sample #084, resulting in the formation of a large amount of ferric iron. However, the olivine crystal and metallic iron nanoparticle did not show obvious L3Fe3+ peak with even prolonged dwell time analysis (~ 30 s for olivine and ~ 10 s for iron nanoparticle), suggesting that they are relatively stable under the electron beam bombardment (Figs. 2 and 4b).
The Fe L-edge EELS analysis of sample #084. a HAADF image shows the position of EELS analysis with different dwell times. To avoid collecting EELS signal from iron and iron sulfide nanoparticles, we changed measurement configuration for sample #084. Here the EELSs are measured at the same location, so the time is cumulative increase, that is, dwell times of 50, 100 and 500 ms for EELS measurement actually corresponds to 50, 150 and 650 ms, respectively. Additionally, EELS with a dwell time of 300 ms was collected independent line scanning, while EELSs with a dwell time of 20 ms were obtained by summing up four line scanning data to improve the signal-to-noise ratio. Fe2+ and Fe3+ lines represent L3 peak positions of Fe2+ and Fe3+ reference materials, respectively. b EELS results of amorphous areas and metallic iron nanoparticle (npFe0). c Variations of Fe3+/ΣFe ratio versus the dwell time. The calculated Fe3+/ΣFe value is −4.5% at 20 ms. The negative value is mainly due to the quantitative method errors
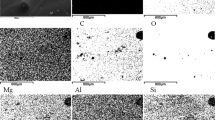
Therefore, we can definitively conclude that ferric iron could be significantly produced in silicate glasses under typical analytical condition (a few seconds of dwell time). To our knowledge, this is the first time that iron valence states in lunar glasses have been systematically analyzed by different EELS measurement conditions, confirming their susceptibility to the TEM electron beam. In order to reveal the formation mechanism of ferric iron, we collected EDS mapping of sample #090 from region where the beam dwelled for 30 s (for EELS measurement). The results show that EELS measurement caused elemental migration (Fig. 5). Cations other than Si are highly depleted in the “dark” spot. Moreover, in low-loss edge EELS (Fig. 5i), the shoulder peaks at ~ 34 (probably Ca or Ti M-edge) and 56 eV (Fe M2, 3-edge) are no longer visible. These results are similar to those previously observed in terrestrial synthetic silicate glasses, which suggested that beam damage is caused by an electric field formed in the glass (Burgess et al. 2016). When the electrons interact with the ultra-thin foils, the emission of secondary and auger electrons generates a region of positive charge in the analysis area, producing an electric field (Burgess et al. 2016; Cazaux 1996). Activation energy for diffusion in silicate glasses follows the sequence Ca ~ Mg ~ Fe2+ < Fe3+ < Al < Si ~ O (Burgess et al. 2016; Zhang et al. 2010). The positive charge causes the cations to migrate out of the analysis area, leaving behind O which can oxidize Fe (Hughes et al. 2020). As the increase of measuring time, Fe3+ also migrated out of the analysis area, which was supported by the fact that the intensity of Fe L-edge peak was lower at dwell time of 30 s relative to that of 5 s (Fig. 6).
Quantification of inherent ferric iron in impact glasses
As shown above, iron EELS with different dwell times can well characterize the change of iron oxidation state, and the results reveal that ferric iron can be significantly produced by electron beam bombardment. Following the modified integral peak intensity ratio method (Aken and Liebscher 2002), it is possible to calculate the Fe3+/ΣFe ratio in impact glasses. The calculated Fe3+/ΣFe values are very low at short dwell times, with a ratio of -3.8% for #090 at 10 ms and -4.5% for #084 at 20 ms (Figs. 3c and 4c), indicating that the glasses contain almost no detectable inherent ferric iron under the measurement accuracy. The quantitative results reveal that these impact glasses are quenched in a highly reducing environment, which is consistent with the absence of Fe3+ in Apollo lunar samples determined by Mössbauer spectroscopy (Burns and Dyar 1983; Jolliff et al. 2006; Morris et al. 1998; Muir et al. 1971; Muir et al. 1970). However, quantitative results with longer dwell times show that there is a large amount of ferric iron. Thus it can be seen that, careful control of experiment conditions and the use of glass standards with known Fe3+/ΣFe ratios are critical to determine the inherent redox state of such beam-sensitive samples. According to our study, we suggest that short dwell time, e.g. < 20 ms, is preferable for EELS analysis to detect the inherent Fe3+ in silicate glasses. However, we can not distinguish a small amount of original Fe3+ from the Fe3+ created under the short dwell time.
The presence of ferric iron under highly reducing lunar surface is a long-standing issue. Disproportionation reaction (3Fe2+ → Fe0 + 2Fe3+) during impact was previously considered as a potential process. This process can produce large amounts of ferric iron, accompanied with the formation of metallic iron. However, in our samples, glass #090 has no metallic iron, and although glass #084 has metallic iron particles, its amorphous region contains no detectable inherent ferric iron, suggesting that no such reaction occurred. Hence, the presence of ferric iron in silicate glasses could be due to the beam damage effects rather than disproportionation reaction. Future identification of this reaction should pay special attention to the beam damage effects during measurement. Another hypothesis is that ferric iron can form in oxidizing hydrothermal conditions (Thompson et al. 2016; Williams and Gibson 1972; Zolensky et al. 1996). For example, the Fe2+ can be oxidized by reacting with water (FeO + H2O → Fe3O4 + H2 gas) (Hicks et al. 2021; Thompson et al. 2016). However, glass #090 contains only 62 ppm of solar wind-derived water in the core (He et al., 2023), which is insufficient to cause the changes of iron valence. CE-5 glass beads and other mineral grains show higher solar wind-derived water at the rims (He et al. 2023; Xu et al. 2022; Zhou et al. 2022). Whether this will produce ferric iron in some localized region is currently unknown.
Conclusion and implications
By taking iron EELS measurements of Chang’e-5 lunar impact glasses with different dwell times, we demonstrate that electron beam-induced oxidation can occur in a very short time (< 200 ms), but was not observed in crystals such as olivine and iron nanoparticle. This is mainly due to the susceptibility of silicate glasses to the high brightness and focused electron beam. The calculated Fe3+/ΣFe with very short dwell times in our Chang’e-5 impact glass beads show no detectable inherent Fe3+, suggesting that the ferric iron is not ubiquitous as previously reported. These results better constrain the impact processes on the moon, and also shed light on the evaluation of inherent redox states of other lunar and extraterrestrial samples.
The change of oxidation state caused by electron beam damage may be widespread in beam-sensitive minerals such as bridgmanite and hydrous Fe-bearing minerals, which are easily overlooked. The influence of beam damage mainly depends on the factors that include incident electron energy, probe-current density and sample thickness (Egerton et al. 1987; Garvie et al. 2004; Jiang 2015). Therefore, accurate and reliable measurements of iron valence states require careful sample preparation and control of experimental conditions, and combined with other complementary techniques such as structural characterization and Mössbauer spectroscopy. In addition, the beam damage identification and short dwell time measurement highlighted in this study present a reliable method for analysing small sized, beam-sensitive samples with a typical electron energy and probe-current density. It is required to further test dwell time effects using a set of glass standards with known Fe3+/ΣFe ratios in the future study. As for the presence of ferric iron and its possible formation mechanism in lunar samples, it remains an open question that needs to be investigated by more detailed experiments.
Availability of data and materials
Data in this manuscript are available online (https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7824122).
References
Bindi L, Shim S-H, Sharp TG, Xie X (2020) Evidence for the charge disproportionation of iron in extraterrestrial bridgmanite. Sci Adv 6:7893
Burgess KD, Stroud RM (2018a) Coordinated nanoscale compositional and oxidation state measurements of lunar space-weathered material. J Geophys Res Planets 123:2022–2037
Burgess KD, Stroud RM (2018b) Phase-dependent space weathering effects and spectroscopic identification of retained helium in a lunar soil grain. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 224:64–79
Burgess KD, Stroud RM (2021) Comparison of space weathering features in three particles from Itokawa. Meteorit Planet Sci 56:1109–1124
Burgess KD, Stroud RM, Dyar MD, McCanta MC (2016) Submicrometer-scale spatial heterogeneity in silicate glasses using aberration-corrected scanning transmission electron microscopy. Am Miner 101:2677–2688
Burns RG, Dyar MD (1983) Spectral chemistry of green glass-bearing 15426 regolith. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 88:B221–B228
Cavé L, Al T, Loomer D, Cogswell S, Weaver L (2006) A STEM/EELS method for mapping iron valence ratios in oxide minerals. Micron 37:301–309
Cazaux J (1996) Electron probe microanalysis of insulating materials: quantification problems and some possible solutions. X-Ray Spectrom 25:265–280
Cymes BA, Burgess KD, Stroud RM (2023) Detection of ferric iron in an exsolved lunar pyroxene using electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS): Implications for space weathering and redox conditions on the Moon. Meteorit Planet Sci 58:259–274
Egerton R, Crozier P, Rice P (1987) Electron energy-loss spectroscopy and chemical change. Ultramicroscopy 23:305–312
Fialin M, Bézos A, Wagner C, Magnien V, Humler E (2004) Quantitative electron microprobe analysis of Fe3+/∑ Fe: Basic concepts and experimental protocol for glasses. Am Miner 89:654–662
Freeman H, Perez J, Hondow N, Benning LG, Brown A (2019) Beam-induced oxidation of mixed-valent Fe (oxyhydr) oxides (green rust) monitored by STEM-EELS. Micron 122:46–52
Garvie LA (2010) Can electron energy-loss spectroscopy (EELS) be used to quantify hydrogen in minerals from the OK edge? Am Miner 95:92–97
Garvie LA, Zega TJ, Rez P, Buseck PR (2004) Nanometer-scale measurements of Fe3+/ΣFe by electron energy-loss spectroscopy: a cautionary note. Am Miner 89:1610–1616
Gloter A et al (2017) Atomically resolved mapping of EELS fine structures. Mater Sci Semicond Process 65:2–17
Griscom D (1974) Ferromagnetic resonance spectra of lunar fines: some implications of line shape analysis. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 38:1509–1519
Gu L et al (2022) Space weathering of the Chang’e-5 lunar sample from a mid-high latitude region on the Moon. Geophys Res Lett 49:e2022GL097875
Guo Z et al (2022) Sub-microscopic magnetite and metallic iron particles formed by eutectic reaction in Chang’E-5 lunar soil. Nat Commun 13:7177
He H et al (2023) A solar wind-derived water reservoir on the Moon hosted by impact glass beads. Nat Geosci 16:294–300
Hicks LJ, Bridges JC, Noguchi T, Miyake A, Piercy JD, Baker SH (2021) Fe-redox changes in Itokawa space-weathered rims. Meteorit Planet Sci 55:2599–2618
Hu S et al (2021) A dry lunar mantle reservoir for young mare basalts of Chang’e-5. Nature 600:49–53
Hughes EC et al (2020) The microanalysis of iron and sulphur oxidation states in silicate glass-understanding the effects of beam damage. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 891:012014
Jiang N (2015) Electron beam damage in oxides: a review. Rep Prog Phys 79:016501
Jolliff B, Wieczorek M, Shearer C, Neal C (2006) New views of the Moon. Reviews in mineralogy and geochemistry. Mineralogical Society of America, Washington
Joy KH et al (2015) Identification of magnetite in lunar regolith breccia 60016: evidence for oxidized conditions at the lunar surface. Meteorit Planet Sci 50:1157–1172
Li S et al (2020) Widespread hematite at high latitudes of the Moon. Sci Adv 6:eaba1940
Li Q-L et al (2021) Two-billion-year-old volcanism on the Moon from chang’e-5 basalts. Nature 600:54–58
Li C et al (2022) Impact-driven disproportionation origin of nanophase iron particles in Chang’e-5 lunar soil sample. Nat Astronomy 6:1156–1162
Long T et al (2022) Constraining the formation and transport of lunar impact glasses using the ages and chemical compositions of Chang’e-5 glass beads. Sci Adv 8:eabq2542
Lucey P et al (2006) Understanding the lunar surface and space-Moon interactions. Rev Mineral Geochem 60:83–219
McCanta MC, Dyar MD, Rutherford MJ, Lanzirotti A, Sutton SR, Thomson BJ (2017) In situ measurement of ferric iron in lunar glass beads using Fe-XAS. Icarus 285:95–102
Mo B et al (2022) In situ investigation of the valence states of iron-bearing phases in chang’E-5 lunar soil using FIB, AES, and TEM-EELS techniques. At Spectrosc 43:53–59
Morris RV, Klingelhöfer G, Korotev RL, Shelfer TD (1998) Mössbauer mineralogy on the Moon: the lunar regolith. Hyperfine Interact 117:405–432
Muir A Jr, Housley R, Grant R, Abdel-Gawad M, Blander M (1970) Mössbauer spectroscopy of moon samples. Science 167:688–690
Muir A, Housley R, Grant R, Abdel-Gawad M, Blander M. 1971. Mössbauer investigation of Apollo 11 lunar samples. Proceedings of the Sixth Symposium on Mössbauer Effect Methodology New York City, January 25, 1970. Springer, pp. 163–176.
Pan Y-H et al (2010) Electron-beam-induced reduction of Fe3+ in iron phosphate dihydrate, ferrihydrite, haemosiderin and ferritin as revealed by electron energy-loss spectroscopy. Ultramicroscopy 110:1020–1032
Pieters CM, Taylor LA, Noble SK (2000) Space weathering on airless bodies: resolving a mystery with lunar samples. Meteorit Planet Sci 35:1101–1107
Sinmyo R, Hirose K, Muto S, Ohishi Y, Yasuhara A (2011) The valence state and partitioning of iron in the Earth’s lowermost mantle. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 116:B07205
Taylor LA, Burton JC (1976) Experiments on the stability of FeOOH on the surface of the Moon. Meteoritics 11:225–230
Thompson MS, Zega TJ, Becerra P, Keane JT, Byrne S (2016) The oxidation state of nanophase Fe particles in lunar soil: Implications for space weathering. Meteorit Planet Sci 51:1082–1095
Tian H-C et al (2021) Non-KREEP origin for Chang’e-5 basalts in the Procellarum KREEP Terrane. Nature 600:59–63
Van Aken P, Liebscher B (2002) Quantification of ferrous/ferric ratios in minerals: new evaluation schemes of Fe L 23 electron energy-loss near-edge spectra. Phys Chem Miner 29:188–200
Wang J, Li J-H (2022) Scanning transmission x-ray microscopy at the Canadian Light Source: progress and selected applications in geosciences. At Spectrosc 43:84–98
Wieczorek MA et al (2006) The constitution and structure of the lunar interior. Rev Mineral Geochem 60:221–364
Williams RJ, Gibson EK (1972) The origin and stability of lunar goethite, hematite and magnetite. Earth Planet Sci Lett 17:84–88
Xian H et al (2023) Ubiquitous and progressively increasing ferric iron content on the lunar surfaces revealed by the Chang’e-5 sample. Nature Astronomy 7:280–286
Xu Y et al (2022) High abundance of solar wind-derived water in lunar soils from the middle latitude. Proc Natl Acad Sci 119:e2214395119
Yang W et al (2022) Geochemistry of impact glasses in the Chang’e-5 regolith: constraints on impact melting and the petrogenesis of local basalt. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 335:183–196
Zhang Y, Ni H, Chen Y (2010) Diffusion data in silicate melts. Rev Mineral Geochem 72:311–408
Zhou C et al (2022) Chang’E-5 samples reveal high water content in lunar minerals. Nat Commun 13:1–10
Zolensky ME, Weisberg MK, Buchanan PC, Mittlefehldt DW (1996) Mineralogy of carbonaceous chondrite clasts in HED achondrites and the Moon. Meteorit Planet Sci 31:518–537
Acknowledgements
The CE-5 samples were allocated by the China National Space Administration.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42241152, 42230206, 42103035 and 42241104), the Key Research program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (ZDBS-SSW-JSC007-1-2 and ZDBS-SSW-JSC007-7) and the key research program of the Institute of Geology and Geophysics, CAS (IGGCAS-202101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LXG contributed to sample preparation, SEM, FIB and TEM analysis, data processing and interpretation, and manuscript preparation. LXG, YTL, YJC and JHL designed the experiments. LXG, YTL, YJC and HKM contributed to data interpretation. All authors contributed to the writing and editing of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Figure S1.
Background subtraction method for Fe L-edge EELS. Figure S2. STEM-EDS mapping of foil 2 (sample #084). Figure S3. Repeated measurements of Fe L-edge EELS at different regions of sample #090. Figure S4. Comparative experiment for sample #090 conducted at the same location with dwell times of 0.02 s and 0.1 s, respectively.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, L., Lin, Y., Chen, Y. et al. Measurement of ferric iron in Chang’e-5 impact glass beads. Earth Planets Space 75, 151 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40623-023-01909-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40623-023-01909-1