Abstract
Highly saline lithium-rich hydrothermal fluids (measured chloride concentration up to 44 g kg−1, lithium concentration up to 162 mg kg−1) occur in the deep calcareous Muschelkalk aquifer beneath the northern Alpine foreland (Molasse) basin. We have combined geologic, hydraulic, hydrochemical, and stress field data of the Triassic Muschelkalk aquifer beneath younger sediments of Triassic–Jurassic successions and the Cenozoic Molasse basin of SW-Germany for a synthesis to constrain the origin and development of these brines. In contrast to the regional southeast plunge of Jurassic and Cenozoic strata, low-gradient groundwater flow in the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer is to the north, induced by regional recharge from west, south, and east. The investigated area is seismically active and north trending maximum horizontal stress likely fosters development of necessary fracture permeability for northward flow in the competent carbonates of the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer. The highest lithium concentrations and total dissolved solids (TDS) can be found in the southern parts of the Muschelkalk aquifer. Here, the Muschelkalk Group overlays directly a crystalline basement swell separating two ENE-trending Permocarboniferous troughs. We argue that the highly saline lithium-rich fluids originate from fluid–rock interaction of meteoric water with Variscan crystalline basement rocks and entered the Muschelkalk aquifer on top of the basement swell by permeable faults and fractures. The marginal calcareous sand-rich facies of the Muschelkalk enables the inflow of brines from crystalline basement faults and fractures into the aquifer. We thus argue for an external origin of these brines into the aquifer and further intra-reservoir development by dilution with meteoric water.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
High lithium concentrations (> 100 mg kg−1) in high-saline, deep sedimentary basin brines occur worldwide (Yuan et al. 2021; Sanjuan et al. 2016; Chan et al. 1994; Fouillac and Michard 1981; Moldovanyi and Walter 1992), but not each sedimentary basin has accumulated high lithium (Li) concentrations in their brines. This is apparently independent of whether a marine, magmatic, or meteoric fluid origin prevails. Furthermore, lithium concentrations may be heterogeneously distributed in a sedimentary basin (Collins 1978; Eccles and Berhane 2011) or rather homogeneously as for example in the deep geothermal fluids of the Upper Rhine Graben (e.g., Sanjuan et al. 2016, 2022). For comparison: lithium concentrations in rainwater, generally in the order of 0.1–1.0 µg kg−1 (Poissant et al. 1994), and in seawater < 0.2 mg kg−1 are very low (Riley and Tongudai 1964). Two major processes are under consideration for the origin of Li-rich brines in sedimentary basins comprising either seawater evaporation and evaporite dissolution (Pauwels et al. 1993; Sanjuan et al. 2016, 2022) or fluid–rock interaction (Drüppel et al. 2020; Yuan et al. 2021; Dini et al. 2022). Experimental and empirical relationships indicate a positive thermodynamic correlation with temperature, given sufficient residence time to achieve equilibrium between fluid and host rock (e.g., Kharaka and Mariner 1989; Millot et al. 2010). Li-rich brines thus may be regarded as a result of both hydrochemical processes and specific geological boundary conditions that each need to be investigated.
The highly saline Li-rich brines of the Muschelkalk aquifer in the subsurface of the Molasse basin were first described by Stober (2014). However, high Li concentrations in the calcareous lithology of the aquifer are—at a first glance—rather unexpected. Far less well-known than the deep Upper Jurassic Malm aquifer is the deep Middle Triassic Muschelkalk aquifer in the Molasse Basin of SW-Germany. First scanty hydraulic and hydrochemical results are provided in Bertleff et al. (1988) and in Stober and Villinger (1997). New geological, geophysical, hydraulic, and hydrochemical results are provided in Grimm et al. (2005), Jodocy and Stober (2009a, b), Stober and Jodocy (2011), Geyer and Gwinner (2011), Stober et al. (2013), Stober (2013, 2014), and LGRB (2005, 2015). Information on the deep Muschelkalk aquifer in northern Switzerland can be found in Nagra (2013, 2014), Aschwanden et al. (2014), Heuberger and Morgenthaler (2023).
Hydrothermal fluids in calcareous aquifers can also be highly enriched in lithium (Li), like in the deep saline Carboniferous limestone aquifer of the Campine basin (Belgium), with a Li concentration of 122 mg l−1 (Bos et al. 2018; Iannotta and Hehn 2022). Thus, the highly saline Li-rich brines in the deep Triassic Muschelkalk aquifer in the Molasse basin comprise not a unique feature and other highly saline lithium-rich hydrothermal fluids in calcareous aquifers may be present and discovered elsewhere in the world.
Previous publications dealing with hydrochemical properties of deep fluids in the Muschelkalk aquifer of SW-Germany have hardly included trace elements, as for example Li, as the focus was on the major elements for water characterization. However, trace elements may reveal processes concerning the origin and the development of highly saline Li-rich fluids, especially in connection with other trace elements like boron (B) and specific isotopes.
A lime-/dolostone reservoir is expected to lack major lithium in rock forming minerals to develop a Li-rich fluid in equilibrium with its host rock. Typically, lithium-containing rock forming minerals like spodumene, petalite, or lepidolite occur in pegmatites, whereas in granites lithium-containing rock forming minerals are rather scarce and lithium occurs dispersed in phyllosilicates (e.g., Drüppel et al., 2020). Therefore, an external fluid source is most likely to understand high Li concentrations in the deep thermal water of calcareous aquifers and we will discuss an external versus an internal origin, inter alia, on the base of alteration experiments at high temperatures, i.e., at 200 °C and 260 °C. The different converging flow directions resulting from analysis of individual hydraulic potential measurements in boreholes of the Muschelkalk aquifer are the reason to review geological boundary conditions, in order to better understand the features of the groundwater contour map (hydraulic potential). In this study, we have compiled yet uncombined geological, hydraulic, hydrochemical, isotopic, and stress field data, to better understand origin and development of these brines.
Material and methods
Muschelkalk aquifer data
Hydraulic well tests provide among others, like static hydraulic potential or static water level, water samples and thus provide key information concerning hydrochemical analyses and isotope studies. Several authors compiled c. one hundred hydraulic and hydrochemical data of the deep Muschelkalk aquifer in the subsurface of the Molasse basin of SW-Germany. These were derived from deep wells in the depth range from several hundred meters to 3500 m. The hydraulic and hydrochemical data of water samples used in this paper are published data from archives (Carlé 1975; Bertleff 1988; Stober and Villinger 1997; Franz et al. 2001; Grimm et al. 2005; Schloz and Stober 2006; Stober and Jodocy 2011; Stober et al. 2013; Stober 2013, 2014). A large number of the reservoir data are from production tests performed by the hydrocarbon industry in the 1970–1990s. In some wells, from the same stratigraphic formation, several hydraulic tests and hydrochemical analyses exist. The original, tested and sampled boreholes are closed, so re-sampling is not possible, except for only few boreholes in the investigation area, e.g., the thermal spa in Tuttlingen or the Pfullendorf geothermal wells (Fig. 1). As hydrochemical analyses were carried out by different laboratories although the hydrochemical data were quality controlled and tested for internal plausibility by the aforementioned authors inter-laboratory bias needs to be taken into account. The overall quality of the data, i.e., 33 hydrochemical analyses of different boreholes, is difficult to assess and should not be overvalued. Nevertheless, the data are considered useful for a future, more detailed exploration work for the development of geothermal projects (in combination with lithium extraction), thermal spas, and other projects.
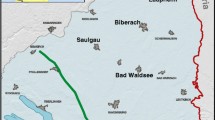
Left: location of the Molasse Basin in SW-Germany in the State Baden-Württemberg (light blue area). The figure shows the location of the Permocarboniferous (Uppermost Carboniferous to mid Permian) North Swiss (or northern Helvetian) and Upper Swabian troughs in the crystalline basement (Rupf and Nitsch 2008) and the so-called Aulendorf swell in between. The ‘blue dotted line’ marks the SE-ward pinch-out of the Buntsandstein Group below the Muschelkalk Group, hence SE of that line—except for the limited areas of the Upper Permocarboniferous troughs—the Muschelkalk Group directly overlies the crystalline basement. Right: schematic stratigraphic column of the main ‘formations’ in the deeper part of the Molasse Basin (T—Upper Carboniferous/Permian trough)
We used maps showing the temperature distribution and the hydraulic potential, displayed as groundwater contour lines, of the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer and hydrochemical standard diagrams (e.g., Schoeller diagrams; Stober and Villinger 1997; Stober and Jodocy 2011; Stober et al. 2013; Stober 2013, 2014) and re-interpreted these data by considering minor elements (e.g., Li, Br, B) and isotope data of fluids and rocks (e.g., Ufrecht et al. 2020; Grimm et al. 2005; Traber et al. 2002).
Structural geology and neotectonics
A comprehensive study on literature concerning regional and structural geology, neotectonics and seismic activity was carried out, to achieve a better understanding of the hydraulic regime, possible flow paths, and hydrochemistry. We used the geological subsurface database compilation provided by the Geological Survey of the Federal State of Baden-Württemberg (Rupf and Nitsch 2008). The orientation of the principal stress axes of the regional stress field is important to know as well as the orientation of major fault zones and their reactivation potential to generate and sustain potential flow paths.
Alteration experiments and analytics
Two alteration experiments with Upper Muschelkalk limestone were performed for 44 days within a stirred autoclave system at 200 °C and 260 °C in a 2 molal Na-Cl solution (116.9 g kg−1). After the experiments, the fluids were hydrochemically analyzed. Characterization and analysis of the pre- and post-experiment rock samples and thin sections were performed with several analytical and imaging methods. Details are given in the Appendix.
Thermodynamic modeling
We used the code PHREEQC and the LLNL data base (Parkhurst and Appelo 2013) to calculate the saturation state with respect to selected minerals of the fluids in the Muschelkalk aquifer.
Additionally, we used the PHREEQC code to re-calculate the measured pH of the alteration experiments to experiment temperatures, whereas the complete data of measured fluid composition at 25 °C have been used as input. Thus, the pH re-calculation considers the high salinity of the fluid as well as the total carbon in the system (alkalinity). Additionally, we calculated with the same program the saturation state with respect to selected minerals.
Geology of the investigation area
Molasse basin
The seismically active investigation area takes part of the German Molasse basin, in the federal state of Baden-Württemberg (Fig. 1). The geomorphologically distinctly exposed Upper Jurassic Subgroup of the Swabian Alb forms the northwestern boundary (Fig. 1). The eastern boundary of the investigation area follows the river Iller, which forms along major parts the border between the federal states of Baden-Württemberg and Bavaria, and the southwestern boundary is linked to the Bodensee (Lake Constance), which includes the border to Switzerland (Fig. 1).
The Molasse basin is the type locality of an orogenic foreland basin that has evolved from sedimentary underfilling (“Flysch stadium”) via sedimentary overfilling (“Molasse stadium”) to the recent “uplift and erosional stadium” due to isostatic re-adjustment of the European lithosphere (e.g., Przybycin et al. 2015). The upper Cretaceous to Eocene turbiditic Flysch units occur close to the orogenic front, but not in the subsurface of the investigation area (e.g., Trautwein et al. 2001). The early Oligocene to late Miocene Molasse stadium formed during flexure of the European plate under the weight of the northward advancing orogenic wedge of the Alps. The total Molasse basin has a length of about 1000 km and stretches from eastern France in the SW via northwestern Switzerland, southern Germany, and northern Austria to the E. The width of this basin increases up to 130 km in the Bavarian Molasse basin. The siliciclastic marly-shaly basin fill is subdivided into Lower Marine Molasse (UMM), Lower Freshwater Molasse (USM), Upper Marine Molasse (OMM), and Upper Freshwater Molasse (OMM) (Fig. 1) (e.g., Geyer and Gwinner 2011). Sediments were transported predominantly by alluvial and delta fans from the Alpine front into the basin. The early Oligocene Lower Marine Molasse consists of shallow marine sand, clay and marl, followed by the late Oligocene to early Miocene Lower Freshwater Molasse with fluviatile sediments due to Chattian regression. The early Miocene Upper Marine Molasse, deposited during Burdigalian transgression, consists of shales and glauconite sands. The fluviatile sediments of the middle-to-late Miocene Upper Freshwater Molasse intercalate with the 14–9 Ma volcanic and volcaniclastic rocks in the Hegau area (Schreiner 1992; Binder et al. 2022). Middle-to-early Miocene regional uplift and erosion affected SW-Germany and consequently parts of the Molasse basin fill have been eroded (Bachmann et al. 1987; Bertleff et al. 1988; Geyer and Gwinner 2011; Stober 2014; Hoffmann, 2017; Schreiner 1992). Gravitational forces may equal or exceed subhorizontal compressional forces exerted by Alpine convergence and hence strike-slip to normal faulting prevails in major parts of the Molasse basin (Reinecker et al. 2010; Przybycin et al. 2015; Warnecke and Aigner 2018).
SE plunging Upper Jurassic rocks, well exposed in the Swabian Alb, plunge beneath the Molasse sediments and comprise the subcrop of the Molasse basin in the investigation area. Triassic sequences below Jurassic successions onlap toward (E)SE onto both the crystalline basement of the Vindelician High and WSW–ENE trending Permocarboniferous troughs (Fig. 1). This study focuses on the Middle Triassic Muschelkalk Group, exposed along the eastern Black Forest margin, plunging ESE beneath the Keuper and Jura Groups reaching a depth of more than 3 km at the Alpine frontal thrust in the area of the Austrian–German border (Bertleff 1988; Jodocy and Stober 2009a, b). The Lower Triassic Buntsandstein Group is missing for most parts in the investigation area. Only in the utmost northwest part of the area few tens of meters of the Buntsandstein Group are present (Rupf and Nitsch 2008) (Fig. 1).
The crystalline basement underlies the Muschelkalk Group directly in most parts of the investigation area except for the eastern and southwestern parts where two SW–NE striking Permocarboniferous troughs, separated by the Aulendorf swell, occur (Rupf and Nitsch 2008) (Fig. 1).
During the Quaternary glaciation phases massive glaciers covered the Molasse basin, reaching a thickness of up to 1000 m near the orogenic front of the Alps, thus causing varying subsidence and uplift of the Alpine foreland during glacial and interglacial periods due to changing glacial load (Schreiner 1992). Glacial erosion generated the over-deepened Bodensee basin and the geomorphologically distinct Schussen valley, while relic moraine deposits are preserved in the Alpine foreland (Schreiner 1992; Beckenbach et al. 2014).
The investigation area is seismically active, but in contrast to the either structurally or geomorphologically well-defined NW-trending Bonndorf-Bodensee graben (Diehl et al. 2022), the N-trending Albstadt shear zone (Mader et al. 2021), and the NNE-trending Alpenrhein graben (Ring and Gerdes 2016) seismicity appears to be rather diffusively distributed. The geomorphologically distinct NNE-trending Schussen valley (Fig. 2) is documented to be of glacial origin (Beckenbach et al. 2014), though some distinct NNE-trending linear features may be related with neotectonic deformation and both the Schussen valley and the Bodensee basin may be structurally controlled. The continuation south of the Bodensee is the seismically active St. Gallen fault zone, which was targeted by a c. 4.25-km-deep geothermal well, which intersected Upper Jurassic rocks at c. 3.8–4.2 km depth, but did not enter the Muschelkalk Group, which is expected to occur deeper (Heuberger et al. 2016).
Stratigraphy, thickness, and facies distributions of the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer in SW-Germany
The deep Muschelkalk aquifer of the Molasse basin comprises a geothermal play type of the Orogenic Belt Type (Möck 2014), stratigraphically controlled by fault-/fracture-permeability. Current geothermal utilization of fluids from the Muschelkalk aquifer, yet solely for heating projects of buildings and greenhouses, is under operation in Pfullendorf (in Germany) and Schlattingen (in Switzerland).
The chronostratigraphic equivalent of the Upper Muschelkalk (Germanic Triassic) is part of the Anis/Ladin of the Alpine Triassic and comprises a 3.8 Myr lasting time interval between 243.3 and 239.5 Ma (timescale of STD 2016 revised by Hagdorn et al. 2019 and Menning 2020). In Switzerland the upper boundary of the Muschelkalk (Schinznach Formation) is defined at a higher level, including the Asp Member, which is equivalent to the Lower Keuper (Erfurt Formation) in Germany (Hagdorn et al. 2019). However, in major parts of SW-Germany “the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer” is hydraulically interconnected with lower parts of the Lower Keuper and upper parts of the Middle Muschelkalk.
The deep Upper Muschelkalk aquifer in the investigation area is a partly fractured and karstified carbonate rock aquifer (Stober et al. 2012), with dolomites preferentially in its upper part and limestones below. Farther to the south dolomites are dominating, i.e., in SE-direction with increasing depth the dolomite-fraction of the Upper Muschelkalk limestone is increasing. Depending on the permeability of the underlying (Middle Muschelkalk) and overburden (Keuper Group, Middle-Upper Triassic) the overall thickness of this aquifer can gain several meters (Hagdorn and Simon 2005). Generally, the thickness of the Muschelkalk Group—and thus also the thickness of the Upper Muschelkalk Subgroup—is decreasing in the investigation area in ESE-direction. While in the western part, the thickness of the Upper Muschelkalk is about 75 m it is dwindling away in the east-southeast of the investigation area (Stober and Villinger 1997). The Middle Muschelkalk Subgroup is dominated by a layered sequence of anhydrite with anhydrite-bearing clays, claystones, few dolomitic marls, and a few thin carbonate- and dolomite-bearing layers (Naef 2008). Rock salt (halite) does not occur in the investigation area, but much further to the W (Hansch and Simon 2003; Bock et al. 2009). In the southern and eastern investigation area the anhydrite-clay layers grade into anhydrite-containing sandstone layers with decreasing thicknesses and completely pinch-out further to the E (Geyer and Gwinner 2011; LGRB 2015). The Lower Muschelkalk in the western Bodensee area and in the north-western investigation area consists of a few meters of clay with thin dolomitic sandstones below (‘Basissand’).
However, thickness and facies of the Muschelkalk Group change significantly from basin to basin’s margin and toward the Vindelician High, a former crystalline basement land surface, i.e., in ESE direction. Near the basin margin the Muschelkalk Group consists mainly of clastic feldspar-rich sediments, quartz-sandstones, partly carbonate and partly siliceous cemented (Grafenwöhr- and Eschenbach-Formation). These sand deposits were transported from the Vindelician land surface and are significantly coarser grained near the basin’s margin. In the Lower Muschelkalk sand-rich deposits are already documented in the area of Überlingen, whereas in the Middle and Upper Muschelkalk, this facies change occurs farther in the ESE. However, the transition zone is not in detail documented due to lack of boreholes (Geyer and Gwinner 2011; Warnecke and Aigner 2018; Warnecke 2019) but is assumed to be about 25 km S of the borehole Neu-Ulm. This deep borehole still showed the Middle Muschelkalk Subgroup in the facies development of the ‘Heilbronn Formation’, i.e., 15-m-thick sediments of anhydrite and clay successions (Franz et al. 2001), separating hydraulically the Upper Muschelkalk from the Lower Muschelkalk. In contrast to the western and north-western part, with very low conductivity layers (Heilbronn Formation) between the Upper Muschelkalk and Lower Muschelkalk, in the southern and south-eastern part of the investigation area this hydraulic barrier disappears with the facies change and pinch-out of the clay-anhydrite bearing Heilbronn Formation towards S and SE.
Noteworthy that in most parts of the investigation area the Muschelkalk Group is the oldest Triassic sedimentary deposit overlaying either directly crystalline basement rocks or Permocarboniferous troughs (Fig. 1).
Groundwater storage and flow in the Upper Muschelkalk occurs mainly along fracture and bedding planes, often enlarged in carbonate rocks due to karstification processes. All drill cores or cutting material of the deep wells showed at least some small karstification processes in carbonate rocks (Stober et al. 2012). The aforementioned tectonic stress field together with the manifold vertical displacement history has most likely caused an increase of fractures and of reactivated faults. In consequence, the hydraulic conductivity of the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer is only slightly decreasing with depth, i.e., to the SE, varying between 5·10–7 m s−1 and 10–9 m s−1 (Stober and Jodocy 2011; Stober 2013).
Results
Recent publications focused as yet on specialized topics and methods, but a synoptic concept for the origin of these highly saline Li-rich brines in the deep Muschelkalk aquifer is missing so far. Within this section, we have re-interpreted published data and assessed new findings and data partly with hydrochemical and isotopic investigation methods and a new hydrogeological flow mechanism for a regional conceptual model on the origin and the development of these highly saline Li-rich brines.
Compilation of new results on the hydrogeology of the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer
First, it is noteworthy to emphasize that the hydraulic potential of the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer is decoupled from that of the Upper Jurassic aquifer lacking hydraulic interaction between these two calcareous aquifers (Stober 2013, 2014). The hydraulic potential, presented as groundwater contour lines, of the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer is shown in Fig. 2. Details to the construction are provided in Stober and Villinger (1997) and in Stober (2013). The hydraulic potential shows trilateral recharge, i.e., from east, south and west, into a central area, between Konstanz and Saulgau. North of Saulgau the contour lines indicate northward oriented discharge out of this central area, which further to the north, bends into a NW-trend toward the Stuttgart—Bad Cannstatt area where natural discharge occurs in artesian springs (e.g., Ufrecht 2018, Uffrecht et al. 2020). Additionally, the hydraulic gradient in the western part is larger than in the south-eastern part of the investigation area. Thus, in consideration of hydraulic conductivity, the western recharge rates into the central area (Konstanz—N of Saulgau) are most probably higher than the recharge rates from south-eastern directions. The lowest hydraulic gradient can be found in the northwards oriented central area, where the hydraulic potential is forming a depression zone, based on the contour lines. The configuration of the contour lines leads to the conclusion, that either the hydraulic conductivity of the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer in this area is very high (e.g., presence of a high conductive fault zone) or additional layers below the Upper Muschelkalk (e.g., Middle Muschelkalk) accommodate major amounts of the incoming recharge. However, no high conductive or permeable, north-east to north oriented single fault zone in the Upper Muschelkalk is documented so far (see Sect. ‘Structural geology and neotectonics’ ). In contrast, the southern and south-eastern groundwater inflows into this ‘depression or central zone’ derive most probably from the entire Muschelkalk Group, consisting mainly of clastic sandstones, but this has not yet been investigated until today.
Temperature in Upper Muschelkalk aquifer generally increases with increasing depth, i.e., in SE-direction due to the SE-plunging of the aquifer. Most of the aquifer temperatures in the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer are elevated with respect to a geothermal reference gradient of 30 K km−1 and geothermal gradients of about 45 K km−1 are common. Locally gradients up to 60 K km−1 and more are measured (Stober 2014). The highest gradients follow a ‘line’ from southeast to northwest: W of Bad Waldsee–Saulgau to E of Sigmaringen (Fig. 3).
Generally, there are several reasons causing increased geothermal gradients, such as upwelling deep waters, low vertical thermal conductive layers, or volcanic activity. The SiO2-geothermometer of Walther and Helgeson (1977) shows that quartz-saturation reservoir temperatures were significantly higher than the measured aquifer temperatures (Stober 2014). Thus, with respect to the local geological conditions, fluids with higher temperatures are most likely upwelling from deeper parts and transported to NW due to groundwater flow (Figs. 2, 3), for which the flow velocity is apparently fast enough and/or flow rate large enough to sustain elevated disequilibria SiO2-concentrations.
Structural geology and neotectonics
Borehole breakout and drilling induced tensile fracture orientations in deep boreholes were used to constrain the regional stress field (Reinecker et al. 2010). In the study area maximum horizontal stress axes (SH) trend N–S to NNW–SSE (Fig. 4). Since the Molasse basin is not in isostatic equilibrium (Przybycin et al. 2015) stress field is not compressive, but characterized by strike-slip to normal faulting as indicated by stress data and fault plane solution (FPS) (Reinecker et al. 2010; Heidbach and Reinecker 2012; Ibele 2015; Heidbach et al. 2016).
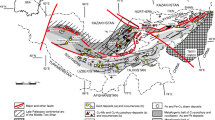
Digital Elevation Model (NASA 2019) showing geomorphic features of the Lake Bodensee basin. Depression areas are shown in darker color (black: < 395 m a.s.l). Elevated areas occur in lighter colors (white: > 1000 m a.s.l.). Recent stress data from the World Stress Map (Heidbach et al. 2016) showing orientation of SH (in red), derived from fault plane solutions, drilling induced tensile fractures, and borehole breakouts. Historically and instrumentally recorded earthquake locations (in yellow) (ref. Earthquake-catalogue). Major fault zones (in violet)
Regionally important structures in SW-Germany are seismically active and comprise the Bonndorf-Bodensee zone, the N striking Albstadt shear zone, the NNE-striking St. Gallen fault zone, and the NNE-striking Alpenrhein graben (e.g., Ibele 2011; Geyer and Gwinner 2011; Reinecker et al. 2010; Egli et al. 2017; Ring and Gerdes 2016; Heuberger et al. 2016; Ring and Bolhar 2020; Mader et al. 2021).
The NE-striking Pfullendorf-Saulgau and the Fronhofen-Aulendorf faults are apparently seismically not active. Fault plane solutions close to the Pfullendorf-Saulgau fault indicate NW- to N-trending p-axes and strike-slip and normal faulting, likely not related with these NE-striking faults. Several hydrocarbon wells were drilled into Cenozoic and Mesozoic reservoir rocks along the NE-trending Fronhofen-Aulendorf fault. Apparently scattered seismicity occurs in the study area and could not yet be assigned to particular structures (Fig. 4).
The as yet only seismically documented Albstadt shear zone (ASZ) is a c. 4–5 km wide, and some 10 km long N–S-striking complex crustal-scale deformation zone (Mader et al. 2021; Reinecker et al. 2010; Reinecker and Schneider 2002) displaying no obvious surface displacements except for the NW-striking Hohenzollern Graben and the NNE-striking Lauchert Graben (Geyer and Gwinner 2011). The Lauchert Graben, about 20 km west of the Albstadt shear zone, is visible in the Swabian Alb; however, a possible southern continuation below the Tertiary sediments of the Molasse Basin is as yet unknown. Fault plane solutions in the ASZ indicate complex interactions of NW- to NNE-striking faults (Mader et al. 2021). Albstadt shear zone related seismic activity cannot be documented S of the area of the Danube River (Mader et al. 2021).
The seismically active St. Gallen fault zone (SGFZ) was target of a geothermal well and therefore relatively well studied by several 2D-seismic lines and one 270 km2 large 3D-seismic survey (e.g., Heuberger et al. 2016). The SGFZ comprises several normal faults rooting in the crystalline basement that were active during Permo-Triassic-Jurassic times and during deposition of the older Tertiary Molasse successions. These faults have been reactivated as sinistral strike-slip faults in recent times (Heuberger et al. 2016; Diehl et al. 2017). Stratigraphic situation in northern Switzerland is similar: Muschelkalk Group overlies either crystalline basement or a Permocarboniferous trough. To the N the SGFZ bends to the NW; a kinematic connection with the Bonndorf-Bodensee graben may exist, but is not clearly worked out in detail. The NNE-trending Roggwil fault and the SGFZ form the Unterlören Graben immediately south of the Bodensee (Heuberger et al. 2016). The SGFZ in its northern parts is characterized by fault linkages and relay ramps connecting fault segments (Heuberger et al. 2016). The NNE-trending Mörschwil and Roggwil faults most likely continue beneath the Bodensee, according to fault plane solutions, as NNE-trending strike-slip fault(s) (Ibele 2015; Heuberger et al. 2016; Fabbri et al. 2021).
Yet there are several 2D-seismic lines and hydrocarbon wells, arranged in NE-SW and NW-SE grids, mainly identified the NE-striking Pfullendorf-Saulgau and the Fronhofen-Aulendorf faults (Fig. 4) that are interpreted as normal faults resulting from flexural bending of the European plate during the Oligocene (Geyer and Gwinner 2011; Bachmann and Müller 1992). If strike-slip faults were present, they may be underestimated by these 2D-seismic lines as apparent displacements may commonly be interpreted as normal fault displacements in tilted Mesozoic rock successions, not affecting the Molasse basin successions (Jodocy and Stober 2009a, b). Few subvertical structures have affected the younger Molasse basin successions and were, inspired from the Hegau volcanic area to the W, interpreted as Miocene dykes or plugs (Jodocy and Stober 2009a, b), though volcanism east of the Hegau area could not yet be documented from surface exposures.
The broad Schussen valley associated with the very small Schussen river (Figs. 2 and 3) is a geomorphologically distinct NNE-trending feature (Fig. 4), recognizable as a lowland trending from the Bodensee in northern direction. Some N- to NNE-striking fault segments are considered for the Schussen valley between Friedrichshafen-Tettnang and Ravensburg (Ibele 2015; Ring and Gerdes 2016; Heuberger et al. 2016). A structural control of the Schussen valley is likely, but not yet documented or established in the published geological maps. The Schussen valley originated during melting of glaciers of the past two glaciation phases (Beckenbach et al. 2014), that possibly eroded any neotectonic evidence. The clearly visible NNE-trending lineaments might be of glacial origin, at least they are found in c. 1 Myr old Pleistocene ‘Deckenschotter’ (personal communication: T. Simon 2022). However, in the seismic 2D-section QD-2a near the borehole Gaisbeuren 1 (Jodocy and Stober 2009a, b) a fault segment is visible, which may be associated with the Schussen valley. South of the Urach volcanic area the Burdigalian kliff was offset sinistrally by N-to NNE-striking faults and N- to NNE-trending lineaments occur frequently there (Illies 1978; Ufrecht 2018). In summary, there are a lot of indications for N–S trending faults and fractures, but a major single fault zone could not yet be identified and deformation appears to be rather distributed than localized. Structural and neotectonic observations suggest for the central part of the investigation area permeable N–S oriented dilational structures that can be reactivated or sustained in the regional stress field to enable northward fluid flow.
Hydrochemical properties of the deep Upper Muschelkalk aquifer with focus on lithium concentration
The total dissolved solids (TDS) in the Upper Muschelkalk fluids are much larger than those found in the Upper Jurassic fluids, which often show drinking water quality down to depths of 1200 m below surface. Contrarily, in the Upper Muschelkalk TDS reaches already in 1300 m depth about 10 g kg−1 and in the 2000 m depth about 65 g kg−1. The highest TDS-values of 75 g kg−1 are found in a borehole at 2500 m depth (Fig. 2), showing much higher salinity than seawater (35 g kg−1). TDS-values of the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer are correlated to depth, with an increase of TDS in southern and southeastern direction in accordance with the SE plunging of the Muschelkalk (Fig. 2). Corresponding to the increase in TDS, other constituents in the deep waters also increase (Stober 2014). Additionally, water type changes: the composition of fluids at shallow depth (< 900 m) with low TDS is strongly controlled by the minerals of the reservoir rock, corresponding to Ca-SO4-HCO3 waters: fractured, karstified limestone, with thin marly clay layers and dolomite, containing sulfate-rich strata underneath the aquifer, rarely within the aquifer. Contrarily, the deeper fluids develop to a Na-Cl-type, independent of the aquifer rock type. Chloride-concentration is increasing in SSE-direction (Stober et al. 2013), reaching values > 40 g kg−1 in the area south of Ravensburg. For comparison Cl concentration of seawater is much lower (Cl ~ 19.4 g kg−1). However, data in Stober (2014) and in Stober et al. (2013) indicate that at about 1300–1500 m depth TDS and Cl are not further increasing in deeper wells, but are remaining more or less constant, leading to the assumption that these waters belong to a uniform reservoir, possibly connected to crystalline basement rocks (Fig. 5).
TDS (a) and Cl (b) concentrations versus depth (data: Stober 2014). The TDS and Cl increase with depth is reaching a limit in about 1300–1500 m depth
Magnesium (Mg) in the fluids of the Upper Muschelkalk is rising with increasing calcium (Ca); no recent dolomitization should occur, because during dolomitization dissolution of the precursor mineral calcite will supply the much-needed Ca wherein Mg (and CO3) is supplied by the dolomitizing fluid (e.g., Merino and Canals 2011). While calcium is increasing, HCO3 is decreasing. Stober (2014) analyzed the temperature and salinity effect on the calcium–carbon ratio (Ca/C) by using the computer program PHREEQC (Parkhurst and Appelo 2013). The results showed that the Ca/C ratio rises with both, increasing NaCl-concentration and/or increasing temperature. So, the observed increase in Ca and decrease in HCO3 in deeper, hotter, and saline-richer fluids of the Muschelkalk aquifer is most probably caused by increasing salinity and temperature.
All deep waters in the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer are saturated with respect to calcite and quartz, more or less saturated with respect to gypsum and anhydrite and slightly oversaturated with respect to dolomite. For barite most waters in the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer seem to be slightly oversaturated, thus having a certain scaling formation potential if pumped and utilized in geothermal energy applications.
To get information concerning the origin of salinity of the Muschelkalk water in the investigation area we had a look at the Cl/Br ratio (mass ratio) and the molal Na/Cl ratio, in addition to previous work by Stober (2014). Unfortunately, bromide (Br) was not often analyzed routinely, thus Cl/Br ratio data are scarce. Additionally, Br-data from the hydrocarbon wells should not be overvalued, especially at very low concentrations (< 1 mg kg−1). The Cl/Br-values of the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer in the investigation area are in the order of Cl/Br = 300 showing more or less modern seawater signature (Cl/Br = 288), but definitely no halite signature (Cl/Br > 2000). Na/Cl-ratios illustrate, that waters with lower concentration (Cl < 800 mmol (eq) kg−1), in the northern part predominantly outside our investigation area, follow exclusively the halite dissolution line (Na/Cl = 1), whereas waters with higher TDS, i.e., in the investigation area, do not show a halite signature (Na/Cl = 1).
In some thermal waters of the deep boreholes boron (B) was measured (see data in Stober 2014). It is interesting to note, that the Cl/B ratios (mass ratio) are decreasing in SE direction of the investigation area. High Cl/B ratios, typically in the order of Cl/B > 1200, can be found for example in the geothermal wells Pfullendorf and Saulgau, whereas lower ones were observed in deeper hydrocarbon bores in the SE part of the investigation area, where higher boron concentrations occur as well (B > 110 mg kg−1). In only 5 hydrochemical analyses both parameters, Li and B, were measured, indicating a positive correlation.
Lithium concentration in the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer is high, especially in the southern part of the investigation area, where concentrations up to 162 mg kg−1 were measured (Fig. 6). In accordance with the flow direction in the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer in the central area, between Konstanz and Saulgau, lithium seems to be transported towards north and concentrations of Li, TDS, and Cl decrease due to dilution (Figs. 2 and 6). According to Fig. 1, Li concentration in the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer, along the Aulendorf swell, i.e., between the two Permocarboniferous troughs in the crystalline basement, is distinctly higher. Thus, Li concentration is in most cases higher where the Muschelkalk is directly underlain by crystalline basement and where Upper, Middle and Lower Muschelkalk seem to be directly hydraulically connected to form a combined or bulk Muschelkalk aquifer. Li and Cl concentrations in the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer are positively correlated (Fig. 7): lg Cl 0.9238 lg Li + 2.5771 (R2 = 0.97).
Lithium versus chloride concentration in thermal waters of the Upper Muschelkalk and corresponding trendline (red line). Black dotted line corresponds to the trendline for deep thermal water in the URG (Drüppel et al. 2020). Seawater data (Li ~ 0.191 mg kg−1; Cl ~ 19,400 mg kg−1) from Riley and Tongudai (1964)
The correlation is quite similar to the trend we found in the Upper Rhine Graben (URG) for deep thermal waters in the crystalline basement, Permo-Triassic siliciclastic reservoir rocks and Black Forest (Drüppel et al. 2020). Note, modern seawater plots away from the trend, having much lower Li concentrations with respect to Cl (Fig. 7).
Isotope data of the deep Upper Muschelkalk aquifer
Isotope data are available mainly for the outer rim of the working area (Benken, Siblingen, Tuttlingen, and Neu-Ulm). Only water isotope samples had been analyzed for Pfullendorf just within and Fronhofen in the central part of the investigation area (Fig. 8).
Hydrogen versus oxygen isotope diagram showing the meteoric origin of the samples (analytical uncertainty: δ18O: ± 0.15 ‰, δD: ± 1.5 ‰; data sources: Grimm et al. 2005, Ufrecht 2018, Ufrecht et al. 2020 and references therein). GMWL, Global Meteoric Water Line; LMWL, Local Meteoric Water Line of Stuttgart area (Ufrecht et al. 2020)
However, already those limited data allow to constrain some important aspects of the origin and evolution of the fluid. Upper Muschelkalk waters of Benken, Siblingen, and Tuttlingen with low mineralization, without magmatic CO2, low 14CDIC and intermediate δ13CDIC values (Table 1) are part of the recharge from the W (i.e., Wutach valley to Donaueschingen). Those waters are characterized by an intermediate isotope exchange with the carbonate aquifer rock (Ufrecht et al. 2020; Graf et al. 1994) and are different to the Muschelkalk waters in the more central part of the Molasse Basin (Fig. 8). The latter are characterized—according to the former interpretation of e.g., Ufrecht et al. (2020)—by a stronger isotope exchange with the aquifer carbonate due to higher temperature and residence time.
The light isotope composition of fluids from Benken indicates recharge from glacial melt water (see Table 2 as well) at comparably high elevation (Traber et al. 2002). The ‘grey arrows’ in Fig. 8 indicate the previous interpretation, i.e., stronger oxygen isotope exchange with aquifer carbonate at increasingly higher temperatures. However, the aquifer temperatures are below 100 °C and the slope of the line defined by data points from Benken, Pfullendorf and Fronhofen exactly represents an evaporation line trend, i.e., consumed H2O during alteration processes. Table 2 shows that the shallow Ca-SO4 waters are characterized by strontium (Sr) isotope ratios of the Muschelkalk aquifer and the mixed Muschelkalk/Basement water of Neu-Ulm by an already crustal-dominated value and the Na-Cl water of Pfullendorf by typical values for the crystalline basement. This is at first glance rather surprising, because at the base of the Pfullendorf borehole anhydrite-clay of the Heilbronn Formation occurs. However, the thickness of the anhydrite layer is not known, but the underlying Lower Muschelkalk consists of calcareous sands of the Eschbach Formation. According to Fig. 2 the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer in the Pfullendorf area has enhanced TDS. TDS is spreading from the SE (Fig. 2), maybe from the crystalline basement into the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer, in agreement with the high Sr-isotope ratio (Sanjuan et al. 2016).
The low noble gas (mean of Kr and Xe) infiltration temperatures of the infiltrated meteoric water in the recharge area for Siblingen (4.0 °C), Benken (3.1 °C), and Tuttlingen (2.9 °C) indicates in combination with determinations of the high mean residence time a Pleistocene recharge for those locations (Ufrecht et al. 2020; Tables 1 and 2).
From the crustal air–He mixing trend, defined by the low-mineralized Muschelkalk fluids shown in Fig. 9, a crustal-dominated endmember composition is also indicated for the high-mineralized, deep Muschelkalk fluids in the central part of the investigation area.
Ne/He ratio versus air-normalized He isotopic composition of shallow, low-mineralized Muschelkalk samples Tuttlingen (TDS = 1.1 g kg−1) and Benken (TDS = 2.4 g kg−1). Showing the mixing relations between the different He sources mantle, crust (crystalline basement), air or air-saturated water (ASW). Data source: Traber et al. (2002) and Nagra (2001)
It can be concluded that the lithium had been released by water–rock interaction (WRI) of meteoric water, which infiltrated the underlying basement during Pleistocene times, based on: (i) the light water isotope composition of Benken and related evaporation line caused by water–rock interaction (Fig. 8); (ii) the low noble gas infiltration temperatures of Siblingen, Benken, and Tuttlingen (Table 2); and (iii) the high Sr isotope signature of Pfullendorf (Table 2).
Results of the high-temperature alteration experiments with limestone of the Upper Muschelkalk
Alteration experiments were performed with limestone of the lower part of the Upper Muschelkalk, containing small shell fragments and are in detail described in the Appendix. Table 3 shows the whole rock composition. Main elements are CaO with over 60 w.%. The sample contains additionally SiO2 and MgO, both more than 3 w.%. Small amounts of Al2O3 and Fe2O3 (< 1 w.%) could be detected as well. Ignition loss is about 42 w.%, corresponding to the high percentage of calcite. Main trace elements (Table 3) are Ba and Sr. XRD investigations showed a practically pure limestone consisting of calcite, dolomite, and quartz (Stober et al. 2018).
After the two alteration experiments with the prepared NaCl solution at 200 °C and 260 °C, both morphology/color of the samples and fluids composition changed. Surface material of both altered samples (200 °C and 260 °C experiment) showed mainly calcite, sparsely any dolomite and halite (due to the NaCl solution). Investigations on the 260 °C sample revealed the formation of new calcite crystals at the sample’s surface. Additionally, we found Na–Mg–Al–Si minerals (maybe Na-saponite). The main effect of the alteration process is a dissolution–precipitation process of limestone to calcite and to traces of dolomite (Stober et al. 2018).
Table 4 shows the analytical results of the two high temperature alteration solutions and of the initial solution for comparison reasons. The initial solution already contained traces of Li. After the two high-temperature alteration experiments no significant changes in Li concentration of the fluids resulted. Thus, the rock sample and potentially fluid inclusions probably does not contain Li, which could be leached even by extremely high temperatures (200 °C, 260 °C). The geochemical/mineralogical investigations revealed neither lithium-bearing minerals in the rock before nor after the experiments. Furthermore, no lithium could be detected in the solution due to the alteration experiments. Therefore, we conclude the high lithium concentrations in the thermal water of the Muschelkalk aquifer are in all likelihood of external origin. Further details are described in detail in the Appendix.
Discussion
The Muschelkalk is in most parts of the investigation area the oldest Triassic deposit overlaying directly crystalline basement rocks (or Permocarboniferous troughs, Fig. 1). The hydraulic potential of the Muschelkalk aquifer shows three different flow directions, i.e., inflows from west, south-east, and south into a central area, where the flow direction is northward oriented toward Stuttgart–Bad Cannstadt (Fig. 2). Thus, in the central area an enhanced permeability is most probably necessary to carry these discharges in northern direction. Due to the structural and neotectonic investigations and the orientation of SH it seems likely, or at least it cannot be excluded, that in the central part of the investigation area N–S oriented dilational fractures are present (Fig. 4) making this northern oriented flow possible. However, enhanced fracture permeability—if present—should be preferentially restricted to the Upper Muschelkalk, especially because of the huge potential differences between the Upper Muschelkalk and the Upper Jurassic aquifer and the strong difference in hydrochemistry of both aquifers.
The southern and especially southeastern inflow into the central investigation area show significantly enhanced temperatures, i.e., enhanced temperature gradients (Fig. 3), and carry highly saline thermal waters (TDS) (Fig. 2) in combination with high lithium concentrations (Fig. 6). The main transport direction is along the so-called Aulendorf swell, i.e., between the two Permocarboniferous troughs (Fig. 1).
Thickness and facies of the total Muschelkalk change dramatically approaching the basin’s margin toward the Vindelician High, a former crystalline basement land surface, in the south and southeast of the investigation area (Fig. 10). Near the basin’s margin the Muschelkalk Group consists mainly of sand-rich sediments (Grafenwöhr- and Eschbach-Formation) mainly from the Vindelician High. In contrast to the western and north-western part, with very low hydraulic conductivity layers (Heilbronn Formation) between the Upper and Lower Muschelkalk Subgroups, in the southern and south-eastern part of the investigation area the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer is expected to interact hydraulically with the Middle and Lower Muschelkalk via these clastic sediments, as result of the facies changes and pinch-put of the Heilbronn Formation (Fig. 10). Thus, in the SE-part of the investigation area only one continuous aquifer exists, the Muschelkalk aquifer. We further assume interaction with altered crystalline basement rocks of the Vindelician High and upwelling of basement waters into the clastic sediments of the Muschelkalk Group. This concept model is supported by thermal waters in the deep Muschelkalk with nearly constant TDS and Cl concentrations for depths greater than 1300–1500 m (Fig. 5), i.e., these waters belong to an uniform reservoir, most likely upwelling waters from crystalline basement rocks, as supported by our hydrochemical and isotopic investigations, and as summarized in detail below.
Conceptual model of the intrusion of thermal waters from crystalline basement rocks preferentially into the marginal Muschelkalk Group (Eschbach- and Grafenwöhr-Formation) near the basin’s margin at the Vindelician High (schematic geological map, after Geyer and Gwinner 2011). In the NW-part of the investigation area the Heilbronn Formation separates the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer from the Lower, while in the SE due to the pinch-out of the Heilbronn Formation and facies changes a combined aquifer exists. Abbreviations: mo—Upper Muschelkalk, mm—Middle Muschelkalk, mu—Lower Muschelkalk
Both, the Cl/Br ratio (mass ratio) and the molal Na/Cl ratio of these highly saline thermal waters definitively do not show halite signature. The salinity in the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer might be caused by upwelling of saline waters. ‘Upwelling’ is deduced by enhanced temperature gradients (Fig. 3) and geothermometry. In the SE part of the investigation area (Friedrichshafen—E of Saulgau—S of Ulm) due to WRI altered and up-concentrated water most probably infiltrates from the underlying crystalline basement into the Muschelkalk. The assumption is further supported by the investigations concerning B and Li concentrations in these brines and by isotope investigations. Boron and B/Cl are increasing in SE direction. An important source of boron are granitic rocks, in which boron occurs in minerals like tourmaline or other mineral phases, as boron can be incorporated in different ways in rock-forming minerals, like muscovite, biotite, plagioclase (e.g., Saurer and Troll 1990; Barth 2000). These minerals are typically found in granitic rocks. Thus, the occurrence and local distribution of boron in the fluids of the Muschelkalk aquifer is also an indication of brines released from the crystalline basement from (S)SE-direction. Furthermore, boron seems to be increasing with Li. Additionally, there is evidence from different isotope systems (especially 87Sr/86Sr ratio, Table 2), that a strong component of the fluids found in the Muschelkalk aquifer originates from the crystalline basement. A comprehensive literature study concerning lithium in sedimentary and crystalline rocks was carried out, to get a better understanding of the potential source rocks of the Li released via alteration (WRI) into the fluids (e.g., Drüppel et al. 2020; Goldberg et al. 2022). In the high-temperature alteration experiments, we could not detect any Li concentrations in the solution released from rock samples of the Upper Muschelkalk despite the high temperatures (200 °C, 260 °C) and long duration of the experiments. Thus, the high Li (and Cl) concentrations in the brines of the deep Muschelkalk aquifer are externally derived, i.e., from the crystalline basement.
Drüppel et al. (2020) found that phyllosilicates are the main source for lithium in the granites (mainly muscovite and biotite/chlorite) and monzonites (mainly biotite and chlorite). They also found that enhanced concentrations of Li are in fluid inclusion-rich quartz, confirming mobility of Li during alteration. These data suggested that Li mainly remains in the leaching fluid and is not efficiently removed from the fluid during precipitation of secondary alteration phases. The relatively high Li and Cl concentrations in natural deep crystalline basement fluids, e.g., in the nearby Upper Rhine Graben with TDS much higher than seawater, indicate that ‘H2O-consuming’ reaction processes took place (e.g., formation of zeolites) and passively increased the TDS, providing a process for the enrichment of Li and Cl in more or less pH-neutral geothermal waters (Stober and Bucher 1999, 2004). Additionally, Drüppel et al. (2020) found that Mg phases fractionate Mg over Li, leading to an accumulation of Li in the fluid over time. Moreover, these mineral reactions bind free H2O into silicate structures, increasing passively the Cl and Li concentrations in the remaining fluid. Furthermore, in deep crystalline basement fluids there is a positive correlation between Li and Cl (Drüppel et al. 2020), which is quite similar to the trend in the deep Muschelkalk aquifer (Fig. 7), supporting as well our statement that in the southern and southeastern part of the investigation area deep crystalline basement fluids are upwelling and infiltrating into the deep Muschelkalk aquifer (Fig. 10).
Conclusion
The significance of our study is that for the first time it was possible to explain the particular flow pattern of the Muschelkalk aquifer and to draw conclusions about the genesis and origin of the high TDS of the deep thermal waters with their high Li concentrations.
We have combined and newly interpreted geological, hydraulic, hydrochemical, isotopic, thermal, and stress field data of the Triassic Muschelkalk aquifer in the Molasse basin of SW-Germany for a spatial synopsis. Low-gradient groundwater flow in the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer is to the north, enabled by the regional recharge from west, southwest, south, and southeast, leading to a very specific flow field pattern. The north–south-trending maximum horizontal stress orientation might provide fracture permeability in the carbonates of the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer. High lithium concentrations of up to 162 mg kg−1 in highly saline hydrothermal fluids occur in the deep saline-rich Muschelkalk aquifer close to the Vindelician High, a former crystalline basement land surface. Towards north lithium concentrations and TDS become diluted.
Both trace elements and isotope data were used to get information on the origin and development of the highly saline, lithium-rich fluids in the Muschelkalk aquifer. Investigations on and with carbonate rocks (alteration experiments) do not support an intra-reservoir, but rather an extra-reservoir origin of the lithium-rich fluids. Towards southeast the Muschelkalk Group thins out, thereby becoming increasingly sand-rich, when approaching the Vindelician High. The highly saline, lithium-rich brines (Cl < 44 g kg−1, Li ≤ 162 mg kg−1) originate from crystalline basement rocks, in which they formed due to fluid–rock interaction, whereas the sand-rich facies of the Muschelkalk Group enables inflow from the crystalline basement into the Muschelkalk.
The presented conceptual model (Fig. 10) has also implications for explaining high Li concentrations of fluids not only in the deep Muschelkalk aquifer of SW-Germany, but also at other sites like Balmatt with the > 3000 m deep limestone aquifer of the Campine basin, Belgium (Iannotta and Hehn 2022; Bos et al. 2018) or it may also apply for the Styrian Basin (Fürstenberg Subbasin) of SE Austria, where a Devonian carbonate aquifer directly overlies the crystalline basement (Goldbrunner 2005). The carbonate aquifer was tapped in 2014 by two wells (Frutura project) with temperatures above 115 °C, salinities of almost 70 g L−1 and Li concentrations of 20 mg L−1 (Haslinger et al. 2016). Hence there may be future potential for the discovery of lithium-rich fluids in calcareous aquifers elsewhere in the world.
Availability of data and materials
All research data were presented or cited in this paper, most of which are freely available. The respective studies have been cited accordingly.
Abbreviations
- a.s.l.:
-
Above sea level
- ASZ:
-
Albstadt shear zone
- FPS:
-
Fault plane solution
- SGFZ:
-
St. Gallen fault zone
- SH :
-
Maximum horizontal stress axes
- SI:
-
Saturation index
- TDS:
-
Total dissolved solids
References
Aschwanden L, Adams A, Diamond LW, Mazurek M, Ramseyer K. Reservoir properties of the Middle- and Upper Muschelkalk carbonate aquifer at Schlattingen, NESwitzerland. 12th Swiss Geoscience Meeting Fribourg. 2014.
Bachmann GH, Müller M. Sedimentary and structural evolution of the German Molasse Basin. Eclogae Geol Helv. 1992;85:519–30.
Bachmann GH, Müller M, Weggen K. Evolution of the Molasse Basin (Germany, Switzerland). Tectonophysics. 1987;137:77–92.
Barth SR. Geochemical and boron, oxygen and hydrogen isotopic constraints on the origin of salinity in groundwaters from the crystalline basement of the Alpine Foreland. Appl Geochem. 2000;15:937–52.
Beckenbach E, Müller T, Seyfried H, Simon T. Potential of a high-resolution DTM with large spatial coverage for visualization, identification and interpretation of young (Würmian) glacial geomorphology. Quat Sci J. 2014;63(2):107–29. https://doi.org/10.3285/eg.63.2.01.
Bertleff B, Joachim H, Koziorowski G, Leiber J, Ohmert W, Prestel R, Stober I, Strayle G, Villinger E, Werner J. Ergebnisse der Hydrogeothermiebohrungen in Baden-Württemberg. Jh Geol Landesamt Baden-Württemberg Freiburg. 1988;30:27–116.
Binder T, Marks MAW, Gerdes A, Walter BF, Grimmer J, Beranoagurre A, Wenzel T, Markl G. Two distinct age groups of melilitites, foidites and basanites from the southern Central European Volcanic Province reflect lithospheric heterogeneity. Int J Earth Sci. 2022;112(3):881–905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-022-02278-y.
Bock H, Werner W, Simon T. Die Verbreitung der steinsalzführenden Schichten in Baden-Württemberg—eine Aktualisierung des Wissensstandes. LGRB-Nachrichten Freiburg. 2009;8:1–2.
Bos S, Ben L, Harcouet-Menou V. The Balmatt demonstration deep geothermal project in Belgium. EAGE Annual Conf. 2018. https://doi.org/10.3997/2214-4609.201800706.
Carlé W. Die Mineral- und Thermalwässer von Mitteleuropa. Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft mbH Stuttgart; 1975.
Chan LH, Gieskes JM, You CF, Edmond JM. Lithium isotope geochemistry of sediments and hydrothermal fluids of the Guaymas Basin. Gulf of California Geochim Cosmochim Acta. 1994;58:4443–54.
Collins AG. Geochemical of anomalous lithium in oil-field brines. Oklahoma Geol Surv Circ. 1978;79:95–8.
Diehl T, Kraft T, Kissling E, Wiemer S. The induced earthquake sequence related to the St. Gallen deep geothermal project (Switzerland): fault reactivation and fluid interactions imaged by microseismicity. J Geophys Res Solid Earth. 2017;122:7272–90. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JB014473.
Diehl T, Madritsch H, Schnellmann M, Spillmann T, Brockmann E, Wiemer S. Seismotectonic evidence for present-day transtensional reactivation of the slowly deforming Hegau-Bodensee Graben in the northern foreland of the Central Alps. Tectonophysics. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2022.229659.
Dini A, Lattanzi P, Ruggieri G, Trumpy E. Lithium occurrence in Italy—an overview. Minerals. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12080945.
Drüppel K, Stober I, Grimmer JC, Mertz-Kraus R. Experimental alteration of granitic rocks: implications for the evolution of geothermal brines in the Upper Rhine Graben. Germany Geothermics. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2020.101903.
Eccles DR, Berhane H. Geological introduction to lithium-rich formation water with emphasis on the fox creek area of west-central Alberta (NTS 83F and 83K). ERCB/AGS open file report 2011-10, Energy Resources Conservation Board, Alberta Geological Survey, Edmonten CA. 2011; ISBN 978-0-7785-8652-4.
Egli D, Mosar J, Ibele T, Madritsch H. The role of precursory structures on tertiary deformation in the black forest—Hegau region. Int J Earth Sci. 2017;106(7):2297–318.
Fabbri SC, Affentranger C, Krastel S, Lindhorst K, Wessels M, Madritsch H, Allenbach R, Herwegh M, Heuberger S, Wielandt-Schuster U, Pomella H, Schwestermann T, Anselmetti FS. Active faulting in lake Constance (Austria, Germany, Switzerland) Unraveled by multi-vintage reflection seismic data. Front Earth Sci. 2021;9:670532. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2021.670532.
Fouillac C, Michard G. Sodium/lithium ratio in water applied to geochemistry of geothermal reservoir. Geothermics. 1981;10:55–70.
Franz M, Simon T, Meyer RKF, Doppler G. Die Thermalwasserbohrung “Donautherme.” Neu-Ulm Geologica Bavaria. 2001;106:81–106.
Geyer OF, Gwinner MP. Geologie von Baden-Württemberg 5th edition. Stuttgart: Schweizerbart’sche Verlagsbuchhandlung; 2011.
Goldberg V, Nitsche F, Kluge T. Herausforderungen und Chancen für die Lithiumgewinnung aus geothermalen Systemen in Deutschland—Teil 2: Potenziale und Produktionsszenarien in Deutschland. Grundwasser. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00767-022-00523-4.
Goldbrunner J. State, possible future developments in and barriers to the exploration and exploitation of geothermal energy in Austria—country update. Proceedings World Geothermal Congress 2005, Antalya, Turkey. 2005.
Graf W, Timborn P, Ufrecht W. Isotopengeochemische Charakterisierung des Karstgrundwassers im Oberen Muschelkalk im Großraum Stuttgart unter besonderer Berücksichtigung von Sauerstoff-18 und Schwefel-34. In: Ufrecht W, Einsele G, editors. Das Mineral- und Heilwasser von Stuttgart. Stuttgart: Schriftenreihe des Amtes für Umweltschutz Stuttgart; 1994.
Grimm B, Franz M, Kilger BM, Lorenz G, Schmidt-Witte H. Die Thermalwassererschließung im Muschelkalk von Tuttlingen. Ber Naturf Ges Freiburg. 2005;95(1):189–212.
Hagdorn H, Simon T. Der Muschelkalk in der Stratigraphischen Tabelle von Deutschland. Newsl Stratigr. 2005;41(1–3):143–58.
Hagdorn H, Menning M, Nitsch E, Simon T. Die Muschelkalk-Gruppe in der Stratigraphischen Tabelle von Deutschland 2016 (STD 2016). [The Muschelkalk group in the stratigraphic table of Germany 2016 (STG 2016)]. Z Dt Ges Geowiss. 2019;2019(173):141–60.
Hansch W, Simon T. Das steinsalz aus dem mittleren muschelkalk südwestdeutschlands. Museo Heilbronn. 2003;20:76–93.
Haslinger E, Goldbrunner J, Dietzel M, leis A, Boch R, Elster D, Fröschl H, Gold M, Hippler D, Knauss R, Plank O, Shirbaz A, Wyhlidal S. NoScale—Charakterisierung von thermalen Tiefengrundwässern zur Verhinderung von Ausfällungen und Korrosionen bei Geothermieanlagen. Technical Report Geoteam. 2016;54.
Heidbach O, Rajabi M, Reiter K, Ziegler M. WSM-team. World stress map database release V. 1. 1. GFZ Data Serv. 2016. https://doi.org/10.5880/WSM.2016.001.
Heidbach O, Reinecker J. Analyse des rezenten Spannungsfelds der Nordschweiz. Nagra Arbeitsber. NAB 12-05, Wettingen. 2012.
Heuberger S, Morgenthaler J. Lithium in geothermal brines, status report on the current situation in Switzerland and in neighbouring countries. Switzerland: Technical report Georesources Switzerland Group ETH Zurich; 2023. p. 43.
Heuberger S, Roth P, Zingg O, Naef H, Meier BP. The St. Gallen fault zone: a long-lived, multiphase structure in the north alpine foreland basin revealed by 3D seismic data. Swiss J Geosci. 2016;109(1):83–102.
Hoffmann M. Young tectonic evolution of the northern alpine foreland basin, southern Germany, based on linking geomorphology and structural geology. Dissertation, Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich. 2017. https://edoc.ub.uni-muenchen.de/21123/1/Hoffmann_Markus.pdf.
Iannotta J, Hehn V. D2.1 Fluid data of geothermal sites (type C). Reflect Project Eur Union’s Horizon. 2020;850626:2022.
Ibele T. Tectonics of the Western Swiss Molasse Basin during Cenozoic Times. Geo Focus. 2011;27:166.
Ibele T. Tectonics of the Hegau and Lake constance region: a synthesis based on existing literature. Arbeitsbericht NAB 12-23, nagra, Wettingen. 2015.
Illies JH. Neotektonik, geothermale Anomalie und Seismizität im Vorfeld der Alpen. Oberrhein Geol Abh Karlsruhe. 1978;27:11–31.
Jodocy M, Stober I. Geologisch-geothermische Tiefenprofile für den südwestlichen Teil des Süddeutschen Molassebeckens. Z Dt Ges Geowiss. 2009a;160(4):359–66.
Jodocy M, Stober I. Das Geothermische Informationssystem für Deutschland (GeotIS). Landesteil Baden-Württemberg GMIT. 2009b;36:24–6.
Kharaka YK, Mariner RH. Chemical Geothermometers and their applications to waters from sedimentary basins. In: Naeser ND, McCulloh TH, editors. Thermal history of sedimentary basins. Hoboken: Springer; 1989.
LGRB. Bereitstellung hydrogeologischer und geothermischer Grundlagen zur Nutzung der tiefen Geothermie/Hydrogeothermie in der Region Bodensee—Oberschwaben. Regionalverband Bodensee—Oberschwaben/Regierungspräsidium Freiburg, LGRB. 2005.
LGRB. GeoMol—geopotenziale für die nachhaltige nutzung des tieferen untergrunds in den alpinen vorlandbecken, abschlussbericht des pilotgebietes bodensee-Allgäu. LGRB-Informationen. 2015. www.geomol.eu.
Mader S, Ritter JR, Reicherter K. AlpArray working group. Seismicity and seismotectonics of the Albstadt Shear Zone in the northern Alpine foreland. Solid Earth. 2021;12(6):1389–409.
Menning M. Geochronologie des Muschelkalks. Deutsche Stratigraphische Kommission für die Subkommission Perm-Trias, Stratigraphie von Deutschland XIII. Muschelkalk Schriftenr Dt Ges Geowiss. 2020;91(1):63–110.
Merino E, Canals A. Self-accelerating dolomite for calcite replacement: self organized dynamics of burial dolomitization and associated mineralization. Amer Jour Sci. 2011;311(7):573–607.
Millot R, Scaillet B, Sanjuan B. Lithium isotopes in island arc geothermal systems: Guadeloupe, Martinique (French West Indies) and experimental approach. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. 2010;74(6):1852–71.
Möck IS. Catalog of geothermal play types based on geologic controls. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2014;37:867–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.05.032.
Moldovanyi EP, Walter LM. Regional trends in water chemistry, smackover formation, southwest arkansas: geochemical and physical controls. AAPG Bull. 1992;76(6):864–94.
Naef H. Stratigrafie, Mächtigkeit und Lithofazies der mesozoischen Formationen in der Nordschweiz. Eine Kompilation von Bohrungen, Übersichts- und Aufschlussprofilen. Nagra Arbeitsbericht, NAB 06-26, Wittingen, Switzerland. 2008.
Nagra. Sondierbohrung Benken—Untersuchungsbericht. Nagra Technischer Bericht 00-01, Beilagenband, Beilage 8.7 Edelgas-Daten in den Tiefengrundwässern und extrahierten Porenwässern, Wettingen, Switzerland. 2001.
Nagra. Hydrogeologische Daten der Tiefenaquifere als Grundlage für die hydrogeologischen Modelle SGT Etappe 2. Arbeitsbericht NAB 13-43, Wettingen, Switzerland. 2013.
Nagra. Hydrochemie und Isotopenhydrogeologie von Tiefengrundwässern in der Nordschweiz und im angrenzenden Süddeutschland. Arbeitsbericht NAB 13-63, Wettingen, Switzerland. 2014.
NASA/METI/AIST/Japan Spacesystems and U.S./Japan ASTER Science Team. ASTER Global digital elevation model V003, distributed by NASA EOSDIS land processes DAAC. 2019. 10.5067/ASTER/ASTGTM.003. Accessed 05 Jan 2023.
Parkhurst DL, Appelo CAJ. Description of input and examples for PHREEQC version 3—a computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. Denver: U.S. Geological Survey Techniques and Methods; 2013. p. 6-A43.
Pauwels H, Fouillac C, Fouillac AM. Chemistry and isotopes of deep geothermal saline fluids in the upper rhine graben - origin of compounds and water-rock interactions. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. 1993;57:2737–49.
Poissant L, Schmit J-P, Béron P. Trace inorganic elements in rainfall in the Montreal Island. Atmos Environ. 1994;28(2):339–46.
Przybycin AM, Scheck-Wenderoth M, Schneider M. Assessment of the isostatic state and the load distribution of the European Molasse basin by means of lithospheric-scale 3D structural and 3D gravity modelling. Int J Earth Sci. 2015;104(5):1405–24.
Reinecker J, Tingay M, Müller B, Heidbach O. Present-day stress orientation in the Molasse Basin. Tectonophysics. 2010;482:129–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2009.07.021.
Reinecker J, Schneider G. Zur Neotektonik der Zollernalb: Der Hohenzollerngraben und die Albstadt-Erdbeben. Jahresberichte und Mitteilungen des oberrheinischen geologischen Vereins. 2002;391–417.
Riley JP, Tongudai M. The lithium content of seawater. Deep Sea Res. 1964;11:563–8.
Ring U, Bolhar R. Tilting, uplift, volcanism and disintegration of the South German block. Tectonophysics. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2020.228611.
Ring U, Gerdes A. Kinematics of the Alpenrhein-Bodensee graben system in the central alps: Oligocene/Miocene transtension due to formation of the Western Alps arc. Tectonics. 2016;35(6):1367–91.
Rupf I, Nitsch E. Das Geologische landesmodell von baden-württemberg: datengrundlagen, technische umsetzung und erste geologische ergebnisse. Freiburg: LGRB-Informationen; 2008.
Sanjuan B, Millot R, Innocent C, Dezayes C, Scheiber J, Brach M. Major geochemical characteristics of geothermal brines from the Upper Rhine Graben granitic basement with constraints on temperature and circulation. Chem Geol. 2016;428:27–47.
Sanjuan B, Gourcerol B, Millot R, Rettenmaier D, Jeandel E, Rombaut A. Lithium-rich geothermal brines in Europe: an up-date about geochemical characteristics and implications for potential Li resources. Geothermics. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2022.102385.
Sauerer A, Troll G. Abundance and distribution of boron in the Hauzenberg (Bavaria) granite complex. Geochemica Et Cosmochemica Acta. 1990;54:49–55.
Schloz W, Stober I. Mineral-, Heil- und thermalwässer, solen und säuerlinge in baden-württemberg. Freiburg: LGRB-Fachbericht 1 (überarbeitete Fassung); 2006.
Schreiner A. 1992. Einführung in die Quartärgeologie. Stuttgart: Schweizerbart‘sche Verlagsbuchhandlung
Stober I. Die thermalen Karbonat-Aquifere Oberjura und Oberer Muschelkalk im Südwestdeutschen Alpenvorland. Grundwasser. 2013;18(4):259–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00767-013-0236-2.
Stober I. Hydrochemical properties of deep carbonate aquifers in the SW-German Molasse Basin. Geothermal Energy. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40517-014-0013-1.
Stober I, Bucher K. Origin of salinity of deep groundwater in Crystalline rocks. Terra Nova. 1999;11(4):181–5.
Stober I, Bucher K. Fluid sinks within the earth’s crust. Geofluids. 2004;4:143–51.
Stober I, Jodocy M. Geothermische nutzhorizonte im westlichen teil des süddeutschen molassebeckens. Z Geol Wiss. 2011;39:161–72.
Stober I, Villinger E. Hydraulisches Potential und Durchlässigkeit des höheren Oberjuras und des Oberen Muschelkalks unter dem baden-württembergischen Molassebecken. Jahreshefte Des Geologischen Landesamts Baden-Württemberg. 1997;37:77–96.
Stober I, Jodocy M, Hintersberger B. Vergleich von Durchlässigkeiten aus unterschiedlichen Verfahren—Am Beispiel des tief liegenden Oberen Muschelkalk-Aquifers im Oberrheingraben und westlichen Molassebecken. Z Geol Wiss. 2012;40(1):1–18.
Stober I, Jodocy M, Burisch M, Person R. Tiefenwässer im Oberen Muschelkalk-Aquifer des Oberrheingrabens und des Südwestdeutschen Molassebeckens. Grundwasser. 2013;18(2):117–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00767-0224-6.
Stober I, Kohl T, Schmidt R, Egert R. Verbundvorhaben „GeoFaces“: Charakterisierung geothermischer Ressourcen unter Berücksichtigung von Grenz- und Trennflächen, Teilvorhaben „Systematische Untersuchung von Fluidwegsamkeiten im Bereich von Trennflächen in Süd-Deutschland, GeoFaces-SD. Endbericht zum Verbundvorhaben „GeoFaces“, Förderkennzeichen: 0324025C, Bundesministerium für Wirtschaft und Energie (BMWi) Projektträger Jülich (PtJ-EEN). 2018.
Traber D, Waber HN, Eichinger L, Heidinger M. Hydrochemie und Isotopenhydrologie von Tiefenwässern in der Region Längeren—Züricher Weinland—Hegau. nagra Interner Bericht NIB 02-50, Wettingen, CH. 2002.
Trautwein B, Dunkl I, Kuhlemann J, Frisch W. Cretaceous-Tertiary Rhenodanubian flysch wedge (Eastern Alps): clues to sediment supply and basin configuration from zircon fission-track data. Terra Nova. 2001;13(5):382–93.
Ufrecht W. Die Tiefengrundwässer im Oberen Muschelkalk zwischen Albvorland und oberschwäbischem Molassebecken—ein Hydrogeologisches Modell. Schriftenreihe Des Amtes Für Umweltschutz, Stuttgart. 2018;1:7–158.
Ufrecht W, Heidinger M, Lorenz GD. Grundwasserneubildung und Fließdynamik im tiefen Oberen Muschelkalk zwischen Donau und Neckar (Südwestdeutschland). Grundwasser. 2020;25:273–84.
Walther JV, Helgeson HC. Calculation of the thermodynamic properties of aqueous silica and the solubility of quartz and its polymorphs at high pressures and temperatures. Am J Sci Stanford/usa. 1977;277:1315–51.
Warnecke M. 3D-Faziesmodelle des Oberen Muschelkalks. Jh Ges Naturkunde Württemberg Stuttgart. 2019;175:273–92.
Warnecke M, Aigner T. Asymmetry of an epicontinental basin—facies, cycles, tectonics and hydrodynamics: the Triassic Upper Muschelkalk, South Germanic Basin. Wiley Depositional Record. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1002/dep2.59.
Yuan X, Hu Y, Zhao Y, Li Q, Liu C. Contribution of hydrothermal processes to the enrichment of lithium in brines: evidence from water-rock interacting experiments. Aquat Geochem. 2021;27:221–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-021-09395-1.
Acknowledgements
The alteration experiments were carried out within the project “GeoFaces“ (No: 0324025C). Thus, we would like to thank the Bundesministerium für Wirtschaft und Energie (BMWi) Projektträger Jülich (PtJ-EEN). We would like to thank Roman Schmidt for support during the alteration experiments and interpretation. Kirsten Drüppel for her help during these investigations. Tobias Kluge for discussion of temperature-dependent oxygen isotope exchange with the carbonate aquifer. Theo Simon for discussion on faults in the northern Bodensee area. We would like to thank three anonymous reviewers for their help to improve our paper.
Funding
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL. No funding for this research. However, we used some data of a funded project mentioned in the acknowledgements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
IS: conception, analysis, and interpretation of data, drafting and revision of the text; JG: analysis and interpretation of data, drafting and revision of the text; MK: analysis and interpretation of data, drafting and revision of the text. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Performance of the alteration experiments
Two alteration experiments with Upper Muschelkalk limestone were performed for 44 days within a stirred autoclave system (Limbo li, buechi) at 200 °C and 260 °C, inspired by maximal temperatures in the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer (Stober et al. 2018). Two limestone samples, cut in a cubic form (27 mm · 21 mm · 14 mm), were used for each experiment. The rock samples were washed properly under a weak jet of deionized water and dried under laboratory conditions before being used in the experiments. The autoclave vessel and its components in contact with the solution consists of stainless steel (X6NiCrTiMoVB25-15-2, EU standard 10269). The vessel volume is 450 ml, which allows a solution volume of 350 ml, with an atmospheric head space. A 2 molal Na-Cl solution (116.9 g kg−1) was prepared with deionized water and NaCl salt and used as starting solution for the experiments. Small amounts of inorganic carbon (alkalinity: < 0.1 mmol kg−1) and O2 are dissolved in the initial solution due to contact with the atmosphere. The initial pH of the solution was 5.5 (at 25 °C). The pressure was given by the boiling pressures of the Na-Cl solutions at experiment temperatures (c. 15 bar). During the experiments the solution was stirred with a speed of about 100 rpm. It has to be mentioned that the artificial solution is at least at the beginning of the alteration experiments undersaturated with respect to most mineral phases.
After the experiments, the fluid was cooled to room temperature rapidly. Electrical conductivity (Mettler Toledo Inlab 371) and pH (ProMinent PHER-112) were measured immediately, and carbonate alkalinity was titrated with 0.01 M HCl. For element analyses the solutions were filtered with 0.45-μm cellulose acetate membranes. The fluid samples were diluted with ultra-pure water by a factor of 10 to ensure solution stability. Additionally, the solutions were acidified with distilled HNO3 for cation measurement. Samples were stored in 30-ml polyethylene bottles and kept cool until analysis.
Major and minor cations were determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) with a Thermo Fisher Scientific X-Series 2. Sample dilution was 1: 100. Dissolved Si and Na concentrations were analyzed by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) with a Varian 715ES and a sample dilution of 1: 200 for Si and 1: 500 for Na. Ion chromatography (IC) was performed with a Dionex, ICS-1000 for dissolved anions. Due to high concentrations of Cl and a consequential need for high dilution of the sample (1: 2000), it was not possible to detect other anions than Cl.
Continuously, standard solutions were remeasured during analysis procedure to ensure quality of measurements. Accuracy of ICP-MS measurements is better than 3% for main cations and better than 8% for Al and Fe, for ICP-OES better than 5% and for IC better than 4%.
Rock samples have been removed from the vessel after solution extraction and washed two times with deionized water to prevent halite precipitation. After both washings, the samples have been dried at laboratory temperature.
Characterization of the pre- and post-experiment rock samples was performed with several analytical and imaging methods. The mineral concentration was identified by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements with a Bruker D8 Discover. System parameters were a Cu anode at 40 kV and 40mA and a silicon strip detector (lynxeye XE-T). The scanning range was 2–82°, with a step size of 0.01° 2 θ. Unaltered samples were measured as representative bulk material, whereas only surface material of the altered samples was used to identify secondary phases formed during alteration.
Alteration processes on sample surfaces and cross-sectional thin sections were detected and visualized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) methods with a FEI Quanta 650 ESEM. Surface characterizations were made in secondary electron (SE) mode with an acceleration voltage of 10 kV. Additional, thin sections were examined for alteration reaction textures in the sample interior under back-scattered electron (BSE) mode at the same device setting. Mineral identification and qualitative analyses have been conducted with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX, Bruker XFlash 5010 detector). Rock samples and thin sections were covered with carbon before SEM analyses (Stober et al. 2018).
Results of the high-temperature alteration experiments with limestone of the Upper Muschelkak
Alteration experiments were performed with limestone of the lower part of the Upper Muschelkalk, containing small shell fragments. The samples originate from the quarry Keltern in the northern Black Forest. The color of the fresh cubic sample was dark blue-grey, whereas the shell fragments are characterized by a lighter color. The mineralogy consists of carbonates plus opaque phases as accessories. The stratigraphic units of the Keltern limestone within the Upper Muschelkalk (mo) comprise the Zwergfauna Layers (moZ) and Haßmersheim Layers (moH) of the Trochitenkalk Formation (moTK) and the Meißner Formation (moM). Table 3 shows the whole rock composition. Main elements are CaO with over 60 w.%. The sample contains additionally SiO2 and MgO, both more than 3 w.%. Small amounts of Al2O3 and Fe2O3 (< 1 w.%) could be detected as well. Ignition loss is about 42 w.%, corresponding to the high percentage of calcite. Main trace elements (Table 3) are Ba and Sr. XRD investigations showed a practically pure limestone consisting of calcite, dolomite, and quartz (Stober et al. 2018).
The two alteration experiments with the prepared NaCl solution at 200 °C and 260 °C lasted 44 days. Afterwards, both morphology/color of the samples and fluids composition changed. However, the samples of the experiment at 200 °C experiment showed macroscopically only slight changes in color, instead of dark blue-gray with light dots, the altered samples were red-brown with beige dots. Contrarily, the 260 °C samples showed additionally dissolution structures and formation of new minerals.
XRD investigations on surface material of both altered samples (200 °C and 260 °C experiment) showed mainly calcite, sparsely any dolomite and halite (due to the NaCl solution). Iron oxides were not detectable, despite the brownish color of the altered samples. SEM investigations on the 260 °C sample revealed the formation of new euhedral minerals, which could be identified as calcite crystals, and depression zones due to dissolution effects. Additionally, we found small areas showing hardly any dissolution at the surface containing shell fragments. In these areas occur due to EDX measurements Na–Mg–Al–Si minerals (maybe Na-Saponite).
The main effect of the alteration process is a dissolution–precipitation process of limestone to calcite and to traces of dolomite (Stober et al. 2018). Generally, no Li-containing minerals could be detected, neither in fresh nor in altered samples.
Fluids of the two alteration experiments were analyzed, as described in "Material and methods" Section. Table 4 shows the analytical results of the two high-temperature alteration solutions and of the initial solution for comparison reasons.
We calculated the saturation state with the code PHREEQC and found that both high-temperature solutions were supersaturated with respect to aragonite, calcite, dolomite, and as well with respect to goethite or hematite, whereas the saturation index (SI) was generally higher in the 260 °C experiments. On the other hand, saturation with respect to quartz or chalcedony was not achieved in both experiments. SIQz was in the solutions of both experiments identical. Both solutions were significantly undersaturated with respect to illite, analcime, laumontite, and stilbite. Supersaturation with respect to saponite resulted. However, it has to be mentioned that it was impossible to determine, e.g., sulfate (SO4) in both saline solutions, thus SI of several minerals could not be calculated. However, already small amounts of SO4 (c. 80 mg kg−1) would lead to saturation with respect to anhydrite and supersaturation with respect to barite, but none of these minerals were detected by mineralogical investigation methods.
Summing up, the thermodynamic results are in line with the mineralogical investigations of dissolution–precipitation processes of the limestone to calcite, to traces of dolomite and maybe saponite. No Li-minerals were detected on the altered material or are to be expected by thermodynamic modeling.
Table 4 shows that the initial solution already contained traces of Li. After the two high temperature alteration experiments no significant changes in Li concentration of the fluids resulted. Thus, the rock sample probably does not contain Li, which could be leached even by extremely high temperatures (200 °C, 260 °C). The geochemical/mineralogical investigations revealed neither lithium-bearing minerals in the rock before nor after the experiments. Furthermore, no lithium could be detected in the solution due to the alteration experiments. Therefore, we conclude the high lithium concentrations in the thermal water of the Muschelkalk aquifer are in all likelihood of external origin.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Stober, I., Grimmer, J. & Kraml, M. The Muschelkalk aquifer of the Molasse basin in SW-Germany: implications on the origin and development of highly saline lithium-rich brines in calcareous hydrothermal reservoirs. Geotherm Energy 11, 27 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40517-023-00270-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40517-023-00270-6