Abstract
Background
The Upper Jurassic (Malm) limestone and the Middle Triassic Muschelkalk limestone 18 are the major thermal aquifers in the southwest German alpine foreland. The aquifers 19 are of interest for production of geothermal energy and for balneological purposes.
Methods
Hydrochemical data from several hundred wells within two deep limestone aquifers in the Molasse basin of SW Germany have been compiled, examined, validated, and analyzed with the aim to characterize the fluids and to investigate the origin of the fluid properties.
Results
The hydrochemical properties of the two aquifers differ in several aspects. The total amounts of dissolved solids (TDS) are much higher within the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer than within the Upper Jurassic. Water composition data reflect the origin and hydrochemical evolution of deep water. Rocks and their minerals control the chemical signature of the water. With increasing depth, the total of dissolved solids increases. In both aquifers, the water evolves to a NaCl-dominated fluid regardless of the aquifer rock.
Discussion
The salinity of the aquifers has different sources. In the case of the Upper Muschelkalk, it is linked to deep circulation systems, while the hydrochemical properties in the Upper Jurassic developed due to changing overburden and hydraulic potential.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Background
Previous investigations
The deep Upper Jurassic carbonates are the most important reservoir rocks for hydrothermal energy use in Southern Germany. Especially in the Munich area of Bavaria (Germany), several geothermal power plants and district heating systems were installed since 2007 (Schellschmidt et al. [2010]). With the data of the new deep wells, it was possible to characterize hydrochemically the Upper Jurassic aquifer in the southern part of Bavaria (Birner et al. [2011]).
In Upper Austria, the thermal Upper Jurassic aquifer is used intensely as well. Balneological applications have a long tradition, but energetic utilization of hydrogeothermal resources started only in the 1970s. Today, there are three geothermal power plants and about eight operating district heating systems (Andrews et al. [1985]; Goldbrunner and Goetzl [2013]).
In northern Switzerland, isotopic investigations of groundwater in the Upper Jurassic were carried out in the 1980s, supported by water chemical analyses and rock resp. mineral analyses. The focus of this study was not on balneology or geothermal energy use but on assessing potential sites for nuclear waste repositories (Pearson et al. [1991]).
In Baden-Württemberg (Germany), the Upper Jurassic thermal aquifer is of shallower depth (Figure 1); therefore, the colder and thermal water is rather used for balneological purposes including heating of nearby buildings. Between 1977 and 1985, the first hydrogeothermal wells have been drilled in the central Upper Jurassic aquifer of the SW German Molasse basin. Two of the eight wells failed, but the others were successful and are in operation until today. Production rates of up to 50 l/s, temperatures of 40°C to 50°C, and total of dissolved solids of 0.45 to 0.55 g/kg were achieved (Bertleff et al. [1988]).
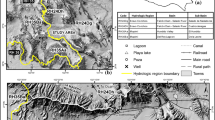
Location of the investigation area in the SW German Molasse basin. The image shows the location of the cross section (Figure 2).
In the 1980s, the flow system of the entire Molasse covered karstified Upper Jurassic (Malm) aquifer was described according to the then available hydrogeological and geohydraulic parameters (Andres and Frisch [1981]; Bertleff [1986]; Stober [1986]; Andrews et al. [1987]; Bertleff et al. [1988]; Prestel [1990]). Recharge and discharge areas were determined. In the northern part of the Upper Jurassic aquifer, extensive investigations were carried out to measure isotope content and to get hydrochemical data. These data led to the first results concerning the different flow systems in the northern Upper Jurassic aquifer (Bertleff [1986]; Andrews et al. [1987]). Most of the hydrochemical and isotopic data were retrieved from relative shallow wells in the border area of the northern part of the Molasse basin.
The now presented hydrochemical analyses complete these data in the SW part of the Upper Jurassic aquifer, additionally with data from deeper boreholes farther in the SE of the investigation area (Figure 1). The data are in agreement with the findings in the Bavarian part of the Upper Jurassic (Birner et al. [2011], [2012]).
Far less well-known than the Upper Jurassic is the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer. First scanty hydraulic and hydrochemical results are given in Bertleff et al. ([1988]). New hydraulic investigation results are presented in Stober ([2013]).
Hydraulic well tests provide among others water samples and thus are the key data on hydrochemical analyses and isotope studies. This paper compiles several hundred checked, validated hydrochemical data of two carbonate aquifers in the Molasse basin of SW Germany. The presented data derive from deep wells in the depth range from several hundred meters to 3,500 m.
The presented hydrochemical data have been made available to the public by several projects supported by the Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation, Building and Nuclear Safety (BMU), Germany (Schulz et al. [2007]; Stober and Jodocy [2011]).
Background
Geological framework conditions of the SW German Molasse basin
Geologically, the investigation area is located in the southwestern part of the German Molasse basin, in the federal state Baden-Württemberg. The course of the river Danube and the Upper Jurassic of the Swabian Alb form the northwest border. The eastern border of the investigation area follows the river Iller, and the southwestern border is linked to the Lake Constance (Figure 1).
The investigation area is part of the so-called Molasse basin, a foreland basin of the Alps that formed during the Cenozoic Oligocene and Miocene as a result of the flexure of the European plate under the weight of the orogenic wedge of the Alps. The Molasse basin has a length of about 1,000 km and stretches over France, Switzerland, Germany, and Austria. The width of the basin increases up the 130 km in its central part, the Bavarian foreland of the Alps. The basin is filled with a sedimentary sequence for the most part removed from the developing mountain chain by erosion and denudation. The lowermost formation is the Lower Marine Molasse (early Oligocene) consisting of shallow marine sand, clay, and marl, followed by the Lower Freshwater Molasse (late Oligocene, early Miocene) with fluviatile sediments due to tectonic uplift above sea level. Later, there was again a tectonic subsidence and the Alpine foreland was flooded with a marine environment forming the Upper Marine Molasse (early Miocene), followed again by a period of uplift and the formation of fluviatile sediments during the topmost Molasse formation, the Upper Freshwater Molasse (middle and late Miocene). During the late Miocene and early Pliocene, a phase of uplift in the Alps and the Alpine foreland, the Molasse basin ceased to be an area of net sedimentation (Geyer and Gwinner [2011]).
The basis of these Molasse sediments - at least in the investigation area - is formed by the Upper Jurassic dipping from the outcrops at the Swabian Alb in southeastern direction below the Cenozoic sediments. Below the Jurassic, follow the Triassic series (Figures 1 and 2). Our investigations are focused on the Upper Jurassic and the Triassic Upper Muschelkalk, two carbonate aquifers, both dipping gently in southeastern direction below the Cenozoic Molasse sediments reaching a depth of more than 3,000 m at the boundary to the alpine orogeny (Bertleff [1986]).
Geological cross section through the Molasse basin showing the Upper Jurassic and the Upper Muschelkalk aquifers. In the Upper Jurassic, the different facies are illustrated: reef and basin carbonates of the Swabian facies and the Helvetian facies (modified after Jodocy and Stober [2009]).
During the Quaternary ice ages, massive glaciers covered the Molasse basin, reaching a thickness of up to 1,000 m near the orogenic front of the Alps, thus causing subsidence and uplift of the Alpine foreland in the interglacial periods due to changing upload (Schreiner [1992]). So, different tectonic forces, like the orogeny of the Alps, the subsidence and uplift of the Alpine foreland (Molasse basin), and the over-regional pressure from S to N direction, influence the geomechanical performance of the total sedimentary sequence in the Molasse basin including as well the Jurassic and Triassic series.
Methods
Hydrogeological properties of the Upper Jurassic and the Upper Muschelkalk aquifers
Reservoir quality of the Upper Jurassic varies strongly, depending on sedimentary facies, diagenesis, dolomitization, karstification, and tectonic situation. The thickness of the total Upper Jurassic in the investigation area can reach values of up to 550 m (Geyer and Gwinner [2011]). The Upper Jurassic carbonate aquifer consists of more than 250-m-thick, locally dolomitized limestone (Bertleff et al. [1986], [1988]; Villinger [1977]). The Swabian facies, located in the middle and northwestern part of the investigation area, developed in a shelf environment with reef facies in the northwest and basin facies in the central part. While reef detritus built up the carbonates of the reef facies, the basin facies consists of banked limestone. Since the matrix porosity of the reef facies tends to be higher than that of the basin facies, the recrystallization of limestone into dolomite, associated with a volumetric reduction, primarily takes place in the reef (Koch [1997]; Böhm et al. [2011]). Therefore, the reef facies in the northwest generally has a higher porosity accompanied with a better hydraulic conductivity (>10-4 m/s) than the thinner bedded, banked basin facies in the central part of the investigation area, which has a lower hydraulic conductivity. Karstification features are present in the entire Upper Jurassic, spatially related to faults and thick bedded to massive dolomites with a gentle decline in the SE direction. Signatures from borehole and seismic data for the central and northern zone characterize the karstification (Stober et al. [2013a]). Farther in the southeast, the Swabian facies of the Upper Jurassic changes into the Helvetian facies, characterized by darker, very tight limestones with a significant amount of marls, developed under distal conditions (Meyer and Schmidt-Kaler [1996]). As a result, the permeability is very low, depending mainly on fissures or the very low matrix porosity of the carbonates (Koch and Sobott [2005]) (Figure 2).
Due to the above-mentioned tectonic stress together with the vertical displacement history, faults and fractures developed, leading to an additional increase in permeability. Fault zones are located preferentially in the northwestern, higher permeable Swabian reef facies and hence the geomechanical weaker part of the Upper Jurassic aquifer.
Facies of the Upper Jurassic is changing from NW to SE, causing more intensive karstification and faulting in the NW part of the investigation area. In consequence, the hydraulic conductivity reduces by several orders of magnitude in the SE direction and thus with increasing depth (Stober and Villinger [1997]; Stober et al. [2013a]). So, the variation of the hydraulic conductivity is related to lithological variations in facies and the resulting degree of karstification and faulting.
The deeper laying Upper Muschelkalk aquifer (Middle Triassic) is a fractured and karstified limestone aquifer, with fractured dolomites. Karstification and fractures are preferentially in the upper part of the so-called Trigonodusdolomit. Depending on the permeability of the underburden (Middle Muschelkalk) and overburden (Keuper formation, Upper Triassic), the overall thickness of the aquifer can gain several meters (Hagedorn and Simon [2005]). Generally, the thickness of the total Muschelkalk is decreasing in the investigation area in the ESE direction. While in the western part the thickness of the Upper Muschelkalk is about 75 m, it is dwindling away in the SE of the investigation area (Stober and Villinger [1997]).
In the SE direction (Figure 1) with increasing depth, the dolomite fraction of the Upper Muschelkalk limestone is increasing and the Lower Muschelkalk develops as a sandstone aquifer. In the investigation area, there should be no or hardly any saline deposits in the Middle Muschelkalk (Bock et al. [2009]; Geyer and Gwinner [2011]). In most parts of the investigation area, the crystalline basement underlies the Muschelkalk. Only farthest in NW, thin Buntsandstein layers form the basis of the Muschelkalk. North of the Lake Constance, some relicts of a Carboniferous/Permian sedimentary basin of northern Switzerland extend, representing there a local basis of the Muschelkalk.
Groundwater circulation in the Upper Muschelkalk occurs along fracture and bedding planes, often enlarged due to karstification processes. Doubtless, the before-mentioned tectonic stress together with the manifold vertical displacement history led to an increase in fracture and fault systems. All drilling cores of the deep wells showed karstification processes. In consequence, the hydraulic conductivity of the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer is only slightly decreasing with depth, resp. in the SE direction (Stober [2013]), contrarily to the strong, facies-derived decrease of hydraulic conductivity in the Upper Jurassic aquifer.
Between the two carbonate aquifers extends the 60 to 130 m thick lithostratigraphic unit of the Keuper, consisting of dolostones, shales, claystones, and evaporates, followed by the Lower and Middle Jurassic series of 20 to 50 m and 120 to 180 m thickness, resp. Especially, the Lower Jurassic is composed of very tight clay and marlstones. Additionally in both series, there are thin layers of limestone and siltstone (Geyer and Gwinner [2011]). Nevertheless, the hydraulic potentials of the Upper Jurassic and the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer are uncoupled from each other, showing very different flow directions and differences in hydraulic head of up to 300 m (Stober [2013]). Obviously, there should be no hydraulic interaction between the two carbonate aquifers.
Results
Hydrochemical properties of the Upper Jurassic and the Upper Muschelkalk aquifers
The temperature in both aquifers is elevated, and geothermal gradients of about 4.5°C/100 m are common (Figure 3). Locally, gradients up to 6.0°C/100 m and more are measured. The normal undisturbed temperature gradient in the Variscan Central Europe is about 3.0°C/100 m. In general, measured aquifer temperatures in the two carbonate aquifers of the investigation area are clearly higher than those associated with a `normal gradient’ (Tables 1 and 2). Because of the elevated aquifer temperatures, the Molasse basin in SW Germany - the investigation area - is especially well suited for balneological and geothermal heat use. Since permeability in the Upper Jurassic aquifer is strongly decreasing with increasing depth, the high temperatures in the Upper Jurassic could not be efficiently used to produce geothermal electricity.
Generally, the chemical data of water samples presented here are old data from archives (Carlé [1975]; Werner [1978]; Bertleff [1986]; Prestel [1990]; Franz et al. [2001]; Schloz and Stober [2006]; Grimm et al. [2005]). Tables 1 and 2 show representative hydrochemical analyses of the Upper Jurassic and the Upper Muschelkalk aquifers. Altogether, we compiled more than 200 water analyses. In some wells, from the same formation, several samples were received. A large number of chemical analyses are from samples, taken during production tests performed by the oil industry in the 1970s to 1990s. The original, tested, and sampled boreholes are closed now, so resampling is not possible. A few recently collected samples from thermal spas are added to the data set. Different laboratories analyzed the water samples. All analyses were, therefore, controlled and tested for plausibility. However, the overall quality of the chemical data is difficult to assess and should not be overvalued. Nevertheless, the data are considered helpful for planning geothermal projects or deep wells for other purposes like CO2 sequestration, thermal spas, and others.
The total amounts of dissolved solids (TDS) in the Upper Muschelkalk waters are much higher than those in the Upper Jurassic, which often show drinking water quality up to depths of 1,200 m below surface (b.s.) (Figure 4a). Below 1,300 m depth, TDS in the Upper Jurassic is increasing significantly, reaching values of more than 10 g/kg in about 2,000 m depth (Figure 4a). The highest TDS value of 35 g/kg is observed in 3,500 m depth. Contrarily, TDS in the Upper Muschelkalk reaches already in 1,300 m depth about 10 g/kg and in the 2,000 m depth about 65 g/kg. The highest TDS values of 75 g/kg are found in 2,500 m depth (Figure 4b), showing a much higher salinity than seawater (35 g/kg). TDS values of the Upper Jurassic and the Upper Muschelkalk aquifers follow distinct correlation curves, showing an increase of TDS with depth. Appropriate correlation curves are given in Figure 4a,b with x = log TDS and y = depth.
Figure 5a,b shows the main constituents of the Upper Jurassic and Upper Muschelkalk waters in a so-called Schoeller diagram with the concentration on the vertical axes. The hydrochemical data bear information on the origin and development of deep water. The composition of fluids at shallow depth (Upper Jurassic <1,300 m; Upper Muschelkalk <900 m) having low TDS values is strongly controlled by the minerals of the reservoir rock (Figure 5a,b; Tables 1 and 2):
-
Upper Jurassic aquifer: Ca-HCO3 water, related to fractured, karstified limestone (calcite, dolomite, quartz, clay minerals)
-
Upper Muschelkalk aquifer: Ca-SO4-HCO3 water, due to the fractured, karstified limestone, with thin marly clay layers and dolomite, containing sulfate-rich strata underneath the aquifer, rarely within the aquifer
The thermal waters in the Upper Jurassic with low NaCl concentrations show in the majority of cases increasing calcium with coexistent decreasing magnesium concentrations (Figure 5a), probably caused by dolomitization of calcite. During this process, by which dolomite is formed, magnesium ions of the fluid replace calcium ions in the calcite. Therefore, the calcium concentration in the fluid is increasing while magnesium is decreasing. This process does not affect HCO3 in the water (Figure 5a). Prestel ([1990]) describes dolomitization processes in the Upper Jurassic limestone using thin sections. Geyer and Gwinner ([2011]) observed in bore cores and cutting material an increase in dolomite in the SE direction. Calculations, using the computer program PHREEQE (Parkhurst et al. [1980]), show that the dolomitization process is strongly temperature dependent. Increasing the temperature from 20°C up to 100°C will double the Ca/Mg ratio in water. Increasing the NaCl concentration in the fluid will only slightly enhance the Ca/Mg ratio. The calculations support the observations shown in Figure 5a and explain the findings in core samples described by Geyer and Gwinner ([2011]).
The NaCl concentrations in the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer are almost in all analyses significantly higher than in the Upper Jurassic. In contrast to the Upper Jurassic waters, magnesium in the fluids of the Upper Muschelkalk is rising with increasing calcium (Figure 5b), so no recent dolomitization should occur. While calcium is increasing, HCO3 is decreasing (Figure 5b). To analyze the temperature and salinity effect on the calcium-carbon (Ca/C) ratio, we used the computer program PHREEQE (Parkhurst et al. 1980). The results showed that the Ca/C ratio rises with both, increasing NaCl content and/or increasing temperature. So, the observed increase in Ca and decrease in HCO3 in the Upper Muschelkalk (Figure 5b) are most probably an effect of increasing salinity and temperature.
All deep waters in the Upper Jurassic and the Upper Muschelkalk aquifers are saturated with respect to calcite and quartz, more or less saturated with respect to gypsum and anhydrite. They are slightly oversaturated with respect to dolomite. With respect to barite, the waters in the Upper Jurassic aquifer are slightly over- or undersaturated, whereas in the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer, most waters seem to be slightly oversaturated (PHREEQE, Parkhurst and Appelo [1999]). Especially, the waters in the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer have a certain scaling potential if pumped and used in geothermal energy applications.
TDS increases with depth (Figure 4), and the thermal water in both aquifers develop to a NaCl-type water independent of the type of the aquifer rock (Figure 5). In both aquifers, the chloride concentration is increasing in the SE direction (Figure 6), resp. with increasing depth (Stober et al. [2013b]). While in the Upper Jurassic aquifer, chloride in the area south of Ravenburg reaches values of up to 10 g/kg; the chloride concentration in the Upper Muschelkalk is higher than 40 g/kg. However, the high salinity within the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer (and Upper Jurassic) is still far below saturation with respect to halite.
Chloride distribution in the Upper Jurassic (a) and Upper Muschelkalk (b) aquifers of the SW German Molasse basin. Modified after Stober et al. ([2013b]).
Especially due to changing facies, the hydraulic conductivity of the Upper Jurassic aquifer is strongly decreasing in the SE direction (<10-10 m/s), reaching as well values significantly lower than in the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer (Stober [2013]). The hydraulic gradient in the SE of the investigation area is very low (<10-3), and the Upper Jurassic water divide passes from NW to SE (Stober [2013]). Assuming a reasonable effective porosity of about 1% or lower, the effective velocity is far below 10-11 m/s. Therefore, the residence time of groundwater in the Upper Jurassic aquifer in the SE part of the investigation area is quite high, and waters seem to be nearly `stagnant’.
Discussion on the origin of salinity
High saline brines have been described from many other deep sedimentary aquifers (e.g., Grasby and Betcher [2002]; Karro et al. [2004]; Carpenter [1978]; Kharaka and Hanor [2004]; Sonney and Vuataz [2010]) and from several kilometer depth in the continental basement of the Canadian, Fennoscandian, and Ukrainian shield, from the crystalline basement in the Black Forest, and elsewhere in the world (e.g., Kozlovsky [1984]; Frape and Fritz [1987]; Edmunds and Savage [1991]; Stober and Bucher [1999]; Stober et al. [1999]).
The origin of the high salinity in deep crustal fluids has been a hotly debated research topic (Edmunds et al. [1985]; Gascoyne et al. [1987]; Beaucaire et al. [1999]; Banks et al. [2000]). In deep sedimentary aquifers or the crystalline basement, salinity could be of recent marine origin, for example, characterized by a Cl/Br ratio of about Cl/Br = 288 (milligram basis), while brines originating from dissolved halite have typically Cl/Br values of some thousands. In the crystalline basement, some Cl-bearing minerals (e.g., biotite) or fluid inclusions within the rock represent a further Cl source. Typically, these waters show Cl/Br ratios <150 (Stober and Bucher [1999]).
The high salinity in the two carbonate aquifers of the Molasse basin seems to be - beside the formation fluid - independent of the mineral composition of the reservoir rocks. There are several possible sources causing the observed salinity in the thermal waters.
Prospecting for a possible chloride source in the Upper Jurassic aquifer, one needs to have a closer look at the overburden Molasse sediments. During the lower Oligocene, the Lower Marine Molasse (LMM) formed, consisting of clastic sediments of alpine erosion material (Piller et al. [2007]). The latest seawater transgressions in the Molasse basin occurred during the early Miocene (Upper Marine Molasse) with sand and limestone deposits. However, evaporate deposits with halite or sylvite are unknown in the Molasse sediments. Therefore, from a geological point of view, the chloride source in the Upper Jurassic aquifer is derived most likely via seawater infiltration of the overlaying LMM sediments (Lemcke and Tunn [1956]), especially during times of enhanced compaction due to increasing thickness of the Molasse sediments and of the glaciers during Pleistocene. During the Pleistocene, below the glaciers, groundwater recharge occurred and fresh water infiltrated in the Upper Jurassic aquifer from the NW direction (Bertleff et al. [2005]), systematically diluting the marine component from NW to SE direction.
In the case of the Upper Muschelkalk, there exist as well several possible chloride sources beside the marine formation fluid. In the investigation area, there should be no or hardly any saline deposits in the Middle Muschelkalk (Bock et al. [2009]; Geyer and Gwinner [2011]). Generally, the Grabfeld formation of the lower Middle Keuper (Upper Triassic) could contain small quantities of halite. In the investigation area, however, the Grabfeld formation is merging into the Benk formation in the SE direction. This formation is characterized by deposition of halite-free sandstone (Geyer and Gwinner [2011]). Since the chloride concentration in the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer is increasing in the SE direction (Figure 5b), the Middle Keuper is very unlikely to be a significant chloride source for the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer. Another possible source could be the crystalline basement being well known for its high saline fluids (Frape and Fritz [1987]; Stober and Bucher [1999]). The crystalline basement underlies more or less directly the Muschelkalk. Since the Muschelkalk formation is declining in thickness in the SE direction, upwelling thermal crystalline basement waters are most likely the chloride source in the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer especially in the SE of the investigation area.
Most of the measured aquifer temperatures in the Upper Jurassic and Upper Muschelkalk aquifers are elevated with respect to a geothermal reference gradient of 30°C/km (Figure 3). Generally, there are several possible causes leading to an increased geothermal gradient including upwelling deep waters, low vertical thermal conductive layers, volcanic activity, and others. We used the SiO2 geothermometer of Walther and Helgeson ([1977]) to calculate the reservoir temperatures and to compare the results with the measured aquifer temperatures of Figure 3. The SiO2 concentrations of the Upper Muschelkalk and the Upper Jurassic waters provide a consistent image. Nearly all calculated quartz-saturated reservoir temperatures of both aquifers are higher than the measured aquifer temperatures (Figure 7). The data show that at present, fluids of higher temperatures are most likely upwelling from deeper parts. These fluids potentially carry hydrochemical signatures of their origin. The measured elevated temperatures indicate an overall upward flow of hot water in the investigation area (Figure 3). The flow is even fast enough to carry elevated disequilibrium SiO2 concentrations from below (Figure 7).
To get in addition detailed information concerning the origin of salinity in both carbonate aquifers, we had a look at the Cl/Br ratio and the Na/Cl ratio. Unfortunately, bromide was not often analyzed routinely; thus, Cl/Br ratio data are scarce. Additionally, Br data from the hydrocarbon wells should not be overrated, especially at very low concentrations (<1 mg/kg). In contrast to balneology or to the mineral water industry, bromide was an uninteresting water component to the oil industry. Therefore, there are only about four relatively reliable Cl/Br values of the Upper Jurassic and three Cl/Br values of the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer left. The chloride concentrations of these Cl/Br values are relatively high.
The Cl/Br values of the Upper Jurassic aquifer are derived from water samples in the SE part of the investigation area. Deep thermal waters there show Cl/Br values in the order of Cl/Br = 200. These values are below modern seawater signature of Cl/Br = 288. Possibly, dilution with precipitation water (glacier water) possessing low Cl/Br values (Behne [1953]) reduced the Cl/Br ratio of the originally LMM water in the Upper Jurassic. Manifold tectonically and due to changing overburden, induced uplift and subsidence caused permanently changing hydraulic potentials and thus fluid fluctuations in different directions (Lemcke and Tunn [1956]). So, the Cl/Br signature in the thermal water seems to have another origin (LMM) than the SiO2 signature showing recently upwelling waters. However, the origin of the chloride component in the Upper Jurassic is not yet fully understood.
The Na/Cl ratio in the Upper Jurassic aquifer has values between 0.1 and 10 for Cl < 1 mmol. With increasing chloride (>1 mmol), the Na/Cl ratio is decreasing from values of 10 to <1. Bertleff et al. ([2005]) explained the enrichment in sodium (Na/Cl > 1) by ion exchange reactions with clay minerals in the lower Upper Jurassic. Due to the measured data, these processes seem to be important only in parts of the investigation area. Nevertheless, parts of the calcium released by dolomitization will be trapped again by ion exchange reactions with clay minerals and thus will increase the sodium concentration there.
The three Cl/Br values of the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer are in the order of Cl/Br = 300 (milligram basis) showing modern seawater signature (Cl/Br = 288). The chloride-sodium plot in Figure 8 illustrates that waters with lower concentration (Cl < 800 mmol(eq)/kg) follow exclusively the halite dissolution line, whereas waters with higher TDS stick as well to the seawater dissolution line. Higher TDS waters in greater depth occur in the SE of the investigation area, where Cl-rich water from the crystalline basement is most likely infiltrating into the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer to mix there with a water of lower concentration and halite signature (Figure 8). Thus, the high salinity in the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer might be caused by upwelling of saline waters of different origin. The results indicate that the thermal waters contain a salinity component from deeper reservoirs (Middle Muschelkalk in NW, crystalline basement in SE). The general groundwater flow direction in the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer in this area is from SE to NW.
Conclusions
The deep thermal waters in the two carbonate aquifers of the SW German Molasse basin have different hydrochemical properties. While the deep waters in the Upper Jurassic still have drinking water quality within depth of up to 1,200 m, the waters in the Upper Muschelkalk are highly mineralized. In both aquifers, the NaCl concentration is increasing with depth, resp. in the SE direction. The salinity is independent of geology and the type of aquifer rock (dolostone, limestone).
In the Upper Jurassic aquifer, salinity is most probably caused by infiltration from the overlaying Molasse sediments. However, during Pleistocene, these saline waters became exchanged with fresh water from the NW direction. In the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer, the high salinity is probably caused by upwelling high saline waters, especially in the SE from the crystalline basement.
The thermal waters in the Upper Jurassic with low NaCl concentrations show in the majority of cases increasing calcium with coexistent decreasing magnesium concentrations, probably caused by dolomitization of calcite. The dolomitization process is strongly temperature dependent and therefore increasing in the SE direction.
In the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer, the Ca/C ratio rises (e.g., calcium is increasing while HCO3 is decreasing) with increasing NaCl concentration and increasing temperature, resp. in the SE direction.
The relatively small amount of dissolved calcium and barium, however, has the potential to form carbonate and barite scales in the wellbore and the surface geothermal installations when decompressed and cooled, especially in the Upper Muschelkalk aquifer. Scaling prevention requires some technical measures.
References
Andres G, Frisch H: Hydrogeologie und Hydraulik im Malmkarst des Molassebeckens und der angrenzenden Fränkisch-Schwäbischen Alb. Schriftenr Bayer Landesamt Wasserwirtschaft 1981, 15: 108–117. München
Andrews JN, Goldbrunner JE, Darling WG, Hooker PJ, Wilson GB, Youngman MJ, Eichinger L, Rauert W, Stichler W: A radiochemical, hydrochemical and dissolved gas study of groundwaters in the Molasse basin of Upper Austria. Earth Planet Sci Lett 1985, 73(2-4):317–332. 10.1016/0012-821X(85)90080-9
Andrews JN, Youngman MJ, Goldbrunner JE, Darling WG: The geochemistry of formation waters in the Molasse basin of Upper Austria. Environ Geol Water Sci 1987, 10/1: 43–57. Springer New York 10.1007/BF02588004
Banks DA, Green R, Cliff RA, Yardley BWD: Chlorine isotopes in fluid inclusions: determination of the origin of salinity in magmatic fluids. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 2000, 64: 1785–1789. 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00407-X
Beaucaire C, Gassama N, Tresonne N, Louvat D: Saline groundwaters in the Hercynian granites (Chardon Mine, France): geochemical evidence for the salinity origin. Appl Geochem 1999, 14: 67–84. 10.1016/S0883-2927(98)00034-1
Behne W: Untersuchungen zur Geochemie des Chlor und Brom. Geochemica et Cosmochemica Acta 1953, 3: 186–214. 10.1016/0016-7037(53)90008-8
Bertleff B: Das Strömungssystem der Grundwässer im Malm-Karst des West-Teils des süddeutschen Molassebeckens. Abh Geol Landesamt Baden-Württemberg 1986, 12: 1–271. Freiburg i.Br
Bertleff B, Hedin K, Stober I, Strayle G, Werner J, Eichinger L, Moser H, Rauert W, Stichler W: Flow System Investigations in the Karstified Thermal Aquifer in the Western Part of the German Molasse Basin. Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration, Athens; 1986.
Bertleff B, Joachim H, Koziorowski G, Leiber J, Ohmert W, Prestel R, Stober I, Strayle G, Villinger E, Werner J: Ergebnisse der Hydrogeothermiebohrungen in Baden-Württemberg. Jh Geol Landesamt Baden-Württemb 1988, 30: 27–116. Freiburg
Bertleff B, Bauer M, Cammerer F, Michel W: Die Thermal- und Mineralwassererschließung von Friedrichshafen. Ber Naturf Ges Freiburg iBr 2005, 95/1: 213–235. Freiburg
Birner J, Mayr C, Thomas L, Schneider M, Baumann T, Winkler A: Hydrochemie und Genese der tiefen Grundwässer des Malmaquifers im bayerischen Teil des süddeutschen Molassebeckens. Z Geol Wiss 2011, 39(3/4):291–308. Berlin
Birner J, Fritzer T, Jodocy M, Savartis A, Schneider M, Stober I: Hydraulische Eigenschaften des Malmaquifers im süddeutschen Molassebecken und ihre Bedeutung für die geothermische Erschließung. Z Geol Wiss 2012, 40(2/3):133–156. Berlin
Bock H, Werner W, Simon T: Die Verbreitung der steinsalzführenden Schichten in Baden-Württemberg - eine Aktualisierung des Wissensstandes. LGRB-Nachrichten 2009, 8: 1–2. Freiburg i.Br
Böhm F, Birner J, Steiner U, Koch R, Sobott R, Schneider M, Wang A: Tafelbankiger Dolomit in der Kernbohrung Moosburg SC4: Ein Schlüssel zum Verständnis der Zuflussraten in Geothermiebohrungen des Malmaquifers (Östliches Molasse-Becken, Malm Süddeutschland). Z Geol Wissenschaft 2011, 39: 117–157.
Carlé W: Die Mineral- und Thermalwässer von Mitteleuropa. Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft mbH, Stuttgart; 1975.
Carpenter AB: Origin and chemical evolution of brines in sedimentary basins. Okla Geol Surv, Circ 1978, 79: 60–77.
Edmunds WM, Savage D: Geochemical Characteristics of Groundwater in Granites and Related Crystalline Rocks. In Applied Groundwater Hydrology: A British Perspective. Edited by: Downing RA, Wilkinson WB. Clarendon Press, Oxford; 1991:199–216.
Edmunds WM, Kay RL, McCartney RA: Origin of saline groundwaters in the Carnmenellis granite (Cornwall, England): natural processes and reaction during hot dry rock reservoir circulations. Chem Geol 1985, 49: 287–301. 10.1016/0009-2541(85)90162-7
Franz M, Simon T, Meyer RKF, Doppler G: Die Thermalwasserbohrung “Donautherme”, Neu-Ulm. Geologica Bavaria 2001, 106: 81–106. München
Frape SK, Fritz P: Geochemical Trends for Groundwater from the Canadian Shield. In Saline Water and Gases in Crystalline Rocks, 33. Edited by: Frape SK, Fritz P. Spec. Pap. Geol. Ass, Canada; 1987:19–38.
Gascoyne M, Davison CC, Ross JD, Pearson R: Saline Groundwaters and Brines in Plutons in the Canadian Shield. In Geological Association of Canada Special Paper. Edited by: Fritz P, Frape SK. The Range Press Limited, Ottawa; 1987:53–68.
Geyer OF, Gwinner MP (2011) Geologie von Baden-Württemberg. Neu bearbeitete Auflage von Geyer M, Nitsch E, Simon T, Schweizerbart'sche Verlagsbuchhandlung (Nägele u. Obermiller), Stuttgart, p 627 S
Goldbrunner J, Goetzl G: Geothermal Energy use, Country Update for Austria. - Abstracts. European Geothermal Congress, Pisa/Italy; 2013.
Grasby SE, Betcher RN: Regional hydrogeochemistry of the carbonate rock aquifer, southern Manitoba. Can J Earth Sci 2002, 39(7):1053–1063. 10.1139/e02-021
Grimm B, Franz M, Kilger B-M, Lorenz G, Schmidt-Witte H: Die ThermalwasserErschließung im Muschelkalk von Tuttlingen. Ber Naturf Ges Freiburg iBr 2005, 95/1: 189–212. Freiburg
Hagedorn H, Simon T: Der Muschelkalk in der Stratigraphischen Tabelle von Deutschland. Newsl Stratigr 2005, 41(1-3):143–158. 10.1127/0078-0421/2005/0041-0143
Jodocy M, Stober I: Geologisch-geothermische Tiefenprofile für den südwestlichen Teil des süddeutschen Molassebeckens. Z dt Ges Geowiss 2009, 160(4):359–366.
Karro E, Marandi A, Vaikmäe R: The origin of increased salinity in the Cambrian-Vendian aquifer system on the Kopli Peninsula, northern Estoria. Hydrogeol J 2004, 12: 424–435. 10.1007/s10040-004-0339-z
Kharaka YK, Hanor JS: Deep Fluids in the Continents: I. Sedimentary Basins. In Treatise on Geochemistry, vol. 5: Surface and Ground Water, Weathering, and Soils. Edited by: Drever JI. Elsevier, Oxford; 2004:499–540.
Koch R: Daten zur Fazies und Diagenese von Massenkalken und ihre Extrapolation nach Süden bis unter die Nördlichen Kalkalpen. Geologische Blätter für Nordost-Bayern 1997, 47: 117–150.
Koch R, Sobott R: Porosität in Karbonatgesteinen - Genese, Morphologie und Einfluss auf Verwitterung und Konservierungsmaßnahmen. Z Dtsch Ges Geowiss 2005, 156: 33–50.
Kozlovsky Ye A: The world's Deepest Well.- Spektrum der Wissenschaft. Springer, Heidelberg; 1984.
Lemcke K, Tunn W: Tiefenwasser in der süddeutschen Molasse und in ihrer verkarsteten Malmunterlage. Bull Ver Schweiz Pet- Geol -Ing 1956, 23(64):35–56.
Meyer RKF, Schmidt-Kaler H: Jura. In Erläuterungen zur Geologischen Karte von Bayern 1:500.000. Bayerisches Geologisches Landesamt, München; 1996:90–111.
Parkhurst DL, Appelo CAJ: User's Guide to PHREEQC (Version 2) - a Computer Program for Speciation, Batch Reaction, one Dimensional Transport, and Inverse Geochemical Calculations. In Water-Resources Investigations Report 99-4259. U.S. Geological Survey, Denver, Colorado; 1999:312.
Parkhurst DL, Thorstenson DC, Plummer LN: PHREEQE - a Computer Program for Geochemical Calculations. U.S. Geological Survey, Water Resources Investigations 80 - 96, Boulder/USA; 1980.
Pearson FJ Jr, Balderer W, Loosli HH, Lehmann BE, Matter A, Peters T, Schmassmann H, Gautschi A: Applied isotope hydrogeology - a case study in northern Switzerland. Studies in Environmental Science 1991, 43: 460. Elsevier, Amsterdam Elsevier, Amsterdam
Piller WE, Harzhauser M, Mandic O: Miocene Central Paratethys stratigraphy - current status and future directions. Stratigraphy 2007, 4: 151–168. New York
Prestel R: Untersuchungen zur Diagenese von Malm-Karbonatgestein und Entwicklung des Malm-Grundwassers im süddeutschen Molassebecken. Diss., Univ. Stuttgart, Stuttgart; 1990.
Schellschmidt R, Sanner B, Pester S, Schulz R: Geothermal Energy use in Germany. Proceedings WGC, Bali/Indonesia; 2010.
Schloz W, Stober I: Mineral-, Heil- und Thermalwässer, Solen und Säuerlinge in Baden-Württemberg. LGRB-Fachbericht 1 (überarbeitete Fassung), Freiburg i. Br; 2006.
Schreiner A: Einführung in die Quartärgeologie. Schweizerbart'sche Verlagsbuchhandlung, Stuttgart; 1992.
Schulz R, Agemar T, Alten JA, Kühne K, Maul AA, Pester S, Wirth W: Aufbau eines geothermischen Informationssystems für Deutschland. Erdöl Erdgas Kohle 2007, 123(2):76–81.
Sonney R, Vuataz F-D: Use of Cl/Br Ratio to Decipher the Origin of Dissolved Mineral Components in Deep Fluids from the Alps Range and Neighbouring Areas. Proceedings World Geothermal Congress, Bali/Indonesia; 2010.
Stober I: Strömungsverhalten in Festgesteinsaquiferen mit Hilfe von Pump- und Injektionsversuchen. Geol Jahrb C 1986, 42: 204 S. Hannover
Stober I: Die thermalen Karbonat-Aquifere Oberjura und Oberer Muschelkalk im Südwestdeutschen Alpenvorland. Grundwasser 2013, 18(4):259–269. DOI: 10.1007/s00767–013–0236–2
Stober I, Bucher K: Origin of salinity of deep groundwater in crystalline rocks. Terra Nova 1999, 11(4):181–185. Blackwell Science Ltd 10.1046/j.1365-3121.1999.00241.x
Stober I, Jodocy M: Geothermische Nutzhorizonte im westlichen Teil des süddeutschen Molassebeckens. Z Geol Wiss 2011, 39(3-4):161–172.
Stober I, Villinger E: Hydraulisches Potential und Durchlässigkeit des höheren Oberjuras und des Oberen Muschelkalks unter dem baden-Württembergischen Molassebecken. Jahreshefte des Geologischen Landesamts Baden-Württemberg 1997, 37: 77–96. Freiburg i.Br
Stober I, Richter A, Brost E, Bucher K: The Ohlsbach plume: natural release of deep saline water from the crystalline basement of the Black Forest. Hydrogeol J 1999, 7(3):273–283. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg 10.1007/s100400050201
Stober I, Jodocy M, Hintersberger B: Gegenüberstellung von Durchlässigkeiten aus verschiedenen Verfahren im tief liegenden Oberjura des Südwestdeutschen Molassebeckens. Z Dt Ges Geowiss (German J Geosci) 2013, 164(4):663–679.
Stober I, Jodocy M, Burisch M, Person R: Tiefenwässer im Oberen Muschelkalk-Aquifer des Oberrheingrabens und des Südwestdeutschen Molassebeckens.-. Grundwasser 2013, 18(2):117–127. 10.1007/s00767-013-0224-6
Villinger E: Über Potentialverteilung und Strömungssystem im Karstwasser der Schwäbischen Alb (Ober Jura, SW-Deutschland). Geol Jb 1977, C18: 3–93. Hannover
Walther JV, Helgeson HC: Calculation of the thermodynamic properties of aqueous silica and the solubility of quartz and its polymorphs at high pressures and temperatures. Am J Sci 1977, 277: 1315–1351. Stanford/USA 10.2475/ajs.277.10.1315
Werner J: Die Thermalwasserbohrung Saulgau (Württemberg), 8. Abh. Geol. Landesamt BW, Freiburg i.Br; 1978.
Acknowledgements
Many thanks to BMU (Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety, Germany (grant nos: 0327542 and 0325136)), to the hydrocarbon industry (ExxonMobil Production Deutschland GmbH, Gaz de France Suez Production Exploration Deutschland GmbH, RWE Dea AG, Wintershall Holding GmbH), to Regierungspräsidium Freiburg, and to the Service Géologique d'Alsace et de la Lorraine (BRGM) for the generous support (www.rp.baden-wuerttemberg.de/servlet/PB/menu/1337770/index.html). Thanks as well to two anonymous reviewers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits use, duplication, adaptation, distribution, and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Stober, I. Hydrochemical properties of deep carbonate aquifers in the SW German Molasse basin. Geotherm Energy 2, 13 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40517-014-0013-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40517-014-0013-1